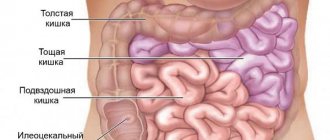
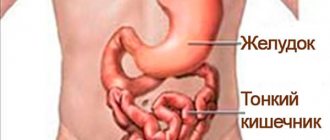
Good afternoon, many will be interested in understanding their health and their loved ones, and I will tell you my experience, and we will talk about what are the symptoms of atonic colitis and how to treat it. Most likely, some details may differ, as was the case with you. Please note that you should always consult with highly specialized specialists and not self-medicate. Naturally, you can quickly find the answer to the simplest questions and diagnose yourself. Write your questions/suggestions in the comments, and together we will improve and supplement the quality of the material provided.
Treatment
Treatment options for the disease depend on the form of the disease. Traditionally, in case of acute colitis, it is first recommended to fast for a couple of days, and then follow the prescribed diet. When an infection is detected, appropriate treatment is required. To relieve a patient from atonic type colitis, the doctor prescribes laxatives, sedatives, antispasmodics and medicinal enemas, vitamins and treatment with medicinal herbs.
When there is no bowel movement for more than three days, treatment of atonic type colitis is directed towards diet. To restore peristalsis, use:
- raw vegetables and fruits;
- products containing coarse fiber;
- pureed dishes.
It is necessary to eat by the hour, trying to bring the periods of food consumption closer together so that there are no long periods of fasting. At the same time, to treat colitis in atonic syndrome, physical activity is increased. It is very useful, in addition to walking, to perform physical activities that help strengthen the abs. It is advisable to massage the peritoneum daily. Use a warm hand to move in a circle on your stomach in a clockwise direction to restore the natural functioning of the intestines.
If the diet does not bring results, medications are prescribed. Usually they are:
- antispasmodics that relieve pain;
- laxatives, stool softeners;
- drugs that improve peristalsis;
- rectal suppositories that cause the urge to defecate;
- oil enemas that promote the release of feces accumulated in the intestines.
Doctors warn against self-treatment if symptoms of atonic type colitis are detected. This is caused by the possibility of an error in diagnosis, because the symptoms are often similar to other dangerous diseases, including colon cancer.
You should promptly visit a specialist who will determine the true cause of constipation. Only then begin treatment.
Classification of the disease
In medical practice, the classification of chronic colitis helps to correctly determine treatment tactics, assess the prognosis of the disease, possible consequences and complications.
According to the etiological (causal) factor, colitis is:
- infectious – due to intestinal infection;
- nutritional – due to poor nutrition;
- allergic – due to allergization of the body;
- intoxication – as a result of poisoning;
- radiation – after exposure to ionizing radiation;
- congenital – due to congenital anomalies of the colon.
According to pathomorphological (intestinal wall structure) characteristics:
- chronic catarrhal colitis - inflammation of the intestinal mucosa;
- chronic atrophic colitis – thinning of the mucous membrane, dysfunction of the secretory glands;
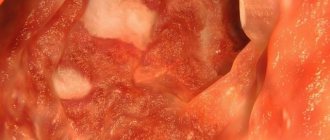
- chronic erosive colitis – mucosal defects prone to bleeding;
- chronic ulcerative colitis - ulcers of the mucous membrane leading to intestinal bleeding.
Functionally:
- chronic spastic colitis – causes a tendency to diarrhea;
- chronic atonic colitis – causes a tendency to constipation.
According to statistics, when visiting a gastroenterologist, 40% of patients are diagnosed with a chronic form of the disease.
Prevention
To prevent the development of atonic type colitis, all preventive measures are used. Their list is short, but they are effective:
- Walk more, move vigorously to develop the framework of muscles that support the peritoneum.
- Enrich your daily diet with dairy products and plant fiber.
- As soon as prolonged constipation occurs, be sure to consume 1 tsp before meals. bran, brewing them in a glass of boiling water.
- After waking up, immediately drink a glass of kefir, diluting 1 tbsp in it. l. any vegetable oil.
It is necessary to eat by the hour, trying to bring the periods of food consumption closer together so that there are no long periods of fasting. At the same time, to treat colitis in atonic syndrome, physical activity is increased. It is very useful, in addition to walking, to perform physical activities that help strengthen the abs. It is advisable to massage the peritoneum daily. Use a warm hand to move in a circle on your stomach in a clockwise direction to restore the natural functioning of the intestines.
