Hemorrhoids are a disease that occurs due to poor circulation in the rectum. Pathology develops in men and women with the same frequency. The main causes of hemorrhoids are sedentary work, heavy physical activity and chronic constipation. Women are most susceptible to congestion in the pelvis during pregnancy. The situation when hemorrhoids bleed during pregnancy is common, since the vessels become brittle and cannot cope with their functions. Bloody discharge may appear even at the initial stage of the disease.
Symptoms
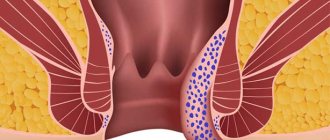
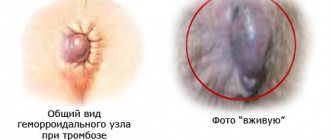
Hemorrhoids are large and small vessels located in the submucosal layer, as well as near the exit of the rectum. These formations perform important functions: they increase the absorption of nutrients and prevent the involuntary passage of stool and gases. Hemorrhoids are a plexus of vessels that gather together into a lump. With chronic stagnation of blood in the pelvis, rupture of the tissues that hold the plexus of veins occurs. They begin to swell and fall down, closer to the exit from the rectum.
You can understand that the cause of bleeding from the anus is hemorrhoids by looking at the symptoms:
- Burning and itching of the anus begin to bother a woman at an early stage of the disease. These manifestations intensify after defecation.
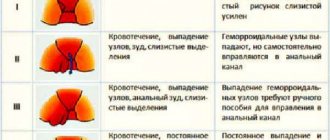
- Loss of plexuses in the form of lumps. When chronic, they are painless and feel like a foreign body between the buttocks. Inflammation of the nodes causes stabbing pain. Bleeding occurs as a result of regular damage to blood vessels.
- Acute pain, prolapse of nodes during bowel movements. The blood is scarlet and does not have time to clot, since the focus is located next to the anus. The intensity of discharge depends on the stage of the disease. Advanced hemorrhoids are characterized by severe bleeding.
The walls of blood vessels become deformed and lose their physiological properties. Because of this, they twist and become pinched when straining. Even slight tension can lead to injury to the nodes and bleeding. The risk of damage increases in the last month of gestation, when the fetus descends into the pelvis.
Blood from hemorrhoids in pregnant women can be observed at any stage of the disease. Already at the first stage, dilated veins lose elasticity and quickly become damaged.
What to do if hemorrhoids start bleeding during pregnancy?
Hemorrhoids are a disease that occurs due to poor circulation in the rectum. Pathology develops in men and women with the same frequency. The main causes of hemorrhoids are sedentary work, heavy physical activity and chronic constipation. Women are most susceptible to congestion in the pelvis during pregnancy. The situation when hemorrhoids bleed during pregnancy is common, since the vessels become brittle and cannot cope with their functions. Bloody discharge may appear even at the initial stage of the disease.
Causes of bleeding
During pregnancy, the risk of venous diseases increases. This pattern is due to the physiological changes that occur in the female body during pregnancy and childbirth. With each pregnancy, the likelihood of hemorrhoids increases.
The nodes become inflamed, thrombose and begin to bleed under the influence of certain factors and reasons:
- Changes in hormonal levels. Under the influence of progesterone, the muscles of the uterus and neighboring organs relax. Reduced tone protects the fetus from premature expulsion. Intestinal peristalsis slows down under the influence of hormonal changes. This leads to hardening of stool and constipation.
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure. The uterus is constantly growing, squeezing neighboring organs. The growth of the fetus provokes congestion in the venous plexuses, and the outflow of blood becomes difficult. The walls of blood vessels constantly change shape and stretch. A decrease in the elasticity of the plexuses inside the rectum provokes hemorrhoids with blood during pregnancy.
- Sedentary lifestyle. Fatigue in the 3rd trimester leads to a decrease in physical activity. Congestive processes in the rectum are aggravated if a woman sits for a long time and does not walk much.
- Changing taste preferences. After conception, the body's demand for vitamins and minerals increases. The lack of useful elements causes a distortion of tastes - a woman constantly craves sweet, salty or spicy dishes. Marinades, smoked foods, and spices cause a rush of blood to the vena cava. The pressure on the walls of blood vessels increases. After eating foods that are difficult for the gastrointestinal tract and having a bowel movement, hemorrhoids are easily damaged, causing bleeding from the anus.
