Causes of candidiasis of the digestive tract
Oddly enough, the main culprit in the development of mycological infections is progress. Medicine is developing at a rapid pace, creating more and more advanced medicines.
But this is a double-edged sword. The invention of antibiotics in the middle of the last century saved millions of lives. But long-term drug treatment negatively affects any type of microbe, creating an imbalance of the microflora.
A holy place is never empty, and the vacated space is populated by colonies of fungi.
- The accumulation of microorganisms of this type is characterized by the formation of a whitish coating, for which it has received the popular nickname “thrush”.
- Hormonal imbalances are another cause of the disease. Pregnancy, menstruation, menopause, and taking contraceptives change hormonal levels, promoting the proliferation of fungal colonies and the formation of candidiasis in women.
- Metabolic disorders and endocrine diseases create favorable conditions for the development of fungal infections. In particular, with diabetes, sugar levels increase - this is the optimal breeding ground for microscopic fungus.
- An unbalanced diet, a passion for sweets and carbonated drinks is a direct path to intestinal thrush.
- A weakened immune system also promotes the proliferation of candida in the digestive system.
- At risk are cancer patients, HIV-infected people, patients suffering from allergies and autoimmune diseases.
- Particular attention should be paid to infants. Intestinal fungus causes diarrhea. Frequent loose bowel movements can cause death from dehydration in an infant.
Causes
Favorable conditions for the development of Candidiasis appear after taking steroids, antibiotics, and oral contraceptives. A person can also provoke the development of fungus by eating large amounts of starch and sugar. The fungus, consuming simple sugars, can cause hypoglycemia and slow down metabolism, which will lead to obesity.
Harmful substances that may be contained in food, water, medicines or cosmetics contribute to the growth of the fungus. Infection with candidiasis is possible through exogenous and endogenous routes. With endogenous infection, one’s own fungi are activated, since there is no factor inhibiting their growth, that is, candidiasis occurs as a concomitant disease that develops against the background of reduced immunity.
With exogenous infection, spores enter the body through direct contact with a fungal infection carrier or from the environment. If the protective mechanisms are strong enough, then pathology will not be able to develop, but with weakened immunity, systemic candidiasis can form, in which the fungus affects the oral cavity, esophagus, and genitals.
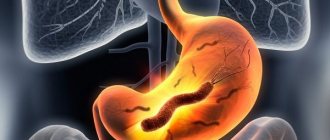
Gastric candidiasis can develop only if the cells of the organ mucosa do not produce enough hydrochloric acid. The most suitable environment for the development of fungus is pH 7.4; at normal pH of gastric juice (namely, up to 4.5), fungal growth is impossible, since it does not tolerate an acidic environment. Thus, for the development of gastric candidiasis, several factors are required:
- decreased immunity;
- reduced production of hydrochloric acid;
- presence of fungus in the body.
If the fungus has “captured” the esophageal tube, then under suitable conditions it can spread to the stomach.
Often, fungal spores enter the esophagus from the oral cavity, so esophageal candidiasis is confirmed by the presence of cheesy formations in the mouth or on the skin. But it also happens that candidiasis develops in the esophagus, but is absent on the oral mucosa. Infection with candidiasis through the endogenous route can be caused by taking medications that affect the composition of the intestinal microflora (antibiotics, glucocorticosteroids, hormonal drugs).
They destroy beneficial bacteria that prevent the development of pathogenic flora by releasing certain enzymes and creating special environmental conditions. With a decrease in local immunity, the fungus multiplies intensively due to the absence of a restraining factor and the presence of a nutrient substrate (sugars, starch), and can cause the development of systemic candidiasis, in which spores are transferred throughout the body.