Forms of colitis
The course of colitis occurs in 2 forms. Determining an accurate diagnosis is difficult due to the similarity of symptoms, and in order to establish the degree of development, you will need to undergo a number of clinical and laboratory tests.
The forms of the disease are as follows:
- Chronic – children and people over 45 years of age are susceptible to the disease. Characterized by prolonged constipation, which can appear and suddenly disappear for a while. There is an inflammatory process in the colon.
- Acute – the risk group includes older people. One-time difficulty defecating. This form is easier to eliminate than the chronic form. And most often there is no repetition.
To clarify the diagnosis, the patient must describe the symptoms in detail.
Treatment of the disease
For the treatment of atonic colitis, therapeutic, medicinal and preventive methods of therapy are used.
The patient is prescribed medications that can get rid of feces and relieve pain.
To recreate artificial stimulation of intestinal motor activity, prokinetics are used:
In advanced cases, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs based on 5-aminosalicylic acid are used. The most effective and efficient drug is Salofalk; these tablets should be taken for a long time.
To normalize the intestinal microflora, probiotics and enzyme preparations are usually used: “Creon”, “Festal”, “Lactofiltrum”.
Treatment of atonic colitis often begins with cleansing the lower gastrointestinal tract. It is necessary to empty the intestines of feces and cleanse the body; for this, therapy with water enemas and the drug “Microlax” (micro-enemas) is prescribed. Next, you need to soften the stool and make it easier to pass. However, such drugs should not be abused.
Long-term use of laxatives leads to the fact that the intestines become unaccustomed to working over time. In addition, tolerance to the drugs develops, and previous doses soon stop working. Therefore, laxatives can be taken only occasionally, when it is urgent to cleanse the body. Mild preparations on an oil and plant basis are prescribed: “Senade”, “Kafiol”, “Mukofalk”, “Fitolax”, castor oil, suppositories with petroleum jelly, glycerin or fennel oil.
We recommend reading: Allergy to corn porridge in an infant: causes, symptoms, what to do
Stem cell transplants are also used in the treatment of colitis, especially if they are formed as a result of a genetic predisposition. The task of stem cells is to cause the growth of new nerve bundles that were destroyed in the initial stages of the disease, which should help restore normal peristalsis.
Recent technologies make it possible to use electrical stimulators (artificial introduction of rhythms that support muscle contraction), which force the intestines to push feces out.
In advanced cases, a chronic form of intestinal obstruction (pseudo-obstruction) may occur, which requires surgical intervention.
As auxiliary measures for this disease, special exercises (physical therapy), microenemas with local medications can be used. Therapeutic massage for atonic colitis also helps to achieve excellent results.
Cause of the disease
Atonic colitis begins with inflammation. Causes of the inflammatory reaction:
- Sometimes the source is a protozoan, as in dysentery or salmonellosis.
- Treatment with antibiotic drugs destroys the intestinal’s own “beneficial” microflora, which will lead to dysbiosis.
- “Harmful” diet (spicy, floury, alcohol abuse).
- Physical and mental stress.
- Allergy.
- Poisoning.
- Heredity (mitochondrial disease was found in patients with AK).
- Age.
Medicines that act as inducers:
- Against heartburn.
- Antidiabetic.
- Painkillers.
- Narcotic substances.
Atonic colitis is predominantly common among the elderly part of the population; doctors have encountered colitis in young people as well. Inflammation occurs as a result of a blockage; the intestine receives insufficient blood supply due to a sedentary lifestyle. In old age, prolonged inflammation leads to the death of cells in the colon mucosa. Nerve death occurs. Reduced conductivity of nerve fibers leads to disruptions in peristalsis, hence constipation.
More about atonic colitis
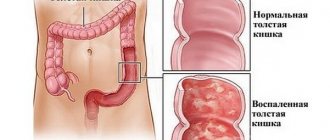
Colitis is a leader among gastrointestinal diseases. The variety of colitis is enormous: collagenous, alcoholic, spastic, atonic, hemorrhagic, pseudomembranous, ischemic and other types. Spastic and atonic colitis are more common. Both types of disease are accompanied by severe constipation.
