Mucus secretion
Mucous discharge appears due to increased production by goblet cells on the intestinal villi. Mucus facilitates the passage of feces and serves as a lubricant for the mucous membrane.
Mucous discharge from the anus appears when the digestive system is disrupted.
They can be called:
Causes of discharge
- gastrointestinal infections;
- vascular diseases;
- haemorrhoids;
- irritable bowel syndrome (Crohn's disease);
- venereal diseases;
- damage to the intestinal mucosa;
- neoplasms;
- intestinal polyps;
- damage to the rectal sphincter (surgery, trauma);
- helminthic infestations;
- condylomas, rectal papillomas;
- colitis;
- colds;
- errors in nutrition (unusual, unusual food).
The color of the discharge depends on the functional system causing its formation.
The color of anal mucus:
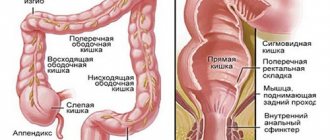
Anatomy of the gastrointestinal tract
- Inflammatory processes that cause mucus (mucus) excessive formation in the intestines - white or grayish mucus.
- Infections (gastroenteritis) or systemic autoimmune diseases of the intestines have clear or colorless mucus.
- Problems with the liver, pancreas and excessive production of bile that colors the discharge from the anus orange.
- Inflammatory processes (hemorrhoids, fissures, polyps), as well as helminthic infestations cause damage to the mucous membrane. Violating the mucous membrane and damaging the integrity of the blood vessels, which, during bowel movements, turn the mucus pink.
- Black mucus and feces indicate bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
Mucus, as a sign of disease, can be released regardless of the act of defecation and cause discomfort.
Diagnosis of mucus discharge from the anus
If a person experiences mucus discharge from the anus, then they should go to a medical facility as soon as possible. First, the doctor interviews the patient and finds out how long ago the unpleasant symptom appeared and whether accompanying signs are present. Then the doctor assesses the nature of the discharge and palpates the anus. After this, the patient is referred for the following examinations:
- general blood analysis;
- stool examination;
- colonoscopy;
- irrigoscopy.
Haemorrhoids
Inflammation of the hemorrhoids can provoke the secretion of mucus by the goblet cells of the intestine and its appearance from the butt along with the feces. The discharge of mucus is a symptom of rupture of the nodes and can turn pink and have an unpleasant odor when smearing.
Weeping hemorrhoids have symptoms specific to it. Skin irritation due to constant humidity leads to the appearance of:
Discomfort in the anorectal area
- itching;
- burning;
- prickly heat.
The progression of the disease is manifested by intense mucus secretion and the development of an abscess. The appearance of pus indicates the addition of a bacterial infection. Such discharge (whitish with an admixture of pus) is characteristic of grade 3 - 4 hemorrhoids.
Diagnosis of anal discharge
If unusual anal discharge appears, you should see a doctor as soon as possible and find out what the cause is. With such a problem, they turn to a proctologist, who collects an anamnesis and examines the anal area. If after these procedures it is not possible to establish a diagnosis, then additional diagnostic procedures are prescribed:
- endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract;
- intestinal radiology.
Microlax will help cleanse your intestines before going to the doctor.
To ensure that the diagnostic results are as accurate as possible, a cleansing enema is performed before visiting the doctor and performing any manipulations. It is also possible to use the drug Microlax, which cleanses the intestines, before diagnosis. During diagnosis, the patient does not feel pain, only mild discomfort is possible. You should not delay diagnosis and treatment of problems in the anal area, since over time the pathology worsens and can lead to oncology.
Crohn's disease
Irritable bowel syndrome is classified as an autoimmune inflammatory disease that has a specific course. Mucus released from the anus in Crohn's disease with impurities of blood and pus during inflammatory processes. The proximity of the prostate gland to the rectum during discharge from the anus provokes an exacerbation of prostatitis in men.
