One of the most common pathologies in children and adults is inflammation of the appendix, or appendicitis. Let's consider whether appendicitis is visible on an abdominal ultrasound, and whether it is advisable to use this diagnostic technique.
Is it possible to reliably see appendicitis on an ultrasound?
To diagnose appendicitis, clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods are used. An experienced doctor can make a diagnosis based on complaints and examination of the patient in 50% of cases. In other cases, the manifestations of the disease may be hidden, or the patient’s complaints resemble other pathologies.
In such cases, X-ray diagnostics were previously used, which helped differentiate atypical forms of appendicitis. With the development of ultrasound, it began to be used when the clinical picture was in doubt and it was necessary to exclude diseases with similar symptoms. These include:
- acute or chronic cholecystitis;
- ovarian cyst rupture;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- acute pilonephritis;
- cystitis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- Crohn's disease;
- omental infarction;
- mesenteric lymphadenitis;
- carcinoid , etc.
Many of these pathologies give a clear picture on ultrasound, and this makes it possible to exclude inflammation of the appendix. But whether it is possible to determine whether there is appendicitis using an abdominal ultrasound depends on several factors, including the following:
- location of the cecum;
- presence of gases in the intestines;
- thickness of the subcutaneous fat layer.
Also, the patient’s individual sensitivity to pain plays a role during the examination, since it is carried out without preparation, the cecum normally contains a certain amount of gases, and the diagnostician uses dosed compression and pressure with a sensor to improve visualization.
This technique allows you to displace gases from the cecum, because they do not allow ultrasound to pass through, thereby creating an acoustic window for searching and studying the appendix.
Carrying out the procedure
If pain is mild, or if the pain area is located in an atypical location, the analysis is carried out in the following way:
- Study of the apex of the cecum.
- Detection of iliac vessels.
- Study of the iliac muscle.
- Study of the place behind the cecum.
- Analysis of the condition of the peritoneal and pelvic organs.
- Especially for women, the right ovary is examined.
The final diagnosis is made by the doctor. There is not always enough data to make an adequate diagnosis. Some cases require additional tests, diagnosis using MRI, laparoscopy or CT. Conclusions are drawn based on the results of all types of research.
Ultrasound is often prescribed after removal of the appendix, especially if complications occur or a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition, allowing one to see the internal source of the complication.
Carrying out in women
The female body is structured somewhat differently. Therefore, the appearance of pain characteristic of appendicitis may indicate gynecological problems in the form of inflammation of the appendages or ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, a doctor cannot make a correct diagnosis only on the basis of palpation of the peritoneum and the results of blood and urine tests. This is exactly the option where ultrasound is indispensable.
During the procedure, a clear source of pain is visible. An examination of the peritoneal and pelvic organs reflects the condition of the appendages and appendix, allowing one to diagnose the exact cause of the ailment. The procedure when examining female patients is performed more often due to the structural features of the female body. The internal reproductive structure of women, the organs of the urinary system are in close contact with the digestive ones. As a result, inflammatory processes in the gynecological parts of a woman’s body spread to the genitourinary system or intestines.
In addition, during menstruation, a woman’s uterus swells, increases in volume and displaces other organs in the abdominal cavity. During pregnancy, the uterus enlarges many times; in addition to displacement, it compresses and disrupts blood circulation in the gastrointestinal tract, which leads to inflammatory processes. In this case, ultrasound remains a relevant research method that can show an accurate picture.
Features of the procedure in childhood
Children are not always able to describe the symptoms of an attack and cannot indicate where the pain is located. Conducting an ultrasound examination in children is a safe and quick way to determine the cause of pain and an accurate diagnosis. The attack itself develops much faster in a child than in adults.
This is due to the physiology of the child’s structure and the course of metabolic processes. An attack can be triggered by ARVI or tonsillitis, poor diet, dysbiosis, or gastritis. An ultrasound will show the source of inflammation and the cause of its development.
In some cases, removal surgery is contraindicated and antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Appendicitis gradually becomes chronic. The described point requires a mandatory ultrasound examination two or three times a year to monitor the condition of the appendix. This is necessary because the disease in a chronic condition can occur covertly and lead to aggravating consequences for human health.
Ultrasound diagnostics is an informative, safe, accessible method for identifying pathology in acute appendicitis. The procedure will help the doctor differentiate the ailment from other diseases, see inflammatory processes, exclude or determine the presence of problems in neighboring abdominal organs. Diagnostics can make it possible to establish the correct diagnosis, and if there is insufficient data, it is supplemented by laboratory tests, MRI or CT.