The clinical symptoms of these pathologies are very similar. The difference is in the mechanism of fecal retention: with atonic intestinal colitis, defecation retention occurs due to weak peristalsis; with the spastic form, the intestinal muscles are very tense, for this reason feces are retained and do not leave the body.
Chronic atonic colitis (ICD10 code - K50) is provoked by external factors - the presence of infections, bacteria in the body, and problems in the functioning of the body of an endogenous nature. A characteristic feature of the disease is inflammation of the colon mucosa.
Colitis is a polyetiological disease (one or more factors trigger other reactions). It is more common in adults aged 35-40 years. Pathology is equally often diagnosed in both men and women.
Due to the fact that the symptoms of different types of this intestinal pathology are very similar, a full examination of the patient is required to prescribe treatment.
Causes
Atonic colitis develops slowly, that is, it has a chronic course. The occurrence of the disease is promoted by both exogenous and endogenous factors. The pathology is most often diagnosed in older people and people leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Dystrophic phenomena in the colon occur due to the following reasons:
- poor nutrition: irregular meals, abuse of diets, lack of fiber in the diet, consumption of unhealthy foods (instant foods, snacks, etc.);
- physical inactivity, sedentary work;
- infectious pathologies;
- frequent stress, emotional stress;
- long-term use of medications;
- frequent bowel cleansing with enemas, laxatives;
- diseases of the rectum;
- endocrine disorders.
The concept of “catarrhal colitis” means a stage of inflammation that lasts several days; the atonic component implies the presence of constipation in the disease associated with weak peristalsis.
Chronic form of the disease
Chronic colitis of the large intestine is a long-term inflammation that can either fade or become more active. Most often it occurs due to a malfunction in the diet and is diagnosed in people after 45 years of age, but in some cases this attack can be detected even in children.
In 70% of cases, this disease appears due to the lack of timely treatment of other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract: ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis, etc.
To avoid developing more serious health problems, patients with this form of the disease need periodic examination by a doctor and courses of treatment.
Against colitis on your own
We looked at what colitis is (symptoms and treatment). Diet for colitis, however, should occupy one of the main places in the treatment of this disease.
If you visit a gastroenterologist, for this disease he will advise you to adhere to the fourth dietary table. His general recommendations are:
- It is not recommended to consume freshly squeezed juices; it is better to replace them with fresh fruits.
- Avoid meat, especially pork and beef.
- It is not recommended to eat bran bread during treatment.
- Remove fried foods from your diet.
- It is forbidden to eat fresh vegetable salads.
- During therapy, food should be at room temperature, avoiding too cold or hot.
- Eliminate hot spices and seasonings from your diet.
- In small quantities, you can include chicken and lamb in the menu.
- It is better to eat vegetables not raw, but to steam them.
- Limit the consumption of animal fats; a little butter is allowed.
- When treating colitis, food should be of a delicate consistency.
- After waking up, before breakfast, you need to drink a glass of water, preferably boiled.
We looked at what chronic intestinal colitis is, symptoms and treatment. Diet in therapy should be an important step. Only then can you expect positive results.
Diet for illness
A properly selected diet will help speed up the healing process and alleviate the patient’s condition. It is recommended to follow these recommendations:
- eat small portions, but often - up to 5 times a day;
- do not eat fatty, smoked and fried foods;
- eat more fresh fruits and vegetables;
- reduce the amount of flour products and sweets consumed;
- exclude from the diet foods with artificial additives, preservatives, and seasonings;
- It is preferable to boil or steam dishes;
- black coffee, tea, and carbonated sweet drinks are excluded from the diet, as they can delay the removal of feces from the body;
- It is recommended to consume fermented milk products, as they help normalize intestinal motility and have a positive effect on the microflora of the organ;
- It is useful to eat dried fruits. They are able to swell in the intestinal lumen and increase contractions of the intestinal walls. Include fiber-rich vegetables in your diet every day. These include zucchini, cabbage, carrots, and beets.
- maintain proper drinking regime. You should drink at least 2-2.5 liters of fluid per day;
- It is useful to use a product made from wheat bran. 2 tbsp. spoons of the product are poured into a glass of warm milk and left for half an hour. This mixture must be eaten every day before breakfast. The product helps improve intestinal motility.
Treatment methods
Intestinal colitis requires serious systemic treatment prescribed by a specialist. Initially, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease, review the diet, and give up alcohol. After eliminating the causes, the doctor prescribes complex therapy, which consists of traditional drug treatment, a special diet and folk recipes.
