Erosive intestinal colitis is considered a serious disease that requires careful attention. In most cases, the development of this inflammatory process requires immediate hospitalization with special therapeutic procedures and compliance with certain dietary restrictions. Inflammation in the colon caused by this disease has several forms, the most dangerous of which is considered erosive, as a result of which ulcers form on the mucous membrane. Without timely therapy and in the absence of a proper diet, chronic colitis easily develops into a peptic ulcer.
Symptoms
Although colitis develops differently in everyone, a characteristic feature of this disease is its symptoms, which are very close to gastritis. It is for this reason that patients put off visiting a doctor and often do not seek medical help in a timely manner. The first symptoms of erosive colitis are as follows:
- pain in the location of the stomach and persistent discomfort;
- attacks of nausea;
- unpleasant odor of breath with a characteristic taste in the mouth;
- disruption of digestive processes;
- loss of appetite.
If such symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist. If you get help at this stage, then in more than eighty percent of cases you can expect a complete cure. Timely initiation of therapy will prevent the development of chronic intestinal colitis. Otherwise, inflammation will continue to develop, involving more and more healthy tissue in the process, with the threat of transition to a malignant state. As pathological changes in the condition of the intestine further develop, erosive colitis manifests itself as follows:
- patients feel an increase in heart rate;
- blood pressure rises;
- symptoms of a fever begin to appear;
- particles of undigested food are found in intestinal secretions;
- attacks of vomiting become permanent;
- acute pain occurs in the intestines and stomach;
- patients feel general malaise, weakness, dizziness.
Changes also occur in the nature of feces, which become more pronounced as the disease progresses, for example:
- there is a large amount of pus and mucus in the feces, and streaks of blood are also observed;
- more than half of the patients begin to suffer from recurring diarrhea, the urge to which can reach up to twenty per day;
- often during bowel movements only mucus containing pus is released;
- the urge to defecate continues at night, which is the main reason for suspecting the presence of chronic erosive colitis;
- confirmation of the erosive form is fecal incontinence with constant bloating.
Colitis of the erosive form can occur with exacerbations, which are replaced by periods of remission. During exacerbations, patients are able to experience symptoms in the form of bleeding from the anus, elevated temperature, and also in the form of rashes on the intestinal mucosa.
Symptoms in adults and children
There are often no clinical manifestations at an early stage . The disease manifests itself with a persistent inflammatory process with the formation of erosive or ulcerative defects.
Specific symptoms of erosive colitis:
- abdominal pain after defecation and eating;
- heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- abnormal stool, blood and pus in the stool;
- nausea, vomiting;
- malaise, weakness.
High temperature is more typical for young children ; adults report persistent low-grade fever. In acute inflammation, along with typical manifestations, a rash, conjunctival manifestations, and disorders of the articular apparatus may appear. The more pronounced the inflammation, the brighter the clinical manifestations.
Note! As the disease becomes chronic, the symptoms soften and are nonspecific. The absence of clear symptoms does not reduce the aggression of erosive colitis; the disease constantly progresses, and inflammation deepens into the submucous membranes of the large intestine.
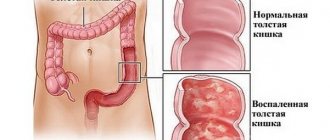
What does it look like
Erosive colitis is an inflammation that develops in the mucous membrane of the large intestine, as it develops, damage in the form of ulcers forms on it. The pathology occurs with equal frequency in both women and men, the average age of patients ranges from 15 to 30 years, and the second peak of the disease is observed in elderly people after 60 years.
Erosive colitis serves as the first stage of inflammatory tissue damage, which, when examined with equipment, looks like damage to the surface layer of the mucosa lining the large intestine from the inside. In the absence of the necessary treatment, a different picture can be observed: inflammation on the mucous membrane deepens and affects the submucosal layers with the formation of areas with erosion.
This disease of erosive colitis is often considered the initial stage of ulcerative colitis, with similar symptoms to the ulcerative form, but with less severity.
How does the inflammatory process develop in the intestines?
At the initial stage, the disease is practically asymptomatic and unnoticed by the patient, when small foci of inflammation appear on the intestinal walls. And, as a rule, the “first calls” are ignored.