It is important to take good care of your health, monitor your physical fitness and well-being, and seek help in a timely manner if you feel unwell. Strong immunity will allow you to maintain health, prevent the development of pathological conditions and complications, and ensure a speedy recovery from illnesses
Well, if the body malfunctions and medical attention is required, modern research methods in the form of diagnostics using ultrasound will help make an accurate diagnosis and identify the true cause of the disease.
What is appendicitis, symptoms of acute appendicitis
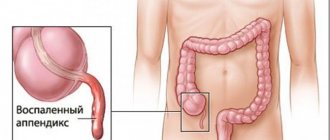
The disease is registered in 10% of children over 5 years of age and people under 40 years of age, although the possibility of development in the elderly cannot be ruled out. The vermiform appendix of the cecum is located in the region of the right iliac fossa and the inflammatory process in it is called appendicitis. The disease begins acutely, with diffuse abdominal pain, then it gradually takes on a focal character and is localized in the lower right part of the abdomen.
Since the appendix can have a length from 0.5 to 25 or more centimeters, be located retrocecally or descend into the small pelvis, in 50% of cases the clinical picture of the disease differs from the classic form of appendicitis. Symptoms can also be erased in children, pregnant women, and the elderly.
The main complaints of patients are the following:
- pain does not always have a clear localization, can radiate to the navel, spine, subsidence and then re-development of severe pain often indicates perforation and the development of peritonitis;
- temperature usually does not exceed 38 degrees Celsius;
- nausea and vomiting, as well as loss of appetite, can mask the pathology as infectious toxic diseases;
- diarrhea, more common in children, together with fever is an important prognostic sign in children who cannot accurately describe their complaints.
Patients also have dry mouth, a coated tongue, and specific symptoms of appendicitis.
Is it possible to detect other abnormalities instead of appendicitis during an ultrasound?
Quite often, the main symptoms of inflammation of the vermiform appendage indicate completely different diseases of the abdominal organs. When performing an ultrasound, doctors can diagnose the following ailments:
- Ketoacidosis.
- Hernia.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Gastroenteritis.
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Mesadenitis.
- Liver abscess.
- Porphyria.
- Inflammation of the ovaries.
- Renal colic.
- Lower lobe pneumonia.
- Acute cholecystitis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Intussusception.
- Salpingoophoritis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes).
- Diverticulitis.
Will an ultrasound show appendicitis or not, and how is the diagnosis carried out?
It is not always possible to see appendicitis on an abdominal ultrasound, especially if it has a retrocecal location. The search starts from the ileocecal angle, where it originates. Despite the fact that its dimensions can vary greatly, the diameter of the organ should not exceed 6 mm, and the wall thickness should not exceed 3 mm. It is the increase in diameter and wall thickness that is the first sign of inflammation.
To find the appendix, the doctor presses a probe on the area being examined to force gases out of the cecum. Also, during the inflammatory process, the appendage swells, which affects its flexibility and mobility. Fluid oozes around it, so when pressure is applied, its cavity does not collapse, and on the cut it looks like a target, due to periappendiceal effusion.
Effusion can also be found in the abdominal cavity, for example, in the pouch of Douglas in women. The tissues surrounding the process become hyperechoic and denser. This is due to their infiltration by leukocytes and macrophages.
In the future, with the development of the disease, perforation of the wall of the appendix and the release of contents into the abdominal cavity are possible, with the formation of purulent cavities. Ultrasound shows discontinuity of the wall and a hypoechoic formation adjacent to the process.
At an early stage of the development of the disease, it is informative to conduct a duplex scan, which shows increased blood flow in the organ. Transvaginal ultrasound is also used in women to detect appendicitis with an atypical low location.
But in some cases, it is not possible to see appendicitis if it is located behind the cecum. Difficulties in diagnosis also occur with chronic appendicitis, when, due to a sluggish inflammatory process, an infiltrate is formed around the appendix, which is a conglomerate of tissues of nearby organs, fatty tissue, and adhesions.
Ultrasound of appendicitis
Appendicitis is a serious pathology that requires urgent surgical intervention. The absence of classic signs of appendicitis can be observed in 50% of cases. For others, the symptoms may be very different and correspond to other diseases. How to avoid making mistakes when diagnosing, choose the right method and help the patient?