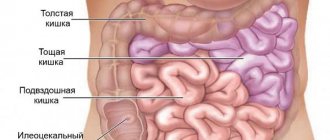
Thrush in the intestines: types of disease
Intestinal fungus actively develops when beneficial bacteria lose the ability to restrain its proliferation. The disease manifests itself in various forms:
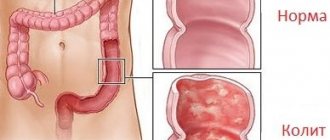
- Non-invasive candidiasis is characterized by a general deterioration in health, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
- Invasive intestinal candidiasis is a severe form of the disease. It is often a consequence of drug treatment with immunosuppressive drugs, glucocorticosteroids or cytostatics. This form of the disease is very rare, usually in patients with AIDS or cancer. Accompanied by diarrhea with bloody discharge and systemic damage to other organs: liver, kidneys, lungs, heart, eyes.
- Focal candidiasis is a consequence of duodenal ulcer. Occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the epithelium.
- Perianal candidodermatosis is a fungal infection of the anus. This occurs most often in homosexuals with AIDS.
Possible consequences and prognosis
Candida poses a threat to life only when it is systemically affected. It is much more important to establish the cause of activation of the fungal flora, so as not to miss and promptly correct a chronic disease, infectious disease or immunodeficiency.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- Details about the coprogram: preparation, conduct and interpretation of the analysis
- Irritable bowel syndrome: symptoms and treatments
- Causes of bloating and increased gas formation, treatment methods
- Rectal cancer: symptoms, stages, treatment and prognosis for life
- Rectal fissure: causes, symptoms and treatment of pathology
- Details about bowel cancer: stages, symptoms, treatment and prognosis
- Why is there mucus in the stool and how to diagnose the cause?
- More about hemorrhoids: causes, symptoms and treatment methods
- Diseases of the small intestine: symptoms and signs of the disease, treatment
- Typhlitis (inflammation of the cecum): symptoms and treatment methods
Be sure to read:
Details about the coprogram: preparation, conduct and decoding of the analysis
Symptoms and features of the disease
It is not so easy to identify intestinal thrush and determine the symptoms. This task is for a specialist. But you should know the signs of intestinal candidiasis.
Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract with intestinal candidiasis is accompanied by pain in the abdomen and stomach, increased gas formation, and a frequent urge to defecate. The stool becomes liquid.
When defecating, discomfort occurs in the intestines. Blood and mucus appear in the stool. It is possible that white particles of a cheesy consistency may be present in the feces. There is a constant feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. Appetite decreases.
An experienced doctor can make a diagnosis based on history, but it is easy for a patient to confuse the symptoms of thrush with other gastrointestinal diseases.
A feature of candida in the intestines are the following symptoms:
- frequent, unformed stools;
- spasm and heaviness in the abdomen;
- a feeling of intestinal incomplete emptying during bowel movements.
Dermatological problems can serve as indirect signs of the disease. An experienced doctor will associate characteristic symptoms with the appearance of pimples and acne on the back and face.
A rash like urticaria, spots and other types of dermatitis accompanied by itching are likely to appear.
Patients often experience general weakness, decreased performance, a feeling of drowsiness, loss of appetite, sleep disturbances and increased irritability.
Prevention
Gastric candidiasis is a disease that is easy to prevent but difficult to cure. The main rule is not to bring the body to exhaustion and dysbiosis.
It is strong immunity and healthy intestinal microflora that protect the body from Candida fungus. To prevent pathogenic microorganisms from having a chance to infect the intestines and subsequently reproduce in it, it is enough to follow the rules:
- take any medications as prescribed by a doctor and in prescribed doses;
- organize a balanced diet;
- maintain oral hygiene, wash your hands more often;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- lead a physically active lifestyle, regularly take walks in the fresh air.
IMPORTANT! People with gastrointestinal diseases are at risk of stomach damage from Candida fungus. They need to especially carefully monitor the appearance of unpleasant symptoms and immediately contact a gastroenterologist.
Gastric candidiasis requires long-term, consistent therapy, especially in advanced conditions. Improvement in health occurs within 1 to 6 months.
Getting rid of fungus in the stomach leads to a general improvement in a person’s condition.
