Rectal ulcer is a rather rarely diagnosed pathology. However, in practice this type of illness occurs frequently. The reason why it is not always possible to make the correct diagnosis lies in nonspecific symptoms. Experts often confuse an ulcerative defect of the rectum with a malignant neoplasm, hemorrhoids or radiation rectitis.
Representatives of the stronger half of humanity between the ages of 40 and 60 are more susceptible to this defect. Moreover, recently the disease is increasingly being detected in younger men.
What is pathology
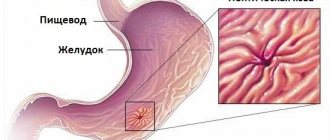
An ulcerative defect of the rectum is a pathology that affects the intestinal tract, worsening or destroying the mucous membrane. Almost every person is susceptible to this disease. Moreover, it is impossible to independently determine the presence of erosive formation. Only a doctor can confirm or refute the diagnosis after a series of studies.
Types of Ulcerative Lesions
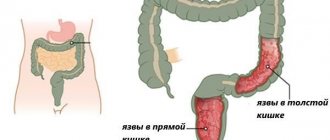
The human intestine consists of two parts: the large and small intestine. In turn, the large intestine is divided into structural parts, one of which is the rectum, ending in the anus.
Among the defects that most often affect the rectum is ulceration. This pathology can be of three types:
- ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- solitary ulcer.
Important: A person diagnosed with a rectal ulcer must change his lifestyle, eat right and avoid constipation.
Each type of ulcer formation has a number of specific causes. Therefore, it is worth considering in more detail which provocateurs cause erosion of the rectal zone.
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammation of the rectal mucosa. This pathology is formed due to the following phenomena:
- constant negative influence from the outside;
- genetic factors.
Important: An ulcerative defect in the rectum can cause severe bleeding and pronounced discomfort during bowel movements.
Ulcerative colitis affects the rectum, then gradually spreads to the colon. More often, the defect in question is diagnosed at the age of 20-30 years. Less commonly, ulcers occur in school-age children.
Solitary rectal ulcer
Solitary rectal ulcer occurs in isolated cases. With this type of pathology, the membrane of the rectal region is severely damaged. However, the defect is not malignant.
Young people are more susceptible to this type of erosive lesion. In this case, the main symptom of the solitary type of ulcer will be prolapse of the intestine through the anus. Therefore, if such a sign appears, you should immediately consult a doctor. It is important to remember that a timely diagnosis guarantees the success of treatment.
Causes of ulcer formation
The mucous membrane is easily damaged by mechanical damage, infectious diseases and stress. Mechanical ones include: coprolites (stool of a hard consistency), carelessness of doctors during a medical examination, anal sex, insertion of objects into the body through the anus. People with rectal prolapse are at risk. They often have a solitary ulcer.
Infectious diseases accelerate damage to the mucous membrane, provoking the process of ulceration. Stress negatively affects the body and takes away the strength to resist diseases.
The exact causes of solitary ulcers in humans have not been identified; research is ongoing. To protect themselves from complications, scientists and doctors were able to prepare a forecast for the risk group. Those with the following diseases are at risk of getting an ulcer:
- Chronic constipation;
- Reduced or low body activity (sedentary work);
- Prolapse of the intestine through the anus at fairly frequent intervals;
- Mechanical damage to the intestine due to fractures of the pelvic bones, bone chips, falling on sharp or protruding objects;
- Excess of unhealthy diet over healthy food, constant consumption of unhealthy fatty or fried foods, low fiber content;
- Anal sex.
Common reasons
Rectal ulcerative pathology occurs due to a number of different factors. In this case, the most common reason for the manifestation lies in the following:
- heredity;
- constant stress and overstrain of the central nervous system;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- poor nutrition;
- weak immunity;
- bad habits
- infectious diseases;
- constant constipation.
Important: Often, rectal ulcers occur as a result of anal sex and after unsuccessful surgery.