Crohn's disease affects the entire gastrointestinal tract, and its clinical picture has the following symptoms:
Blood from the anus
- false urge with mucus secretion;
- sudden weight loss;
- intoxication;
- abdominal pain;
- anal ulcers;
- defecation up to 8 times a day;
- blood in stool;
- skin rashes (erythema, pyoderma);
- eye diseases (iridocyclitis, uveitis);
- stomatitis;
- rectal fistulas.
The localization of the inflammatory process upon examination has the form of an infiltrate, which is found in the iliac region or in the projection of the rectum. The disease occurs with alternating exacerbations and periods of remission.
Causes of pathology
The simplest reason for mucus discharge from the anus is food poisoning or a long period of poor nutrition. As a result, the intestinal mucosa is irritated, and the body produces an increased amount of mucus as a defense against the harmful effects of feces. Mucus envelops the walls of the intestines and protects them from irritation and injury. In addition, excess mucus formation accelerates the evacuation of feces from the intestines. Similar processes occur during alcohol poisoning.
Abundant mucus secretion accompanies intestinal dysbiosis. With the help of mucus, the intestines try to protect themselves from harmful microbes. Often the stool takes on a green tint. Due to an imbalance in intestinal bacteria, vitamins and nutrients are less absorbed. Improper functioning of the intestines can cause inflammatory reactions, since against the background of dysbiosis, immunity sharply decreases. In this case, treatment consists of taking probiotics.
Clear mucus may come from the anus if you have a food allergy. This is observed when:
- intolerance to dairy products (lactose);
- malabsorption syndrome (failure to absorb fats from food);
- intolerance to gluten from cereals (celiac disease).
Food intolerances can be lifelong.
Mucous discharge from the rectum with hemorrhoids has some differences. Transparent or cloudy discharge does not mix with feces, but envelops it. At the end of a bowel movement, a certain amount of mucus comes out of the anus, which can be seen on used toilet paper. Along with this, the following are considered signs of hemorrhoids:
- itching in the anus;
- pain during and after bowel movements;
- chronic constipation;
- prolapse of hemorrhoids;
- drops of scarlet blood on stool or on toilet paper.
This chronic disease can develop throughout the digestive tract, from the mouth to the rectum. Most often, the inflammatory process affects the intestines, especially the ileum, colon and rectum. For some unknown reason, cells of the immune system begin to attack all layers of the intestine, resulting in deep erosions and ulcers. Over time, purulent fistulas and scars form, narrowing the intestinal lumen. Due to nonspecific inflammation, mucous and purulent discharge may occur. The disease is accompanied by pain and false urge to defecate.
Marta Volkova: “The only remedy that is suitable for the full treatment of hemorrhoids at home and which I could recommend is this. » Read more >>>
This inflammatory disease of the rectum affects the soft tissues surrounding the organ from different sides: the pelvic-rectal, ileal-rectal and retrorectal space. With chronic paraproctitis, a pararectal fistula forms, that is, a canal filled with purulent contents. It connects the rectal area and the skin of the perineum. The inflammatory process is accompanied by purulent discharge from the anus with an unpleasant odor.
Proctitis and proctosigmoiditis
As a result of infection in the intestines (gonorrhea, herpes, staphylococci, streptococci, etc.), inflammation of the rectum and sigmoid colon may begin. Inflammation causes pain, bowel movements and other unpleasant sensations. Sometimes with these diseases, mucus comes out after defecation.
Irritable bowel syndrome
This disease develops due to disturbances in the digestive system. It is accompanied by nausea, flatulence, rumbling in the stomach, constipation, diarrhea, painful cramps and frequent urge to defecate. A distinctive feature is repeated diarrhea. Frequent mucous stools, liquid like water, can quickly lead the patient to dehydration. He urgently needs to drink a lot, the liquid can be replenished with light broth, jelly, fruit drink, chamomile infusion, etc.