In the absence of treatment, combined with an unhealthy lifestyle, the disease begins to progress. During this period, the symptoms are already more pronounced and are characterized by the formation of ulcers on the lining of the stomach and the surface of the intestines, which means the disease has become chronic.
We recommend reading: Should subchorionic hemotoma be treated in the early stages?
Causes
Factors that can cause intestinal colitis can be completely different reasons, but the main ones are considered to be a genetic predisposition to the development of such pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract, as well as a gross violation of the diet. The underlying causes that led to the development of colitis must be determined by the attending physician and, based on the examination, outlined the course of treatment necessary in each individual case. Most often, the development of colitis can occur when the following conditions are created:
- Failure to maintain a balanced diet.
- A long course of treatment with medications that destroy the intestinal’s own beneficial microflora, thereby weakening the body’s defenses and facilitating the penetration of pathogenic pathogens.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Advanced stages of chronic allergies.
- Exceeding radioactive exposure standards.
- Impaired blood supply to internal organs.
- Infectious or bacterial pathologies developing in the intestinal cavity.
- Poisoning with harmful substances that disrupts the intestinal microflora.
- Overwork, long-term stressful situation, turning into depression.
- Disruption of normal intestinal function caused by various pathological conditions in it in the form of gastritis, pancreatitis and the like.
- Infection with parasitic types of infections.
Any of these conditions can lead to changes in the intestinal mucous membranes. It is necessary to take all measures to prevent provoking factors, which will avoid the development of such a serious lesion as erosive colitis.
Factors influencing the development of the disease
Erosive-ulcerative colitis can form under the influence of many internal and external factors. Some are purely individual. It is impossible to independently determine the root cause. Only a doctor can do this, taking into account all the characteristics of the patient’s condition. All provoking factors are described in the table.
| Internal factors |
|
| External factors |
|
Often the pathology develops against the background of a long-term dietary disorder. The risk of developing a disorder increases if a person has a hereditary predisposition or addiction to alcohol-containing drinks.
Read more: what is colitis.
As the disease develops, minor inflammatory lesions appear on the intestinal mucosa. If left untreated, the defects become erosive. Over time, they increase in size and deepen.
One of the reasons for the development of the disease is poor nutrition.
A through defect may appear. The speed of the deviation directly depends on the negative factors that affect the body.
Main types and forms of the disease
One of the features of erosive colitis is the difficulty in its classification, so it is divided into types and forms according to specific characteristics.
Acute form of erosive colitis
It is this form of colitis that forces patients with this disease to seek medical help. Since the condition accompanying this form is accompanied by rather painful manifestations, often reaching such intensity that it is impossible to get rid of the pain even with the help of antispasmodics. Moreover, the pain only increases as inflammation develops, causing the need for immediate medical attention. If this does not happen and drug therapy has not been applied to the patients, then over time the painful symptoms subside, which does not mean recovery, but rather, on the contrary, the acute form of the disease takes on a chronic form, which is much more difficult and longer to treat.
Chronic form of colitis
The disease acquires such properties as a result of untreated acute colitis, as well as in the case of a complete lack of medical care. If the acute state of the disease is accompanied by non-compliance with the correct diet, which is mandatory for inflammation in the intestines, then colitis most often takes a chronic form with frequent periods of exacerbation and subsequent states of remission. During relapses, painful symptoms manifest themselves quite actively, without subside, but only reducing their intensity even during periods of calm.
In addition to the forms of colitis, it has several types that characterize it, such as:
- Ulcerative - determined by the presence of ulcerative lesions on the mucous membrane of the large intestine. For its development there must be a reason in the form of previous dysbiosis, violation of the principles of proper nutrition, as well as insufficient physical activity. It can take three stages of development, the most dangerous of which is the last third stage, often ending in rupture of the intestinal wall, and in the absence of emergency treatment, the development of sepsis and death.
- Spastic - occurs against the background of decreased intestinal motility. It manifests itself as a persistent violation of defecation in the form of prolonged constipation, which cannot be eliminated even with appropriate medications. Causes the formation of cracks in the walls of the colon caused by dryness of its walls. When diagnosing, it requires the use of rectoscopy.
