Stomach cancer is one of the biggest problems in gastroenterology. In the general structure of oncological pathologies, it ranks 4th in frequency (about 1 million diagnosed cases per year), and in overall mortality it is second only to lung cancer. However, it is often diagnosed only at stages 3-4, when there are already local or distant metastases.
Therefore, the issue of using an imaging technique that shows the disease and makes it possible to make an early diagnosis is very relevant in clinical practice. Today we will consider the role and capabilities of the method in this process, whether ultrasound of the abdominal cavity can show oncology, how to prepare in such a way as to maximize the information content of the examination.
Possibilities of the technique
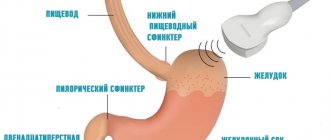
Ultrasound examination is prescribed for almost all patients with suspected benign or malignant disease in the stomach . High-frequency waves pass well through human tissue and are partially reflected from them (depending on the density indicator). They are then captured by a sensor located on the front wall of the abdomen, processed by a computer and displayed as an image on the screen.
Ultrasound is a routine test if there are symptoms of dyspepsia, decreased appetite or pain in the upper abdomen. In addition to the stomach, the condition of the pancreas, liver, gallbladder, spleen, lymph nodes and large vessels of the abdominal cavity is examined.
With high-quality preparation of the patient, ultrasound allows one to clearly visualize the walls of the antrum and body of the stomach . The bottom of the organ in most patients is poorly visible due to the presence of gases in it (even a small amount). If the study is carried out by an experienced specialist, he can also approximately estimate the volume of gastric juice that is in the cavity.
Cancer diagnosis using ultrasound
Ultrasound is a simple, effective and fast diagnostic method for diagnosing cancer in the early stages. The doctor may diagnose you using other methods of determination. For example, MRI, X-ray or biopsy, etc.
, an ultrasound examination is painless and completely safe and very informative, which is why it is prescribed to most patients. Screening will 100% show whether you have a tumor in your organ or not and what stage it is at?
Ultrasound technologies are improving and a specialist can do an ultrasound of the intestines and stomach and determine whether there is cancer in those organs or not? This examination is possible due to the fact that ultrasound scanners have an elastography function.
Many patients who had problems with the thyroid glands and the doctor suspected a neoplasm were sent by the specialist for an ultrasound scan. The tumor will be detected quickly, but whether it is malignant or benign needs to be determined. In a suspicious node, the ultrasound specialist assesses the condition of the vessels.
The device records the spectral characteristics of the blood flow in the node. Additionally, the doctor will refer you for a biopsy of this area and the established diagnosis will be 100% confirmed by several examination methods. Additionally, lymph nodes are examined. According to the theory, cancer cells can enter them.
If the doctor suspects a tumor in the brain, he will most likely prescribe you an MRI rather than an ultrasound. An ultrasound examination with duplex scanning can reveal a lot. What is the condition of the vessels in the brain, are they displaced, is there a developed vascular network that should not be there? If the latter is detected, the patient is given a referral for an MRI. An accurate diagnosis will be established.
Causes
Gastric cancer is a malignant tumor with uncontrolled growth that develops from the cells of the mucous membrane of the organ. Separately, lymphoma is distinguished - a tumor that is formed from lymphatic tissue (there is a lot of it between the layers of the wall). However, during the initial diagnosis before biopsy, they cannot be separated, since symptoms and signs often overlap.
Among the causes of oncological pathology it is necessary to highlight:
- infection with Helicobacter pylori infection;
- chronic inflammatory and erosive processes (gastritis and peptic ulcer);
- long-term presence of Crohn's disease;
- genetic predisposition;
- decreased reactivity of the immune system;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- irregular meals;
- exposure to ionizing radiation and environmental pollution.
Modern principles of gastric cancer treatment
The main treatment method for stomach cancer is surgery. The extent of the operation depends on the stage at which the tumor is detected. If it has not yet spread deep into the wall of the organ, endoscopic resection is performed - removal of the affected area using an instrument inserted through the mouth, as during gastroscopy.
With a subtotal gastrectomy, the part of the organ affected by the tumor process is removed. In later stages, the entire organ must be removed along with surrounding tissue. In this case, the esophagus is connected to the small intestine. If the lymph nodes in the abdominal cavity are affected by metastases, they also need to be removed.
In advanced cases, when cure is impossible, palliative surgery is performed. The surgeon removes the affected part of the stomach to relieve the patient's condition.
Radiation therapy for stomach cancer is:
- neoadjuvant - performed before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor and facilitate its removal;
- adjuvant - to destroy cancer cells that remain in the body after surgery.
The most common side effects of radiation therapy when irradiating the abdominal area are nausea, indigestion, and diarrhea.
