Classification of neoplasms
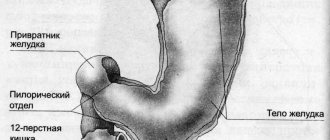
Neoplasms of the cardiac part of the stomach are divided into:
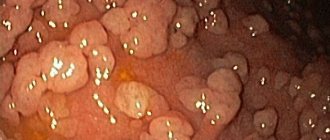
- hyperplastic. They occur most often. What it is? Extension with a pedicle or wide base. Not aggressive, do not degenerate into oncological tumors. If the polyp is small, then anti-inflammatory therapy is used and simply observed. After reducing the number of Helicobacter pylori, they disappear without a trace;
- adenomatous. There are tabular and papillary. They are the least common, but have a tendency to degenerate;
- glandular. Polyps grow from glandular cells. New growths on a thin stalk are gray or pink. Require prompt surgical removal;
- hyperplasiogenic. They arise due to impaired regeneration of the gastric mucosa. They never degenerate into malignant tumors. For single formations of small size, conservative methods of therapy are used.
The exact type of neoplasm is determined after MRI or histological examination. After this, the gastroenterologist selects a correction method.
Treatment of polyps in the stomach
As mentioned, treatment for polyps depends on their type, size and number.
Small polyps that are not adenomas do not always require treatment, although neither one nor the other should be allowed - observation is necessary. So you will need to periodically undergo endoscopic examination by a gastroenterologist. If the polyp begins to grow or is detected clinically, it must be removed.
Antibacterial therapy is necessary for chronic gastritis and Helicobacter pylori infection. This will prevent the formation of polyps and may even cause hyperplastic polyps to disappear.
Antibacterial therapy for chronic gastritis
Large polyps and adenomas must be removed surgically. Polypectomy in this case is also performed during endoscopy. The introduction of this technique has greatly simplified the treatment of gastric polyps.
Alarming symptoms
A polyp in the stomach signals itself:
- aching pain in the area of the pancreas and on the left side. Discomfort occurs immediately after eating and lasts for several hours. Patients relieve this condition with analgesics, but this negatively affects the activity of the liver and kidneys;
- bad breath. The phenomenon occurs not only with rotten teeth or inflamed gums. Polyps in the upper stomach and esophagus often rot or decay. At the same time, a characteristic, sharp, unpleasant odor is noticeable, which is not interrupted by chewing gum or mints;
- increased gas formation. With polyposis, food stays in the stomach longer than expected. It is poorly saturated with enzymes and hydrochloric acid. Then the masses rot in the intestines for a long time, mercaptan and other toxic metabolic products are produced;
- vomit. In advanced stages, patients suffer from vomiting. Blood may be present in the masses. This happens if the polyp is inflamed or decomposing;
- feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach. The presence of a cardia polyp interferes with the movement of food to other parts of the intestine. Because of this, even a small portion of light food lingers in the organ for a long time. A cluster of polyps or a large-sized tumor brings a lot of discomfort. Therefore, it is removed surgically as a matter of urgency.
Causes
The main cause of violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes of the stomach is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. The microorganism of the genus Helicobacter pylori is opportunistic and is normally part of the gastric microflora.
However, under the influence of negative factors of the Helicobacter colony:
- are rapidly increasing,
- reduce local endothelial immunity,
- contribute to the destruction of the mucous epithelium and the formation of neoplasms of the cardia.
Contributing factors are:
- heredity;
- age-related changes, impaired cell division of the mucous membranes;
- bad habits (systemic alcohol abuse, smoking);
- human papillomavirus infection with frequent relapses (how HPV is transmitted to women and men, read more here);
- diseases of the digestive system: stomach ulcers, erosions, duodenitis;
- tumors, cystic lesions of the mucous membranes.