Perianal dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin around the anus. There is swelling and redness on the skin, and the patient suffers from itching. Fungal, allergic and bacterial skin lesions develop against the background of hemorrhoids, anal fissures, inflammatory diseases of the large intestine and rectum, as well as disorders of the intestinal flora. The disease can occur in men and women. Less than 10% of cases are associated with the spread of candidiasis. In this case, the discharge from the anus is white. White mucous discharge from the anus occurs when there is fungal damage to the colon, which can be caused by taking antibiotics.
Colon polyps
A polyp is a benign neoplasm that grows on the intestinal wall. Often it grows towards the intestinal lumen. Thus, it narrows the intestinal passage and can be injured by feces. A large polyp leads to intestinal obstruction. Injured polyps become infected, which causes pain, inflammation, spasms and other unpleasant symptoms, including mucus in the stool. Trauma to the rectal polyp causes blood and mucus to leak from the anus. A similar phenomenon accompanies anal condylomas.
Tumors of the rectum, sigmoid and colon
At an early stage, colon cancer does not show obvious signs. Primary symptoms include mucus discharge and blood from the anus. Initially, there may be streaks of blood in the stool. A growing tumor is more prone to injury, so the amount of blood increases over time. In this case, the stool becomes dark brown or black in color due to altered blood mixed with the stool. Sometimes the passage of dark blood precedes the stool. Late stages of cancer may be accompanied by foul-smelling stool in which blood clots are visible.
Transparent mucus from the anus with malignant tumors of the rectum is rare. Most often, the mucus contains streaks of blood, sanguineous discharge, and in the later stages - foul-smelling pus or purulent-bloody fluid.
Colitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the large intestine. Under the influence of infections or pathogenic flora, an inflammatory process develops. Swelling begins in the intestinal wall, peristalsis and mucus production are disrupted. Colitis is accompanied by a painful urge to defecate, abdominal pain, and diarrhea mixed with mucus and blood. After bacterial waste products enter the bloodstream, an adult patient's body temperature rises. Non-infectious colitis can cause strands of mucus or mucous lumps to appear in the stool.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis is a chronic autoimmune disease prone to frequent relapses. The immune system attacks the cells of the large intestine, causing destructive and ulcerative inflammation of varying intensity. Most often, the disease begins in the rectum and then spreads to other parts of the large intestine. The patient's body temperature is usually not elevated, but he experiences a painful, false urge to defecate. There may be mucus and thin streaks of blood in the stool.
Rectal ulcer
A rectal ulcer is a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane. It can be single or multiple, and also have different depths of tissue damage. Most often, the disease develops due to injury to the intestinal mucosa by solid feces due to constipation or fecal stones. Rectal ulcers occur in people with rectal prolapse. Another cause of pathology can be a variety of infections, including sexually transmitted infections. Pain in the rectum intensifies during defecation. Bloody discharge from the anus of varying intensity is also characteristic. When an ulcer becomes infected, mucus and pus begin to ooze from the rectum.
Liver diseases layered on rectal pathologies
Sometimes, when problems in the large intestine are accompanied by liver disease, bile begins to be produced in excess. As a result, orange discharge with an unpleasant odor may appear from the anus, or orange streaks will be visible in the stool.
Ulcers occur in those who suffer from rectal prolapse. By its nature it is a benign formation, that is, formed from the cells of the organ itself.
Dysbacteriosis
Violations of the barrier function of the digestive system and intestinal microbiota lead to the development of dysbiosis. The clinical picture of dysbacteriosis depends on the microflora that caused it.
Such pathogenic microorganisms are:
Intestinal infections
- staphylococcus;
- fungi;
- proteas;
- enterococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- coli;
- salmonellosis.
Discharge from the anus due to dysbacteriosis has a liquid consistency with mucus impurities and a foul odor.
Symptoms of dysbiosis appear:
- intoxication;
- loose stools;
- abdominal pain;
- weakness;
- fever.
Mucous discharge that appears from the anus is a product of the vital activity of microorganisms that have infested the intestines. Mucus, as a product of their vital activity, causes disruption of intestinal motility and poisons the body. An abundance of mucus can cause false tenesmus and be excreted in scanty quantities in the form of feces.