Two main conditions for the development of venous expansion are increased rectal pressure and weakness of the vascular walls.
Consequences of bleeding
The danger of hemorrhoids lies in its consequences for the health and development of the fetus. At the initial stage, a woman may notice small blood stains on a napkin or underwear. As a rule, discharge appears after bowel movements. As the disease progresses, the internal cones fall out and do not refill.
Possible complications of bleeding:
- Blood clot formation. The release of blood clots into the blood vessels threatens the life of a pregnant woman.
- Development of anemia. Even minor discharge leads to a decrease in iron in the body. With severe blood loss, the fetus develops oxygen starvation (hypoxia), which has a negative impact on development and growth.
- Decreased immunity. Against the background of regular bleeding, the body's defense reactions decrease.
- Attachment of a bacterial infection. Pathogenic microflora that is present in feces can lead to the development of proctitis and pararectal fistulas. The inflammatory process in the intestines is dangerous due to the penetration of infection into the uterus.
If the nodes constantly bleed during pregnancy, after childbirth the situation only gets worse. Internal hemorrhoids can come out and become inflamed, so the disease should be treated when the first symptoms are detected (itching, burning, weeping in the perineum).
The danger of hemorrhoids with blood during pregnancy
Sometimes pregnant women hide incomprehensible signs of their condition from their obstetrician-gynecologist, tolerate or try to use traditional methods of treatment. More often they are driven by the belief that they will definitely be admitted to a hospital. But this is a mistaken opinion. Bleeding hemorrhoids during pregnancy are not uncommon, but quite expected. Doctors know how to deal with it without hospitalization.
When the condition is neglected, acute blood loss creates dangerous conditions for the fetus and the woman’s condition. The likelihood of complications increases significantly.
Anemia (anemia) - the daily release of 50 ml of blood during bowel movements reduces the level of hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells. Since the mother's body provides nutrition to the fetus, the child lacks oxygen, which is carried by hemoglobin, and nutrients. A dangerous condition occurs - hypoxia or oxygen starvation.
Lack of compensation affects the formation and functioning of organs, if hemorrhoids bleed at the beginning of pregnancy, contributes to premature birth, frequent illnesses, and lagging behind peers in physical and mental development. Women more often experience complications during childbirth, muscle weakness, and atony.
Thrombosis in the hemorrhoidal node - active platelet aggregation is stimulated by overstretching of the wall of the cavernous cavity, pro-inflammatory substances (kinins) are released, and the activity of the coagulation system increases. A local blood clot is dangerous because a small piece (embolus) breaks off and enters the general bloodstream. A fatal complication is pulmonary embolism.
A decrease in protective forces (immunity) - during pregnancy, immune cells are “busy” protecting the fetus from harmful substances and stress factors, and preparing for childbirth. The process is disrupted by blood loss. The woman begins to catch colds frequently, chronic inflammatory foci worsen (teeth hurt, runny nose turns into sinusitis, symptoms of cystitis bother her). Contraindications to antibiotics complicate treatment.
Activation of opportunistic microflora in the intestines - constipation is accompanied by signs of inflammation spreading to surrounding tissues (paraproctitis), fistulous tracts are formed, and the likelihood of infection penetrating the placental barrier and intrauterine infection of the fetus increases.
First aid
Hemorrhoids are a chronic disease. A damaged node may bleed during pregnancy after each bowel movement. Regular blood loss is dangerous for a woman during this period. It is advisable to visit a proctologist after the first discharge from the anus to avoid complications.
To stop bleeding from the anus, pharmaceutical and home remedies are used.
Cold compress
This method is used to stop bleeding if a woman has external hemorrhoids. A bandage moistened with cold water is applied to the injured area for 1-3 minutes. The bandage needs to be rolled up to create several layers.
Sterile hemostatic sponge
This remedy for hemorrhoids is a plate of dry collagen impregnated with furatsilin and boric acid. The sponge adheres to the surface of the affected node. As a result of platelets sticking together, bleeding stops.
For external hemorrhoids, the plate is applied to the lump for 20-30 minutes. Internal bleeding is stopped by inserting a sponge into the anus. There is no need to remove the product, since the dry substance is absorbed inside the rectum.
