Gallbladder deformity - what is it? This diagnosis refers to modifications of the constituent organs, which can lead to all sorts of complications and are congenital or acquired. This pathology can take various forms and depends on many factors.
Gallbladder deformity is a widespread disease in Russia and throughout the world. It may be congenital or acquired.
When the position of the neck or body of the gallbladder changes, its deformation occurs. It may look like a bend of the neck or a constriction. Other variants of this pathology are also possible.
Some forms of such deformation do not require treatment at all and go away on their own. But in general, this pathology is fraught with serious consequences, including death.
It can appear in different places of the gallbladder. It depends on where the partition is located. The consequences of gallbladder deformation are largely determined by how much its shape changes.
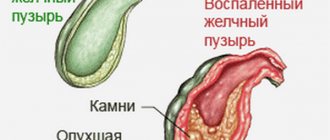
Under the influence of this process, stagnation of bile can occur. Stones, folds and bends may form in the gallbladder. It is important to diagnose this disease in time and receive the necessary treatment.
What it is?
A disease such as gallbladder deformity can be present in a person from birth or acquired during life.
When the position of the neck or body of the gallbladder changes, its deformation occurs.
It may look like a bend of the neck or a constriction. Other variants of this pathology are also possible.
As a result, cholecystitis forms and adhesions form. The gallbladder may also become enlarged or blood flow to the liver may be impaired.
In this condition, the patient may experience very severe pain and dyspeptic disorders. For deformation associated with intense physical activity, no treatment is needed. She can go away on her own.
Often, patients exhibit deformation of the neck of the gallbladder itself. It often occurs when the patient has chronic cholecystitis. Due to the formation of adhesions on the walls of the gallbladder, this organ can also change its shape. In this case, the composition of bile changes and indigestion occurs.
Sometimes the gallbladder is completely twisted around its axis. This happens with prolonged physical activity. Also, the cause of torsion can be elongation of the neck of the gallbladder. If the cervix is twisted many times, blood flow is instantly disrupted. Deformation of the gallbladder of the contour type manifests itself in changes in the boundaries of this organ. With this form of the disease, the patient experiences pain after eating. They also appear if you constantly carry various weights.
In the case of an S-shaped deformation of the gallbladder, it is double bent. Most often it is associated with heredity. If such a deformity is acquired during life, it is caused by the rapid growth of the gallbladder compared to other organs. This form of deformation does not cause any problems for the patient and there are no symptoms either.
Sometimes bitterness appears in the mouth, stool changes and belching. When the outflow of bile is disrupted, flatulence and dyspepsia occur. There are also problems with the quality of digestion of fatty foods. Any type of gallbladder deformation requires a visit to the doctor.
ICD 10 code
The ICD, tenth revision, is a unified list for classifying diseases and maintaining statistics of patient requests for medical help. The next revision of this register is planned for 2015.
Gallbladder deformity may be noted in ICD 10 in the following categories:
- Q44 – congenital defect or malformation of the biliary organs;
- 1 – other congenital defects of the gallbladder;
- K82 – other gallbladder diseases;
- 0 – narrowing of the gallbladder or ducts, not associated with stone formation;
- 9 – unspecified gallbladder disease.
Classification
A twisted gallbladder is studied in each specific case several times: the first - on an empty stomach, the second - after eating egg whites. This allows us to determine the nature of the pathology. If the condition is congenital, the constriction of the gallbladder in a child and an adult will not change its position, and the shape of the organ itself will remain the same.
A functional bend is one that occurs for a certain time; a fixed bend is persistent. The condition is also distinguished by the localization of the pathological process. Experts highlight:
- bending of the gallbladder in the cervical area;
- inflection in the body of the gallbladder;
- bend of the lower third;
- bile duct torsion.
A bend in the neck of the gallbladder occurs most often, and pathology in the middle third causes the most dangerous consequences.
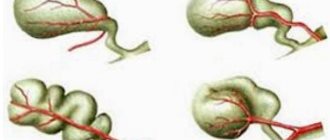
The disease manifests itself in various degrees of organ deformation, which depends on the location of the pathological process. The bubble can take the form of a hook, an hourglass, an arc, or a spiral. If the organ is bent twice, experts talk about an S-shaped deformation of the gallbladder (or a C-shaped gallbladder, as people who are not related to medicine write).
This problem is most typical for young children.
