A liver tumor is a pathology formed from a mixture of tissues and mutated cells. As a result, the liver material becomes a foreign object for the human body. According to hepatology, liver growths are divided into benign and malignant types. The choice of appropriate treatment is influenced by data on the form and origin of the formation. In medical practice, there is a high probability of the development of malignant cells in the liver. Benignity in this area is rare.
Causes
A malignant liver tumor (ICD-10 code C22) develops as a result of a failure in cell division. Many factors provoke intense division of liver tissue. The process of disease development goes unnoticed, without symptoms. Often the disease is detected during an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, prescribed for other reasons. There are no exact reasons for the occurrence of growths in the organ. However, experts note a number of reasons that influence the formation of pathology and the behavior of affected tissues. They increase the risk of developing pathological abnormalities:
- Bad habits – smoking, alcoholic drinks, drugs.
- Unhealthy diet - food is dominated by fats, preservatives and dyes, fried and meat products. There is a shortage of fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Long-term use of hormonal drugs prescribed for the treatment of endocrine diseases, or constant use of oral contraception.
- Genetic predisposition - if there are relatives in the family with cancer, the likelihood of developing cancer increases 3 times.
- Work in hazardous industries involving constant contact with chemicals.
- Living or working in an unfavorable environmental atmosphere.
The presence of chronic diseases can become a trigger for the appearance of concomitant malignant growths. Pathologies develop under the influence of external stimuli. Among them are:
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- helminthic infestation, as well as schistosomiasis;
- hemochromatosis;
- benign tumor of the large intestine, formed from the glandular epithelium;
- syphilis;
- disruption of endocrine function and metabolic process, diabetes mellitus and excess weight;
- systematic consumption of alcoholic beverages up to the development of alcoholism;
- entering an environment full of toxins and chemicals: pesticides, chlorine, carbon tetrachloride.
Secondary liver metastasis appears with a probability 20 times higher than the primary transition of hepatocytes. The situation is explained by filling the organ with blood from all organs. Together with blood cells, malignant elements enter the organ. With a tumor of the intestine or pancreas, the cancer affects the liver structure in 75% of cases. The neoplasm is formed under the influence of inflammatory manifestations in the body and kidney disease. The presence of an ulcer or cirrhosis can provoke a pathological growth.
Symptoms of Klatskin tumor
The most common manifestation of hilar cholangiocarcinoma is jaundice, a condition in which the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow. This occurs due to the fact that a malignant tumor disrupts the outflow of bile, that is, in this case it is obstructive jaundice. Usually it indicates an advanced disease. In addition to changes in skin color, such patients experience itching, their urine becomes dark, and their stool becomes light. The reason for these symptoms is that bilirubin - a compound that is formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin - is not released into the intestines with bile, but enters the blood.
Most often, jaundice occurs first, and after some time itching begins to bother you. Sometimes, on the contrary, itching becomes the first symptom.
At the time of diagnosis of the disease, approximately a third of patients note that they have recently lost a lot of weight. In the later stages, Klatskin's tumor causes dull pain under the ribs on the right.
Request a call back. We work around the clock
Symptoms
The clinical picture of benign and malignant tumors progressing in liver cells is different. The development of a benign growth in the structure of the organ occurs without clearly noticeable symptoms. The development of oncology is proceeding at a slow pace. For a long time, a person does not feel discomfort in his own well-being or disturbances in the functioning of the body. Signs that appear after a significant expansion of the affected cells should alert the patient:
- A large hemangioma is accompanied by severe pain and heaviness in the abdomen. Vomiting and belching appear from time to time. The tumor in the vessel can become damaged and rupture, causing bleeding in the abdominal cavity or biliary tract.
- The spreading formation causes pain in the abdominal area, a feeling of nausea, and increased sweating. The epidermis takes on a pale tint. Rupture of the growth is also accompanied by intense bleeding.
- The development of a large cyst occurs with a feeling of heaviness and pain in the hypochondrium on the right side. Nausea, widespread flatulence, and diarrhea are noted. With complications, purulent discharge and hemorrhages appear.
