Causes of leukoplakia
The causes of the pathology are not fully understood.
We can only say with certainty that leukoplakia develops under the influence of irritating factors: The greatest danger is a combination of several provoking factors. Why do lesions of the mucous membranes of organs occur:
- The use of dentures made of different metals provokes the occurrence of a galvanic current, which has a destructive effect on the epithelium of the oral cavity. During prosthetics, injuries to the mucous membrane occur. In people with nicotine addiction, damage to the membranes occurs under the thermal and chemical effects of cigarette smoke.
- Pathology of the cervix develops as a consequence of diathermocoagulation (cauterization of affected areas of the organ with high-frequency current).
- The pathology is caused by inflammation and neurodystrophic changes in the epithelial layer of the mucous membranes. It is a consequence of frequent stomatitis, cystitis, and vaginitis. Chronic forms of these diseases are dangerous.
- One of the causes of the disease is heredity. Statistical data confirms the high process of patients with leukoplakia who have congenital dyskeratosis (impaired keratinization of the epithelium).
- The general state of health plays an important role in the development of pathology. Hormonal imbalances, hypovitaminosis or vitamin A deficiency, involutional restructuring of the genitourinary system (transformation reverse to the natural state), gastroenterological diseases, low immune status are risk factors.
- It is impossible not to take into account harmful working conditions and diseases associated with them.
Leukoplakia of Tappeiner smokers
Esophageal cancer - causes and symptoms, treatment and complications of esophageal cancer
Leukoplakia affects the hard palate and adjacent areas of the soft palate. Some patients experience negative changes in the marginal area of the gums. In some fragments the mucous membrane is folded and, due to the disease, acquires a grayish-white tint. The light spot is covered with visible red dots of cyst-like dilated ducts of the salivary glands.
Leukoplakia of this form often occurs in conjunction with other types of disorders that are associated with damage to the corners of the mouth, cheeks and lower lip. The disease in question is characterized by the ability to restore its previous state.
After getting rid of the bad habit, the spots disappear, because the soft tissues of the oral cavity are no longer affected by irritants that contribute to negative changes.
The concept of leukoplakia of the esophagus
Many diseases of the digestive tract are associated with damage to the mucous epithelium. Therefore, leukoplakia of the esophagus is not an exception, and everyone needs to know what it is. The disease manifests itself not only as an inflammatory process on the mucous membrane, but also during the course of the pathology, keratinization of the affected tissues occurs. In medicine, pathology is designated under the ICD-10 code – K13.2.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane occurs due to the formation of plaque. After some time, the affected areas die off. Then the destruction of the tongue occurs. This process extends to the inner surface of the cheeks and the mucous epithelium of the oral cavity as a whole. During the course of the disease, the tissues of the esophagus undergo a process of deformation. This leads to dysfunction of the organ, and food is completely unable to reach the stomach.
The danger of leukoplakia of the esophagus is the occurrence of cancer of the affected organ. If help is not given in a timely manner, the process of deformation of the mucosa is complicated by the rejection of the upper layers of the epithelium. People under 30 years of age are at risk.
Causes
Esophageal atresia. tracheoesophageal fistulas. achalasia of the esophagus
Different localizations of leukoplakia are caused by different reasons and require an individual approach in developing a treatment strategy.
Hairy leukoplakia develops against a background of reduced and weakened immunity, so most often this type of disease is diagnosed in patients with HIV, various immunodeficiencies and during rehabilitation after organ transplantation, when a course of immunosuppressants is prescribed.
- Leukoplakia of the external genitalia in women develops most often during menopause, when reverse development processes occur in tissues and cells. Mucous tissues and skin become drier, hair loss is observed, which is a normal physiological process.
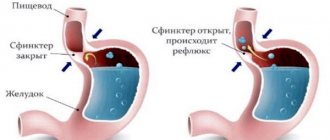
- Leukoplakia of the esophagus develops after heartburn or burns of the mucous membrane of this organ; more than half of the cases of this disease cause the appearance of a cancerous tumor.