There is another problem that belongs to the list of deformations - the presence of constrictions. This is a narrowing of the organ in a circle. Usually the condition is congenital, but it can disappear without a trace after the child reaches 3–5 years of age. The types of pathology and their anatomical features can be seen in the photo below.
Concept of deformation
To understand what deformation of the gallbladder (gallbladder) is, you need to have an idea of the structure of the organ and its functionality. Outwardly, it looks like a bag or a pear, the size of which increases with age. In a newborn child, the length and width of the gallbladder are about 40*10 mm, and in an adult (on average) – 90*25 mm.
The organ consists of three main parts:
- bottom;
- body;
- neck.
The cervix opens into the cystic duct, which connects to the hepatic duct. Deformation of an organ can occur in different parts of the organ; the type of pathology, its symptoms and possible complications depend on this.
There are two types of deformation of the gallbladder:
- congenital - disturbances in the shape and structure of the organ occur in the embryo when it is inside the womb; pathology is usually diagnosed during the first year of life;
- acquired - diffuse changes occur in an adult and are provoked by various factors, including an unhealthy lifestyle.
Congenital pathology is rare; more often the disease occurs over the years. The risk group includes older people over 50 years of age. Many people do not suspect for years that the gallbladder is deformed; they find out about it only when obvious symptoms appear and their health deteriorates.
Contour and other types of deformation
A deformed gallbladder can look different, it all depends on what type of pathology has developed. There are three main varieties:
- curvatures or kinks;
- wall compaction;
- contour changes.
If the gallbladder is bent, that is, bends or kinks appear, this means that the first type of pathology has developed. It can be functional or labile. Functional deformation appears when there is a change in posture, sudden movement, heavy lifting, or other physical activity. Labile deformity appears only after excessive tension of the abdominal muscles or after stress.
Most often, there is an inflection in the body of the gallbladder or between the body and the bottom. There is also a complicated form of organ curvature - multiple bends, in which several bends occur. An s-shaped deformity is common.
The next type of pathology – hardening of the walls – is less common. Normally, the walls of the bladder do not exceed 5 mm in thickness; if this figure is exceeded, problems arise. There are no special signs that arise when an organ hardens; usually this type of deformation is diagnosed by chance when viewed on an ultrasound.
The last type - contour deformation of the gallbladder means a change in its shape. Depending on where the changes occur, the bubble begins to resemble an hourglass, an arc, or a pear. With this pathology, constant acute pain quickly develops. Due to a violation of the integrity of the walls, bile can enter the stomach cavity, causing severe complications in the digestive system.
Types of deformation
There are such damages as kinks and constrictions, twisting of individual parts of the organ, and the appearance of partitions. In shape they can be hook-shaped, S-shaped, in the form of a horn or a cap. Most often, the anomaly occurs at the junction of the neck and the body and in the area of the bottom of the organ. Several bends at once seriously interfere with the secretion of bile, and subsequently lead to organic diseases.
It is easy to understand what it is - a congenital deformity. The main anomaly is a twisted shape, with the bubble having a double bend. This pathology is mainly hereditary. It occurs in children when the growth of the bladder itself occurs faster than the development of other organs located in the neighborhood. Often this phenomenon goes away on its own over time.
Among the anomalies there is labile deformation. It occurs as a result of excessive physical exertion and can disappear on its own.
Organ doubling also happens. With this pathology, there are two bubbles, from each there is a neck and a duct. With incomplete doubling, a septum is formed in the bladder, dividing it into two parts.
The bubble can be gigantic in size or very small without disrupting its basic functions. Finally, the organ may be completely absent. Sometimes there is no elastic muscle frame in the walls of the bladder. Because of this, the walls protrude and a diverticulum is formed.
Definition and classification
Gallbladder deformation is a condition in which the shape, size or structure of the tissue changes. With pressure and displacement, constrictions and kinks can occur, and such anomalies can cause malfunctions in the functioning of the organ and the digestive process.
There are the following types of deformation.
Kink (boomerang)
In this case, deformation appears in the transition area from the neck to the body. Stagnation of bile occurs, followed by rupture, and the gallbladder itself takes on the shape of a boomerang, for which it received its second name. When bending, the pain can be localized in different parts, increasing gradually.
Padding
Quite a dangerous type of pathology. Most often it occurs as a congenital anomaly in children, but can also occur in an adult with severe intestinal diseases or difficult pregnancy.