- Nodular hyperplasia of the liver is characterized by asymptomatic progression even in the last stages. Doctors identify the only symptom of the presence of pathology – noticeable growth of the liver. The situation is rarely accompanied by breaks.
Signs of cell malignancy, which appear in the early stages of tumor formation, are similar to the symptoms of other diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract. The following factors are particularly similar:
- general malaise and feeling of weakness in the body;
- nausea and vomiting, belching, flatulence;
- loss of appetite, weight loss;
- low-grade fever;
- a feeling of heaviness and painful manifestations in the right hypochondrium.
A significant increase in the shape of the neoplasm is signaled by liver swelling. The organ extends beyond the edge of the rib, which is noticeable even with a casual glance. Lumps appear on the surface and compaction is felt. The stage of progression of the pathology is similar to the appearance of:
- anemia;
- jaundice;
- fever;
- ascites;
- nntoxication;
- liver failure;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- swelling of the lower extremities.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms of liver tumors in the early stages practically do not appear. The compensatory capabilities of the body determine the preservation of the functions of the gland. As they develop, neoplasms disguise themselves as inflammatory diseases of the hepatobiliary system. The patient may experience only general symptoms: malaise, fever, headache. Depending on the quality of the tumor and the speed of its growth, characteristic symptoms also appear over time.
Clinical signs of malignancy
Cancer begins with signs of intoxication. A sick person complains of decreased appetite, irritability, drowsiness, and increased fatigue. As the pathology progresses, pain on the right side, enlarged liver, and splenomegaly appear. Blood tests indicate a decrease in glucose and hemoglobin levels and an increase in the concentration of transaminases and bilirubin.
Compression of the portal vein leads to portal hypertension and the development of ascites. The patient quickly loses weight, while his abdomen becomes greatly enlarged. Veins are clearly visible on the skin of the abdominal wall, and swelling appears on the legs.
Such signs usually indicate the last stages of cancer, except in cases where the tumor is located near large bile ducts. Late symptoms include jaundice, vomiting, diarrhea, bleeding tendency, and exhaustion.
Secondary dysfunctions of other organs (paraneoplasia) occur. The most common skin changes are: pigmentation, dryness, itching. Sometimes, even before a malignant tumor is diagnosed, black keratinizing spots appear in the patient’s armpits, inner thighs or neck. This disease is called papillary skin dystrophy. Other changes include hormonal disturbances and encephalopathy.
Clinical signs of benign formations
Features of the clinical picture of benign tumors are associated with their slow growth. Patients are unaware of the presence of pathology for a long time. Manifestations of the disease become noticeable as the formations increase. A person experiences a feeling of heaviness on the right side, belching, and flatulence.
In rare cases, a growing tumor leads to ascites. For example, a hemangioma can occupy the entire abdominal cavity and completely replace gland tissue. Total destruction of the parenchyma in some types of neoplasms causes liver failure.
Symptoms of hamartoma include loss of appetite, pain, dyspeptic disorders, and breathing problems. With focal nodular hyperplasia, signs of chronic inflammation occur: periodic aching pain and nausea. However, in most cases the disease is asymptomatic.
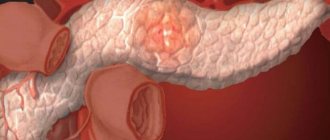
Liver tumor classification
A liver tumor is a growth formed from the material of the organ (parenchyma) and its vessels. Neoplasms vary in benign and malignant nature. The first category of growths spreads slowly and does not metastasize. Studying the types, shape and behavior of the tumor helps to accurately select the appropriate treatment and get the maximum effect from therapy.
Benign types of tumor
Sometimes, among benign lesions, a cyst of non-parasitic origin can be found. The tumor has a cavity shape with a shell clearly outlined by healthy cells. Inside the capsule there is a liquid filling. Depending on the origin, the cyst is divided into true and false. The latter type is formed after injury or inflammation in the hepatic environment. For benign tumors, classification (according to WHO) is as follows:
- Angiolipoma. It is formed on the basis of fibrous vessels and fat cells. May appear on the spine.