- Catarrhal – represents one of the stages of a general disease. It is characterized by rapid development with the presence of pronounced characteristics. May be a consequence of food and alcohol poisoning.
- Atrophic – serves as the final stage of the spastic form, accompanied by a weakening of smooth muscles in the intestines, and if left untreated, it easily takes on an ulcerative appearance. Threatens perforation, turning into sepsis and peritonitis.
- Erosive - considered the initial stage of the ulcerative type, exhibits symptoms similar to the latter, but to a less pronounced degree.
- Diffuse is the most severe condition, affecting the large intestine and small intestine, manifesting itself with severe symptoms from the beginning of its formation.
Since colitis can have many types, it is often quite difficult to make a diagnosis and determine the nature of the disease. The doctor needs to conduct a careful examination, on the basis of which he will draw conclusions about further therapy necessary in the case of each specific type of colitis.
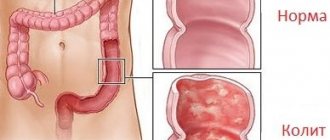
What is colitis
Colitis has nothing to do with intestinal colic. It is an inflammation localized in the large intestine and occurs in both acute and chronic forms . The disease affects the mucous membranes and is observed in 50% of patients complaining of problems with the digestive system.
In the case of an acute form, the symptoms can be so severe that it is difficult to neutralize even with the help of antispasmodics. Ulcerative colitis is characterized by the appearance of tiny ulcers and abscesses, which lead to the development of pathological processes and blood impurities accompanying the act of defecation.
It is characterized by alternating periods of remission and exacerbations. Remission can last from two to three weeks to many years. The inflammatory process that accompanies colitis usually begins in the rectal area, after which it spreads to other segments of the large intestine . It happens:
- Spicy . It is characterized by rapid development, loose stools, vomiting, fever, malaise, weakness, loss of appetite and the presence of dull pain in the form of spasms.
- Chronic . Occurs due to previous colitis left without proper treatment. It is non-infectious in nature, and is most often triggered by allergic reactions, dysbacteriosis and poor nutrition.
- Medicinal . Appears due to prolonged use of medications. Such forms of colitis most often occur in patients who prefer self-medication and abuse pharmaceutical drugs.
The spastic type of colitis occurs against the background of weakened peristalsis of the intestinal tract and frequent disorders of the stomach.
One of the main symptoms is the presence of problems with bowel movements and chronic constipation.
Spastic colitis is characterized by swelling of the colon and dryness of its walls, which entails the appearance of cracks, which are revealed by ultrasound and rectoscopy.
The catarrhal type of colitis manifests itself mainly in the initial stages of the disease and has pronounced symptoms.
If you suspect catarrhal colitis, you must immediately consult your doctor , since the disease, left without proper treatment, is fraught with transformation into an ulcerative form. With atrophic colitis, the walls of the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract atrophy, and lack of treatment leads to sepsis and perforation of the intestinal walls.
The diffuse type of colitis affects two segments of the intestine (large and small), but the symptoms in such cases are rather mild. Diagnosing such colitis is extremely difficult. Often, in the first days of an exacerbation, pain localized in the lower abdomen or in the right hypochondrium is observed.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing erosive colitis, various methods are used, ranging from interviewing the patient and ending with the most complex instrumental examination of the intestinal cavity. In this capacity the following is used:
- Laboratory tests, including:
- general blood test to determine the level of ESR, the presence of leukocytosis;
- carrying out a coprogram with the detection of leukocytes and blood in feces;
- examination of stool cultures for the presence of bacteria;
- PCR to determine the presence of parasitic and viral presence.
- Instrumental research:
- carrying out irrigoscopy with contrast to determine the places of narrowing in the intestines;
- Ultrasound – checking the presence and size of a lumen in the intestinal cavity;
- conducting an examination using fibroileocolonoscopy to determine the site of inflammation;
- examination using MRI.
It is not at all necessary that all these diagnostic methods will be applied to one patient. Often the disease has pronounced symptoms that do not require multiple confirmations.