In this case, the shape of the gallbladder is completely modified, which can cause serious problems.
Favorable prognosis is possible only in case of early detection of pathology in children; in the presence of the disease in adults, only palliative measures can be prescribed.
S-shaped deformation
This type of anomaly can be dangerous only if it appears after severe stress, heavy exertion, obesity or cholecystitis. In a child, this pathology goes away without medical intervention with age.
Bend of the neck
Most often, this anomaly appears as a result of progressive cholecystitis, when the walls of the gallbladder are affected by the inflammatory process. Without quality treatment, adhesions form, which can cause stagnation of bile and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
Labile bend
This pathology is temporary. Most often it occurs as a result of severe stress or tension - it usually goes away quickly on its own. This type of bending does not require treatment, but the sick person must follow a regimen: no serious stress, no strong emotional disorders.
Contour deformation
This type of anomaly is characterized by curvature of the contours of the bladder and may be a congenital pathology. Usually occurs as a result of severe physical exertion, tension, or as a result of the inflammatory process.
It is dangerous because it can cause rupture of the bile ducts.
Diagnosis of gallbladder inflection.
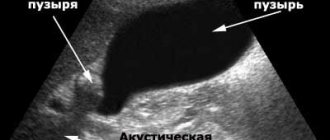
The diagnosis is made as a result of an ultrasound examination. Ultrasound allows you to determine the localization of the deformation, identify the degree and type of gallbladder motility disorder: hypokinetic (hypomotor) or hyperkinetic (hypermotor) type of dyskinesia.
To accurately determine the type of bend in the gallbladder, an ultrasound is performed first on an empty stomach, then 30 minutes after taking a choleretic breakfast (for example, egg yolks, sour cream). With congenital inflection, the shape of the gallbladder does not change after breakfast. And with an acquired bend after eating, the size of the gallbladder decreases after the evacuation of bile into the intestinal lumen from the gallbladder. Normally, after breakfast, the volume of the gallbladder decreases by 40%. Depending on the degree of development of dyskinesia, the volume of the gallbladder decreases in different ways.
Prevalence and significance
According to statistics, gallbladder kinks occur in half of the Russian population. The statistics are approximately the same for other countries of the world.
Deformation of the gallbladder can lead to a variety of diseases:
- various neoplasms;
- adhesive process;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- weak diaphragm;
- chronic inflammation in the biliary tract and others.
This disease often develops in patients with kidney stones. In older patients, the gallbladder and internal organs descend. The cause of this may be abdominal surgery or a hernia.
Congenital and acquired deformity
Since there are various ways to acquire this pathology, appropriate treatment is prescribed. If the s-shaped gallbladder is a congenital disease, this may not be called a pathology, but simply an unusual shape of this organ. In frequent cases, this goes away with age in the child. Such deformation in a child is possible for several reasons: prolonged stress, obesity, heavy physical activity, chronic cholecystitis.
Cases of the bladder deformation form lead to a number of certain complaints. A kinked bladder is often accompanied by nausea, dull pain under the right hypochondrium, severe loss of appetite, constipation or diarrhea. There is also often a bitterness in the mouth.
The reasons for the acquired s-shaped bladder, which often occurs in adults, are quite different: enlargement of nearby organs, heavy lifting, long periods of sitting, poor nutrition (prolonged fasting or overeating), a number of diseases (acute or chronic cholecystitis), significant prolapse of internal organs, obesity. Quite rarely, deformation of the gallbladder occurs in women during pregnancy (the uterus enlarges and puts pressure on the liver and bladder).
The question often arises as to how dangerous it is to bend the gallbladder. This disrupts the movement of bile through the bile ducts, subsequently causing disruptions in the digestive process, since fats cannot naturally emulsify. Cholelithiasis or calculous cholecystitis may occur.
Causes of gallbladder deformation
An acquired disease with timely response can be successfully treated. With a congenital disease, the task of doctors is to provide the patient with a long period of remission and prevent the appearance of pain. To ensure that the positive dynamics do not turn out to be short-lived, it is first of all important to determine the causes of the gallbladder inflection, and then productively eliminate them from the life of the clinical patient and select an adequate treatment regimen.
