Proctitis is an inflammation of the rectal mucosa. Proctitis should not be confused with paraproctitis, in which inflammation of the tissues located next to the rectum occurs.
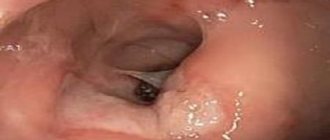
Proctitis begins with simple redness and can progress to deep ulcers. The disease is quite delicate, so not every person immediately consults a doctor when the first symptoms appear. But in vain! Constant pain and itching in the anus, insomnia, and difficulty defecating can lead to nervous breakdowns and problems at work and in your personal life. In addition, proctitis can develop against the background of such serious diseases as hemorrhoids, microcracks of the anus and rectal cancer!
Structure of the rectum
The rectum is the final section of the intestine, it begins in the sigmoid colon and ends in the anus. The lining of the rectum is made up of muscle and has a large amount of mucus, which helps push down leftover food.
Two muscle rings (anal sphincters) contract and retain feces. And during their relaxation, defecation occurs. In men, the rectum is connected to the prostate and bladder, in women - to the vagina and uterus.
When the rectum functions properly, all processes go unnoticed, but if there is any malfunction, inflammation of the rectum can develop. More than 30% of people with inflammatory bowel disease have inflammation of the rectum. One of the most common diseases is proctitis.
1 Consultation with a proctologist
2 Consultation with a proctologist
3 Consultation with a proctologist
Relevance of the problem of intestinal pathologies
Today, problems associated with various types of rectal dysfunction are very common.
However, not many people rush to visit a doctor due to the delicate nature of the problem.
And this is a big mistake, since it is simply impossible to imagine the vital functions of the body without the participation of the rectum.
It is as hard a worker as the heart, lungs or stomach.
Therefore, you should be attentive to malfunctions in its operation and visit a specialist in a timely manner in order to provide your body with all possible help.
Diseases of the rectum are a pressing problem in the modern world. The reason for this phenomenon is lifestyle, unhealthy diet, characteristics of professional activity (sedentary work), excessive physical activity, bad habits, and excess weight.
Nowadays, few people can boast of leading a healthy lifestyle, although there is undoubtedly a positive trend in this direction. But it is still far from completely eliminating all provoking factors.
Proctitis, its types
Proctitis can be acute or chronic.
Acute proctitis has permanent symptoms that appear in a person for a short time. Inflammation of the rectum in acute form is accompanied by fever, general weakness, and malaise. It can be caused by acute infectious diseases and rectal injuries.
Types of acute proctitis:
Catarrhal proctitis
Catarrhal proctitis is the first stage of inflammation of the rectum in its acute form. It is characterized by pain in the abdomen and anus, and the appearance of droplets of blood on toilet paper after defecation.
Catarrhal proctitis can be divided into:
- catarrhal-hemorrhagic proctitis (the rectal mucosa is red, swollen, and has a large number of hemorrhages);
- catarrhal-purulent proctitis (pus appears on the rectal mucosa);
- catarrhal mucous proctitis (swelling, inflammation of the rectum accompanied by the appearance of a large amount of mucus).
Polypous proctitis
With polypous proctitis, small seals resembling polyps grow on the rectal mucosa.
Erosive proctitis
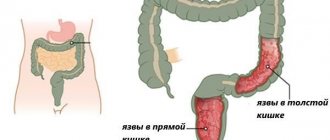
Erosive proctitis is characterized by the formation of erosion on the mucous membrane. Ulcerative proctitis is a type of erosive proctitis, when ulcers begin to open on the mucous membrane of the rectum. There are ulcerative-necrotic and purulent-fibrous proctitis.
Radiation proctitis
Radiation proctitis appears at the end of radiation therapy. It is characterized by attacks of acute pain, stool is accompanied by pus and blood, ulcers form on the rectum, a fistula or even lymphostasis may open, which, growing, can close the space in the rectum.
Chronic proctitis
Symptoms of proctitis in chronic form are not as intense, but can bother you for a long time. Cycles of exacerbation and remission are periodically repeated. This type of inflammation of the rectum is caused by chronic infections, autoimmune diseases, malignant tumors of the rectum, and vascular pathology.