You can often hear that a rectal ulcer can be provoked by radiation therapy given for malignant tumors in the intestine. In fact, the consequence of this type of treatment is often ulcerative rectitis. But erosion of the rectal region is provoked by the above factors.
Causes
In addition to the infectious factor and Helicobacter pylori infection, the following contributes to the formation of rectal ulcers :
- hereditary predisposition;
- injuries of the abdominal organs, intestinal tract;
- damage to the integrity of the walls of the rectum (surgeries, diagnostic procedures);
- chronic dysbacteriosis;
- constipation, diarrhea;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- intestinal infections with complicated course;
- parasites;
- lack of food discipline;
- concomitant pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
The stress factor is of no small importance . Constant overexertion, psycho-emotional instability, irritation and stress affect the condition of the intestinal tract. In adults, the ulcerative process can be a consequence of prolonged consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Causes of ulcerative colitis
Unfortunately, the causes of ulcerative colitis today remain not fully understood. All that scientists have been able to find out is that the following factors play a major role in the formation of the type of defect under consideration:
- autoimmune process;
- genetic predisposition;
- some infections.
However, these factors are also in question.
Causes of Crohn's disease
The origin of Crohn's disease, as well as ulcerative colitis, is not precisely known. Currently, there are two theories, which do not have scientific confirmation, about the development of pathology. However, thanks to a number of studies, it was possible to determine that there is a high probability that this disease is caused by the following provocateurs:
- heredity. According to the observations of doctors, this type of pathology most often occurs in relatives;
- intestinal infection. Numerous studies have shown that the likelihood of developing this type of pathology increases several times in people who have previously suffered inflammation of the intestines.
Also, provocateurs of Crohn's disease include bad habits, consumption of low-quality and harmful food, and taking certain medications.
Symptoms
If an ulcer has formed in the rectum, the symptoms will not be specific. It is for this reason that specialists are not always able to determine the existing pathology. However, there are still certain symptoms that indicate the development of a defect:
- causeless appearance of watery stools;
- pain during defecation;
- unpleasant feelings disturbing a person in the anus area;
- blood fragments may be observed in the stool;
- at the last stage of pathology progression, purulent discharge and mucus are observed in the stool;
- mostly false urge to go to the toilet;
- feeling of intestines not being completely empty after defecation;
- constipation that occurs regularly;
- decreased hemoglobin;
- burning and severe itching in the anal area;
- redness of the skin around the anus.
If the ulcer formation occurs as a consequence of radiation therapy, the symptoms will be much more serious. In this condition, the patient suffers from pain in the form of contractions, bleeding from the anus and swelling of the mucous membrane are common.
Symptoms of acute proctitis
Acute proctitis develops quickly. Typically, the first symptoms of the disease appear within a few hours or days. In some cases, the body temperature rises, the patient’s well-being worsens, headache and weakness appear, appetite decreases, and sometimes nausea occurs.
The first symptoms of the disease are pain in the rectum and discomfort:
- The pain is sharp, intensifies during defecation, radiates to the perineum and lumbar region, in women - to the labia and vagina, in men - to the penis and scrotum.
- Burning, itching, feeling of heaviness and sensation of a foreign body in the anus.
- Irritation of the mucous membrane leads to the appearance of a false urge to defecate (tenesmus).
- In some cases, mucus, pus, fresh blood or blood in the form of a clot are released from the rectum.
Signs and symptoms of catarrhal proctitis
This form of the disease can occur in isolation or be a complication of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Simple catarrhal (profuse secretion of mucus, hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane).
- Catarrhal-purulent (profuse secretion of mucus, the mucous membrane is hyperemic and covered with purulent plaque or fibrinous films).
- Catarrhal-hemorrhagic (profuse secretion of mucus, the mucous membrane is hyperemic, pinpoint hemorrhages are recorded, sometimes traces of bleeding can be seen).