The precursor to the disease will be catarrhal colitis. This disease is characterized by inflammation and hardening of the intestinal mucosa. Lack of treatment guarantees the transition of the disease to the form of atrophic colitis, the lower gastrointestinal tract suffers, and thinning of the intestinal walls occurs. The complications in this case are much more serious.
How to treat chronic colitis
During the period of remission of chronic colitis, doctors recommend actively engaging in sports, choosing non-strength activities. Exercises that involve the abdominal muscles are prohibited.
It is recommended to give up bad habits.
Another important point is to avoid wearing tight clothing and compressive belts. If intestinal prolapse is observed, then a special bandage is prescribed that does not compress the vessels, but has a supporting effect.
In the acute stage, the patient is hospitalized or prescribed bed rest, and is also prescribed complex therapy, which includes drug treatment, a therapeutic diet and physiotherapy.
Therapeutic diet
Correction of diet is of great importance in treatment. If there is an exacerbation of colitis, then on the first day it is recommended to completely abstain from food, which will eliminate the burden on the intestines. The following liquids are allowed: herbal or green tea, and also rosehip decoction. The next day of the diet you can eat and you should do it often, but the portions should be small.
It is important to choose dishes that will not provoke fermentation and rotting processes in the stomach, as well as increase gas formation. The diet allows the consumption of low-fat first courses, steamed meat and fish cutlets, liquid porridges made with water, and low-fat cottage cheese, which must be pureed. Vegetables need to be boiled and pureed. You can drink not only the above drinks, but also jelly.
For treatment to be successful, you must stop eating fatty dairy products, fried, canned, salty, baked goods and sweets. Vegetables that cause flatulence, such as cabbage, legumes and beets, are undesirable. Fresh fruits and berries should also not be eaten - and it is better to boil them. Gradually introduce white bread, chopped vegetables, and fruits into your diet, but just exclude those that have a laxative effect on the body.
Medications
Treatment necessarily includes taking medications, but they are selected depending on the cause that caused the colitis and on the patient’s individual characteristics.
Usually the doctor prescribes:
- If the disease is infectious, short courses of antibiotics and sulfonamides are prescribed, since they can cause dysbacteriosis;
- If parasites are to blame, then treatment is carried out using antiparasitic drugs;
- To cleanse the intestines of toxic substances and inflammatory elements, it is recommended to take sorbents, for example, activated carbon and Enterosgel;
- In case of severe spasms, you cannot do without antispasmodics. So, a doctor may prescribe No-shpa or Platyfillin;
- If other problems with the digestive system are observed, then enzymes, for example, Pancreatin or Festal, may be prescribed;
- For diarrhea, you need to drink Smecta or Loperamide, and for constipation, laxatives are recommended: Senade or Guttalax;
- To restore the intestinal microflora, probiotics and prebiotics are prescribed for treatment, for example, Linex or Normobact;
- To restore immunity, it is recommended to take a course of vitamins B, C, A and E.
It is important to consider that each drug has its own contraindications and side effects, which will be taken into account by the doctor when prescribing the dosage.
Physiotherapy
For such a disease, sanatorium-resort treatment is recommended, which involves taking mineral baths, intestinal lavage, treatment with microenemas, etc. Gastroenterologists recommend the following physical procedures: mud applications, magnetic or acupuncture therapy. Operations are performed only when the patient’s condition is complicated
Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia in adults
The symptoms of colon dyskinesia vary significantly among patients, so it is often difficult for a doctor to diagnose the disease. Characteristic symptoms of spastic colitis:
- Pain in the abdominal area is the main symptom of the disease. Often the patient is not able to explain where it hurts, since the pain is localized widely.
- Varied nature of pain. This is a boring or aching, dull or paroxysmal, cutting pain that lasts from several minutes to several hours.
- Another sign of the disease is that the pain stops at night, but returns again when the person wakes up.
- Feeling of pain in the intestines after meals, against the background of psycho-emotional disorders.
- Spastic colitis is manifested by frequent bowel movements in the form of diarrhea.
- Frequent constipation, followed by loose stools with or without mucus. Many people note relief after bowel movements and the release of gases that swell the stomach and cause bloating.