- Leukoplakia in the oral cavity is most often localized on the mucous membranes of the inner side of the cheek, the hard and soft palate, as well as in the angular folds of the mouth. Leukoplakia of the tongue is extremely rare in medicine.
To this day, official medicine does not know the exact reasons for the development of this disease in the mouth. However, a number of factors have been identified that increase the chances of developing leukoplakia:
- metabolic disorders;
- genetic predisposition;
- lack of vitamin A;
- smoking;
- chronic injuries to the mucous membranes (for example, due to improperly manufactured dentures);
- activities associated with direct contact with coal and coal tar, as well as their processing processes;
- HIV and AIDS;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the mouth associated with neurological disorders.
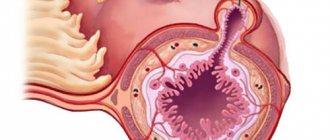
Leukoplakia of the bladder is a protracted chronic disease that is characterized by the degeneration of transitional epithelial cells into squamous epithelial cells. The keratinized epithelium is unstable to urine components, which causes inflammation in the bladder cavity. The main cause of the development of the disease is ascending infection with sexually transmitted pathogens. Therefore, leukoplakia in the bladder develops more often in women - their urinary canal is much shorter than the male one, so it is easier for infections to penetrate through it.
In some cases, the cause of leukoplakia can be a downward infection, when a pathogen penetrates through the bloodstream from nearby organs: staphylococci, Proteus, streptococci, E. coli and others. The development of the disease is favored by:
- chronic diseases of the abdominal organs located next to the bladder;
- all factors that reduce immunity: hypothermia, stress, bad habits, chaotic lifestyle;
- foci of chronic inflammation located at a distance from the bladder: tonsillitis, caries, sinusitis, etc.;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- the IUD was not removed in time in the uterine cavity;
- promiscuous sex life without the use of barrier contraception.
Leukoplakia of the cervix is called whitish formations (spots or plaques) that appear on the mucous membrane. To diagnose the disease, a preventive examination using a gynecological speculum is sufficient.
Like dysplasia, cervical leukoplakia requires mandatory treatment, since it is a precancerous disease. There are many reasons for the appearance of such tissue changes:
- decreased immunity for various reasons;
- injuries due to careless examination, termination of pregnancy, childbirth;
- interruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- current or previous infectious diseases of the genital organs.
Treatment methods
Classification of strictures (narrowings) of the esophagus
Leukoplakia of the esophagus requires complex treatment
It is important to seek medical help immediately when the first symptoms appear, because only in this case can the pathology be quickly and effectively cured
Drug therapy consists of the following drugs:
- vitamin therapy: the patient is prescribed a complex of vitamins, where vitamin A and B4 will predominate; vitamin preparations are needed to strengthen the immune system, because the disease significantly reduces the body’s defenses;
- sedatives: this can be tincture of valerian or motherwort, and in individual cases the doctor may prescribe tranquilizers;
- antiviral drugs: needed to relieve the inflammatory process, drugs are prescribed individually to each patient.
Treatment of leukoplakia of the esophagus with conservative methods involves a gentle medicine that will not irritate the mucous membrane of the upper digestive system.
Chemotherapy
Since the esophageal mucosa is resistant to chemotherapy, this method is rarely used. However, medicine does not stand still, and in recent years, chemoradiotherapy has pleased many with its positive results.
The following drugs are used in complex chemoradiotherapy:
- Methotrexate;
- Etoposide;
- Fluorouracil;
- Cisplatin;
- Bleomycin.
The method is prescribed to reduce the inflammatory process and slow down the degeneration of healthy cells into malignant ones.
The patient must adhere to the prescribed diet, stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages. You will have to completely eliminate fast food, fried, smoked, and spicy foods from your diet. In addition, you will need to strengthen your immune system through exercise, regularly visit the dentist, and practice good oral hygiene.
