Characteristics of the pathology
Any pathological process in the pancreas, accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the organ, usually occurs gradually. In case of an infectious lesion, the healthy epithelium of the organ dies and is replaced by a fatty layer. The process of structural changes does not have retroactive effect. Diffuse liver changes such as lipomatosis can be blocked at the treatment stage.
Lipoma is a benign process that affects the tissue of the pancreas. A single formation or multiple accumulation of neoplasms can be characterized by serious disruptions in the functioning of the organ. The disease is often associated with hormonal imbalance in the body. Lipomatosis can occur in three forms - nodular, diffuse and diffuse-nodular.
Fibrolipomatosis of the pancreas is a fatty degeneration of the organ with an uneven distribution of connective tissue. Fibrolipoma occurs in the form of the formation of nodules with compactions of various shapes and sizes. Lipofibromatosis is characterized by a predominance of the fat layer over the connective epithelium.
Pancreatic lipomatosis
Lack of treatment is dangerous due to deep germination of atypical neoplasms into the organ, which causes serious complications in the patient’s health.
The ICD-10 pathology code is K86 “Other diseases of the pancreas.”
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound.
Ultrasound diagnostics is aimed at assessing several parameters of the pancreas:
- current size and shape of the organ;
- location in the abdominal cavity;
- echogenicity (degree of homogeneity and structure of pancreatic tissue).
Fibrolipomatosis is a constant companion of pancreatitis. It can accompany a person all his life, practically without bothering him, reminding him of himself with infrequent exacerbations. For this reason, the disease progresses very slowly. Unfortunately, even modern medicine cannot always detect fibrolipomatosis in a sick person in a timely manner.
It will be very good if the doctor notices on an ultrasound that the patient has increased echogenicity, which occurs against the background of impaired metabolism or inflammation of the pancreas. Also, the presence of this pathology is indicated by organ obesity.
Causes of the disease
An atypical cell in the epithelium of the pancreas during development affects healthy tissue and causes pathological disturbances in the functioning of the organ. Doctors do not name the exact reason why cell replacement may occur.
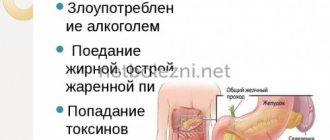
The disease can be triggered by existing chronic pathology or poor diet and alcohol abuse. Hereditary predisposition plays a major role. If someone has a history of pancreatic disease in their family, the risk of developing lipoma increases.
Doctors identify the following factors that can cause the disease:
- presence of excess body weight;
- there is a confirmed diagnosis of pancreatitis or another disease of the digestive system - lipomatosis in this case is a severe form of complication;
- alcohol and smoking abuse;
- viral pathology occurring in the pancreas;
- metabolic disorders;
- pathology of an endocrine nature - diabetes mellitus;
- people over 70 years of age experience natural tissue degeneration;
- oncological disease of the respiratory system;
- unbalanced diet – there is a deficiency of vitamins;
- unfavorable ecology of the area of residence.
Lipomatosis can be provoked by one existing factor or several at once. Depends on the physical indicators of the body and other related reasons. The disease requires urgent medical attention. Therefore, you should carefully monitor your health and well-being.
Principles of fibrosis treatment
Treatment of pancreatic fibrosis involves a whole range of measures:
- Dietary food - table No. 5 is prescribed, the patient's diet includes foods that stimulate the production of pancreatic digestive enzymes, which are a source of protein. Simple carbohydrates (sugar, sweets, sweet fruits) are prohibited. When the body is exhausted, nutrition (special emulsions) is administered using droppers.
- Etiotropic therapy - allows you to eliminate the cause of fibrosis. If this is cholelithiasis, then the patient undergoes cholecystectomy. For papillostenosis (pathology of the major papilla of the duodenum, through which digestive enzymes and bile penetrate into the intestine), surgical treatment is indicated.
- Taking enzyme preparations (Pancreatin, Panzinorm, Panzistal, Lipase) is necessary to compensate for exocrine insufficiency of the gland. If complete fibrosis of the pancreatic parenchyma has occurred, then enzymes are prescribed in maximum doses constantly. Indicators of the effectiveness of taking enzymes: normalization of a person’s weight, disappearance of symptoms of indigestion.