Chronic proctitis is divided into:
- atrophic proctitis (thinning of the rectal mucosa);
- hypertrophic proctitis (thickening and loosening of the mucous membrane).
1 Treatment of proctitis in MedicCity
2 Treatment of proctitis in MedicCity
3 Treatment of proctitis in MedicCity
Common signs in women
Since women's pelvic organs are located slightly differently than men's, the symptoms of diseases may differ slightly. Often, rectal disease in women is manifested by unpleasant sensations not only in the anus, but also by a feeling of fullness in the vagina. Often the pain spreads to the back wall of the vagina, so rectal disease can be mistaken for a pathology of the female genital organs. If a woman has diseases in the rectum, then during sexual intercourse there will be discomfort and pain.
Symptoms of proctitis
All symptoms of rectal inflammation can be divided into local signs of rectal inflammation and general ones (reaction of the whole body to inflammation).
Local symptoms of rectal inflammation:
- discomfort, feeling of fullness in the rectum;
- constant desire to defecate;
- anal itching and pain in the rectal area, worsening with bowel movements;
- pain in the left side of the abdomen, cramps;
- mucous and purulent discharge from the anus, which may contain blood;
- pain in the perineum, radiating to the lower back and genitals;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- fecal incontinence (see sphincter incontinence).
General symptoms of proctitis may be as follows:
- increased body temperature;
- anemia, weakness, loss of strength;
- sudden weight loss;
- loss of appetite;
- joint pain;
- skin rash;
- inflammation, redness of the eyes, tearing;
- depression or frequent mood swings.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional medicine for rectal ailments can be quite effective if you know how to use it correctly. It is used as an additional treatment method. People know thousands of recipes for relieving not only pain, but also other symptoms.
All recipes can be divided into two types:
- For oral administration. Decoctions of millennial, spotted arum, elderberry, bittersweet, tartar, nettle, chamomile.
- For local use - suppositories, ointments, baths, microenemas. They use celandine, sea buckthorn oil, camphor oil, and calendula for this.
In any case, before using traditional medicine, you need to consult a proctologist, otherwise the treatment may not alleviate the course of the disease, but, on the contrary, do harm.
Causes of proctitis
The causes of proctitis can be very diverse:
- Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis;
- non-inflammatory diseases of the rectum (hemorrhoids);
- infectious causes (presence of streptococcal infection, protozoan parasites, viruses);
- infectious sexually transmitted disease (gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis and other STDs);
- tuberculosis disease;
- chronic constipation;
- poor nutrition;
- long-term use of certain medications, especially antibiotics;
- food allergies;
- damage to the rectum (for example, due to a foreign body in the intestine);
- side effect of radiation treatment for some forms of cancer.
1 Preparation for rectoscopy
2 Preparation for rectoscopy
3 Rectoscope
Basic recommendations for therapy
Regardless of the nature, location and cause of rectal disease, its treatment is complex. It includes several areas of therapeutic interventions:
- etiotropic therapy;
- pathogenetic therapy;
- symptomatic therapy.
Be sure to read:
Endoscopic methods for examining the intestine: description and preparation
Etiotropic therapy. Aimed at eliminating the causative factor and may include the following measures:
- Prescription of antibiotics for bacterial inflammatory processes (proctitis, paraproctitis, complicated hemorrhoids).
- The use of medications that prevent the intravascular formation of blood clots, as well as strengthen the walls of venous vessels. They are prescribed for the conservative treatment of hemorrhoids.
- Removal of polyps and hemorrhoids using modern methods of physical or chemical treatment (sclerotherapy, electrocoagulation, laser therapy, cryodestruction).
- A surgical intervention aimed at removing large formations (polyps, hemorrhoids) or a malignant tumor (cancer), as well as tissue plastic surgery for ulcers, erosion or prolapse of the rectum.
Pathogenetic therapy. It involves medication reducing the severity of the inflammatory process, as well as improving the functional state of the lower gastrointestinal tract.