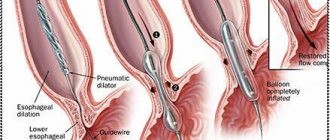
Surgical intervention
Surgery is resorted to only if conservative treatment does not bring the desired results. It is worth considering the fact that even after removing the keratinized area of the esophageal mucosa, you cannot stop taking the prescribed medications. This is the only way to protect yourself from relapses of pathology and speed up the recovery process. Surgery is performed in several ways.
Let's take a closer look:
- electrocoagulation: carried out using high-frequency current, the action of which is directed to the problem area; with the help of current, keratinized cells of the mucous membrane are burned;
- laser surgery: in this case, neoplasms are burned out with a beam of light directed to the right place;
- cryosurgery: the method uses ultra-low temperatures to freeze and destroy keratinized tissue, liquid nitrogen is used for this, the procedure does not cause pain to the patient.
What type of surgical intervention will be prescribed is decided only by the doctor, based on the specific case. Symptoms, stage of development of pathology, patient’s age and concomitant diseases will be taken into account.
What is the treatment approach?
Leukoplakia can be treated with complex therapy. First of all, the doctor requires the patient to eliminate all factors that constantly irritate the esophageal mucosa. In this case, you can only rely on the integrity of the patient himself.
Thus, a person must:
- stop smoking and drinking strong drinks;
- adjust your daily diet;
- do not drink hot water and food, as well as highly carbonated drinks;
- remove fillings, replace metal prostheses with some other ones.
In this case, the patient must undergo drug treatment, which includes:
- taking vitamins;
- intramuscular injections of 6% thiamine bromide solution;
- taking psycholeptic drugs, such as tranquilizers, infusion of valerian, motherwort, combined mixture of Quatera.
Types of disease
In gynecology, the following types of cervical leukoplakia are distinguished:
- simple cervical, which is represented by a background change in the epithelium in the form of a thin, rough film of a grayish tint. The pathology does not protrude above the layer of cells. It is difficult to detect during an examination on a gynecological chair. The disease is diagnosed by colposcopy with staining, which is the safest type;
- squamous leukoplakia, characterized by thickened epithelium with a tuberous structure. White plaques protrude above the cell layer by approximately 2 mm. The mucous membrane looks keratinized due to the layering of pathological spots on top of each other. The disease is determined during a routine examination by a gynecologist; this species has a high cancer risk;
- erosive, characterized by the appearance of white plaques with erosions on the mucous membrane. Pathological spots have varying degrees of severity and unequal size. Cracks may form on erosions. This type of disease occurs with pronounced symptoms.
Leukoplakia begins its development with minor inflammation in a small area of the epithelium. Next, the affected area becomes keratinized, a white lesion is formed, which in its shape resembles a plaque.
Oral leukoplakia
The oral cavity is another area most susceptible to leukoplakia. Due to the most frequent trauma, patients with pathology localized in this part most often turn to doctors. Children and people suffering from nervous disorders are characterized by frequent biting of the lips, tongue and inner surfaces of the cheeks. As a result, inflammation may begin in the injured oral mucosa and the process of epithelial death may begin—the formation of leukoplakia.
The pathology of the tongue in its simplest form looks like a cloudy film. In a more complex form, due to keratinization of areas of the oral mucosa, folds or white spots may form.
Leukoplakia also often forms on the gums - with improper care, most bacteria accumulate in the oral cavity on the gums, which lead to the development of inflammation and diseases.
In the oral cavity, leukoplakia is also treated using a laser or radio wave method - these methods have proven themselves and give good results in this case.
Chemotherapy and surgery
As for chemotherapy, it is used very rarely, because diseases of the esophageal mucosa are chemoresistant. However, medicine does not stand still. There are recent developments in this area that give good results. The patient must also undergo radiation therapy. It helps reduce inflammation and slow down the change in esophageal cells in the affected area.