- Constant rumbling in the abdomen also makes it difficult to feel comfortable. There are cases that rumbling in the stomach is the only symptom that manifests itself with dyskinesia, making it difficult to make a diagnosis of an insidious, hidden disease.
- Patients complain of dull pain in the heart or back, sleep disturbances, nervousness, and depression.
Diet for chronic spastic colitis
Treatment of chronic spastic intestinal colitis should begin with the most accessible and harmless method - keeping a diary of your diet.
Patients are recommended to increase their intake of fiber: vegetables, fruits, beans, lactic acid products, dried fruits, bran and whole grain bread. It is necessary to exclude or at least limit animal products, such as butter and fat, and it is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol, coffee, sparkling water and strong tea. You should avoid foods that can provoke an exacerbation of the disease or cause a spasm: chocolate, fatty meats, creams, cheeses, butter, whole milk.
Attention! If the patient’s condition does not improve after following all dietary recommendations, they resort to drug treatment.
Diet for acute spastic colitis
The diet for acute spastic colitis is based on excluding or limiting the consumption of fatty, spicy, salty foods that irritate the intestinal mucosa. The diet should include vegetables, fruits, beans, and whole grain bread. You need to eat fractionally: in small portions several times a day. This will help reduce diarrhea, reduce gas formation and make the patient’s condition more stable.
Symptoms of atonic colitis
In the presence of atonic colitis, the patient has difficulties with bowel movements for several days, and there is not even the urge to defecate. In advanced cases, fecal stones form, which have to be removed mechanically.
Other reasons for concern include:
- discomfort in the abdomen, turning into pain;
- flatulence, gases;
- bloating.
Over time, feces in the intestines poison the body. Intoxication provokes nausea, fever, and pale skin. With a good appetite, weight is lost.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of dyskinesia is based on the use of an exclusive exclusion method. A phased examination includes:
- exclusion of dangerous pathologies of the large intestine (tumors, polyps, diverticulum),
- scatological research,
- stool analysis for the presence of bloody discharge,
- irrigoscopy,
- endoscopy,
- intestinal biopsy if necessary.
Find out more: intestinal diverticulosis - what it is, how to treat the disease.
Atonic or hypomotor dyskinesia is characterized by a sharp weakening of peristalsis and tone of the colon and, as a result, intestinal constipation occurs. This problem is often aggravated by bursting pain in the lower abdomen from the accumulation of dense fecal masses. Against the background of constant constipation, the general condition of the body worsens, the patient suffers from nausea, belching, weakness, and constant mood swings. Chronic intestinal constipation leads to the formation of hemorrhoids, fissures, and rectal polyps.
Clinical signs
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by an undulating course - periods of well-being (remission) are followed by deterioration of the condition (exacerbation). During remission, the general condition is not disturbed, the intestines function normally. Sometimes patients note a decrease in appetite, weight loss, and bloating.
We recommend reading: What eye drops can be used while breastfeeding?
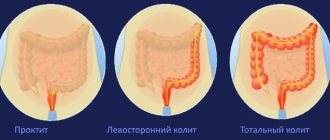
Clinical signs of the disease appear during the period of exacerbation. Chronic left-sided colitis is more often associated with damage to the sigmoid colon, and right-sided colitis is often associated with inflammation of the cecum.
Symptoms of chronic intestinal colitis:
- bloating due to increased gas formation in the colon (flatulence);
- rumbling, feeling of transfusion in the intestines 1.5–2 hours after eating;
- dull or cramping pain in the abdomen after eating or during bowel movements;
- pain occurs in the lower and lateral parts of the abdomen, sometimes without clear localization;
- bowel dysfunction (constipation, diarrhea, constipation alternating with diarrhea);
- false urge to defecate;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the rectum;
- feces in “lumps”, an admixture of mucus, streaks of blood;
- foul odor of stool;
- temperature rise to 37.2–37.7 degrees with an infectious form of the disease;
- skin rash;
- loss of appetite, weakness, weight loss, impaired performance.
In infectious colitis, the chronic form is preceded by an acute course of the disease: diarrhea 3–15 times a day, nausea, vomiting, cramping abdominal pain. In some cases, intestinal infection has a mild course with minor clinical manifestations and often goes unnoticed.
Signs of chronic intestinal colitis gradually increase and, if left untreated, disrupt the evacuation function of the colon, which leads to intoxication of the body with feces.