Treatment principle
To eliminate colitis, the patient must undergo drug treatment along with a strict diet. The very principles of therapy for this disease can be classified into two types: inpatient or outpatient treatment. Both types require an examination by a physician, certain dietary restrictions, and medications. The inpatient treatment method is used for patients with severe colitis to apply serious treatment methods to them, including removal of the affected tissue. The treatment provided must take into account the characteristics of the infectious process, its stage and the damage caused.
Drug treatment
As the main treatment for patients with colitis, various medications are used, each of which has a whole set of properties aimed at the inflammatory process, namely:
- antibiotics that are prescribed in case of an infectious nature of the disease, most often Cifran, Enterofuril or Rifaximin are used in this capacity;
- anthelmintic drugs prescribed when parasites are detected;
- painkillers prescribed for severe pain in the form of Papaverine, No-shpa;
- means that can normalize the processes of defecation, for diarrhea - oak bark, tabalbin, and for constipation - drugs that have a laxative effect.
When choosing among medications, it is necessary to pay special attention to diseases associated with colitis, such as cracks formed in the anal mucosa or sigmoiditis, as well as other possible pathologies. All of them also need treatment.
Folk remedies
According to official medicine, it is impossible to cure colitis with folk remedies alone. But it is quite possible to increase the duration of the remission period, as well as to ease the course of the exacerbation period, with recipes based on medicinal plants. For this, a variety of components are used in the form of decoctions, infusions, healing baths, compresses and much more. Such recipes include:
- Honey water prepared from 1 tbsp. l. honey and a glass of warm water, which is drunk a third of a glass up to three times a day.
- Eat a small spoonful of bee bread every day, washed down with warm water.
- A mixture of a spoon of honey and 200 g of apple juice, drink 0.5 glasses in the morning and evening.
- Dry herb St. John's wort in the amount of 2 tablespoons. lie Brew 0.5 liters of boiling water and keep on fire, without bringing to a boil for no more than 10 minutes, leave for about an hour.
Any remedy used to treat colitis should use pharmaceutical ready-made herbs and formulations. Before using one of them, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Treatment of erosive colitis
Depending on the stage of erosive colitis, your doctor may recommend one treatment option or another. In any case, first of all, this is a certain diet and appropriate drug therapy.
Drug treatment
There are different treatment options for erosive colitis, so the list of drugs may vary. Usually the following groups of drugs are distinguished:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. They contain 5-acetylsalicylic acid - sulfasalazine. The active substance has an anti-inflammatory effect on the body and has a positive effect on immune responses in general. These could be Pentasa or Salofalk.
- Glucocorticosteroids are mainly used for severe forms of the disease. Their main goal is to reduce inflammation and eliminate bleeding in the intestines. Represented by the drugs Hydrocortisone and Prednisolone.
- Immunosuppressants are drugs aimed at suppressing immune responses and relieving symptoms of the disease. They act so that colitis goes into remission. Medicines include Cyclosporine, Methotrexate, Azathioprine and others.
- Antibiotics are used to control infection and come in a wide range of different medications.
- Painkillers - Paracetamol is mainly used.
Remember that it is not recommended to take drugs such as Diclofenac, Ibuprofen or Naproxen, as well as substances that contain them.
Diet
One of the important points of treatment is following a special diet that will help bring the body back to normal. A gastroenterologist or nutritionist will create such a diet based on tests and characteristics of the disease. The list of foods and drinks must be selected so that not a single element contributes to the development of inflammatory processes.
One of the basic principles of the diet is fractional meals. This means that a person needs to eat up to 6 times throughout the day. The main idea is to reduce the amount of carbohydrates consumed and at the same time get 100-120 grams of protein and fat per day.
Among the general recommendations, we can highlight that the food itself during meals should be at normal temperature (not too hot or cold).
strictly forbidden to use:
- salted, smoked and pickled;
- roast;
- foods that contain large amounts of fiber;
- chocolate and sweets, fast food;
- alcohol and carbonated drinks;
- dairy products;
- flour;
- fatty meats;
- porridge - barley, millet and oatmeal.
Recommended to use:
- soups;
- lean meat in the form of meatballs and cutlets;
- chopped boiled vegetables;
- porridge cooked in water from cereals.
Drinks allowed include weak coffee, tea and fruit juice (except apricot and grape). You can also include jelly and a decoction of rose hips or black currants in your diet.