Diagnosis of gastrointestinal candidiasis
If persistent discomfort in the intestinal area occurs, you should seek help from a medical specialist.
The attending physician prescribes a comprehensive examination to clarify the diagnosis. Feces are examined in laboratory conditions for the composition of the intestinal microflora and bacterial culture is carried out to clarify the causative agent of the disease.
Blood sampling is carried out for analysis in order to detect candida antibodies and immunoglobulins. The final result will show the number of colonies of the pathogenic microorganism.
For dysbacteriosis studies, not only feces, but also urine are taken to identify or exclude the spread of infection in the small intestine and upper intestine.
The genus Candida has many varieties. For each pathogen, it is necessary to select the appropriate drug.
The full clinical picture can be revealed using endoscopic examination, histological analysis of internal tissues and blood testing for immune status.
You can conduct a preliminary mini-test for intestinal candidiasis yourself at home, which should not exclude a visit to the doctor.
After waking up in the morning, before brushing your teeth, you need to spit into a glass of clean drinking water. If after 30 minutes the spit sinks to the bottom, there is a high probability of an excessive number of candida colonies. If the spit remains on the surface or mixes with water, the cause of intestinal inflammation is different.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is possible to determine whether you have fungus in the intestines and stomach or whether you suffer from any other digestive system disorders only in a hospital. Antibiotics should not be used to eliminate symptoms of fungus in the stomach. They are one of the main reasons for the development of candidiasis, because. greatly weaken the body.
To make a diagnosis and begin treatment, the doctor:
- analyzes the symptoms described by the patient;
- sends for a blood test to determine whether antibodies to the genus Candida are present in it;
- determines drugs to which gastric candida are sensitive.
A low level of immunoglobulin is the first symptom that fungi are operating in the body. Due to the weakness of the immune system, the body is exposed to various pathogens, including candidiasis. If the doctor determines that the body lacks a certain list of antibodies that block the extensive growth of fungus in the gastric mucosa, the patient is prescribed immunostimulating and immunomodulating drugs.
Endoscopy and examination of vomit/stool allows one to definitively determine whether the patient has candidiasis. During an examination with an endoscope, the doctor will be able to determine whether the patient’s gastric mucosa is inflamed or whether there are any other changes in the organ. Gastric candidiasis also manifests itself as low acidity. The most important thing during diagnosis is to determine the type of candida, because The range of medications that the patient will have to take during treatment depends on this.
Treatment method
Self-diagnosis and self-treatment of digestive tract thrush is unacceptable. Only a doctor can decide how to treat intestinal candidiasis. There is no single recipe.
When selecting funds, it is necessary to take into account many factors: the general condition of the patient, the presence of systemic diseases, the severity of damage to the gastrointestinal tract by pathogenic microbes, height, weight, gender and even the age of the patient.
Intestinal fungus, depending on the symptoms, can be treated with different methods. The doctor prescribes a therapeutic course individually for each patient based on medical history and laboratory tests.
Antimycotic drugs are used in combination with immunocorrective agents.
For non-invasive forms of the disease, medications such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, and fluconazole are recommended. The drugs are taken topically, orally, or injected. The dosage and methods of administration are selected by a specialist.
To treat intestinal candidiasis, intravenous drug administration is used. The tablet form of drugs may not achieve the goal, being absorbed through the digestive tract prematurely.
Drugs for the treatment of candidiasis, such as nystatin, levorin, pimafucin, can cause allergic reactions, side effects, and, with long-term use, provoke toxic hepatitis.
Using these tablets in accordance with the recommendations of a specialist gives good results. They are even prescribed to pregnant women.
Ketoconazole, fluconazole, and intraconozole cope well with the fungus. The peculiarity of the drugs is their surface effect.
Pathogenic microflora is concentrated in the lumen and on the intestinal epithelium. Effective therapy requires drugs that are poorly absorbed. Their task is to penetrate into the lower intestines.