Nutrition for atonic colitis
When choosing a diet, the following are taken into account:
- 1. The absence of irritating natural (spicy seasonings) and artificial (preservatives) ingredients in food.
- Food should be high in calories, but at the same time easily digestible. At the initial stages of treatment, it is recommended to eat boiled or steamed food. In the future, you can also eat moderately fried foods. Smoked meats are not recommended.
- The ratio of animal to plant foods depends on the type of intestinal disorder. So, with irritable bowel syndrome or functional diarrhea (accelerated bowel movement), protein products, preferably of animal origin (except whole milk), should predominate in the diet. Fermenting products (grape, plum juice) are also undesirable. Fermented milk products have a positive effect on intestinal function. Plant foods must be heat treated and should not contain coarse fiber.
For atonic constipation with reduced activity of intestinal contractions, it is advisable to eat a significant amount of fiber: fresh vegetable and fruit juices, boiled vegetables, fresh vegetable salads; bread mixed with bran or made from wholemeal flour.
For atonic constipation, consuming steamed bran before meals often has a good effect: 1 tbsp. pour boiling water over the bran, cover and leave to steep for 5 minutes, then drain the water and eat the bran with the first portion of food. Boiled beets and steamed peeled pumpkin also stimulate the intestines well. Eating dried fruits such as figs, prunes and, to a lesser extent, dates, activates intestinal function. This activation is explained by the ability of dried fruits to swell in the intestinal lumen, which prompts their accelerated expulsion.
Diagnosis of atonic colitis
During the initial examination, the medical history is studied and the abdomen is palpated. In the abdominal cavity, a compaction is determined due to intestinal overcrowding. When severe blockage of the gastrointestinal tract is diagnosed, the patient is sent to the treatment room for treatment with water enemas.
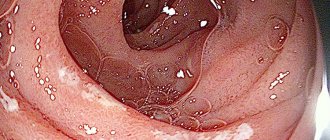
If pathology is suspected, macro- and microscopy of stool is performed, and a general blood test is performed. The presence of helminths and their eggs in the body is also detected. Using irrigoscopy, it is possible to determine pathologies of the functional and anatomical state of the colon. The use of colonoscopy helps to obtain data on the condition of the patient’s mucosa throughout the entire length of the colon and take a tissue sample for histology. Diagnosis is also carried out using abdominal ultrasound and fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment, which is also used during the remission stage, also helps:
- Stimulators of intestinal motility (Dokusate);
- Saline laxatives (Bisacodyl, magnesium sulfate).
- Herbal laxatives (Senade).
- Antispasmodics (Papaverine hydrochloride, No-spa, Duspatalin).
- Enzyme preparations to improve digestion (Creon 10000, Mezim).
- Adsorbents for removing toxic substances from the body (activated carbon, Smecta and Neosmectite).
- Nicotinic acid and B vitamins to accelerate the renewal of damaged tissues.
- Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs (Loperamide, Furozolidone, Tetracycline, Enterofuril).
- Choleretic agents for gallbladder pathology and deficiency of bile acids in the digestive system (Holosas, Chofitol, Allochol).
It is recommended to take medications only after consulting a doctor. [adsen2]
Symptoms
In order to fully appreciate the seriousness of this disease for the body and understand what chronic colitis is, it is necessary to understand the general picture of its symptoms.
- Most often, the disease is accompanied by sensations of dull, aching or cramping pain in the abdomen, which are localized in its lower and lateral parts, and may not have a specific location. The pain intensifies, as a rule, after eating, or before defecation. Sometimes after this they weaken for a short time, especially if gas has passed or an enema has been given.
- Symptoms of the disease are accompanied by dyspeptic disorders, there is a lack of appetite, the appearance of belching and nausea, and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth. With long periods of the disease, a decrease in body weight is observed.
- Patients often suffer from flatulence caused by disorders of the digestion process. The main symptom is a violation of bowel movements, accompanied by diarrhea (it can become frequent up to 15 times a day), or, conversely, the appearance of constipation. These states can alternate. Patients complain of sensations of incomplete emptying. There is mucus in the stool. False urges are possible; they are accompanied by the release of gases, the release of small lumps of feces, as well as mucus containing streaks of blood.
People with chronic colitis may generally feel quite well, but if the disease is severe, signs of malaise, weakness, and decreased ability to work may appear. [adsen]
Causes
The factors for the development of atonic intestinal colitis are varied. Inflammation appears for external reasons or processes that occur in the human body, due to the influence of medications.