- Lipoma. Adipose tissue is used for support. It is considered a universal neoplasm that spreads throughout the mucous membranes of human organs.
- Leiomyoma. Appears in rare cases. It has the shape of a nodule, develops slowly, but can reach a gigantic size.
- Angiomyolipoma. The target of the lesion is the kidneys and adrenal glands. Sometimes the tumor cell moves to the liver. It is characterized by asymptomatic occurrence. Most often it manifests itself in the female half between the ages of 30 and 60 years.
- Epithelioma. It is considered a benign growth of an organ, characterized by an increased likelihood of malignancy.
- Fibroma. It is formed from connective tissues and has a fibrous shape. High risk of progression to malignancy.
Liver fibroma
- Cystadenoma. Rarely seen. Consists of material from the bile ducts. The appearance and structure are similar to papilloma. There is mucous exudate inside the tumor.
- Hamartoma. It is considered a cavity growth. Often degenerates into cancer. The distribution area is in the gallbladder. The capsule is filled with thick bile, mucus and blood clots.
- Liver adenoma. It has no obvious signs. Sometimes pain is felt in the abdominal area. It is characterized by the absence of malignancy.
- Hemangioma. Grows at a slow pace. Blood clots often form without symptoms.
Malignant types of tumor
The malignancy of the neoplasm can be either primary or secondary. In its primary form, a cancer cell appears specifically from liver material. And the latter type is characterized by the spread of metastases from other organs. Metastasis occurs in the presence of intestinal cancer, sometimes due to a lung tumor. The primary type of neoplasm varies (according to WHO):
- Hepatoblastoma. Of the recorded cases, it most often develops in children aged three years.
- Carcinoma. Accompanied by aching pain in the upper abdomen.
- Cholangiocarcinoma. This type of tumor targets the bile duct.
- Angiosarcoma. It is characterized by high metastasis. It appears in people over forty years of age.
- Cystadenocarcinoma. The cyst can reach enormous sizes, causing severe pain.
- Hemangiosarcoma. Characterized by aggressive behavior. The growth progresses at a high rate and is difficult to cure with therapy.
- Hemangioendothelioma. A rare type of liver growth. Development proceeds at a reduced pace and takes on the symptoms of jaundice.
- Adenocarcinoma. A growth formed from glandular material.
A malignant tumor poses a great danger to human health and life. Small benign neoplasms need to be observed by a doctor. However, cancer cells require immediate removal.
Classification
Tumors vary in origin and growth characteristics. In order to predict the further development of the pathology, select adequate treatment and conduct clinical monitoring of the patient, the doctor needs to differentiate the neoplasms. The most acceptable histological classification of cancer tumors is the WHO.
The first group includes formations from epithelial tissue:
- Hepatocellular: hepatoblastoma, hepatocellular carcinoma (carcinoma).
- Cholangiocellular: cystadenocarcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma.
The second group includes mesenchymal tumors:
- From blood vessels: angiosarcoma, epithelioid and neoplastic hemangioendothelioma.
- Fibrosarcoma.
- Leiomysarcoma.
- Fibrous histiocytoma.
- Non-Hodgin lymphoma.
- Undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma.
- Kaposi's sarcoma.
The third group consists of mixed epithelial neoplasms, and the fourth group includes metastatic cancer.
Benign liver tumors are also classified by origin:
- Epithelial: adenoma, biliary papilomatosis.
- Mesenchymal: hemangioma, lymphangioma, fibroma, myxoma, angiomyolipoma.
- Tumor-like formations: cysts of non-parasitic origin, focal nodular hyperplasia, peliosis.