The disease is highly treatable. The prognosis is favorable.
Rice. 6 and 7. The photo shows inflammation of the rectum.
Signs and symptoms of erosive proctitis
In the erosive form of inflammation, erosions (surface defects) are formed against the background of inflammation of the rectal mucosa, which, with adequate treatment, heal without scarring.
There are many reasons for the development of the disease. With erosive inflammation, in addition to the usual symptoms (see above), bloody or bloody-mucous discharge from the rectum appears, and there may be a gaping of the anus, which occurs as a result of relaxation of the sphincter, from which mucous-bloody masses and liquid feces flow.
Of the complications, the danger is the transition of the erosive form of inflammation to the ulcerative one. During sigmoidoscopy, hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane are visible, on which erosions and, in places, fibrinous-purulent plaque are visible. Erosions can be single or multiple; sometimes a significant surface of the rectum and sigmoid colon is affected (proctosigmoiditis).
The prognosis of the disease with adequate treatment is favorable.
Signs and symptoms of ulcerative proctitis
The ulcerative form is a form of inflammation of the rectum that forms under severe exposure to damaging factors. When the disease occurs, ulcers form on the mucous membrane, healing of which occurs with the formation of scar tissue. The disease is severe with a pronounced clinical picture. Blood, pus and mucus are released in the stool. Scarlet blood is located on the surface of the stool or inside it in the form of clearly visible inclusions. The stool is loose and frequent. In some patients, tenesmus becomes continuous.
Rectal stenosis is a dangerous complication of the disease. With deep damage to the rectal wall, peritonitis may develop. The disease negatively affects the patient’s quality of life, physical and mental state.
Rice. 8 and 9. The photo shows inflammation of the rectum, erosive form.
Diagnostics
Successful therapy largely depends on a correct diagnosis. Therefore, if the pathology in question is suspected, the specialist prescribes a number of diagnostic measures, the purpose of which is to refute or confirm the preliminary diagnosis.
But first, the patient must undergo differentiated diagnostics, the task of which is to exclude other dangerous pathologies, such as:
- malignant neoplasms;
- haemorrhoids;
- proctitis;
- rectal polyposis;
- anal ring fissures.
Important: Differentiated diagnosis of the most common pathologies must be carried out as a mandatory procedure. Since the symptoms of these diseases are in many ways similar to ulcers.
If diagnostic measures have refuted suspicions of one of the above ailments, then we can judge the presence of erosion in the rectal region.
As for a comprehensive examination, it includes the following manipulations:
- examination of the patient;
- collection of biological fluid for biochemical examination and determination of anemia;
- examination of the rectum by palpation;
- examination of stool for blood.
In addition to collecting biological material, to obtain the most detailed data, they resort to the use of some diagnostic techniques:
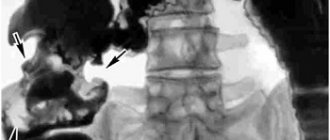
- Sigmoidoscopy. This type of diagnosis involves the use of a portable sigmoidoscope device, a thin flexible tube equipped with an optical mechanism and illumination. A tube is inserted through the anus to examine the rectum;
- Colonoscopy. This method is in many ways similar to the one described above, but it has a slightly different mechanism. The technique under consideration allows for a detailed examination of the intestine and, if an ulcerative defect is detected, to collect material for histological examination;
- Irrigoscopy. This diagnostic method involves the introduction of a special substance into the intestines, with the help of which it is possible to detect the slightest changes in the structure of the mucous membrane, including neoplasms of various origins. The component is administered using an enema.
To diagnose a rectal ulcer, in some cases, a gastroenterologist may prescribe other methods. However, more often they resort to the above.
Differentiated diagnosis and direct diagnosis of ulcers
Before diagnosing an ulcer, it is necessary to undergo a differentiated diagnosis to identify foreign diseases whose symptoms are similar to those of an ulcer. Often differentiated with diseases:
- Various malignant tumors;
- Internal hemorrhoids;
- Proctitis;
- Rectal polyps;
- Anal ring cracks.