Acquired
Only a specialist can determine the presence of an anomaly, and for clarity, it is better to use clinical diagnostic methods. More often, the gallbladder is deformed due to age-related changes in the body, when internal organs descend, change shape and location, and exert harmful pressure on neighboring structures. All this can be seen on an ultrasound. Some patients find out what a gallbladder bend is by chance - during a routine medical examination or examination by a doctor.
If the anomaly is acquired, the prerequisites for the development of the disease are the following factors:
- chronic inflammatory process of the bile ducts;
- alternating a strict diet with systematic overeating;
- poor nutrition, a consequence of a hunger strike;
- systematic overstrain of the abdominal muscles;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- malignant and benign tumors;
- adhesions on the wall of the organ;
- stone formation;
- bile duct dyskinesia;
- increase in organ size;
- chronic pericholecystitis;
- weakness of the diaphragm.
Congenital
A characteristic deformity may turn out to be a congenital disease with which a person will have to live for the rest of his life. At first, the deformed gallbladder does not manifest itself in any way, but over time it leads to dysfunction of the digestive system. The patient will have to constantly adhere to a therapeutic diet and undergo a course of medication to avoid relapses.
The provoking factors of the congenital form of the disease are as follows:
- pregnancy and childbirth with pathologies;
- bad habits of a pregnant woman;
- genetic predisposition;
- excessive physical activity during pregnancy;
- a number of chronic diseases of the female body;
- emotional instability.
The causes of gallbladder deformation in children and adults usually differ.
In children:
- as a consequence of the inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract;
- after gallbladder diseases.
In teenagers:
- chronic inflammatory diseases characterized by a slow course and mild symptoms;
- hormonal surge during rapid growth (usually in boys).
In adults, as a result:
- chronic cholecystitis;
- cholelithiasis;
- dystrophy of the diaphragm;
- infections;
- presence of intestinal parasites;
- excessive loads;
- tumors;
- internal adhesions;
- constant stress;
- surgical intervention.
Causes of deformation of the gall bladder in an adult
These include:
- hepatitis type A;
- age-related changes or prolapse of internal organs, which can also manifest as deformation of the bile organ;
- hernia;
- cholelithiasis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- adhesions of internal organs;
- chronic stagnation of bile in the bladder;
- poor diet, changes in life schedule and alcohol abuse;
- increased physical activity, including lifting heavy weights with an unprepared body, less often when engaging in strength sports, when the muscle corset is not ready for such work;
- biliary dyskinesia.
Leading an incorrect lifestyle can be the beginning of an acute period, when the flow of bile is disrupted and the symptoms worsen. Deformations of the gallbladder also often occur due to constant stress. A temporary change in its shape occurs during a long stay in non-physiological positions.
In newborn children, deformation of the gallbladder appears for the following reasons:
- genetic disorders;
- disorders of intrauterine development of the fetus at the stage of formation, including genetic abnormalities in the formation of internal organs due to a difficult pregnancy or the presence of bad habits in the expectant mother - smoking or alcohol abuse, use of drugs, certain medications;
- the presence of severe chronic diseases in a pregnant woman.
In adolescents, gallbladder deformation is detected in the following situations:
- inflammatory processes in the abdominal organs;
- detection of congenital anomalies of internal organs or liver, ducts.
These unfavorable changes can be triggered by hormonal fluctuations and the onset of the active growth phase at this age.
Features of deformation in children
Irregular shape of the gastrointestinal tract organs, in particular the bladder, is usually observed at the age of 13-16 years. Distortion of the shape of the gallbladder is provoked by chronic inflammation in the digestive system. Also, bile stagnation, which occurs due to improper nutrition of the child, can distort the bladder. Congenital problems in the functioning of the gall bladder are provoked in children by: poor nutrition or lifestyle of the mother during pregnancy; maternal poisoning (chronic bad habits or acute); bacterial and viral infections affecting the embryo; genetic abnormalities in the development of the bladder.
Causes of acquired curvature of the body and neck of the gallbladder: excessive loads; emotional stress; obesity. In the acute stage, deformation of the gallbladder makes itself felt by severe periodic pain in the side on the right, as well as signs of intoxication. The child is pale, there may be a small red rash on the skin, he complains of weakness and nausea, and indicates discomfort in the bladder area. The listed signs should be a reason to immediately contact a pediatrician or gastroenterologist at the hospital.
Deformation of the gallbladder in a newborn
Deformation of the gallbladder in a newborn is usually congenital. There are often cases when pathology occurs in some members of the same family and close relatives: brothers and sisters, parents and children, etc.