For the treatment of invasive candidiasis, agents exported into the systemic circulation are used. The combination of candidiasis with bacterial infections requires the use of antibacterial drugs.
Candidiasis is one of the manifestations of dysbiosis. Complex treatment involves the inclusion in the therapeutic course of drugs containing coli-, bifido- and lactobacilli. This promotes the formation of healthy intestinal microflora.
To improve the functioning of the digestive tract, the doctor may supplement treatment with simultaneous administration of pribiotics.
Antifungal drugs are always used in combination with vitamins or vitamin-mineral complexes in order to strengthen the body's immune defense.
The effectiveness of treatment increases with diet.
How to properly treat intestinal candidiasis
Treatment of this disease requires a comprehensive and analytical approach. Medicines used for candidiasis may vary. But the treatment regimen for any form of intestinal candidiasis is the same. Here it is necessary to coordinate therapy that restores the patient’s immunity and intestinal microflora, as well as destroys the fungus and its spores.
When a non-invasive form of the disease is established by laboratory means, the following is prescribed:
- Vitamin therapy. To increase the body's defenses, various vitamin complexes are prescribed, containing a small percentage of essential minerals. For the most part, B vitamins are used, vitamin A, P, E and C. Remember that uncontrolled use of them can cause undesirable consequences.
- Antifungal agents. The doctor prescribes medications (fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, etc.), monitoring the patient’s weight. The most common treatment for intestinal candidiasis is fluconazole, namely “flucostat”. Flucostat is a drug of the latest generation that prevents the proliferation of fungi in case of intestinal candidiasis. In addition, it helps restore microflora. The release form of medicines can be in tablet form, in suppositories, or in solution for injection. Tablets are usually taken orally, but there is one “BUT”. It is not always possible to achieve the desired result with the help of tablets, so the solution is administered intravenously. Medicines have side effects, so they should be used only as prescribed by a doctor. If used incorrectly, they can cause liver problems.
The least number of side effects among antifungal drugs have:
- Pimafucin. Excellent for treating children, ladies in an “interesting” position and breastfeeding mothers. Has minor side effects.
- Nystatin and levorin. Successfully, practically without being destroyed during movement through the digestive tract, they suppress the fungus, but provoke the occurrence of allergic reactions and improper absorption of nutrients in the intestines, especially in children.
The invasive or diffuse form is cured with the help of resorptive drugs, the action of which begins after absorption into the blood. In connection with the addition of dysbacteriosis symptoms, antimicrobial agents, antibiotics, as well as probiotics, for example: Linex and bifidumbacterin, are additionally prescribed.
To achieve the best treatment results, medications are prescribed that eliminate abdominal pain and improve intestinal motility.
Folk remedies against candidiasis
Traditional medicine for the treatment of intestinal thrush suggests a healthy lifestyle.
To maintain the balance of intestinal microflora, it is recommended to eat fresh wild berries: blueberries, blueberries, honeysuckle. Leafy vegetables, greens, cabbage have a beneficial effect on intestinal function.
Eating garlic daily reduces the risk of developing a fungal infection. Horseradish has a depressant effect on the fungus.
Oatmeal jelly has a good effect on the condition of the intestines.
Oatmeal jelly recipe for treating intestinal thrush
Oatmeal is placed in a glass jar (shoulder-deep) and filled to the top with water mixed with kefir and covered with gauze.
The container is placed in a warm place for 3 days. Then the liquid is drained and the sediment is placed in the refrigerator. To brew jelly, take 2-3 tablespoons of sediment, add 0.5 liters of water, bring to a boil and remove. The healing jelly is ready.
For intestinal fungus, take herbal infusions:
- oak bark;
- burnet and calendula;
- yarrow;
- chamomile;
- St. John's wort;
- sage
Before using traditional recipes in practice, you should consult your doctor.
Which doctor should I contact for intestinal candidiasis?