Chemotherapy can also be adjuvant or neoadjuvant. It is often combined with radiation therapy. Chemoradiation therapy can become the main treatment method for metastatic cancer in the later stages, when the prognosis is poor, but there is an opportunity to alleviate symptoms and prolong the patient's life.
In some cases, targeted drugs are effective: trastuzumab, ramucirumab, imatinib, sunitinib, regorafenib. But they are suitable only in cases where tumor cells have certain molecular genetic properties.
Classification
A classification of stomach cancer is often used depending on the degree of progression and spread of the cancer process:
- Stage 0 – the process affects only the mucous membrane;
- Stage 1 – growth of pathologically altered cells into the submucosal layer is observed, distant foci cannot be detected;
- Stage 2 - the process spreads to the muscular and serous layers of the wall, several foci were also found in the nearest lymph nodes;
- Stage 3 – the tumor actively metastasizes through the regional lymphatic system (more than 3 confirmed foci), but without involving other organs;
- Stage 4 - when performing an ultrasound, CT or MRI, it was possible to find foci of the process in other organs (liver, spine, brain, spleen, kidneys or others).
Stages of development of stomach cancer
Symptoms as the first indicator
Despite the fact that the pathology often occurs without any symptoms, if you pay close attention to your health, you can notice the presence of abnormalities in a timely manner. Suspicion of stomach cancer should be caused by the following symptoms:
- causeless weight loss;
- lack of appetite;
- pain not associated with eating;
- feeling of pressure after eating a small amount of food;
- heartburn;
- nausea.
With the development of stomach cancer, the patient loses appetite
Of course, all of the listed signs may be present in any other disease of the stomach, but only a competent differential diagnosis of stomach cancer will help to exclude other pathologies and confirm the presence of a tumor.
So how do you know if you have stomach cancer? Theoretically, no way. It is impossible to say exactly how stomach cancer hurts and how it manifests itself in all patients. Everything is individual. Only a full examination will help make a diagnosis of stomach cancer. Therefore, if you suspect a disease, you should see a doctor.
First of all, a careful examination of the patient is carried out. When palpating the abdomen, painful areas and areas of compaction are determined. Particular attention is paid to the lymph nodes, since they are the first to respond to tumor development and metastasis is also observed in these organs. Only after this will instrumental and other methods of identifying pathology be prescribed.
The initial diagnosis of cancer is palpation
People with chronic pathologies should undergo regular stomach cancer screening to timely identify abnormalities in the course of the disease.
Instrumental diagnostics
Diagnosis of stomach cancer should include all possible research methods. Each of them has its own advantages. Some give instant results, while others, although expensive, reflect a complete picture of the patient’s condition.
Only a combination of several methods at once will help not only determine the presence or absence of a tumor, but will also make it possible to assess the stage of cancer, its spread to neighboring organs and the general condition of the body.
In most cases, methods for diagnosing stomach cancer include the following procedures.
Endoscopy
This is the most accessible examination for stomach cancer. A tube with a camera and light is inserted into the esophagus. Due to this, it is possible to examine the organ tissue and identify abnormalities. Of course, the procedure must be performed by an experienced specialist who knows exactly how to recognize stomach cancer during a visual examination.
One of the methods for diagnosing cancer is endoscopic examination of the stomach.
If a defect is detected, a biopsy is recommended for stomach cancer. Thanks to this analysis, it is possible to obtain a piece of tissue from the formation, which will subsequently be examined for cancerous degeneration.
X-ray
The stomach is a hollow organ, so the use of a contrast agent is required to obtain results. Typically barium is used. After the substance is administered, several photographs are taken. They will show all changes in the mucous membrane, including cancerous formations. The procedure does not cause significant discomfort and is performed in most clinics.
Ultrasound
Next, we’ll find out whether stomach cancer can be seen on an ultrasound. The method is different in that it suits everyone without exception. It is performed superficially, meaning no tubes or instruments are required. In addition, it is important to emphasize that the results are obtained immediately on the screen, which is especially beneficial in emergency cases.
Ultrasound cannot always detect stomach cancer
Using ultrasound, it is possible to assess the shape of organs, their position, and the thickness of the walls. Due to this, the slightest deviations are immediately detected.
As for the question of whether stomach cancer is visible on an ultrasound, here, again, it all depends on the experience of the specialist and the equipment used.
An ultrasound will show the outline of the formation, its texture, that is, whether it is hollow or not. But it is impossible to say with certainty that it is a polyp, cancer or cyst.
Ultrasound can be considered as an early diagnosis of stomach cancer. This is explained by the fact that the method is safe and can be performed quite often. There will be no negative consequences for the body.
Tomography
CT and MRI are more often used if confirmation of stomach cancer is required - a biopsy, ultrasound and radiography have already been completed and the doctor requires comprehensive information regarding the formation. Only with the help of tomography is it possible to carefully examine all tissues layer by layer, revealing the presence of metastases in other organs.