Treatment methods
The detection of bloody discharge, as well as clear mucus in the stool, is a reason for prompt treatment. The tactics of such treatment will ideally be determined by a group of doctors, which includes a proctologist, infectious disease specialist, hematologist, surgeon, and oncologist.
If during treatment a sharp increase in blood in the stool is detected, then it is necessary to call an ambulance. Massive bleeding can be life-threatening for the patient, but emergency hospitalization can save his life.
The method of treating blood in stool will be determined by the nature of a particular disease. Treatment is prescribed by the doctor according to whose profile the bleeding occurred. For example, if mucus and blood in the stool are a consequence of cancer, then the person should go to an oncologist. If the red clots have a bright shade, then this is a sign of a fissure in the anus, so treatment will be carried out by a proctologist.
During a consultation with a doctor, it is necessary to list the complaints, as well as indicate external signs of mucus and blood in the stool. Thus, it will be possible to create a clinical picture, which is the key to a correctly drawn up research plan, as well as prescribed therapy. The majority of pathologies that are accompanied by bloody spots in the stool are chronic, so without proper treatment, the patient’s condition will only worsen over time.
Urgent Care
Proctitis
Inflammation of the intestinal mucosa that develops in its end section is called proctitis.
Causes of mucus discharge from the anus during proctitis:
Proctitis
- sexually transmitted infections (anal sex);
- intestinal infections;
- colitis;
- Crohn's disease.
The disease occurs in waves, alternating exacerbations and remissions. During the period of asymptomatic remission, the main natural manifestations are an admixture of mucus.
An acute period of proctitis develops within a few hours. Main symptoms:
- tenesmus;
- nagging pain;
- pain in the perineum;
- discharge mixed with pus and blood;
- heaviness and burning in the rectum.
Mucous discharge is pink or yellow in color and its intensity depends on the development of the inflammatory process. Pathological impurities in the stool cause irritation of the anus, and when liquid stool wets the anus, irritation and secondary infection appear. The spread of infection along the ascending path in the rectum leads to the development of complications.
What to do if blood and mucus appear?
Lumps of mucus, as well as blood clots in the stool appear for various reasons.
Some illnesses are dangerous to health and can also cause death. That is why you should not ignore mucus with blood in the stool. Let us consider in more detail the reasons for the appearance of such a symptom. Blood clots and lumps of mucus appear in the intestinal contents for various reasons. Some diseases are dangerous to the health and even life of the patient. Therefore, it is so important not to ignore the appearance of inclusions in the stool with mucus and blood in an adult; the reasons for the appearance of these impurities are listed below.
Anal fissure
This condition (characterized by the appearance of red blood in the feces) is very painful, since the patient feels pain from a tear in the lining of the anus. There is itching and bleeding from the anus, sometimes it can be quite severe. An anal fissure is treated using local remedies, for example, suppositories, ointments with anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effects.
It is difficult to treat fissures, since this problem is often accompanied by chronic constipation. In this case, healing is slow: hard feces in the process of leaving the body damage the intestinal lining and lead to exacerbation and inflammation. Blood flow begins. The pain is sometimes so severe that it stops the desire to have a bowel movement.
The most common disease characterized by the appearance of mucus and blood is ulcerative colitis. This disease is autoimmune in nature, it is extremely difficult to treat, and the effectiveness of therapy can be low. The inflammatory process entails the formation of erosions and ulcers, which cause bloody spots to appear. In some cases, pus is released, which gives the stool an unpleasant odor.
In addition to changes in the type of discharge, ulcerative colitis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain – its intensity can be very strong;
- diarrhea - the urge to empty the colon occurs about 20 times a day;
- elevated temperature – the indicator can reach subfebrile values;
- loss of appetite - in some cases this leads to exhaustion of the patient;
- flatulence.
The true causes of ulcerative colitis have not yet been established, but it is known that autoimmune inflammation and genetic predisposition play fundamental roles in the onset of the disease.