Stress, psycho-emotional instability, unfavorable living conditions, long-term drug therapy, and nutritional factors can contribute to the development of growths. The latter play a key role in irritating the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Surgery for polyposis
A polyp of the cardiac part of the stomach can only be removed surgically. For this use:
- radio wave or laser surgery. The methods are new and have no contraindications. After such surgery, the patient does not need long-term rehabilitation;
- endoscopic manipulations. A small incision is made and polyps are removed from the cardia of the stomach using a flexible manipulator;
- resection is used only in advanced cases when alternative, low-traumatic methods will not give a normal result. After a surgical intervention of this kind, a person completely changes his lifestyle, and disability is possible.
What results does modern treatment give? The statistics are not rosy. High-quality removal of polyps does not protect against relapse. In 50% of patients, tumors grow again within 3 years. If the cones have not grown during this period, then the risk of reappearance is reduced several times.
Diagnostics
The most reliable method for diagnosing cardiac polyps is endoscopy and x-rays, including with a contrast agent. Usually these methods are secondary, prescribed after traditional ultrasound examination and laboratory tests.
The main methods of accurate diagnosis are:
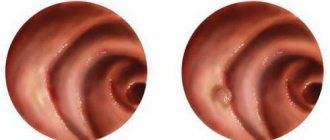
- gastroscopy - allows you to assess the size of the tumor, the number of polyps on the mucous membranes, the degree of tissue damage;
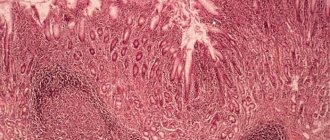
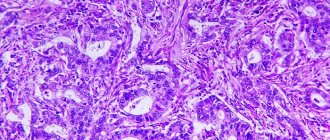
- biopsy for cytological and histological examination - helps to assess the degree of cancer risks and morphological changes;
- X-ray contrast methods to determine the contours of the stomach walls;
- analysis of stool for occult blood;
- general and detailed blood test (hemoglobin, PCR reaction, ELISA method);
- Analysis of urine.
Diet therapy
A hyperplastic polyp requires a change in diet. Nutritionists and gastroenterologists advise:
- Avoid fatty meat and fish dishes, sausages, sausages, canned food, and stewed meats. They contain a lot of salt, spices, and preservatives that irritate the sensitive surface. Replace foods with light poultry dishes, lean beef, and rabbit. It is optimal to steam, stew or boil them;
- cream, fatty homemade sour cream, cottage cheese are also not advisable for polyps in different parts of the stomach or intestines. Sources of essential amino acids include kefir, low-fat milk and cottage cheese, hard cheese and feta cheese;
- sour vegetables and unripe berries irritate the endothelium. But you shouldn’t give up a valuable source of vitamins, minerals and fiber. Choose zucchini, eggplant, pumpkin, peas and different types of legumes;
- marinades, pickled mushrooms, sauerkraut, Korean salads should leave your table. Give preference to stewed, baked, boiled vegetables;
- Keep the amount of coffee and strong black tea to a minimum. Caffeine and other stimulating extractives irritate the surface. Hyperplastic polyps and other neoplasms are actively growing among coffee lovers and steep tea drinkers. So think about it. If you cannot stop drinking these drinks at all, then reduce your intake to 2 cups per day;
- mayonnaise, store-bought ketchup and other ready-made sauces also have no place in the kitchen. They have no nutritional value but are high in fat, carbohydrates and sugar. And synthetic dyes, stabilizers, emulsifiers provoke hyperplasia and the degeneration of healthy cells into cancer cells;
- store-bought sweets and cream products stimulate the growth of fatty deposits and yeast in the intestines and stomach.
Removal
A promising method of treating cardia polyps is surgery, but not all surgeons strive to remove tumors at once. If the cardia polyp is single and does not bother you clinically, then a wait-and-see approach can be chosen with monitoring the condition and dynamics of the tumor at least twice a year.
There are three types of surgery for cardial polyps.
Endoscopic correction
Endoscopic manipulations are among the most common and safest methods of removing tumors. The indication for the procedure is a cardia rosette polyp with a diameter of no more than 3.5 cm and no signs of cancer.
Contraindications include:
- presence of a pacemaker,
- complicated clinical history,
- high risks of gastric bleeding,
- some blood diseases.