Using MRI, you can make a more accurate diagnosis and select the necessary treatment based on the results of the study.
The procedure is the most informative, but its disadvantage is that it is quite expensive. It is for this reason that patients wondering how to check the stomach for cancer are primarily offered the above methods, and only if there are abnormalities in their results, CT is used.
PAT
When figuring out how to diagnose stomach cancer, it is worth noting the modern technique. It involves the introduction of radioactive glucose into the body. After a certain period of time, it is distributed throughout all tissues. But the main feature of the substance is that it can accumulate in the tissues of a malignant tumor.
After administering the substance, the required area is examined using a scanner. This makes it possible to determine the localization of the lesion and even its stage of development. The method is expensive and is not performed in all clinics. But at the same time it is quite informative.
Laparoscopy is used both for diagnosis and treatment
Laparoscopy
This method is already used in cases where, for example, stomach cancer is detected on an x-ray. In other words, the method is intended to evaluate an already diagnosed tumor. The technique involves inserting instruments through small incisions on the abdominal wall.
Laparoscopy makes it possible to view tissue from the inside. This is especially important at the treatment planning stage. This is explained by the fact that not all tumors are allowed to be operated on, so it is important to exclude the presence of a contraindication for intervention. It may be either the location of the formation next to a large vessel or the involvement of neighboring organs, which does not allow it to be completely removed.
Laboratory diagnostics
Having figured out how to test for stomach cancer using hardware methods, you should not forget about laboratory methods.
The fact is that a tumor, from the moment of its formation, causes changes both in the blood picture and in the state of the immune system. First of all, a general blood test is taken. This will help identify signs of anemia.
In addition, an increase in ESR is indicative. A stool test is also required to detect occult blood. There are other examination methods.
Clinical picture
The symptoms of the disease also differ greatly depending on the stage of the process. But the problem with this oncological pathology is that the clinical picture, even in stage 3, may not differ from gastritis or peptic ulcer. In patients with first detected stomach cancer, the following complaints are most common:
- periodic pain of varying intensity in the upper abdomen (on an “empty” stomach, or after eating);
- feeling of abdominal discomfort or fullness after a small snack
- nausea;
- a sharp change in diet, the appearance of aversion to certain types of dishes;
- decreased appetite and decreased body weight (even with an unchanged diet);
- black feces;
- belching with an unpleasant odor.
Important If you have the symptoms listed above, you should immediately seek qualified medical help.
How to prepare for an abdominal diagnosis?
Usually, ultrasound of the stomach is performed routinely, both in outpatient and inpatient settings. After ordering a test, the doctor must tell the patient about all the nuances of preparation and diagnostic methods.
The study is carried out on an “empty” stomach, so on the day of the ultrasound the patient should not eat anything.
It is allowed to drink regular table still water an hour before the start of the diagnosis. All prescribed medications are taken as usual in the morning.
If a patient has problems with increased gas formation (especially in older patients), then a special diet is prescribed a few days in advance , from which all foods and dishes that may contribute to it are removed. Additionally, it is possible to prescribe medications that reduce flatulence (simethicone, absorbents, antispasmodics).
What pathologies will the study show?
Using ultrasound, the following pathological conditions can be determined:
anatomical abnormalities of the stomach;- gastritis with hypersecretory state;
- benign and malignant neoplasms of the stomach;
- peptic ulcer;
- metastases of tumors from other localizations;
- intragastric bleeding;
- enlargement of the lower esophageal veins (with increased pressure in the portal vein system of the liver);
- narrowing of the antrum of the stomach;
- the presence of third-party bodies;
- enlargement and inflammation of nearby lymph nodes.
Why is an ultrasound of the stomach prescribed?
Using ultrasound, parenchymal organs are best visualized: pancreas, spleen, liver, kidneys, endocrine glands. To examine the bladder, it requires forced filling with liquid, while the organs of the gastrointestinal tract are usually filled with food and gases, which creates certain difficulties for their examination.
Ultrasound of the upper digestive system is especially important in pediatrics and surgery, as it can reliably detect some diseases. Indications for the study:
- sharp pain in the upper abdomen;
- excessive regurgitation in children or constant vomiting;
- dysphagia – impaired swallowing and discomfort;
- “high” bleeding – from the esophagus, stomach or duodenum;
- palpable mass formation in the upper abdomen.
In addition to ultrasound of the stomach, the examination includes the study of the biliary system, pancreas, spleen, liver and visible lymph nodes. The optimal time for conducting the study is the morning, provided that the patient comes for the procedure on an empty stomach.
Whether it is possible to see stomach cancer on an ultrasound depends on the age and build of the patient, the size and location of the tumor itself. Upon careful examination, you can detect all 5 layers of the organ: the mucous membrane, the muscular layer of the mucous membrane, the submucosa, the muscular layer itself and the serous, integumentary layer. With slow evacuation of food, even on an empty stomach, fine gastric contents will be visible.