10 meters - this is the length of the human digestive tract. This means that blood rarely enters the stool in its original form. Almost always, by the time of defecation, it undergoes some biochemical changes.
Detection of fresh blood is possible if the source of bleeding is in the immediate vicinity of the anus. In most cases, bleeding is localized in the rectum or lower colon. Then the blood in the stool is dark in color. Detection of blood in stool in the form of hidden inclusions is possible only through a series of diagnostic procedures. When visiting a doctor, you should immediately tell about alarming symptoms. The specialist will give you a referral for blood and stool tests.
Important! If you have stool of an uncharacteristic color, you should analyze your diet over the past two to three days. If coloring foods such as blueberries, beets, currants, and tomatoes were not used in your diet, then this is a reason to visit a therapist or proctologist. Some medications can radically change the color of stool.
Neoplasms
Neoplasm in the intestine
Oncological diseases are asymptomatic and at the stage when treatment of neoplasms does not bring results, symptoms of inflammatory processes appear. The breakdown of tumor tissue leads to the appearance of pus, mucus, and foam in the stool, released from the anus. Oncological diseases have a complex treatment process and can cause disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract in its early stages.
Such disorders are dyspeptic disorders, manifested by nausea, vomiting, and loose stools. Mucus and food impurities may be released from the anus, which are not a pathology, but are a protective mechanism in response to chemotherapy.
What if mucus comes out with blood?
Blood entering the stool in the gastrointestinal tract turns the feces dark. This is due to the breakdown of hemoglobin, which is converted into iron. The blood turns black, and so does the stool. Also, these processes become symptoms of such diseases:
- Varicose veins of the esophagus. This is a component of portal hypertension syndrome, which occurs when diagnosing liver cirrhosis. Black stools, vomiting, chest pain after eating and increased heart rate are the main signs of this pathology. If a vein in the esophagus ruptures, a probe must be inserted to compress the veins and stop the bleeding.
- Stomach ulcer, duodenal ulcer. The feces become tar-colored, liquefy, nausea leads to vomiting, and the vomit contains blood clots like “coffee grounds.” To solve the problem, surgery is required.
- Perforation of the ulcer. The patient complains of acute pain in the abdomen and chills. Covered in cold sweat, in some cases even loses consciousness. The main way to urgently help a patient is resection of the stomach and duodenum.
- Stomach cancer. The patient experiences an aversion to food, especially to meat products. Blood tests show anemia. A person who has lost a lot of weight becomes weak. The breakdown of tissue provokes bleeding, which can be determined by the admixture of blood in the stool.
- Bowel cancer. The main symptom of this pathology is alternating constipation with diarrhea, constant rumbling in the stomach. Defecation does not bring satisfaction. The urge to have a bowel movement is often false. The character of the stool is ribbon-like, thin, and in the later stages of the disease there are noticeable traces of blood in it.
Interesting! Blood in the stool can be a sign of not only diseases of the internal organs. This can be a sign of stomatitis and nosebleeds. When impurities are detected during defecation, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the body's condition.
Blood may be a result of intoxication. Thus, poisoning from rat poison or some poisonous plants can be so severe that internal bleeding occurs. Sometimes bloody bowel movements become a side effect of drug therapy using Aspirin, Diclofenac, Xarelto or Heparin. Use of these medications should be discontinued if such problems are detected.
Oily discharge
The consumption of fatty, fried foods in the diet of some people leads to the development of inflammation of the gallbladder and pancreas. Normally, in a person’s diet, the amount of fat per 70 kg of weight should be 80-90 grams. This amount is the daily norm. Oily mucus released from the anus has causes related not only to diet, but also to the use of certain medications and intestinal inflammation.
Enzyme preparations for the breakdown of fats serve as a provoking factor for the appearance of oily discharge. The appearance of such discharge from the anus is an indicator of pancreatic dysfunction. Taking drugs that break down fats disrupts the basic physiological mechanisms in its work, and when they are discontinued, it can no longer cope with the breakdown of fats.