- Correction of carbohydrate metabolism - carbohydrate metabolism in the body is restored with oral hypoglycemic agents (Metformin, Nateglinide, Repaglinide).
- Surgical intervention is indicated for constant pain in the area where the pancreas is located, a rapid decrease in the patient’s body weight, and frequent exacerbation of pancreatitis. Resection of the gland is performed. The extent of the surgical operation depends on the extent of organ damage.
After the symptoms of exacerbation are relieved, the patient is recommended sanatorium-resort treatment, with the help of which it is possible to slow down the fibrosis of pancreatic tissue.
Signs of the disease
At the initial stage, the pathology occurs secretly - there are no manifestations. The first symptoms appear in the second stage of the disease. The person clearly shows suspicious signs that affect the general well-being and digestive processes. A product that is not perceived by the diseased organ, taken orally, causes severe vomiting. Also, the presence of foreign seals on the body indicates the presence of a disease.
The pathology is characterized by the following signs:
- attacks of nausea while eating;
- increased gas formation in the small intestine;
- pain in the stomach area, moving to the chest or hypochondrium;
- belching after every meal.
With further progression of the disease, more serious symptoms appear:
- gagging after eating;
- severe painful spasms of a constant nature;
- pain during urination;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract - constipation or diarrhea;
- decrease in skin turgor and moisture;
- increased appetite, which leads to excess weight.
The disease often occurs with the active development of type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus. Fatty pancreas causes insulin deficiency, which leads to the disease.
The symptoms present in lipomatosis resemble the development of pancreatitis, which sometimes makes diagnosis difficult. The pathology is easily diagnosed at the initial stage, so doctors recommend undergoing annual scheduled examinations at the clinic. If you have the first suspicious symptoms, you should immediately contact your doctor and get tested - this will allow you to start treatment early and increase the chances of a full recovery.
Pancreas damaged by lipomatosis
Clinical course of the pathology
The clinical picture of the disease directly depends on the extent of organ damage, that is, on the stage of development of the pathology.
| Stages of development | Characteristic symptoms | Possible complications |
| Stage 1, in which no more than 30% of the pancreatic tissue is changed. | The pathology at this stage of development is often asymptomatic; the patient may feel only minor discomfort and heaviness after eating. In most cases, pathology is detected during a comprehensive examination. | In the absence of treatment, the pathological processes of replacement of pancreatic tissue continue, the disease enters the 2nd stage of its development. There are no other complications at this stage. |
| Stage 2, in which 30-60% of the organ tissue is damaged. | There are symptoms such as:
| At this stage of pathology development, various complications may occur. For example, if fatty tissues occupy large areas of the organ, the patient's body may not accept food entering the stomach. This only applies to heavy meals (for example, spicy, fatty, fried foods). As a result, a person experiences a significant deterioration in health, vomiting, and weakness after a meal. |
| Stage 3, characterized by almost complete replacement of organ tissue. | At this stage, the clinical manifestations of the pathology become more and more pronounced, symptoms such as:
| The main and most dangerous complication is the threat of dehydration, which, in the absence of proper treatment, can even lead to death. With the development of stage 3 lipomatosis, not only the digestive system, but also the endocrine system is affected. All this leads to a sharp deterioration in health and well-being. |
Stages of pathology development
Lipomatosis occurs in three stages, which are characterized by certain symptoms:
- At the first stage, the level of atypical cells is within 30%. The fat layer occupies a small area of the organ, which is characterized by the presence of mild symptoms. In some cases, the disease may be asymptomatic at this stage. Mostly there are mild sensations of discomfort in the stomach area.
- At the second stage, the fat layer increases to 50%, i.e. The pancreas is half occupied by atypical tissue. Neoplasms grow inside the organ, which is accompanied by painful sensations that intensify during or after eating. No serious violations in the activities of the body are recorded at this stage.