Is cancer visible during the procedure?
Although ultrasound examination of gastric cancer is performed routinely, the informative value of this examination (especially not in specialized oncology clinics) remains low. Whether cancer can be seen on an ultrasound depends on the following factors:
- Sensitivity of information content to the quality of training. In addition, it is not always possible to completely get rid of the presence of gases in the lumen of the stomach (even when using medications).
- Lower quality of visualization of hollow organs. This is the main disadvantage of ultrasound research methods. Therefore, clinical guidelines recommend the use of contrast-enhanced computed tomography if gastric cancer is suspected.
- Depends on the qualifications of the specialist. In most general clinics, gastric examination is carried out by doctors who do not always pay attention to nonspecific signs of the oncological process.
- Use of outdated equipment. In small regional centers, ultrasound is usually performed on devices that are more than 5-7 years old, which reduces its information content.
Whether an ultrasound will show stomach cancer depends on the qualifications of the doctor. A stomach problem can be detected in large oncology clinics, where such patients are diagnosed every day.
Please note: It is impossible to make a diagnosis of stomach cancer based on ultrasound. It is imperative to supplement the diagnostic program with gastroscopy, biopsy with cytological examination and computed tomography with contrast.
Useful video
When to undergo an abdominal ultrasound and how to prepare for it, a specialist explains in this video.
In addition, ultrasound diagnostics allows for timely detection of metastases - daughter tumors. They can be located in regional lymph nodes, liver, pancreas, greater or lesser omentum.
Malignant tumors of the stomach on ultrasound
To obtain reliable results and facilitate examination, the patient must be fasting and the physician must use a convex or high-frequency linear transducer. The examination is carried out in the supine position and usually takes no more than 30 minutes.
On the ultrasound screen, benign and malignant tumors may have similar echogenicity and structure. The final morphological type of the neoplasm is established only after histological examination. There are several sonographic signs, the presence of which will indicate more in the direction of a malignant process.
Options for the ultrasound structure of stomach cancer:
- hypoechoic heterogeneous formation with a hyperechoic (bright white) central part due to the contents in the organ cavity;
- hypoechoic (darker compared to normal stomach tissues) space-occupying formation, which is intimately adjacent to the pancreas, the left lobe of the liver in the projection of the body of the organ - infiltrative cancer of the body of the stomach;
- asymmetrical thickening of the stomach wall, heterogeneity of its structure, increased blood flow in this area - another variant of the infiltrative form of oncological formation;
- a volumetric hypoechoic formation with a heterogeneous structure and fuzzy uneven contours without signs of invasion in the projection of the body - antral cancer.
An important sign of tumor malignancy is metastatic damage to regional lymph nodes. The altered lymph nodes have a rounded shape, a heterogeneous structure with no demarcation into the cortical medulla, and are enlarged.
It is also important to understand that whether an ultrasound will show stomach cancer depends on the class of equipment and its resolution, the presence of a Doppler mode for assessing blood flow or elastography.
Decoding the results
Ultrasound symptoms, which may indicate oncological pathology, differ at different stages of the process:
– absence of any ultrasound signs of cancer;
Stage 0- Stage 1 – an increase in the thickness and layering of the suspicious area of the wall, a moderate decrease in echogenicity;
- Stage 2 – there is a significant change in echogenicity, the surface of the mucous membrane becomes uneven, a defect in the form of a crater or depression may be detected, a sharp change in the diameter of the wall, narrowing of the lumen of the stomach, tuberosity of the external contour, disappearance of the boundary between the different layers (mucosal, muscular and serous);
- Stage 3 - in addition to symptoms of gastric damage, significantly enlarged hypoechoic lymph nodes are detected;
- Stage 4 – additionally, metastases can be detected in neighboring anatomical structures (most often in the liver).
All detected changes are carefully documented in the results, which are given to the patient or attending physician after the end of the study.
Additional Methods
A number of other diagnostic methods are used to diagnose stomach cancer. Their comparative characteristics are given in the table:
| Ultrasound | FGDS with biopsy and cytological examination | CT with contrast | MRI | |
| Characteristic | Non-invasive ultrasound examination | Endoscopic examination with tissue sampling | X-ray examination with intravenous contrast | Using the phenomenon of magnetic resonance |
| Symptoms of stomach cancer | Changes in echogenicity, wall thickness, contour evenness | Violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane, change in its color, proliferation of tissue of various shapes, deformation | “Defect” of contrast accumulation, wall deformation, change in its thickness and shape | Thickening of the wall, changes in the shape of the stomach, changed lymph nodes |
| Information content of primary tumor diagnosis | ++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ |
| Information content of metastasis detection | ++ | – | +++ | ++++ |