Treatment at home
There are various traditional medicine methods that can be used to relieve symptoms and cure colitis. Here are a few recipes that you can prepare at home:
- Mix propolis with alcohol in a ratio of 1:2. Take half a glass 3 times a day, after dissolving the mixture in 100 grams of warm heated milk.
- Treatment with raspberries. Take half a glass of fresh fruit and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over it. After this, let it sit for about 30 minutes. You need to consume about 100 g 3 times a day before meals.
- Mint infusion. Grind 2 tablespoons of mint leaves and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over them. Leave for at least 2 hours. Drink half a glass 3 times a day.
- Herbal collection. Take equal amounts of centaury, chamomile and sage leaves. Pour 250 ml of boiling water and let it brew for 30 minutes. Drink the infusion throughout the day in small sips with a break of about 2 hours.
- Bird cherry. Take 2 tbsp. l. cherry berries and fill them with water, bringing to a boil. It is necessary to boil for about 5 minutes, then let it brew for 2 hours. Drink 50 ml 3 times a day.
In addition to taking infusions and proper nutrition, if necessary, pharmacological drugs can be administered into the rectum. One of the most effective and simplest is a glycerin enema.
It is very simple to prepare it at home: take half a glass of glycerin and fill it with two liters of water. Alternatively, glycerin can be replaced with 6% apple cider vinegar.
Surgical intervention
One of the main disadvantages of this option is its increased trauma, because the basis of surgical intervention is the removal of part of the large intestine. At the same time, holes are made to remove feces and small bags are attached to them - colostomy bags.
The procedure is unpleasant, and the solution can be either temporary or lifelong. Interventions are of the following types:
- Laparoscopy. The patient is given 4-5 punctures or an incision in the lower abdomen.
- Today in medicine, the single-port access , in which the surgeon makes only one hole in the abdominal wall, through which the inflamed piece of intestine is removed.
In any case, surgery is a last resort method of combating erosive colitis and is used in severe forms of the disease, or if the intervention is urgent.
Prevention
Prevention against the development of erosive colitis is simple; it does not require much time or effort, and timely prevention is preferable to treating an advanced disease.
In order not to provoke the development of colitis in the large intestine, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- at the first suspicion of changes in the condition of the intestinal mucosa, immediately visit a doctor;
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle, devote more time to movement and eat right;
- try to give up your existing bad habits forever.
The state of his gastrointestinal tract depends on how much the patient cares about his body and what foods he eats. Proper nutrition plays a large role in preventive methods aimed at preventing erosive colitis.
Traditional methods of treatment
Folk remedies for the treatment of erosive colitis include a large number of recipes:
- 2 tbsp. spoons mix chamomile, cyanosis and buckthorn bark, add 3 tbsp. spoons of dried marsh grass, 1 teaspoon of dill seeds. Pour 2 tbsp. spoons of the collection mixture with boiling water (300 ml) and leave for 2 hours. Drink the infusion 30 minutes before meals three times a day, 70 ml;
- Mix 20 g of dry pomegranate peels and 50 g of fresh pomegranate with seeds and add 200 ml of water. Boil the mixture for half an hour and drink 2 tbsp. spoons twice a day;
- to alleviate the condition and get rid of symptoms, you should eat 8 g of propolis every day for a month on an empty stomach;
- 100 g of dried watermelon rinds are poured with 400 ml of boiling water and infused. The infusion is taken 6 times a day, half a glass;
- 1 tbsp. pour 200 ml of boiling water over a spoonful of cumin seeds and leave for half an hour. Drink 1 tbsp of the product. spoon 3-4 times a day;
- Onion juice helps solve colitis problems well; it is consumed 3-4 times a day, 1 teaspoon;
- 1 tbsp. a spoonful of elecampane root is poured into a bottle of Cahors (or port). Add 1 tbsp. spoon of honey, cook for 10 minutes. You should drink 50 ml of the product after meals;
- 50 g of black poplar buds are poured into 0.5 liters of vodka, left in a dark place for 14 days, periodically shaking the container with the product. Take the tincture a quarter of an hour before meals 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. spoon;
- mix 20 g of wormwood leaves and 20 g of sage leaves. Pour 1 tbsp. spoon of mixture 200 ml of boiling water. They insist for half an hour. Drink the infusion every 2 hours, 1 tbsp. spoon.