- The third stage of the disease is characterized by the active progression of the spread of the fat layer to 60-70%. Here, pronounced symptoms of pathology are observed - painful spasms, diarrhea or constipation and bouts of vomiting. There are serious disturbances in the functioning of the organ.
Modern advances in medicine make it possible to identify the disease at the initial stage of its formation, so doctors advise not to postpone a visit to the clinic when the first suspicious symptoms appear. Early initiation of treatment guarantees recovery without complications.
Degree of development of lipomatosis
The mildest degree of the disease is the first . With it, fat cells are single, which does not affect the functioning of the pancreas or the well-being of the patient. Most often, he learns about his disease by chance, when he undergoes an examination, for example, an echography of the abdominal organs.
The second degree is much more serious. Here, lipomas replace 30 to 60 percent of the total volume of the organ, which, naturally, cannot but affect the pancreas. Due to a decrease in the production of enzymes, the patient begins to have serious digestive problems: dyspepsia, bloating, flatulence, nausea (especially after eating), belching with an unpleasant odor, and abdominal pain.
Troubles, as they say, intensify when the third degree of the disease is noted: overcoming the “threshold” of 60 percent, when wen, like raiders, captures more than two | third of the organ. As the disease progresses, endocrine disorders join dyspeptic symptoms.
Abdominal pain becomes constant, diarrhea becomes more frequent, which can alternate with constipation, vomiting often occurs, appetite increases, and the feeling of thirst increases. As adipose tissue grows, it compresses the organ and nearby tissues, which leads to poor circulation. With a deficiency of insulin, diabetes mellitus develops.
However, before moving on to treatment, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis, and for this it is necessary to take tests and undergo examinations.
Diagnosis of the disease
Before choosing a therapy method, it is necessary to undergo a detailed examination of the body in order to make a diagnosis and identify concomitant chronic pathologies. Diagnostics includes the following activities:
- The doctor conducts a physical examination of the patient to look for external signs of illness. A medical history is collected.
- An ultrasound examination of the pancreas and abdominal organs is prescribed. Ultrasound allows you to identify neoplasms on the walls of the organ and assess the degree of damage to the body.
- A puncture is prescribed to collect biological material in order to conduct a biopsy to determine the structural composition of the tumor. The procedure allows you to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
- Computed tomography (CT) is more informative and able to examine the organ structurally. A CT scan can determine the degree of growth of atypical tissue into the depths of the pancreatic epithelium.
- Blood and urine must be submitted for a general analysis of the main elements. Deviation from the norm will show the level of disturbance in the functioning of the organ.
After receiving all the test results, the doctor can assess the patient’s condition and choose the direction of therapy.
Types of pancreatic lipomatosis
Lipomatosis is classified according to the stage of damage to the pancreas. At grade 1, up to 30% of the organ is occupied by adipose tissue, while no major changes in the functionality of the pancreas occur, symptoms are either completely absent or not expressed. With grade 2 lipomatosis, adipose tissue occupies up to 60% of the gland's volume. In this case, there are already clinical signs of the disease, the functionality of the organ is slightly impaired, but the risk of exacerbation is high. In the 3rd degree, over 60% of the pancreas is replaced by adipose tissue, gland insufficiency occurs, metabolism is complexly disturbed, and lipoidosis occurs (disorder of fat metabolism).
Lipomatosis is also classified into:
- diffuse;
- focal (local).
In the first case, adipose tissue is distributed evenly throughout the gland, often increasing in volume. When focal, lipomas appear, that is, fatty tumors with clear boundaries that literally grow through the pancreas (and tend to increase over time).
Treatment of pathology
The choice of treatment method depends on the degree of damage to the body, the age and well-being of the patient. The disease cannot be completely cured due to a structural disorder of the tissue layer of the pancreas. The actions of doctors are aimed at restoring the functioning of the organ. To do this, they resort to methods of conservative therapy:
- The patient is prescribed a special diet that will reduce the load on the pancreas and other organs of the digestive tract. It will also help reduce weight and alleviate the patient’s condition.
- Painful spasms can be relieved with medications based on painkillers - No-shpa, Baralgin or Spazmalgon.