Surgery is used if treatment by other means has not produced any results. During the operation, the affected areas of the walls of the esophagus are removed using radiation, laser, electrocoagulation methods and cryotherapy.
Of these, the best method is cryodestruction, during which inflamed lesions are cauterized using liquid nitrogen. After the operation, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory, keratoplasty, antiviral drugs, the use of interferon ointments or interferon injections.
Causes
The etiology of the disease is still not fully understood. A variety of factors can contribute to this development.
You need to understand that the condition of the esophagus is negatively affected by such things as smoking, alcohol or poor diet.
The most common reasons:
- Lack of vitamins and other important components in the body. It is these factors that have a positive effect on the birth of a malignant tumor.
- Bad habits. Such as alcohol or smoking. When a person smokes a cigarette, tar enters the esophagus with each breath. It turns out that it is an irritating effect that causes inflammation of the mucous membrane and has a destructive effect on cells, provoking various changes. Alcohol has never benefited anyone either. A high degree of drink burns the lining of the esophagus, the walls thicken and pathological changes begin. This phenomenon, perhaps, should be attributed specifically to those who like to indulge in alcoholic beverages very often. Alcoholics are at risk. They most often have problems with the esophagus and other important organs.
- Papillomavirus.
- Any food must be chewed thoroughly. And these are far from fashionable statements of nutritionists and the elite population of the earth. This advice has many benefits. First of all, poorly chewed food moving through the tube can injure it. Often a person swallows large pieces of food if he eats constantly on the go. This is a habitual way of life, but over time, unpleasant pathologies are discovered because of it.
- Heredity.
- Wrong food. First of all, you need to reduce your consumption of hot or spicy foods. At such moments, the mucous membrane is injured, it becomes rougher and becomes covered with scars. As a result, narrowing and leukoplakia are observed in the esophagus.
- Dentures made of metal alloys can also negatively affect the condition of the esophagus. Over time, they oxidize and begin to produce harmful compounds that poison the organ. Naturally, this is a long process that does not develop in one day.
Why does pathology occur?
The course of leukoplakia of the esophagus occurs in stages, first affecting the organ tube along its length. Then there is a thickening of the mucous membrane, the formations become more pronounced, ulcers appear, the healing of which does not occur, which brings significant discomfort to the patient’s life.
The main causes of leukoplakia include:
- Smoking. Cigarettes contain tars, which regularly have a negative effect on the mucous membrane of the esophageal tube, causing it to become keratinized and inflamed. The smoke inhaled by a smoker can provoke modification of the organ at the cellular level.
- Abuse of high alcoholic beverages. When they are consumed, a burn to the mucous membrane may occur, leading to its thickening. If a person constantly drinks alcohol, the membrane does not have time to heal and the condition of the organ worsens.
- Lack of vitamins in the body. The development of neoplasms can cause a deficiency of vitamins such as A, C, B, as well as insufficient amounts of folic acid and selenium.
- Availability of dentures. People who correct their bite with metal prostheses are also at risk, since metal negatively affects the condition of the esophageal mucosa.
- Dental diseases. Certain dental diseases interfere with the normal grinding of food, which can lead to injury to the esophagus.
- Eating hot foods. Such food can cause severe burns to the walls of the organ, which will then lead to scars appearing on them.
- Genetic disorders. If the disease is caused by genetics, then its treatment is carried out only with the help of a surgeon.
- The presence of papillomavirus in the human body.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies for a disease such as leukoplakia is primarily aimed at eliminating factors that contribute to the progression of pathology in the body. It is best when treatment with folk remedies is combined with drug therapy, which will speed up the recovery process.
Use of herbs and vegetables
Leukoplakia develops in the human body as a result of a decrease in the body's protective functions, so treatment of the disease should be carried out using means that help increase immunity. A good effect is achieved by using herbal tea and decoctions that can be prepared based on various herbal infusions.