If we do not take into account the hereditary factor of deformation, then the cause of changes in the shape of the organ may be external influences on the fetus during pregnancy:
- taking medications prohibited during pregnancy;
- exposure to nicotine (both active and passive);
- various diseases of the expectant mother (especially in chronic form);
- regular consumption of alcoholic beverages during pregnancy.
The greatest risk of harm to the child can be traced in the first trimester of pregnancy, when the formation of the digestive system of the unborn baby occurs). But during other periods of gestation, the danger of a negative impact on the child is also present, although to a lesser extent.
A woman carrying a baby must feel the level of responsibility that is entrusted to her. This applies to both her own health and the health of her unborn child.
Symptoms of the disease
The patient's pain depends on the form of the deformity. Problems with bile secretion can lead to problems with the digestive tract. Twisting of the gallbladder is accompanied by pain in the right side. Inflammation and poor circulation in this organ lead to a deterioration in overall health.
One of the symptoms is a change in complexion, bitterness in the mouth, and increased sweating. When the neck of the gallbladder is twisted, bile immediately enters the abdominal cavity. As a result, acute pain may occur in the left side and throughout the abdomen. Sometimes, when the gallbladder is deformed, the temperature rises and weakness appears.
Also a sign of the disease is bloating after eating food. During the examination, the pain may become stronger and take on the character of an attack. This requires immediate contact with a specialist. With the sudden development of the disease, the patient feels pain in the liver and gall bladder. Another symptom is yellow skin and nausea.
An aversion to any food may also appear. A yellow coating may be found on the tongue. With the gradual development of the disease, the functioning of the biliary tract occurs. As a result, faeces become discolored, loss of appetite occurs, and the patient begins to lose weight.
Also characteristic signs of gradual deformation are dyspepsia, pain in the intestines and right hypochondrium. Necrosis of the gallbladder neck as a result of prolonged deformation is accompanied by the penetration of bile into the abdominal cavity.
As a result, peritonitis develops and the patient may die without medical attention.
Symptoms
Signs of pathology depend on the speed of development of the abnormal process. Since bile controls the processing of food, the first symptoms of the disease are a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, bitterness in the mouth, heartburn and pain in the right hypochondrium. This process can be normalized only with the help of special medications. Therefore, if these symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor who will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of a bent gallbladder:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Belching.
- Regular bloating after every meal.
- Clear signs of dyspepsia and digestive disorders.
- Acute pain syndrome in the area of the right hypochondrium, which can radiate to the spine, collarbone and scapula.
It is very important to correctly differentiate the pathology. This is due to the fact that the anomaly can be characterized by echo signs of other diseases:
- cholelithiasis;
- inflammation;
- various tumors;
- complications of hepatitis;
- abnormalities in the digestive tract.
Is there any danger
An anomaly in the shape of the gallbladder is not considered a particularly dangerous condition and is not life-threatening, but it can significantly impair your health. Negative severe consequences arise due to the lack of timely therapy. They often affect the digestive tract, which, due to stagnation of bile, ceases to function normally. Dysfunction of the bladder and neighboring organs gradually leads to gallstones, which can compress blood vessels.
This leads to the destruction of the walls. Necrosis causes perforation (the appearance of holes) in the gallbladder, through which fluid penetrates into the abdominal cavity. This is dangerous due to the development of peritonitis, a fatal inflammation of the peritoneum.
Drug treatment
By prescribing medications for the treatment of pathology, gastroenterologists mean taking choleretic drugs. Such as: Flamin (a drug used for diseases of the digestive system, a choleretic agent for inflammation of the bladder or bile ducts), Odeston (increases the outflow of bile, prevents the formation of stones in the gall bladder), Aristochol (normalizes the secretion of bile, restores liver function and relieves spasms) , Hofitol (also a choleretic drug, often prescribed as a drug for complex therapy), Csqualon (choleretic and anti-inflammatory drug, enhances the outflow of bile, it is often prescribed before probing), Gepabene (choleretic drug of plant origin, also improves the outflow of bile), Ursofalk (hepatoprotective agent, dissolves cholesterol in gallstones), Nicodin (choleretic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory agent). These medications must be taken in periodic courses prescribed by your doctor.