Before the procedure, patients drink a sodium bicarbonate solution to completely dissolve the mucous component of the stomach.
There are two operational approaches:
- Laparoscopy - punctures in the peritoneum in the projection of the cardia of the stomach and the introduction of endoscopic instruments;
- Endoscopy is the insertion of flexible probes with paths for surgical instruments through the pharynx and esophagus, as during gastroscopy.
Removal is carried out under general anesthesia (anesthesia is used). During endoscopic manipulation, the patient is placed on his left side, with his knees brought to his stomach. During laparoscopy, the patient is placed on his back. A tube with an optical tip and a special loop is inserted into the esophagus. The stalk of the polyp is cut and removed using an endoscope. The resulting polyp is sent for histological examination. The total duration of the operation is 30-60 minutes. The rehabilitation period lasts up to 14 days.
Regular endoscopic examinations and therapeutic manipulations damage the gastric mucosa, which can provoke relapses or intensive growth of small polyps.
Treatment with coagulation
Electrocoagulation is carried out according to the same algorithm as endoscopic polypectomy. The main difference is the use of biopsy forceps with a current function instead of a metal loop.
The method has many advantages, including:
- stopping bleeding,
- reduction of infectious risks,
- availability.
An analogue of coagulation with electric current is electroexcision. During the intervention, a dielectric loop is used.
It is possible to coagulate blood vessels and the wound bed using a laser, but laser removal of cardiac polyps is rarely used due to the complexity of the procedure and multiple limitations.
Abdominal surgery
A radical surgical method is indicated for:
- total polyposis (the number of neoplasms cannot be counted),
- the diameter of the growth is more than 3.5 cm,
- high risks of malignancy of tumor cells.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The patient is placed on the operating table, an incision is made along the anterior wall of the peritoneum, and gastric juice is removed. The polypous tissue is scraped off with a scalpel, and the resulting material is sent for histology.
If the result for cancer cells is negative, then the stomach is sutured with self-absorbable threads. If the risks are high or an oncological process occurs, then the damaged part of the stomach is removed within healthy tissue.
The indication for resection is necrotic changes in the mucous membranes.
Postoperative recommendations and rehabilitation
With endoscopic removal methods, the rehabilitation period lasts up to 14-18 days. Abdominal surgery requires a longer recovery.
Among the main medical recommendations are::
- Following a gentle diet (puree-like lean dishes, weak broths);
- Taking enzymes and drugs to restore gastric microflora;
- Elimination of physical activity;
- Medical examinations and monitoring of the condition of the gastric mucosa.
Conservative treatment
Typically, treatment is conservative, symptomatic, and has virtually no effect on the structure of the polyp.
The main indications for drug treatment are :
- exacerbation of the underlying disease,
- recovery after surgery,
- impossibility of performing the operation,
- small size of the growth.
The following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Antacids to normalize stomach acidity and relieve heartburn (Almagel, Smecta, Maalox);
- Defoamers for severe flatulence, increased gas formation (Espumizan, Kolikid, Metsil Forte);
- Painkillers (Almagel A with lidocaine, ibuprofen-based drugs);
- Antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverine, Spazgan, Omeprazole);
- Enzyme products (Mikrazim, Mezim, Gastenorm forte).
During the inflammatory process, it is important to prescribe antibiotics and antibacterial agents. For ulcerative-erosive process, medications are prescribed (Thiosulfate, Apilak, Amizil).
If polypous foci of the cardia tend to become malignant or the histology results reveal clear signs of oncological degeneration, then cytostatic drugs are prescribed. The mechanism of action is due to the destruction of the DNA of altered cells. Disadvantage: multiple side effects. Popular cytostatics are Busulfan, Teniposide, Azathioprine, Bicalutamide, Edercolomab).
The use of traditional methods of treatment is futile:
- Firstly, oral use requires strict adherence to the regimen and long-term treatment (up to several months).
- Secondly, some herbs are toxic when used over a long period of time and have a lasting negative effect on the gastric mucosa.