Another cause of oily discharge is gallstone disease. Violation of the outflow of bile, which emulsifies fats and breaks them down, causes such discharge. Such discharge does not have a distinct odor. The stool is viscous and sticky and leaves marks.
Nature of the discharge
Oily
Yellow oily discharge does not always signal a problem. Sometimes they are associated with the consumption of certain foods: tomatoes, fatty fish. Also, the release of oily fluid from the anus is associated with taking tableted drugs for weight loss or dietary supplements. If the oily liquid appears in the stool and gives off a special shine, the following diseases appear:
- colitis;
- inflammatory process in the bile ducts or bladder;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- internal form of hemorrhoids.
Return to contents
Blood mixed
The release of mucus and blood is not normal and indicates damage to the integrity of the intestine. Often, red anal discharge is the first sign of a malignant neoplasm in the intestine. The table shows the main diseases and the nature of bleeding characteristic of each deviation.
Character of bloody discharge
| Deviation | |
| A thin line of blood or dark blood clots | Diverticulosis |
| Tumor in the colon | |
| Black stool | Pathology of the stomach, duodenum or small intestine |
| Scarlet blood | Malignant tumor |
| Pathological growths | |
| Formation of hemorrhoidal cones inside the anus | |
| Cracks in the anus | |
| Dark cherry clumps | Impaired colon function |
Return to contents
Mucous
Mucous transparent discharge from the anus is observed in 10% of patients, which is caused by hemorrhoids. Mucus discharge from the anus is observed in an adult in the following cases:
PAY ATTENTION! This home remedy will help ANYONE who is tired of suffering every time they go to the toilet. It works quickly and naturally, without injections or surgeries! what kind of remedy >>
What to do
Impurities in stool, discomfort and pain become the main reasons for visiting a doctor.
Consultation and treatment of problems with weeping hemorrhoids, fissures in the rectum, and irritable bowel syndrome are provided by:
Coloproctologist
- proctologist;
- coloproctologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- oncologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- therapist;
- surgeon;
- dermovenereologist.
Treatment of the disease that provokes the secretion of mucus is the main way to solve the problem. The nature of the discharge, quantity, color are the main indicators for determining diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
Diseases of the small intestine
It should be taken into account that at home it is not easy for the woman herself, who does not have medical knowledge in the field of gynecology, to determine the nature of the discharge and answer the question posed. One of the cases of immediately contacting a doctor in order to find out the root cause is the discovery of severe bleeding or discharge with any impurity. Often, blood mucus itself, which appears once, can indicate serious diseases in the field of gynecology.
For what other reasons may mucus with streaks of blood appear in the stool? The most common disease characterized by the appearance of such a symptom is ulcerative colitis. This disease is autoimmune in nature, and its treatment is quite difficult. The effectiveness of treatment can be quite low.
The entire inflammatory process entails the appearance of ulcers and erosions, which become the main cause of mucus and blood in children and adults. Sometimes there is also an admixture of pus in the stool, which causes the stool to emit an unpleasant odor. In addition to the fact that mucus comes out with blood during colitis, the following symptoms of the disease may also be present:
- Painful sensations, the intensity of which can be very strong.
- Diarrhea. It should be noted that the urge to have a bowel movement occurs about 20 times a day.
- Increased body temperature. This indicator can reach subfebrile values.
- Poor appetite or complete absence of it. Sometimes this symptom provokes exhaustion of the patient.
- Flatulence.
At present, the main cause of the development of ulcerative colitis has not yet been identified. But experts know that autoimmune inflammation and genetic predisposition play a fundamental role in the occurrence of this disease.
Small intestinal bleeding has one feature: changes in stool are noticeable only a day after the development of the disease. Blood with mucus in the stool of an adult with diseases of the small intestine is poorly visible, since during the day such inclusions are exposed to digestive enzymes. This is the reason why stool is colored not the scarlet color characteristic of blood, but black.