Treatment of the disease can be carried out using fresh squeezed juices from vegetables and fruits, the use of which will not only strengthen the body’s protective functions, but also enrich it with vitamin A. Large amounts of the vitamin are found in foods such as:
Fresh juice from vegetables and fruits is a strong irritant, so it is recommended to dilute it with a small amount of water. It is for this reason that treating the disease at home is best done without consuming citrus and sour fruits.
Antiseptics
Leukoplakia is accompanied by the formation of keratinized areas of the epithelium, so treatment of the pathology should be carried out using local antiseptic agents. A good effect is achieved by rinsing the mouth at home using medicinal decoctions based on herbs such as:
Thanks to rinsing with decoctions based on these plants, the oral cavity is disinfected, which significantly speeds up the healing process. Leukoplakia of the oral cavity, which is accompanied by the formation of erosive and ulcerative affected areas, is treated with such folk remedies as Kalanchoe juice. Local applications are carried out using only special medications, but also with the help of sea buckthorn oil and rose hips.
If a patient is diagnosed with a mild form of pathology, then its treatment can only be carried out with the use of herbal preparations that have a supporting effect. A severe course of the disease is unlikely to be cured with folk remedies alone and you will have to resort to drug therapy.
We should not forget that leukoplakia is a dangerous precancerous condition, the progression of which in the human body can lead to the development of various complications. It is for this reason that treatment of pathology should be aimed at the speedy restoration of the affected areas of the mucosa, which will significantly reduce the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome.
Treatment of a mild form of the disease with folk remedies often gives positive results. However, even if the symptoms of leukoplakia completely disappear, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the mucous membranes. This is due to the fact that the pathology has a tendency to relapse and most often this occurs when exposure to external irritants on the mucous membrane is resumed.
Leukoplakia is one of the dangerous pathologies, therefore, even if the symptoms of this disease are completely eliminated, it is recommended to be monitored by a specialist. Any treatment should be carried out only after consultation with a specialist, which will quickly achieve a positive result and prevent the development of severe complications.
Treatment of leukoplakia with folk remedies has gained enormous popularity over the past couple of decades. And this is not surprising, because homemade recipes do not require a lot of effort, time, or money. In addition, such products are not inferior in effectiveness to medications.
Leukoplakia is a very serious disease, during which damage to the mucous membranes and keratinization of the skin epithelium occurs. This condition is classified as precancerous. Leukoplakia can affect both the female and male population.
Stages and forms of the disease
The disease is divided into stages. They are listed in only 3 theses, which differ in the degree of damage:
- only the submucosal layer of the esophagus becomes inflamed;
- destructive stage;
- proliferation of the affected lesion throughout the esophageal tube.
At the primary stage, damage to the epithelium occurs. Treatment at this stage of esophageal leukoplakia is carried out freely and is amenable to the recovery process. When destruction of the wall occurs without damage to other layers of the epithelium, this occurs at the second stage of the pathology. However, this causes damage to the lymph nodes. At the last stage, the affected area enlarges and spreads throughout the esophagus. At the same time, a narrowing of the organ lumen occurs. Inflammation does not spread to adjacent tissues.
In addition to stages, there are forms of the disease. In this case, the following types of esophageal damage are observed:
- flat;
- verrucous;
- erosive.
With flat leukoplakia, a whitish film appears that cannot be removed mechanically. The location and duration of the pathology affects the shade of inflammation. The color of the film varies from white to dark gray.
If a patient has verrucous leukoplakia, the mucous membrane becomes covered with white plaques. Without timely treatment, this form of the disease develops into cancer. There is an erosive type of pathology, which manifests itself in the form of ulcers and cracks at the sites of inflammation. This process occurs after the development of flat and verrucous leukoplakia. The erosive form can be single or multiple.