Ice candles
The method is suitable for stopping bleeding from internal hemorrhoids. Thick paper is cut and rolled into cones. Water or herbal infusion is poured into the resulting container and immediately placed in the freezer. After hardening, the paper is removed and the resulting candle is inserted into the anus for 15-20 seconds. The procedure is repeated 3-4 times at short intervals. Paper cones can be replaced with a medical fingertip or foil.
Herbs with a healing and anti-inflammatory effect: chamomile, calendula, nettle, yarrow. Decoctions and infusions of these plants can be used to prepare ice candles.
Treatment
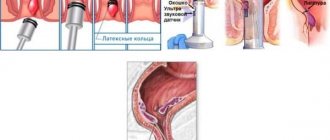
For moderate and severe bleeding, vasoconstrictor, anti-inflammatory, and painkillers are prescribed. Treatment of hemorrhoids includes a set of measures to eliminate symptoms and prevent the development of the disease. The list of medications during pregnancy consists mainly of external agents (creams, ointments, compresses) and rectal suppositories. Excision of the affected veins is carried out if conservative methods of therapy do not bring results. In most cases, surgery is postponed until the postpartum period.
Features of the treatment of hemorrhoidal angles with signs of bleeding:
- Revising the menu. If the cause of the disease is chronic constipation, include more fiber in the diet. To normalize stool and soften stool, it is useful to eat salads with boiled beets, apples, plums, and fermented milk products. Chronic diarrhea also causes damage to the nodes. To find out the cause of loose stools, a woman needs to undergo a stool test. After this, the doctor will select a therapy regimen and a suitable diet.
- Using microenemas with medicinal solutions. They can be used for minor bleeding. An enema softens stool and makes bowel movements easier. The product is suitable for the treatment of internal hemorrhoids. To stop bleeding, microenemas with a 1% tannin solution are administered. The medicine has an astringent effect, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, and prevents relapses.
- Use of sclerosing drugs. They are used for scarring and “gluing” damaged areas. Almond oil with carboxylic acid and a 20% sodium chloride solution have a sclerosing effect.
- Using ointments with a hemostatic effect for external bumps. Approved agents are Troxevasin, Methyluracil, Proctosan.
- Rectal suppositories to relieve inflammation and improve vascular elasticity. A pregnant woman can be prescribed Relief, Proctosan, Nigepan as part of complex therapy. These suppositories relieve and also prevent bleeding.
Traditional methods of treatment are used in combination with medications. During pregnancy, it is safe to use lotions with sea buckthorn oil, herbal decoctions and clean water. Such remedies will help stop minor bleeding.
Medications
During pregnancy, treatment of bleeding hemorrhoids with medications can only be prescribed by a specialist. In such a situation, relying on the advice of friends is extremely unwise and dangerous. Usually, vasoconstrictor drugs with additional anti-inflammatory effects are selected for expectant mothers. These are the so-called venotonics. They specifically act on the affected vessels of the rectum, strengthen their walls and promote blood microcirculation. Moreover, these medications usually contain an anesthetic. If the bumps start to bleed, then Detralex is ideal for a young mother. This effective and safe drug for the baby has virtually no side effects (with the exception of allergic reactions due to individual intolerance to its components). An alternative drug is Ginkor Procto.
Of course, if hemorrhoids bleed, you cannot do without topical medications. These are all the same ointments and suppositories that are already familiar to a woman who has the problems being discussed. In this case, they must contain the following components:
- novocaine;
- anesthesin;
- vitamin A;
- sea buckthorn oil;
- aloe extract.
All these substances have analgesic, hemostatic, anti-inflammatory and wound healing effects. They are used strictly according to the doctor’s instructions and only after bowel movements and hygiene procedures.
During pregnancy, you can safely use topical medications such as Troxevasin, Gepatrombin G, Relief, Posterizan. Suppositories with papaverine have an antispasmodic, hemostatic and analgesic effect.
Important: it is strictly forbidden to use suppositories, ointments and tablets for hemorrhoids containing belladonna extract while carrying a child. This is an excellent remedy that stops bleeding, relieves pain and inflammation, but in an expectant mother it can cause miscarriage or premature birth. You should also give up Anuzol and Bellatamine.
As a rule, bleeding in pregnant women occurs after defecation, when you have to push hard. To relieve constipation, your doctor may recommend laxative medications. Duphalac, Forlax, Prelax, Regulax are considered safe. But you shouldn’t abuse them - it’s better to follow a diet, don’t overeat and move more.