If you have black, liquid stools, this is a signal that the bleeding occurred a day ago, so there is no need for therapeutic actions. A different situation will develop if the pathology continues to manifest itself, especially in children. This means that blood flow is still ongoing.
In addition to the fact that diarrhea with blood and mucus may occur, the patient’s appetite and general health also worsen, nausea and vomiting appear. Blood pressure decreases, the skin becomes pale, and stool looks like coffee grounds. The patient’s performance also decreases due to the weakness of the whole organism.
Blood with mucus in children and adults can occur with the development of Crohn's disease. It is a chronic, serious condition that affects absolutely the entire intestine, and not just any part of it. The pathology is quite rare and can result from an allergic reaction to food, smoking or stress.
When the first symptoms appear, including the appearance of blood in the stool, you should definitely visit a proctologist’s office. This specialist must examine the tissues of the rectum, after which he will determine a list of additional necessary diagnostic procedures. As a rule, for diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a general blood test, bacteriological analysis of stool, coprogram, and colonoscopy.
If during such diagnostics there is a suspicion of the development of concomitant diseases of the internal organs, then the patient is prescribed procedures such as gastroscopy, as well as ultrasound examination.
Diagnostics
When visiting a doctor, the main procedures that are performed are:
Examination using a sigmoidoscope
- Blood analysis. Biochemical, general, serological (syphilis, hepatitis), PCR. The parameters allow the doctor to make an interpretation - inflammatory processes, metabolic disorders and others.
- Stool analysis. Feces are checked for helminthic infestations and bacteriological (intestinal microbiota).
- Instrumental studies – FGDS, colonoscopy, abdominal x-ray, ultrasound, irrigoscopy.
- Digital rectal examination.
- Biopsy of intestinal tissue.
Characteristic symptoms that cause discomfort during discharge are:
- orange oily discharge from the anus;
- irritation in the anal area;
- the appearance of blood, stains on clothes and underwear;
- impurities in feces (white plaque, flakes, blood, pus);
- skin rashes;
- burning, itching of the anus;
- discomfort in the anal area.
Research results determine the choice of therapy.
The main reasons for bleeding from the anus
The root causes of hemorrhoidal bleeding are:
- hard consistency of stool;
- problems with stool;
- diarrhea.
Often, patients do not take emergency measures because they do not experience pain when bleeding occurs. But this behavior is a big mistake. Delay in this matter is inappropriate and destructive.
Bleeding from the anus during stool without pain can occur for various reasons. The shade of bloody discharge may vary depending on which part of the gastrointestinal tract the problem occurs in.
When blood loss occurs in the area of the rectum or sigmoid colon, a bright, red tint appears. In case of gastric or esophageal bleeding, the blood will be much darker.
When you eat fermented foods, the color of your blood discharge is also distorted. So, what are the main factors that contribute to a person bleeding from the anus?
The appearance of scarlet blood during bowel movements
Scarlet blood from the anus during defecation is usually found on toilet paper.
Bloody discharge comes out during bowel movements. The fact that the blood after defecation is bright scarlet indicates the development of pathology in the colon, or damage to tissue near the anus.
The patient experiences unpleasant, painful symptoms. This situation is typical for:
- Hemorrhoids . Bright red bleeding, in the form of drops, from the anus, mixed with feces, or blood clots. As a rule, it is not abundant (however, sometimes it manifests itself in the form of a blood stream). Occurs due to solid masses of feces and their large accumulation. It can also be triggered by excessive physical exertion on the body. If the situation is long-term, with hemorrhoids, not only inclusions of blood, but also pus are observed in the stool.
- Heavy bleeding with diverticula of the intestinal area: occurs with a certain frequency, in the postpartum period, as well as in older people.
- The appearance of cracks in the tissues of the rectum: very noticeable pain appears, quite a lot of blood is released.
- Scarlet blood during defecation without pain , caused by the presence of polyps. Bleeding occurs rarely and is accompanied by the presence of mucus in the feces.