Diagnostics
The final diagnosis is established after receiving the results of laboratory tests and using analysis tools. Laboratory diagnostics consists of performing a general blood sampling and biochemical analysis of blood cells. When diagnosing, the following signs of the presence of a tumor are revealed:
- significant weight loss, the presence of protein in urine;
- high level of concentration of urea, creatinine, residual nitrogen;
- low level of hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells in the blood;
- a general decrease in the level of protein and albumin in the blood structure, an increase in fibrinogen;
- high activity of liver enzymes;
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- liver tissue samples;
- blood test for tumor markers;
- histological examination of tissues and cells obtained as a result of the biopsy procedure.
With the help of an instrumental examination, you can double-check the existing diagnosis and get a general picture of the type and size of the growth. The process of searching for the location of the cancer focus and metastases is facilitated. To do this, the following procedures are carried out:
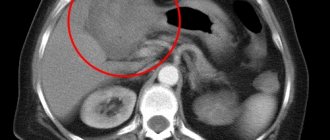
- Ultrasound examination of the liver. Helps check the type, size and location of the tumor in the liver. However, there is no way to distinguish a benign lesion from an advanced malignant action.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. The most accurate way to determine the location and behavior of the growth is to find out the distance between the lesion and the gallbladder, pancreas, colon and cells entering the stomach.
- Hepatoscintigraphy. During the diagnostic process, the patient is injected with radioactive iodine ions, which have the property of accumulating in the affected areas and can be detected by an X-ray device. This way you can get the exact size of the formation and detect the presence of metastases.
- Liver biopsy and further morphological examination of the collected materials to clarify the type of tumor.
When detecting the spread of metastases, it is important to find the organ affected by cancer cells first on ultrasound. For the procedure, you will have to resort to esophagogastroscopy, radiography of the stomach and lungs, ultrasound of the mammary glands and mammography, irrigoscopy and colonoscopy.
Treatment
In the early stages of the disease, it is possible to use special drugs that promote the death of cancer cells (by disrupting their nutrition) or stopping their development; removal of part of the liver or its complete removal with subsequent replacement with a donor organ is used.
Scientists have made a breakthrough in the diagnosis of liver cancer. During a contrast study using MRI, the coloring agent was quickly neutralized by the organ due to the specifics of its functions, so only tumors larger than 1 cm could be detected. A new substance is currently being used that makes it possible to diagnose a malignant formation measuring 0.25 mm in diameter. This is a real breakthrough that allows for gentle treatment of the patient and completely rids him of liver cancer.
Author:
Selezneva Valentina Anatolyevna physician-therapist
Liver tumor treatment
The method of treating liver tumors is selected based on the active or passive behavior of the growth and its volume. If the formation is small and does not spread intensively, doctors wait a certain period of time. At the same time, the patient undergoes restorative procedures. Intense tumor growth requires surgical intervention to prevent possible tissue mutation in a malignant direction.
Removal of the affected area is performed using resection. During liver surgery, mutated cells are cut out. The amount of resection is determined based on the location and size of the growth. To excise tumor tissue, they resort to marginal resection, segmentectomy, lobectomy, and hemihepatectomy.
A malignant liver tumor is eliminated directly by surgery. Patients with liver cancer are prescribed a hemihepatectomy procedure. During the process, the affected cells are cut out. In the presence of cholangiocarcinoma, the bile ducts are excised using hepaticojejunostomy, then the damaged area is covered with anastomoses to stabilize the outflow of bile secretion into the small intestine. There are other ways to treat liver pathology:
- Radiation therapy. It affects tumors with ionizing rays. The method is considered effective when faced with single tumor nodes in an organ.
- Chemotherapy. Treatment involves the use of drugs that inhibit the spread of cancerous tissue. Therapy is carried out by subcutaneous or intravenous administration of drugs.
- Embolization. It is considered a minimally invasive method. Emboli are launched into the vessel associated with the formation. This leads to blockage of blood vessels, and the tumor is left without blood flow and micronutrients. As a result, the neoplasm dies.
- Cryoablation. The therapy is performed using liquid nitrogen to freeze the cells.
- Chemoembolization. Characterized by the introduction of chemicals inside the capsule.