Symptomatic therapy. Prescribed to improve the patient's condition and reduce discomfort.
Treatment of proctitis
To prescribe the correct treatment for inflammation of the rectum, you need to conduct a complete examination of the human body. The diagnosis is established on the basis of all data, including digital examination of the rectum, examination of the intestine using proctoscopy, colonoscopy, biopsy of the intestinal wall, and stool culture.
The method of treating proctitis is determined by the nature of the disease, its severity, the presence of symptoms, the development of complications, etc. Some patients require short-term treatment for rectal inflammation, while others require long-term treatment and medical supervision.
Drug treatment of proctitis
Any treatment for inflammation of the rectum should be selected individually by a doctor; self-medication is unacceptable!
Depending on the severity of the disease and the causes of proctitis, a qualified specialist may prescribe you antibiotics, antiparasitic, antifungal agents, anti-inflammatory, painkillers, and hormonal drugs.
If there is an allergic component to inflammation of the rectum, an antihistamine may be prescribed. For constipation, laxatives and a gentle diet are prescribed.
The treatment regimen for inflammation of the rectum is selected individually for each patient.
1 Preparing for a colonoscopy
2 Colonoscope
3 Colonoscope
Local treatment of proctitis
In the treatment of proctitis, the role of local therapy is very important.
Typically the treatment regimen includes:
- using enemas with a solution of colibacterin, potassium permanganate, warm infusion of chamomile, oak bark;
- treatment of proctitis with suppositories (anuzol, proctosedyl, etc.) will help reduce itching and eliminate inflammation in the rectum;
- warm baths with infusion of knotweed (knotweed), immortelle;
- the use of ointments (bezornil, proctosan) will relieve pain and promote the rapid healing process of damaged tissues;
- For inflammation of the rectum, sea buckthorn oil and sea buckthorn suppositories are used as a local remedy. This quickly relieves inflammation and leads to tissue regeneration.
Diet for proctitis
To avoid complications with proctitis, you need to remove from your diet fatty, spicy, salty and sour foods that cause irritation of the rectum. For inflammation of the rectum, it is recommended to eat soups made from pureed vegetables, porridge with water, low-fat cottage cheese and meat, jelly, and fermented milk products. It is necessary to exclude sweets and alcohol.
The multidisciplinary clinic "MedicCity" places great importance on the treatment of proctological diseases. Our center employs highly qualified and sensitive coloproctologists who are proficient in advanced diagnostic and treatment methods. Here you can cure hemorrhoids, anal fissure, anal sphincter insufficiency, coccyx cysts, paraproctitis and many other diseases.
Depending on the severity of the disease, you may be offered a conservative or surgical treatment method. Modern minimally invasive operations make it possible to cure diseases such as hemorrhoids in 1 day, without hospitalization, on an outpatient basis!
What is rectal prolapse and why is it dangerous?
Rectal prolapse is not a life-threatening condition, but it brings a lot of inconvenience to the patient’s life: constant physical and psychological discomfort, the inability to do usual activities, etc. The condition is characterized by weakening and stretching of the terminal intestine (sigmoid and rectum) and increased mobility.
Sometimes, with rectal prolapse, there is a sharp tension in the mesentery connecting the anterior and posterior abdominal walls. At this moment, the patient experiences severe pain, which can cause pain shock or collapse. Such conditions are life-threatening and require urgent medical intervention.
In adult patients, rectal prolapse is directly associated with intussusception, when one part of the intestine descends and penetrates the lumen of the underlying intestine.
In this case, discomfort is accompanied by the appearance of round formations in the anus, which can easily be mistaken for hemorrhoids if you do not know the features characteristic of prolapse. As the disease progresses, the rectal mucosa falls out of the anus, and as the disease progresses, the submucosal and muscular layers fall out.
If treatment for rectal prolapse is not started in time, there is a risk of complications:
- acute intestinal obstruction;
- peritonitis;
- intestinal necrosis;
- psychological and mental disorders (they develop against the background of constant stress).