A gastroenterologist is exactly the specialist who will tell you how to get rid of the fungus. He will prescribe all the necessary medications and help rid the gastrointestinal tract of parasites. The doctor’s responsibilities include restoring the intestinal microflora, diagnosing the gastric mucosa, performing smears, and studying secretions. It is equally important to understand your diet. All this will help avoid the development of complications and other consequences of the fungus.
Did you like the article? Like ♥, subscribe to our channel and you will be one of the first to know about new publications!
And if you have something to share, leave your comments! Your feedback is very important to us!
Diet for gastrointestinal candidiasis
The process of treating gastrointestinal candidiasis is long and complex. The effectiveness of drug treatment can be enhanced by proper selection of food products.
A balanced diet inhibits the growth of fungus in the digestive system. It is necessary to reduce the number of sweet, starchy and yeast products in the diet, normalize the intake of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins and microelements.
When starting treatment, it is necessary to completely exclude citrus fruits, sour berries and fruits from the diet for a month. The list of undesirable foods includes fruits like bananas and grapes.
It is strictly forbidden to consume alcoholic beverages, fresh baked goods, honey and other sweets during treatment. The use of enzyme-containing products is not recommended.
Marinades, vinegar, nut oil, mushrooms, wheat germ, potatoes and sausages are contraindicated.
Gentle cooking methods are recommended for heat treatment of products: boiling, steaming, stewing.
Treatment
Candidiasis developing in the gastrointestinal tract requires immediate treatment, since the fungus penetrates the submucosal layer, muscle tissue, and blood vessels. The inflamed mucous membrane can bleed, erosions and ulcers form. When actively multiplying, the fungus causes allergic reactions (bronchial asthma, urticaria, dermatitis).
There are many antimycotic agents that can effectively fight yeast-like fungus, but despite this, the disease is quite difficult to treat, since an integrated approach is required. The development of candidal infection is a marker of an immunodeficiency state, so it is necessary first of all to restore the immune system.
Candida, in the process of vital activity, releases many toxins that cause intoxication of the body and have an estrogen-like effect
Treatment of gastric candidiasis also requires correction of the intestinal microflora. Following a diet will help deprive the fungus of nutrients and speed up the restoration of mucous tissue. In addition, drug therapy is required, which is aimed at destroying the organism itself and regenerating the mucous membrane.
Diet therapy
Since the yeast-like fungus feeds on simple sugars, they must be excluded from the patient’s diet. It is necessary to remove from the menu sweets (refined sugar), dishes and drinks containing yeast (baked goods, beer, food additives, fermented foods), salad sauces, mayonnaise, pickled and smoked foods, blue cheeses.
You also need to beware of fruits that quickly begin to ferment in the gastrointestinal tract (grapes, melon). You need to eat small portions 4-5 times a day. To normalize the intestinal microflora, it is recommended to consume more fermented milk products, for example, kefir, sugar-free yogurt, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, yogurt, and mild cheeses.
Vitamins and microelements will improve the functioning of the immune system, so you need to add fresh vegetables and fruits, nuts, and cereals to your diet. Since the acidity of gastric juice is reduced, products that enhance the separation of hydrochloric acid are recommended. These are sour fruits and berries (apples, citrus fruits, lingonberries, cherries, cranberries, pomegranates, rose hips, viburnum) and juices from them, sprouted wheat grains, birch sap, koumiss, sauerkraut, cabbage juice, fruit juice, tea and coffee.
If you need to take medications (antibiotics or steroids, drugs that reduce immunity), you must tell your doctor about the presence of candidal infection so that preventive therapy can be prescribed.
Prevention of fungal diseases of the intestines
Fungal diseases are difficult to treat. It is easier to follow preventive measures to prevent intestinal pathology.
It is necessary to treat diseases of the digestive system, follow a diet, avoid long-term use of antibiotics, use purified water for drinking, avoid prolonged exposure to damp areas, avoid synthetic clothing, wear cotton underwear, change your toothbrush monthly, strengthen the immune system by hardening the body and taking vitamins.