Treatment of formations
Therapy for a liver tumor depends on its nature, size, age of the patient and symptoms. Treatment of benign liver tumors, if they are small in size and have no symptoms, do not require therapy. The patient should be examined by a doctor three times a year in order to notice the growth of the tumor in time. To relieve clinical manifestations, it is necessary to take medications. The drugs relieve pain, improve digestion, eliminate belching and bloating, and also improve the functioning of the liver itself.
Large tumors, as well as the malignant course of the process, require removal of tumors. When performing an operation, doctors try to preserve the healthy tissue of the organ as much as possible, excising only two centimeters of tissue around the tumor, but in some cases it is necessary to remove not just the affected area, but the entire liver, followed by transplantation. For cancer, after surgery and before it, the patient is prescribed chemical and radiation therapy, this reduces the size of the tumor and reduces the risk of relapse.
Danger and prognosis
Survival in patients with normal benign liver tumors has a favorable prognosis. The patient should be regularly monitored by a doctor to monitor behavior and tumor development every 3 months. An unfavorable prognosis is made for patients with large growths similar to cystadenoma, due to the high likelihood of malignancy.
Liver cancer is characterized by intensive growth of affected cells. Neglect of treatment leads to death within one year. The largest number of deaths of patients with liver oncology occurs in the first half of the year. If the growth is resectable, the patient's life is prolonged. According to the average survival rate after surgical interventions, 3 years are added to a person’s life. Approximately 25% of patients live up to 5 years after tumor excision.
Taking preventive measures will help prevent the disease. Refusal of irritants and provoking actions reduces the risk of dangerous pathologies. Following the recommendations allows you to maintain the health of the organ and human body. However, if a tumor is detected in the liver, you should fully follow the doctor’s instructions and be systematically checked by an oncologist, even if the growth is benign.
Differential diagnosis of liver cancer
When analyzing CT data, you should always keep in mind that some liver lesions may resemble liver cancer. An inexperienced doctor may confuse different conditions and make an incorrect diagnosis. The pathology with which it is necessary to differentiate HCC is:
1) Liver hemangioma. To clarify the conclusion, delayed scanning (10-20 minutes after contrast administration) and visualization of vascular lacunae help.
2) Hepatocellular adenoma. Large adenomas may have the same structure as HCC and contain fat inclusions, necrosis, cystic cavities, and calcifications. However, adenomas are characterized by slow growth of the expansive type (without invasion) and the absence of intrahepatic metastases.
3) FNG. With focal nodular hyperplasia, the CT picture may be similar to that of liver cancer. Sometimes it is impossible to distinguish these diseases only from CT examination data - a biopsy is necessary.
4) Metastases. In some cases, the idea of secondary tumors may be suggested by the multiplicity of organ damage and the identification of the primary focus. However, an experienced radiologist with extensive experience in diagnosing liver disease can usually reliably distinguish between primary cancer and secondary metastatic lesions.
Prevention and complications
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of a tumor appearing in an organ. Prevention consists of limiting the influence of negative factors on human health. The main cause of tumor foci in the organ is viral hepatitis. To prevent its development, it is recommended:
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis B regularly;
- maintain moderate sexual intercourse;
- be extremely careful when performing actions that violate the integrity of the surface of the epidermis.
Following a healthy lifestyle plays an important role in preventive actions. It is recommended to stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking. Avoiding bad habits will reduce the likelihood of liver cancer by 2 times. You should create the right diet.
Products that have a high content of fats, chemical additives and dyes, as well as a large amount of animal fats are excluded. Adjusted meals will help maintain the healthy state of the organ and the body as a whole. To prevent growths, other preventive measures should be explored:
- Completely abandon the use of hormonal drugs and anabolic steroids in the absence of indications and a doctor’s prescription.
- Reduce connections with chemical elements and carcinogens to a minimum.
- Take medications only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Timely treatment of pathologies of the biliary tract and gastrointestinal tract.
If a cancerous tumor has grown into the tissue of an organ, corresponding negative consequences arise. When talking about liver cancer, you should familiarize yourself with the possible complications. After surgery, complications can cause infectious lesions. Regardless of the nature of the growth, the following outcomes are possible:
- Failure of organ functioning.