Direct diagnosis of ulcers is carried out by research and analysis:
- Objective examination, verification by a doctor of the indicated symptoms:
- Mucus and blood in the stool;
- Paleness of the skin.
- Analysis of the patient's medical history, complaints: how long ago, when pain appeared, during or after defecation, whether the stool contained mucus or blood, whether there was constipation, tenesmus, with what circumstances or diseases the patient associates the pain;
- Analysis of family and relatives for diseases associated with the rectum;
- Analysis of the patient’s living conditions, what diseases of the gastrointestinal tract he suffered from, working conditions, diet and nutrition, lifestyle;
- Laboratory research and information collection:
- A blood test for biochemical testing is necessary to determine whether the body suffers from other diseases that accompany the ulcer;
- A general blood test reveals anemia in the setting of blood loss;
- Examination of the intestine using a finger. Passes by inserting the doctor’s finger into the lower part of the patient’s rectum, which is subsequently examined for neoplasms and wounds;
- Stool blood test. Using a microscope, the doctor examines the stool to identify blood elements. If found, it is assumed that there is a lesion in the intestine causing bleeding, possibly an ulcer;
- Sigmoidoscopy. The procedure is carried out using special equipment called a sigmoidoscope. The device looks like a pipe with illumination and an optical mechanism, with a flexible structure. The device is inserted into the lower part of the intestine through the anus, giving the doctor a chance to identify various deviations from the norm, unfavorable growths, wounds, etc.;
- Colonoscopy. Almost sigmoidoscopy, only the entire intestine is subject to examination. If an ulcer is detected, the doctor is able to immediately obtain a tissue sample for subsequent histological analysis, to examine this sample under a microscope;
- Irrigoscopy. Examination of the intestines using a substance that allows you to clearly and accurately detect various formations. The substance is administered through an enema.
Treatment methods
Treatment of rectal ulcers consists of a complex of therapeutic measures. In this case, the choice of one method or another directly depends on the severity of the pathology. In general, to eliminate the consequences and the root cause, a number of treatment methods are prescribed, consisting of the following:
- behavioral therapy;
- drug treatment;
- surgical intervention;
- auxiliary traditional medicine;
- lifestyle changes and diet.
Symptoms and treatment of rectal ulcers, main causes of the disease, diagnosis
One of the rare but dangerous diseases is a rectal ulcer. Such a pathology can manifest itself at absolutely any age; there are also no gender differences. The ulcer is accompanied by quite painful sensations, since the intestinal walls have a number of nerve endings.
An ulcer can cause the development of serious complications: severe inflammatory processes, severe disruption of the functionality of the digestive system. In addition, in the absence of existence, there is a threat not only to health, but also to life. In this regard, it is necessary to understand what a rectal ulcer is, its symptoms, and treatment of the pathology.
What is pathology and causes of development
An alternative name for this disease is ulcerative proctitis; such a diagnosis is made quite rarely. An ulcer is a pronounced violation of the integrity of the membranes of the rectum, varying in the degree of damage and the number of affected areas. In ICD 10, an ulcer of this part of the intestine has its own code K62.6.
Proctitis is extremely rare; as a rule, ulcerative pathologies are divided into three main subtypes:
- Crohn's syndrome,
- Ulcerative colitis is the most common disease that is easily treatable,
- solitary type of ulcer - a chronic form of pathologies associated with the intestines, which can affect the rectum and large part of the organ.
The therapeutic course for proctitis largely depends on the cause that provoked the development of the pathology. Today, there are a number of factors influencing the development of ulcers:
- genetic predisposition to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract,
- infectious pathologies affecting the intestines,
- radiation, chemotherapy,
- unhealthy diet, lack of proper eating habits,
- psycho-emotional stress,
- chronic or erosive gastritis,
- long-term use of strong medications.