In order not to bring the condition to a critical level, if you suspect rectal prolapse, you should not expect the disease to go away on its own. It is even more dangerous to use unconventional treatment at home. The only way to get rid of rectal prolapse is to consult a proctologist and undergo complex therapy for the disease.
Classification
To facilitate diagnosis and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen, doctors divided all PC diseases into several groups. The criterion for classification is the cause of the development of the disease. Taking this into account, the following stand out:
- inflammatory processes in the intestines - paraproctitis and proctitis;
- tumor formations - polyps, condylomas and cancer;
- damage to the rectal mucosa - ulcerative lesions, hernias, anal fissures, cysts;
- vascular diseases - hemorrhoids.
Treatment - general principles
Treatment of rectal diseases includes medical and surgical methods, and adherence to a special diet. For some diseases, treatment with folk remedies is allowed, which is agreed with the attending physician. For severe attacks of pain and constipation, painkillers and laxatives are prescribed. If an inflammatory process occurs, it must be stopped with the help of medications. Surgery is used for cysts, benign and malignant tumors. In the latter case, treatment is supplemented with chemotherapy. To avoid gastrointestinal diseases, you should eat right and move more.
How does rectal disease manifest in women and men?
In addition to specific symptoms of PC damage, men and women may show signs of general intoxication. In severe cases of inflammatory processes, the temperature rises, muscle aches, general weakness, and loss of appetite are noted. Chronic forms of diseases are accompanied by such symptoms only during exacerbations. To differentiate one disease of the rectum and anus from another, you need to know about their characteristic signs and causes.
Proctitis
The disease proctitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the PC. It is caused by general or local factors. The latter include mechanical injuries, the introduction of cold or hot solutions into the anus, the transfer of infection from neighboring organs, and neoplasms in the intestines. Common causes of proctitis are:
- eating disorders;
- intestinal motility disorders;
- abuse of alcohol, spicy or spicy foods;
- autoimmune diseases;
- digestive tract infections;
- disturbances of the innervation or blood supply to the lower intestines.
A characteristic symptom of proctitis is discomfort during bowel movements. Against this background, there is a frequent urge to have a bowel movement, itching and a feeling of a foreign body in the anal area. Proctitis causes a number of other unpleasant symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen and anus (it decreases after defecation);
- diarrhea;
- the appearance of mucus and streaks of blood in the stool;
- false urge to defecate.
Article on the topic: Nettle - medicinal properties and contraindications
Paraproctitis
Paraproctitis is characterized by inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue, which is located next to the rectum. The disease develops as a result of the penetration of a bacterial infection into the deep layers of the pararectal area. The causative agent of the disease is a mixed flora, including staphylococci, E. coli, and streptococci. Paraproctitis is often a consequence of bowel problems (constipation or diarrhea). The clinical picture of the disease depends on the nature of its course:
- Spicy. This form of paraproctitis is characterized by signs of local purulent inflammation: hyperemia and swelling of tissues, suppuration, pain in the perineum.
- Chronic. It is the result of an untreated acute form. Chronic paraproctitis is a pararectal fistula, due to which ichor and pus are constantly released into the perineal area. They cause skin irritation, which leads to itching.
Proctalgia
Proctalgia is understood as a pain syndrome in the area of the PC, which occurs without good reason and does not cause other specific symptoms of proctology. This disease is accompanied by attacks of spastic pain that goes away on its own within 10–15 minutes. Doctors do not name the exact cause of proctalgia, but several provoking factors are identified:
- emotional disorders;
- short-term intestinal spasms;
- inflammatory processes in the genitourinary organs;
- history of surgical intervention on the pelvic organs;
- neoplasms in the intestines.
Anal fissure
This is the name for defects in the anal wall. They have an oval or linear shape, and reach up to 1–2 cm in length. Causes of anal fissures:
- colitis;
- haemorrhoids;
- chronic constipation;
- thrombosis of hemorrhoids.