- The development of ascites is the accumulation of a large volume of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
- The appearance of obstructive jaundice - yellowing of the surface of the epidermis, discoloration of enzymes, a bright shade of urea, a high level of bilirubin in the blood.
- Internal hemorrhage as a result of rupture of liver vessels.
- Metabolism failure.
Malignant tumors
Oncology can be primary in nature, i.e. form from liver tissue, or secondary - in the form of metastases formed from other organs affected by oncology.
Secondary cancer is most often diagnosed, since tumor cells penetrate the liver tissue through the hematogenous route.
Such types of formations as angioma and liver fibroma do not cause malignancy.
The classification of oncological tumors in the liver has the following structure:
- Hepatocellular cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma). The most common type of cancer. Men aged 55-65 years are more susceptible. The main causes of malignant degeneration of liver tissue are hepatitis B and C, cirrhosis, and systematic intake of hepatocarcinogens.
- Cholangiocarcinoma. Formed from cells of the epithelial tissue of the bile ducts. Factors that provoke the appearance of oncology are congenital defects and parasitic infestations.
- Hepatoblastoma. Appears from pluripotent cells during embryonic development. It is registered mainly in young children under 3 years of age. Well-differentiated hepatoblastoma is less dangerous, is more treatable and is most often located in the right lobe of the gland.
- Cystadenocarcinoma of the bile ducts. The oncological formation has a cystic structure of many cavities formed from glandular cells of the bile ducts.
- Hepatobiliary cancer. Combines features of hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. Rarely seen.
- Angiosarcoma. Formed from the endothelium of the hepatic vessels. Refers to aggressive forms of cancer, vascular formations can completely destroy the parenchyma of the gland, bile ducts and capsule.
Treatment methods
The only treatment method that can completely get rid of Klatskin’s tumor and significantly increase survival is radical surgery. It is used in stages I–II of the disease. Liver resection is performed, bile ducts and regional lymph nodes are removed.
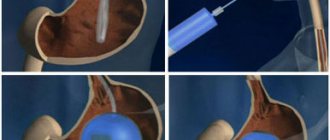
With obstructive jaundice, surgery is associated with a high risk of complications, so you must first restore the flow of bile. Currently, stenting is often used for this purpose. A stent, a small tube with a metal mesh wall, is placed in the blocked area of the bile duct. To do this, you do not need to make incisions or punctures on the abdominal wall - the manipulation is carried out during endoscopy of the duodenum. After 4–6 weeks, surgery can be performed.
When resection of the liver, it is important that a sufficiently large part of the organ remains that can cope with its functions. If the remaining liver tissue volume is expected to be less than 25%, it is advisable to perform portal vein embolization 3 to 5 weeks before surgery. Due to this, hypertrophy of the liver tissue occurs, and after surgery it is possible to preserve its larger volume. This helps prevent liver failure.
The removed malignant tumor is sent to the pathological laboratory, where histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic studies are carried out. Mutations in the BRAF, KRAS, ALK genes, translocation of ROS1, Her-2new, microsatellite instability are determined. These genetic changes occur in about 10% of cases, and they make the cancer sensitive to certain targeted drugs.
Some patients with inoperable Klatskin tumor may be offered a liver transplant.
After surgery, adjuvant therapy may be prescribed, for example, radiation therapy in combination with the chemotherapy drug 5-fluorouracil. In a number of studies, this approach has shown improved survival rates. There is currently no evidence that neoadjuvant therapy would be beneficial before surgery - research on this topic is ongoing.
For inoperable cancer in the area of the porta hepatis, chemotherapy (usually a combination of gemcitabine with platinum drugs) and radiation therapy are used.
In some cases, photodynamic therapy (PDT) is used. The patient is injected intravenously with a special compound, a photosensitizing agent that accumulates in cancer cells, and then activated with light. As a result, free radicals are formed that destroy tumor cells.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number