- intense pain during defecation is the primary symptom of the pathology,
- unpleasant sensations are located not only in the abdominal cavity, but also in the anus,
- manifestation of false urge to evacuate,
- bleeding from the anus, or the appearance of blood streaks in the stool.
Peptic ulcer
In addition, such a diagnosis may be a consequence of radiation therapy. Root causes are a prerequisite for successful therapy.
Important! The solitary type of the disease is the most common and requires competent and timely therapy.
Symptoms of the disease
Most often, an ulcer occurs in the stomach as a result of gastritis or poor-quality surgery. However, there are cases when a disorder occurs in the intestines; if the pathological process is localized in the rectum, then the following characteristic symptoms may appear:
A pathological symptom that occurs with the progression of the disease is chronic constipation. In addition, over time, pus and mucus may be observed in the stool, which indicates the development of an infection.
Diagnostic procedures
Making a diagnosis is always a painstaking process, requiring diagnostic testing in most cases. In the case of an ulcer, at the first stage, the doctor must identify the symptoms and medical history. Only after analyzing the information provided, the specialist prescribes the procedures.
Instrumental diagnostics for any type of ulcer is a prerequisite for therapy. Currently actively used:
- anoscopy,
- colonoscopy,
- irrigoscopy,
- recomanoscopy.
Colonoscopy
As additional measures, a general and biochemical analysis of blood, urine, and stool may be prescribed.
How to treat an ulcer
The treatment complex against ulcers is complex, systemic in nature. A narrowly targeted effect has an unexpressed effect. Modern therapy may include: taking medications, performing surgery, using unconventional techniques.
The duration of treatment, the number of directions included, and the list of medications are prescribed only by the attending physician. Otherwise, the effect may not be achieved, therefore, the pathology will progress.
Important! Self-medication for ulcers is harmful to your overall health and can cause complications.
Drug therapy
Conservative treatment relies on taking medications and normalizing the diet. Laxatives are used as medications for proctitis to prevent the development of chronic constipation.
- Bisacodyl is an effective drug used in the treatment of ulcers. Main contraindications: pregnancy, allergic reactions to the components included in the composition.
- Glycerin suppositories are a safe medication that can be used both during pregnancy and lactation. A candle containing glycerin is one of the effective, but at the same time gentle, remedies.
Medicines for ulcers
If the disease is detected late and inflammation has begun, the doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics.
Traditional treatment of pathology
A special place in modern therapy is occupied by a non-traditional form of influence. The traditional type of treatment is effective and has a narrow list of contraindications and undesirable effects.
To treat ulcers localized in the rectum, mumiyo, potatoes, honey, and various herbal infusions are actively used.
Traditional therapy for ulcers
Note! Before including such methods in the course of treatment, you must obtain your doctor's permission.
Ulcer recovery prognosis
If the treatment was timely and comprehensive, then the chance of a complete recovery is quite high. However, there are several rules that can reduce the risk of relapse of the pathology. Ignoring such recommendations may lead to the formation of new ulcers. In this regard, a person with a history of proctitis should take a more responsible approach to their health.
Preventive measures
In some cases, ulcers are quite difficult to treat, so gastroenterologists have identified a number of recommendations for secondary and primary prevention.
- Proper nutrition, that is, including healthy foods in the diet, excluding unhealthy, fatty and fried foods.
- Normalization of water and electrolyte balance. Reducing the risk of vitamin deficiency by taking multivitamins.
- The diet doesn't have to be strict. The main rule is moderation.
- Regular preventive medical examinations.
- Timely treatment of any kind of disease.
An ulcer affecting the rectum is a rare pathology that requires proper therapeutic intervention. Ignoring symptoms can lead to the development of adverse complications.