ICD 10 code
Erosive chronic colitis is an inflammatory process that affects the mucous tissue of the colon. The disease is accompanied by characteristic symptoms such as flatulence, constipation and diarrhea, bloating and painful manifestations. Pathological changes in the condition of the intestines are caused by a decrease in immune defense, dysbiosis or inflammation in one of the gastrointestinal tract organs. According to ICD-10, the chronic form of erosive colitis is designated by code K50-52.
How does intestinal inflammation develop?
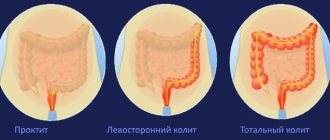
In addition to Crohn's disease, erosive colitis is the most common chronic inflammatory bowel disease. EC only affects the colon and does not affect other parts of the digestive tract. The disease begins in the last segment of the rectum. From there it migrates to the rest of the intestine.
Doctors talk about proctitis if only the rectum is affected. Proctosigmoiditis occurs when EC migrates into the sigmoid colon. If the disease spreads to the entire colon, doctors call the disease pancolitis.
Pancolitis
Diet
The leading role in the treatment of colitis is given to nutrition, not only during periods of exacerbations and intensive care, but also during long-term remission. The main requirements that must be adhered to are:
- do not eat food that is difficult for the stomach to digest;
- stick to fractional meals;
- increase the share of vitamins, fresh fruits and vegetables;
- do not eat at night;
- give preference to steamed dishes.
If, following these tips, your health continues to deteriorate, then you should reconsider your diet and exclude from it anything that can disrupt the normal functioning of the intestines.
Complications
Since erosive colitis cannot always be diagnosed in the early stages, its development is often not accompanied by the necessary treatment. Without treatment, the risk of complications remains very high, which manifests itself in the following conditions:
- development of intestinal or gastric bleeding;
- perforation of the walls of the large intestine;
- changes in the condition of the oral cavity in the form of stomatitis;
- pathological disorders in the liver;
- oncological diseases.
The erosive form of intestinal colitis requires immediate medical assistance to avoid irreversible consequences. A variety of factors can contribute to its development, and even in the absence of characteristic symptoms, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and following a light diet is of great importance and can influence the nature of the disease.
Disease prevention
To avoid the development of erosive colitis, the following preventive measures should be followed:
- get rid of bad habits - drinking alcohol and smoking;
- Avoid drinking coffee, as it can aggravate the course of the disease, cause bloating, and contribute to diarrhea and abdominal pain. It also causes re-development of erosive colitis;
- regularly carry out preventive examinations, which will allow you to identify the problem at an early stage and promptly prevent its development;
- lead an active lifestyle and follow the principles of proper nutrition;
- treat caries and other diseases of the oral cavity in a timely manner - this will prevent the infection from entering the food tract;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- eliminate any stress.
References: nadejdamed.ru/medical/proktologiya/lechenie-kolita/erozivnyj-kolit/ https://yandex.ru/health/turbo/articles?id=4413 https://www.nrmed.ru/rus/dlya- vzroslykh/proktologiya/kolit-kishechnika/ https://www.rlsnet.ru/articles_431.htm med.vesti.ru/articles/zabolevaniya/kolit-kishechnika-simptomy-i-lechenie-u-vzroslyh/ med.vesti.ru /articles/zabolevaniya/vospalenie-tolstoj-kishki-simptomy-i-lechenie-kolita/ https://fnkc-fmba.ru/zabolevaniya/yazvennyy-kolit/ https://www.msdmanuals.com/ru/occupational/diseases -gastrointestinal-tract/inflammatory-intestinal-diseases-ICD/ulcerative-colitis https://empendium.com/ru/chapter/B33.II.4.17. https://www.gosmed.ru/lechebnaya-deyatelnost/spravochnik-zabolevaniy/gastroenterologiya-bolezny/nespetsificheskiy-yazvennyy-kolit/ https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ulcerative_colitis https://www.gmsclinic.ru /specialist-services/ulcerative-colitis-treatment Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/18/2020