Over time, the anal fissure regenerates and is replaced by connective tissue. This is how the defect becomes more severe and becomes chronic. The following symptoms indicate fresh anal fissures:
- bleeding (the appearance of a few drops of blood after a bowel movement);
- burning and feeling of fullness in the anus;
- sharp pain during and after bowel movements;
- anal sphincter spasms;
- pain radiating to the sacrum, perineum, genitourinary organs.
Rectal prolapse
If the intestine extends beyond the anus, doctors diagnose it as prolapse. The reasons for this deviation are inflammatory processes in the rectum, hemorrhoids. The clinical picture depends on the stage of the disease:
- First. Only the mucous membrane prolapses during the act of defecation, after which the PC is automatically reduced.
- Second. Prolapse is observed not only during bowel movements, but also during physical activity. At this stage, the patient has to adjust the intestine independently.
- Third. Loss occurs even after the slightest physical exertion in an upright position. The intestine falls out immediately after reduction.
Frequent prolapses cause bleeding and pain in the anus. Ulcerations may appear on the intestines. In addition to these signs, the patient has the following symptoms:
- frequent urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- sensation of a foreign object in the anus;
- mucus discharge from the anus;
- false urge to have a bowel movement.
Tumors
The most severe and dangerous PC disease is cancer. This is a malignant tumor that does not make itself felt for a long time. Only when the tumor is large in size causes the following symptoms in a person:
- constipation;
- bleeding from the anus;
- discomfort in the anus;
- ribbon-like stool;
- impurities of blood and mucus in the stool;
- decreased performance;
- fatigue;
- weight loss;
- frequent viral diseases.
The main causes of cancer of this part of the intestine are heredity, age-related changes, exposure to alcohol and smoking, chronic constipation and dysbiosis. Excessive intake of meat and fatty foods is also a risk factor. Precancerous conditions that lead to cancer include:
- Crohn's disease;
- intestinal polyposis;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
Another type of tumor is genital warts. The cause of their appearance is human papillomavirus. If the patient has encountered it at least once, then this virus will remain in the body for life and, against the background of weakened immunity, will make itself felt. Condylomas are growths that resemble the shape of cauliflower inflorescences. They appear not only in the rectum, but throughout the entire groin area.
In addition to cancer and condylomas, there are tumors in the form of polyps - benign neoplasms on legs. Polyposis is often caused by heredity, chronic intestinal inflammation and an unhealthy lifestyle. Polyps, depending on their structure, are fibrous, adenomatous, villous and mixed. Regardless of the type, they cause the following symptoms:
- painful act of defecation;
- bleeding from their anus;
- constipation;
- sensation of a foreign object in the anus.
Haemorrhoids
This is the medical name for the expansion of the cavernous corpuscles of the PC. Depending on which hemorrhoids become inflamed, hemorrhoids can be internal or external. The main cause of this disease is increased load on the pelvic area, which is caused by:
- chronic constipation;
- heavy physical work;
- eating spicy, irritating foods;
- alcohol abuse;
- sedentary work;
- repeat pregnancy.
Hemorrhoids often occur in a chronic form. When internal nodes become inflamed, hemorrhoidal bleeding may develop. The external ones do not bleed, but thrombose, which causes severe itching and pain in the anus. Other characteristic signs of hemorrhoids:
- palpation of nodes in the anal area;
- discharge of mucus from the anus;
- infrequency of bowel movements;
- prolapse of hemorrhoids;
- pain during bowel movements;
- flatulence;
- fissures in the anus.
Article on the topic: Duspatalin - instructions for use, release form, composition, dosage, indications and price
Prevention
To prevent rectal disease, patients are advised to pay attention to their diet. It should contain at least 1.5–2 liters of liquid and plant dietary fiber in the form of bran and vegetables. At the same time, you should avoid the abuse of flour and dairy products. This is necessary to achieve optimal stool consistency and normal evacuation from the body. In addition to diet, you must follow the following rules:
- avoid straining during bowel movements;
- do not sit on the toilet for a long time;
- normalize physical activity;
- observe the rules of intimate hygiene;
- treat constipation promptly;
- walk more, as this strains the muscles of the pelvic area and normalizes bowel movements.