Loading…
Source: https://MedBoli.ru/gemorroj/drugie-zabolevaniya/simptomy-i-lechenie-yazvy-pryamoj-kishki-osnovnye-prichiny-zabolevaniya-diagnostika
Behavioral therapy
The goal of this type of treatment is to stop the bowel from straining as it moves. The fact is that some patients habitually strain during bowel movements due to psychological problems. However, such a condition only contributes to the progression of the disease.
A visit to a psychologist will allow the patient to learn to control the body’s involuntary reactions. In addition, the patient will learn to relax the muscle mass of the pelvic area at the time of bowel movement.
Drug treatment
This type of treatment includes the use of a number of medications:
- topical preparations are indicated to stimulate cell growth;
- It is necessary to carry out therapeutic enemas with solutions that cover the ulcerative formation and thereby create a protective barrier from irritants. Such remedies will allow the erosive formation to heal faster;
- corticosteroids. This type of medication is also used for enemas. The main task of such drugs is to ensure rapid healing of the defect.
Important: Regardless of the severity of the pathology, at first the patient must undergo treatment in a hospital setting and follow a strict diet.
In addition, drug therapy includes laxatives, with the help of which the patient will get rid of constipation. It is important to remember that only a qualified doctor should prescribe medications and treat. Independent use of rectal suppositories that have a laxative effect may worsen the condition.
Treatment
How and with what to treat a rectal ulcer? Methods to combat this disease depend on the severity of the pathological process.
Conservative therapy should begin, first of all, with lifestyle changes, increasing healthy fiber in the daily diet, and eliminating salty, fried and peppered foods.
Behavioral therapy is widely used for this disease to stop straining during bowel movements. Some people tense up during bowel movements out of habit or due to certain psychological problems. Treatment by a psychologist using behavioral therapy methods helps a person learn to relax the muscles of the pelvic region during bowel movements.
In one method, called biofeedback , the doctor teaches the patient to consciously control certain involuntary reactions of the body, such as the strong retraction of the muscles of the anus or pelvic floor during a bowel movement.
Medication
Conservative therapy may include topical application of drugs (fibrin) to stimulate cell growth.
A sucralfate enema contains aluminum complex salts that coat the ulcer in the distal intestine and form a barrier against irritants, allowing the ulcer to heal. Corticosteroids and sulfasalazine enemas can also help the ulcer heal by reducing the inflammatory response.
Sulfasalazine enemas may help ulcer healing
Therapy includes laxatives to prevent chronic constipation. Treatment must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-administration of laxatives, suppositories and enemas may worsen clinical symptoms.
Operational
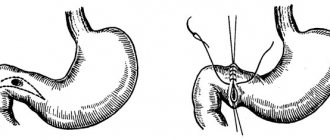
Surgical treatment may include suturing ulcerated areas or removing ulcerated areas of the distal bowel.
If rectal prolapse occurs, part of the intestinal mucosa that has become necrotic can be removed (prolapse) or repaired.
In severe cases, the patient may have the entire section of intestine with the ulcer removed. For some patients who undergo surgery, a temporary or permanent opening (stomy) may need to be surgically created to allow bowel movements (colostomy).
Folk
Treatment of rectal ulcers with folk remedies involves the use of various herbal remedies.
Herbs that help heal ulcers:
- Comfrey.
- Tansy.
- Calendula.
- Strawberries.
- Yarrow
Herbs to reduce pain and swelling of the intestines:
- Kalgan.
- Angelica.
- Celandine.
- Oregano.
- Hop.
It is best to purchase herbs for treatment in pharmacies, where they have passed sanitary and radiological control, and not to collect them yourself.
You need to take 3-5 types of herbs from each group and mix them together. Then pour one tablespoon of the resulting mixture into 2 glasses of cold water, bring to a boil and simmer over low heat for 8-10 minutes , then cool. After the decoction has been infused for 1-1.5 hours , it can be taken ½ glass 30 minutes before meals and before bed. The medication can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 3 days .
Herbal medicine for this disease should be used with extreme caution in patients who have allergic diseases.