- In what cases is it necessary to do an ultrasound of appendicitis?
- Preparation for the procedure
- Progress of the ultrasound procedure for appendicitis
- What can an ultrasound show (deciphering the procedure)
Ultrasound of appendicitis in this case is one of the common research methods. Ultrasound examination of appendicitis is a painless procedure that uses ultrasound waves to diagnose and detect signs of inflammation of the appendix or their absence.
The accuracy of diagnostics such as ultrasound reaches 90%. In addition, ultrasound of appendicitis has a number of advantages
First of all, with such a study there is no radiation, which is very important if an ultrasound of appendicitis is performed on a child or a pregnant woman. Ultrasound diagnosis of appendicitis allows you to focus exactly on the area where it hurts
This method is very helpful for abnormal appendix positions or other pathologies with similar symptoms. Other advantages of the ultrasound method include the speed of the study, the availability of ultrasound (performed using a conventional sensor), and the low cost of the study.
Features of the procedure in childhood
When diagnosing appendicitis in children, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is used most often, since in childhood the disease is atypical, and the child cannot always explain what is bothering him or where the pain is localized. The vermiform appendix is involved in the formation of immunity, so removal of appendicitis in children should be carried out only after the diagnosis has been clarified using ultrasound.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity in most cases shows a disease such as appendicitis, so it is used for primary and differential diagnosis. No special preparation is required to conduct the examination. It is performed transabdominally, less often transvaginally. Ultrasound is a simple, inexpensive and informative technique used in the diagnosis of appendicitis.
Preparation requirements
Given the urgency of appendectomy in most cases, preparatory measures for ultrasound are ignored. Often, patients come to the doctor with acute pain in the lower abdomen on the right already at an advanced stage, when treatment is immediate and urgent. Ultrasound examination of the appendix does not have special preparation, the organ does not change during food intake, and inflammation is either present or absent.
Features of diagnosis in women
Diagnosing appendicitis in women can be difficult due to the similarity of some symptoms with other causes. The purpose of the study in women involves conducting differential diagnostics. Appendicitis is verified from endometriosis, ectopic pregnancy, acute inflammation of the bladder, sexually transmitted diseases, abscess or polycystic ovary syndrome.
Be sure to pay attention to external manifestations, the location of the appendix relative to the norm and the topography of the intestinal loops, concomitant anamnesis, and medical history. Sometimes aching pain in the appendix is caused by the onset of menstruation or early pregnancy. Here it is necessary to exclude various pathologies regarding the location and development of the fertilized egg, the bending of the appendix as a result of displacement of the organ by the uterus.
Pregnancy study
An ultrasound scan for appendicitis in pregnant women is prescribed jointly with an obstetrician-gynecologist or surgeon. Inflammation of the appendix is indicated not only by the picture on the computer monitor, but also by other clinical manifestations:
- sweating;
- weakness;
- hyperthermia;
- intoxication (vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration);
- wandering soreness in the peritoneum and pelvis.
Inflammation of the appendix poses a danger to the woman and fetus due to the close location of the organs. The risks of an unfavorable outcome remain after appendectomy, which are expressed in late pregnancy termination, infection, placental abruption, oligohydramnios and hypoxia.
In children
The difficulty in diagnosing appendicitis in children lies in the inability to describe the exact or approximate location of pain and fear of medical procedures. In most cases, young children will prefer heroic silence and patience.
Typically, a visit to a doctor occurs when the inflammatory process cannot be tolerated, and the symptoms force an acute response to pain. When acute abdominal pain occurs in children, the first step is to prescribe an ultrasound of the abdominal organs due to the rate at which serious complications develop.
Important! Other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and hepatobiliary system can provoke acute pain. The surgeon may decide on drug treatment for appendicitis, especially if the treatment was timely.
What are the characteristics of men and women
Ultrasound for appendicitis in adult men and women is not much different. Some female diseases (we are talking about ectopic pregnancy, inflammatory processes in the appendages or the right ovary) are very similar in symptoms to the pathology in question. Only an ultrasound will show the girl has appendicitis or something else. A specialist will reliably determine what is the source of the problem. If necessary, additional radiography and other diagnostic measures are prescribed.
The female half is almost 2 times more likely to encounter this disease. This is explained by the close location of the organs of the genitourinary system and the gastrointestinal tract.