- Fermenting drugs that improve the functioning of the digestive system are prescribed - Pancreatin or Creon. The products relieve unnecessary stress and alleviate the patient’s condition.
- Treatment of the pathology requires completely quitting smoking and drinking alcohol.
- You can stop attacks of nausea and vomiting with Loperamide or Domperidone.
Conservative treatment is used in the first and second stages of the disease. At the third stage, drug therapy does not have a positive effect, since there are serious disturbances in the structure of the pancreas, which lead to complete dysfunction of the organ.
At the last stage of the disease, surgical intervention to remove the pancreas is required. During the operation, the ducts of the organ are also removed. The process of replacing healthy tissue with fat is irreversible. During the last stage, atypical cells penetrate inside the pancreas, causing severe complications. New methods are required for the functioning of the digestive tract.
After surgical removal, the patient requires a rehabilitation course, including diet and lack of exercise. After a course of therapy, you need to follow all the recommendations of your doctor - this will speed up the recovery process.
Signs and symptoms
Lipomatosis, like any disease, conditionally develops in several stages. Depending on the degree of pathology, specific symptoms appear:
- First stage. At this step, partial replacement of organ cells with adipose tissue occurs, up to 30%. At the same time, the healthy part of the organ is quite capable of functioning at 100%. As a result, the sick person is not even aware of his problem. Lipomatosis at this stage is detected, as a rule, by chance, with ultrasound or x-ray. It is clear that the pancreas has not changed in size, only its structure has changed. In some cases, the patient has symptoms of the third degree of damage, but this occurs when fat cells have captured the tissue near the excretory ducts.
- Second stage. This stage of the development of pancreatic lipomatosis is characterized by classic symptoms of disruption of the digestive system. The patient experiences problems with bowel movements, he is often bothered by diarrhea, belching, heartburn, heaviness in the abdomen, especially after eating. A sick person begins to feel something is wrong and seeks help from a doctor. Unfortunately, other people suppress the symptoms with medications and are not aware that the disease is gradually moving into the last phase.
- Third stage. At this stage of development of the disease, pancreatic lipomatosis has already managed to capture more than 60% of healthy cells. The pancreas is simply not able to cope with such an attack of fat mass. At the same time, the pancreas also remains within the “healthy” size. At this stage, a person feels constant weakness, he is tormented by nausea and vomiting after each meal, as well as girdle pain in the abdominal area.
In addition, some patients complain of ulcers of the oral mucosa, general weakness, dizziness, and loss of appetite. Of course, any of the above symptoms could mean a common stomach upset or other illness. However, if the painful condition does not go away within a few days, it is best to seek help from a doctor. An accurate diagnosis can only be made by a specialist after a complete examination.
Lipomatosis is an irreversible phenomenon, that is, it is unfortunately impossible to return fat cells to their primary purpose. It is for this reason that doctors advise conducting a complete examination of the body at least once every year or two. This is especially true for obese older people who are at risk, and close attention should be paid to the gland. As mentioned above, the first stage of the disease is asymptomatic, therefore, health monitoring is necessary.
Treatment with alternative medicine
Treatment with folk remedies is allowed after consultation with your doctor. It is worth combining the methods with conservative therapy methods. Medicinal herbs stimulate the natural production of pancreatic enzymes necessary to normalize the digestive process. The healing properties of herbs remove toxins from the body and improve the functioning of the stomach and intestines.
Nettle, yarrow, plantain, St. John's wort, rose hips, valerian, immortelle and calendula are used as infusions and decoctions. Herbs (1 tbsp) are poured with boiling water (500 ml) and placed in a water bath. You need to keep it for 15 minutes. After this, remove from heat and cool. Drink 100 ml 3 times a day before meals. The course of treatment is 21 days.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
Fibrofatty degeneration of the pancreas cannot be determined with the naked eye during a routine objective examination of the patient. Diagnosis is especially difficult at an early stage, when there are no symptoms of the disease. That is why it is necessary to conduct a whole range of studies and analyzes in order to promptly identify the process while the treatment is still effective.