Diagnostic methods
The most informative method for examining the abdominal organs is ultrasound. It allows you to quickly detect the disease and prescribe treatment. This method can be used to monitor the condition of organs in pregnant women and children due to its safety.
An ultrasound can show deformation of the walls of the gallbladder and their thickening. It manifests itself as calcium deposits, depressions and protrusions. Using ultrasound, you can see the deformation of the gallbladder from different angles.
Consequences
In some cases, the condition causes the development of various diseases.
Deformation of the gallbladder, the consequences of which can lead to various disorders, most often causes: Due to the bend, a disruption of the blood supply to the organ may occur, which will lead to necrosis of its part. As a result, bile enters the abdominal cavity, and peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum) develops. In some cases, this leads to the death of the patient.
A deformed gallbladder leads to stagnation of bile and the occurrence of cholelithiasis. In severe cases, the affected organ must be removed.
If exacerbations occur, the patient may have a fever, nausea or vomiting. However, in many cases, pathology does not have a significant impact on well-being.
With any clinical picture, the condition requires regular visits to the doctor for prevention and control.
Treatment
Conservative therapy is used for almost any deformation of the gallbladder. A congenital change in the shape of the gallbladder does not cause problems for the patient and does not require treatment. But acquired organ deformation with painful symptoms requires treatment. It allows you to eliminate pain and inflammation, as well as restore bile excretion.
Treatment of gallbladder deformation involves mandatory bed rest in the acute period. It is also important to drink plenty of fluids other than mineral water. The immune system is strengthened with the help of various vitamins, for example, ascorbic acid, B vitamins, tocopherol and others.
Physiotherapy procedures, for example, electrophoresis with novocaine, are of great importance. Abdominal massage and exercise therapy help remove bile and prevent the formation of stones. To prevent the bladder from twisting along the longitudinal axis, it is important not to carry heavy objects and avoid heavy physical exertion.
If the irregular shape of the gallbladder was formed during intrauterine development, this deformation only in rare cases requires the intervention of specialists. Usually, this pathology does not cause noticeable discomfort to the patient and does not require treatment. Acquired deformity, on the contrary, is not only possible, but absolutely necessary to be treated in a timely manner.
The main treatment measures in this case are aimed at:
- Elimination of pain;
- Reducing the inflammatory response;
- Restoring normal bile excretion.
The patient must undergo several courses (usually three or four) of therapy, each of which takes from one and a half to two weeks. Treatment of acquired gallbladder deformity is based on:
- Strict adherence (during the acute period) to bed rest;
- Eating only dietary foods;
- Taking antispasmodics and analgesics - in the form of intramuscular injections of Baralgin or Drotaverine, if the pathology is in the acute phase.
If cholelithiasis occurs, atropine sulfate 0.1% is administered. If the course of the disease is more severe, it may be necessary to take Tramadol.
- Taking broad-spectrum antibiotics - ampicillin, augmentin, cephalosporin antibiotics), which are used together with taking probiotics and antifungal drugs;
- Detoxification therapy – if there are signs of intoxication;
- The use of choleretic drugs - cyclone, nicodine, odeston, oxyfenamide, flamin and others, but only after the acute period ends and the patient takes antibiotics (and only if there are no stones in the gall bladder);
- Strengthening the body's defenses through the use of vitamins - such as ascorbic acid, tocopherol, B vitamins, retinol acetate and others.
After remission occurs, treatment can be supplemented with physiotherapeutic procedures (as prescribed by a doctor), herbal medicine, massage of the abdominal area - the latter helps facilitate the process of bile excretion and reduces the likelihood of gallstones forming. To prevent twisting of the deformed organ along the longitudinal axis, the patient must strictly limit physical activity, avoid carrying heavy bags and rearranging furniture, and move calmly, without making sudden movements. All these measures contribute to a speedy recovery.
Surgery
If a bend in the gallbladder blocks the outflow of bile, a rupture of its wall may occur. In this case, the gallbladder is surgically removed.
Folk remedies
Drug treatment can be combined with folk treatment. The main thing is to coordinate all your actions with your doctor so as not to harm the bladder even more. Effective folk remedies for improving the functions of the gallbladder are:
Herbal collection. Mint, sage, lemon balm, chamomile are taken in equal quantities. The dry mixture is brewed with boiling water (2 tablespoons per 250 ml), infused for 5 hours. Drink small portions throughout the day.