All directions of doctors in Izhevsk:
- Obstetrics
- Allergology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Venereology
- Vertebrology
- Physiotherapy
- Functional diagnostics
- Gastroenterology
- Hematology
- Genetics
- Hepatology
- Gynecology
- Hirudotherapy
- Homeopathy
- Dermatology
- Dietetics
- Immunology
- Infectious diseases
- Cardiology
- Kinesiology
- Cosmetology
- Speech therapy
- Otolaryngology
- Mammalogy
- Manual therapy
- Massage
- Mycology
- Narcology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Neonatology
- Nephrology
- Ophthalmology
- Oncology
- Orthopedics
- Osteopathy
- Pediatrics
- Plastic surgery
- Podology
- Proctology
- Psychiatry
- Psychology
- Psychotherapy
- Pulmonology
- Rehabilitation
- Rheumatology
- Radiology
- Reproductology
- Reflexology
- Sexology
- Somnology
- Sports medicine
- Dentistry
- Audiology
- Therapy
- Trichology
- Ultrasound
- Urology
- Physiotherapy
- Phlebology
- Phthisiology
- Surgery
- Cytology
- Endocrinology
- Endoscopy
- Epileptology
- Gynecology-endocrinology
- Dentistry-surgery
- Dentistry-therapy
- Dentistry-orthopedics
- Dentistry-orthodontics
- Dentistry-periodontology
- Dentistry-hygienology
- Dentistry-implantology
- Oncogynecology
- Maxillofacial Surgery
- Family medicine
- Coloproctology
- Traumatology
- Vegetology
- Reanimatology
- Otoneurology
- Transfusiology
- Thoracic surgery
Symptoms
As already mentioned, leukoplakia most often affects mucous tissues in the mouth, tongue, cheeks, lips, corners of the mouth, etc.
The pathological process also affects the genitourinary mucous membranes of the vulva, cervix, clitoris, vagina, head of the penis, bladder and urethra.
Leukoplakia can also affect the respiratory tract, localizing on the larynx, ligaments, etc.
The clinical picture of the pathology is determined by its type and location, so it is necessary to consider different types of leukoplakia separately.
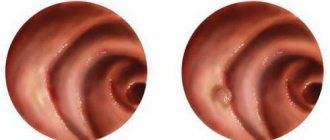
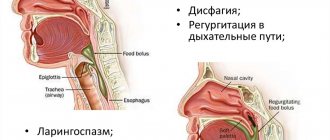
Esophagus
Clinical manifestations of esophageal leukoplakia are determined by the specific location of the inflammatory focus. Quite often, the pathology is accompanied by lesions on the oral mucosa. A characteristic film appears on the corners of the lips and cheeks.
The disease is characterized by:
- Hoarseness and hoarseness;
- Persistent cough;
- Feeling of sore throat;
- If ulcers, scratches and cracks appear, the patient is bothered by characteristic pain.
Over time, plaque degenerates into plaque formations, which are characterized by serous growths. If there is no treatment, the plaques become thicker and harden, and stenosis forms.
Externally, the esophagus acquires a warty or eroded surface. It is at this phase that malignancy occurs, when leukoplakia degenerates into a cancerous process.
Lips
Leukoplakia usually develops on the lower lip or in the corners of the mouth.
First, hyperemic spots appear, on the surface of which thickenings form. Gradually, these spots transform into white or gray plaques, and dense epithelial formations become even more pronounced.
Photo of leukoplakia lips
Over time, deep enough cracks form on the plaque formations, causing pain. The inflammatory process becomes chronic and, if left untreated, worsens.
Stomach
Gastric leukoplakia is often asymptomatic and becomes an unexpected finding during gastroenterological studies.
A similar form of pathology can occur against the background of tobacco smoking, alcohol abuse, burns from hot food, etc.
Urethra
Leukoplakic processes in the urethra usually occur against the background of hormonal imbalance, infectious lesions, STDs, etc. Often accompanied by painful sensations when urinating, cramping, etc.