Blood from diarrhea
When blood during bowel movements in women or men is accompanied by a phenomenon such as stool liquefaction, this is an extremely alarming symptom. In this case, such serious diseases as:
These diseases are characterized by the following manifestations:
- high body temperature;
- gagging;
- cutting nagging pain in the abdominal cavity;
- the appearance of chills;
- severe itching and burning in the anus.
If the stool is dark in color (black stool), various tumors and gastric ulcers may occur.
Loose stools with blood in men and women directly indicate the following conditions:
- cancer tumors in the rectum;
- the occurrence of dysbacteriosis;
- food poisoning;
- infection with helminth infections and parasites;
- dysentery;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
Blood clots in feces
If blood is present in the stool during bowel movements in women and men, this is an almost one hundred percent indicator of Crohn's disease. This condition is accompanied by such symptoms as:
- the appearance of a rash on the skin;
- pain;
- febrile conditions.
In addition, blood clots during bowel movements are released in nonspecific ulcerative colitis. Symptoms of the disease:
- loss of appetite;
- pain in the left side of the abdominal cavity;
- feeling of nausea.
Another disease characterized by the presence of blood in the stool is an intestinal infection. In this case, the disease will necessarily be accompanied by:
Treatment
The treatment method depends on the etiological factors and the main methods are:
- medicinal;
- surgical;
- conservative;
- invasive.
Each disease is treated using an integrated approach.
| Treatment method | Techniques and remedies |
| Medication | Antispasmodics. Their mechanism of action is aimed at relieving muscle spasms, abdominal pain, inflammatory processes, and improving intestinal motility. Medicines in this group:
Gastroprotectors. Protects the mucous membrane of the gastroduodenal part, reduces the effects of acids and alkalis on the mucous membrane. Funds from this group:
Laxatives. Prescribed for a tendency to constipation, it softens stool, facilitating its passage and evacuation. These include:
Adsorbents. Medicines have absorptive capacity and absorb substances regardless of their harm or benefit. These include:
Rectal suppositories. They relieve inflammatory processes, heal mucous membranes, and have an antibacterial and antimicrobial effect. Dissolving in the intestines, they are like an ointment that moisturizes the skin of the perianal area from wet calluses. These include:
Antibacterial agents. This is a group of drugs that reduce the activity of pathogenic flora. These include:
Medicines have a complementary, preparatory and anti-inflammatory effect during treatment. |
| Invasive | Colonoscopy. An endoscopic examination of the lower intestine will allow you to assess the condition of its mucous membrane and take histological material. X-ray with contrast. Examination of the walls, lumen and shape of the intestine allows you to assess its condition and detect a neoplasm. |
| Conservative | The use of distracting procedures (baths, massage) is common in the absence of inflammatory processes, in the treatment of children and the acute period in the development of a chronic disease. |
| Surgical | Surgical treatment is indicated for neoplasms and complications of hemorrhoids and is carried out under anesthesia. |
Diseases for which drugs are used:
- Crohn's disease;
- dysbacteriosis;
- proctitis;
- haemorrhoids.
Treatment of weeping, purulent hemorrhoids with complex therapy using antibacterial, rectal suppositories and examination of the condition of the rectum. When complications develop, surgical treatment methods are used.
Anal fissures
This condition is very painful, as a person experiences pain due to a tear in the lining of the anus. With anal fissures, mucus and blood appear in the stool. In parallel with this, itching and bleeding from the anus appear. In some cases it can be quite strong. Anal fissures are treated with local remedies, for example, suppositories, ointments with wound healing and anti-inflammatory effects.
It is quite difficult to treat such cracks, since this problem is often accompanied by chronic constipation. In this situation, healing will be slow. The fact is that solid feces, when the body leaves a person, damages the intestinal lining, which leads to exacerbation and inflammation. Mucus streaked with blood begins to appear. The pain can be so severe that a person loses the desire to empty his bowels.