A decoction of flax grains. 50 g of grains per 250 ml of water, boil for 5-10 minutes, leave until cool. It turns out a thick jelly, which you need to drink on an empty stomach, half a glass daily.
Decoction of corn silks. 30 g per 250 ml of water, boil for 10 minutes, cool, take half a glass before meals twice a day.
In the absence of complications, you can use traditional methods of treating gallbladder deformity. But treatment with herbal infusions should be long-term, at least 3 months. The following herbs are most often used individually or in combinations: buckthorn, marshmallow, mint, tansy, sage, immortelle, St. John's wort, celandine, lemon balm and chamomile.
Instead of tea, it is recommended to use decoctions of rose hips, pine needles, and oats. Natural fresh juices are also useful: pumpkin, carrot. It is better to replace sugar in the diet with honey.
Physiotherapy
Physical exercise improves the outflow of digestive secretions and restores its properties. Simple exercises will help cure a deformed organ:
- "bike";
- raising your legs while lying on your side;
- "scissors";
- pressing your legs to your chest while lying on your back;
- breathing from the diaphragm while standing;
- squats.
You can start performing exercise therapy only after consulting a doctor. To make exercise as effective as possible, exercises should be performed regularly, 10-15 minutes a day.
Lifestyle
Deformation of the gall bladder requires a person to maintain a healthy lifestyle. You cannot get carried away with bad habits, overexert yourself physically and mentally, or eat junk food, otherwise the bladder will constantly work for wear and tear. It is also advisable to observe the correct drinking regime - at least 1.5 liters per day for an adult.
Diet
Diet plays a big role in the treatment of this disease. It is important not to eat spicy, salty, sour, fried, smoked or fatty foods. It is allowed to eat boiled, steamed, baked and raw food. It is not recommended to eat cold or very hot food.
Also, avoid drinking carbonated drinks. Food should be light: soups, purees or porridge. Diet is important and we eat small portions. The patient needs to drink about 2 liters of water per day.
Forecast
The consequences of gallbladder deformation are largely determined by how much its shape changes. Under the influence of this process, stagnation of bile can occur. Stones, folds and bends may form in the gallbladder. Long-term circulatory disorder in the biliary organs occurs when the bladder twists and is completely bent.
As a result of this deformation, necrosis of the bladder tissue and perforation of its walls may begin. In this case, the bile secretion enters the abdominal cavity. This leads to the development of bile peritonitis. Intoxication of the whole body begins, and dysfunction of all organs is observed.
Lack of timely assistance for peritonitis can lead to death. But some forms of gallbladder deformity may disappear on their own without any treatment. This applies to labile and congenital deformities. But medical supervision is required in any case to prevent complications.
Causes
The condition can be caused by various factors.
Among them are congenital and those arising in the process of life. Deformation, the causes of which are acquired, is often caused by:
- Chronic cholecystitis. It is an inflammation of the gallbladder. Mostly occurs against the background of cholelithiasis.
- Gallstone disease. It is the appearance of stones in the gallbladder or its ducts.
- Failure to follow the principles of proper nutrition or lack of a meal plan.
- High intensity physical activity aimed at the anterior wall of the peritoneum.
- Formation of adhesions in the small intestine.
- Dystrophy of the diaphragm.
- Pathologies and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Biliary dyskinesia.
- Malignant tumors or cysts.
- Infectious diseases.
- Helminths.
In addition, the pathology can be a consequence of heavy lifting, overexertion, or even a stressful situation.
Congenital deformity
Occurs due to a disturbance during embryonic development. Highlight:
- According to the configuration of the organ: hook-shaped, S-shaped, bovine horn, development of septa and bends.
- Based on size: hyperplasia (which means deformation due to excessive enlargement) or underdeveloped gallbladder.
- Depending on the location: intrahepatic localization, location in the midline of the abdominal cavity, pelvis, etc.
In rare cases, the following are found:
- Agenesis. With this pathology, there is no gallbladder. Part of its activity is carried out by the bile duct
- Presence of a second hard drive. An extremely rare pathology, which is the formation of a cavity in the bile duct, which performs similar functions to the gallbladder.
- Doubling shares. Two GBs are formed in the cavity, united by a common duct.
- Diverticulum. This is an abnormal protrusion of the organ wall and defects in the structure of the gallbladder muscles.
Types of gallbladder deformities