In the mouth
The pathology is usually localized in those areas where frequent trauma to the mucous tissues by teeth, fillings or dentures occurs. A white-gray coating appears in this area, which is later replaced by a scaly coating.
If an erosive or hairy form of leukoplakia develops, then ulcerative and erosive lesions appear on the mucous surfaces.
Throat
Leukoplakia of the larynx or throat is a pathological degenerative change in the mucous tissues of the throat, accompanied by epithelial keratinization.
This pathology is called differently - pachydermia, keratosis, leukokeratosis, etc.
As with esophageal localization, the pathology is accompanied by discomfort when speaking, coughing and hoarseness. A laryngoscopic examination reveals areas with a white filmy coating.
Gums
With such localization, white spots appear on the affected areas of the gums. The pathology is most typical for smokers.
White spots are plaque-like lesions with a pearlescent tint, which, if not treated properly, enlarge and may crack or ulcerate.
In gynecology
In the field of gynecology, leukoplakia is usually found on the mucous membrane of the vulva, cervical canal or vaginal walls.
Quite often, leukoplakia is asymptomatic, and keratinized areas of the mucous membrane are accidentally detected during a medical examination.
In some patients, when leukoplakia is combined with gynecological inflammation, leucorrhoea appears, having an uncharacteristic odor and shade, accompanied by itching of the genitals.
Some girls note increased pain during menstruation and pain during sexual intercourse.
Leather
In skin lesions, the dry, rough surface of the leukoplakoplakia lesion usually causes the skin to feel tight. There are pronounced hyperemic foci around the lesion.
In children
In young patients, leukoplakia is usually localized in the oral cavity during puberty. Children complain of tingling in the mouth and painful areas that interfere with eating.
Typically, children themselves bite off the rough surfaces of the plaques, which only worsens the clinical picture of the disease, causing ulcerative processes.
Treatment with folk remedies
If the situation has not yet gone far and the patient has not developed cancer, treatment with folk remedies can help. However, before starting therapy in this way, you should consult your doctor. In addition, it is necessary to use folk recipes in combination with conservative methods. This method of treatment will definitely give a positive result.
There are several recipes, the use of which is recommended for the treatment of esophageal leukoplakia:
- Hemlock is considered one of the most suitable plants for this situation. It’s not difficult to make a tincture: to do this, chop the flowers and pour them into the jar to the very top, lightly tamping them down. Then pour the raw material with vodka. The infusion matures in a cool, dark place for 20 days; it must be shaken from time to time. After the preparation period has expired, the liquid is filtered and subsequently used according to a certain scheme: for 150 g of water, 2 drops of tincture on the first day of use, every day the content of the drug in the water should be increased by 1 drop, thus bringing the dose to 40 drops per 150 g water.
- Another way is a decoction of fir or pine. Needles from the plant should be brewed in boiling water in a ratio of 130 g of raw material per 0.5 liter of water. The broth should not cool for 15 minutes, that is, it can be kept on low heat all this time. Afterwards, you should wrap the container with the broth in a blanket and let it steep for at least 10 hours. Then the product is filtered, and it can be taken throughout the day, several sips at a time.
- Freshly squeezed carrot and beet juices are very useful for leukoplakia of the esophagus. Even an inexperienced person can cope with the preparation of such a product. In addition, the abundance of vitamin A in these juices is of great importance for recovery.
How does a doctor detect a disease?
After the patient sees a doctor and talks about his complaints, he will be sent for examination. The set of diagnostic measures includes the following:
- histological examination, during which a sample of organ tissue is taken during fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- performing gastroscopy of the stomach in the presence of endogenous factors that can provoke leukoplakia;
- examination by probing in the presence of a pathological inflammatory process in the stomach.
After receiving the diagnostic results, the specialist prescribes the appropriate treatment.