The most common causes of colitis:
- psychological, physical stress;
- development of infectious diseases, presence of bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract;
- age-related changes;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- allergy;
- inactive lifestyle;
- heredity;
- taking foods that disturb the walls of the rectum (sweets, alcohol, spicy foods);
- consumption of medications (painkillers, antibiotics, narcotics);
- incorrect performance of abdominal surgery.
As mentioned earlier, atonic colitis occurs in the mature population, but today inflammation of the colon mucosa can also be found in young patients. Eating unhealthy food, alcoholic drinks, and a sedentary lifestyle lead to atony.
Types of dyskinetic colitis
The disease is classified according to the nature of the clinical picture. The following forms of irritable bowel syndrome are distinguished: with diarrhea, constipation, mucous colic. Abnormal bowel movements are almost always detected; long-term constipation is often replaced by short-term diarrhea. Depending on the nature of the intestinal motility disorder, the following forms of the disease are distinguished: spastic intestinal dyskinesia, dysfunction of the organ of the hypomotor type.
According to the etiology of dyskinesia there are:
- Neurogenic. Occurs with organic lesions of the nervous system, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Psychogenic. They develop against the background of depressive states, asthenic syndrome, and neuroses.
- Endocrine-hormonal. For diseases of the endocrine system: hypothyroidism, dysfunction of the pituitary gland and gonads.
- Toxic. They appear against the background of alcohol abuse, as well as during intoxication with lead and aniline dyes in hazardous industries.
- Medication. They develop as a result of prolonged unjustified use of laxatives or fixative drugs.
- Nutritional. With an excessively sparing diet, malnutrition, or, conversely, excessive amounts of food consumed.
- Hypodynamic. They develop with asthenic syndrome, hypokinesia, after operations on the abdominal organs.
- Due to metabolic disorders, lactase deficiency, due to parasitic and infectious diseases, allergic reactions.
- As a result of developmental anomalies (megacolon, diverticula) or proctogenic factors (hemorrhoids, rectal fissures, cryptitis).
Doctors pay attention to the fact that the patient may be diagnosed with different types of disease. It is capable of developing in hypotonic and hypermotor types.
Colitis of the hypotonic type. When dyskinetic colitis of the hypotonic type develops, the peristalsis of the large intestine slows down. Bowel movements occur rarely, and feces are released in small quantities. The patient complains of heaviness in the abdomen, a feeling of bloating, and strong passing of gas. A sharp pain appears in the abdominal area, but the patient cannot say where exactly it is localized. He usually says that the whole stomach hurts, pointing to the entire abdominal area.
Dyskinetic colitis of the hypotonic type occurs if a person’s life contains an excessively “sterile” diet, the absence of fermented milk products, fruits and vegetables, products with coarse fiber, and whole grains. Dysbacteriosis is the shortest path to the described disease. Family history, pathological state of the endocrine system, chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and all other organs located in its vicinity are also of great importance.
The appearance of stagnation can provoke a sedentary lifestyle and abuse of various diets for weight loss. It has been noticed that the tone of the intestinal muscles directly depends on the skeletal mass of a person, therefore, when a person suddenly loses weight, he is faced with problems of the large intestine.
The disease is treated with drugs that restore colon motility; moderate physical activity, therapeutic massage, physiotherapy and sanitary spa treatment are useful.
Hypermotor dyskinetic colitis. Today, chronic dyskinetic colitis of the hypermotor type is as common as hypotonic colitis. But its appearance is always associated with food poisoning. Often it also occurs due to eating foods that are incompatible with each other. Negative factors lead to the fact that peristalsis is noticeably activated, and excessive mobility of the organ appears. It prevents food from being absorbed, so the body does not receive the necessary nutrients.
It is not difficult to recognize such hypermotor chronic dyskinetic colitis. Instead of constipation, the patient develops diarrhea, bowel movements become very frequent, and paroxysmal pain occurs in different parts of the abdomen. They bother you almost constantly.
A one-time case of intestinal upset is not dangerous; it is a completely harmless phenomenon, which can be eliminated with a regular home first aid kit. But dyskinetic colitis is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. The disease can provoke the development of intestinal obstruction. In this case, without timely medical care, the patient may die.