Auxiliary folk methods
First of all, folk remedies can be used as auxiliary methods. Before using decoctions or infusions, you should consult a gastroenterologist. It is important to understand that ulcer formation is considered a dangerous pathology that can lead to death. Therefore, self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Currently, there are many plants that can alleviate negative symptoms and speed up the healing process of erosion. But the following are considered the most effective:
- tansy and calendula;
- yarrow;
- strawberry leaves.
Also, for ulcer formation, herbs are used that have an anti-edematous effect and relieve pain:
- galangal;
- oregano and hops;
- celandine;
- hop.
It is better to purchase herbs in pharmacies. In addition, gastric preparations have proven themselves to be effective.
As for the method of application, dosage and frequency, it is better to discuss these points with your doctor.
Folk remedies
By combining a diet with traditional methods of treatment, an ulcer can not only be slightly treated, but also get rid of it altogether. However, you should not expect a quick effect, but there will be practically no side effects. Before using traditional methods, you should find out the names of herbs that promote wound healing and also relieve swelling.
Pain-relieving and swelling-healing herbs:
- Linden;
- celandine;
- oregano;
- chamomile;
- thyme;
- hop;
- willow.
Wound healing plants:
- strawberries;
- calamus;
- yarrow;
- comfrey;
- plantain;
- tansy;
- aloe;
- needles;
- blackberry:
- St. John's wort;
- nettle;
- eucalyptus;
- series.
To treat an ulcer, you need to take 5 herbs from the above lists. The complete collection should weigh approximately 500 grams. The herbs need to be chopped and mixed. They should be stored in a well-closed jar. The mixture is brewed every day and taken fresh.
Daily dosage – 1 tbsp/l of collection. Fill with water (400 milligrams), boil in a water bath for about 15 minutes. Next, the broth is filtered and cooled for at least an hour. A tablespoon of honey, the same dose of propolis and plantain or St. John's wort juice are added to the resulting liquid. Take the medicinal mixture one hundred milligrams three times a day thirty minutes before meals. The rest should be drunk before bed. Course – 45 days.
Diet
Diet for rectal ulcers must be followed without fail. Moreover, any therapeutic measures should begin with lifestyle changes:
- introducing foods rich in fiber into the diet;
- exclusion of salty, fatty and fried foods;
- rich smoked broths;
- marinades, fatty meats and fish;
- spices, chocolate, citrus fruits, mushrooms and other products that hold the stool together.
Ulcer sufferers should pay special attention to nutrition. A correct and healthy menu will help you fight the disease more effectively.
Symptoms
Discomfort and pain in the anus are signs of a rectal ulcer
Symptoms of the disease:
- Loose stools for no reason (the earliest sign).
- Pain during bowel movements.
- False urge to defecate.
- Discharge of drops of blood from the anus after defecation.
- Discomfort and pain in the anal area.
Persons with ulcerative lesions of the distal intestine usually complain of blood discharge from the anus, which is a hallmark of this pathological condition. In addition, there is mucus discharge, pain and cramps in the abdomen, pain and tension when passing even a small amount of feces (tenesmus), constipation, diarrhea and painful spasms of the anus.
The patient may also complain to the doctor about the sensation of intestines not being completely emptied. The pain is often localized around the anus (perineum) or lower back (sacral area) and is usually described as aching, continuous, constant, or not associated with bowel movements.
Preventive actions
You can reduce the likelihood of developing an ulcer by following a few simple rules:
- The diet should not include harmful foods;
- Coffee lovers are advised to reduce the amount of coffee they drink, this also applies to soda;
- if a person suffers from frequent constipation, you should consult a doctor about preventing constipation;
- following a diet should be mandatory for persons diagnosed with an ulcer;
- At the first symptom of the pathology in question, you should immediately consult a doctor.
And in conclusion, we note that timely steps taken when negative symptoms appear will help you live for many years. Therefore, you should never ignore the first alarm bells that your body gives.