Laboratory
Each patient who consults a gastroenterologist must undergo a mandatory list of laboratory tests, namely:
- clinical blood test;
- blood glucose level;
- biochemical analysis with determination of the levels of enzymes, bilirubin and total protein fractions;
- coprogram for detecting free fat in feces.
This minimum range of tests must be done 2-3 times a year. To monitor cystic fibrosis, you should take a stool test once every 2 months.
Blood tests
Functional
The most accessible and safe diagnostic method is ultrasound. The structure of the pancreas changes diffusely and, if fibrosis predominates, has increased echogenicity. If adipose tissue grows to a greater extent in the gland, then the echogenicity of the reflected ultrasound signal is reduced, which is characteristic of lipomatosis. Fibrous nodes and cysts of the pancreatic glands are clearly visualized on the ultrasound screen.
Ultrasound of the abdomen
With cystic fibrosis, the doctor can record an increase in the size of the gland, dilated and cystic changes in the excretory ducts. With a total change in the gland, it can all be filled with liquid round formations. At the same time, the liver is examined; as a rule, it increases in size.
Important! If multiple cysts are detected, the specialist will prescribe a sweat test to determine sodium and chlorine ions in sweat. An increase in the level of these microelements in sweat reliably indicates cystic fibrosis.
To exclude gastritis or ulcerative lesions of the gastric and duodenal mucosa, esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy is performed.
If the gland cannot be clearly visualized on ultrasound, then an MRI is performed. This is an expensive but highly informative method that provides comprehensive information regarding the location and structure of the pancreas and surrounding tissues. Magnetic resonance imaging is contraindicated during pregnancy, the presence of heart rate drivers, metal bodies or implants in the body.
CT allows you to obtain layer-by-layer sections of any organ. In this case, the patient is exposed to x-ray radiation, so the study must be carried out strictly according to indications.
As a differential diagnosis with oncological neoplasms, a biopsy of the gland is performed under the control of an ultrasound sensor. The results of histological examination play a key role in choosing treatment tactics.
Diet during and after treatment
During and after therapeutic manipulations, the patient is required to strictly follow a diet. Once the pancreas is removed, the diet is set for the rest of your life. Nutrition is selected individually for each patient - it depends on the degree of damage to the body and the general well-being of the patient.
If lipomatosis is diagnosed, it is prohibited to consume fatty and pickled foods, canned and smoked products. Dishes prepared with mushrooms should be excluded from the diet - this can provoke a deterioration in the patient. You cannot drink alcoholic beverages. It is also recommended to exclude sweet pastries.
The diet should consist of the following products:
- meat allowed is chicken, turkey, rabbit and young lamb or veal;
- fruits and vegetables, steamed or boiled;
- Use yesterday's bread and slightly dried;
- fermented milk products should be low in fat;
- porridges are cooked in water;
- eggs can only be consumed boiled;
- It is recommended to add vegetable oil to every dish.
All products are steamed or boiled, and can be baked in the oven or grilled. Food consumption should be divided into 6 meals per day. You can eat up to 300 g of food at a time.
List of permitted and prohibited products
With the development of diseases of the digestive system, it should be understood that nutrition will depend on the foods allowed and prohibited for consumption.
List of allowed products for pancreatic lipomatosis:
- dietary meats - chicken, turkey, rabbit, beef;
- low-fat fish varieties - cod, pike, pike perch, bream, pollock;
- low-fat dairy and fermented milk products;
- cereals – buckwheat, barley, rice, oatmeal;
- durum wheat vermicelli;
- soft-boiled eggs (chicken, quail), steam omelettes;
- jelly, herbal tea, dried fruit compote.
Alcoholic drinks, smoked meats, pickles, hot spices, beans, mushrooms, cabbage, baked goods and flour products should be excluded from the diet. It is forbidden to consume fatty broths, fish, and meat. This contributes to the treatment of pathology.
Reduce your intake of sweets or completely avoid them.
Contraindications: sweet carbonated drinks, any “street” food.
Disease prognosis
The prognosis for life expectancy depends on the degree of damage to the body and compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. Following a diet and quitting alcohol and smoking increases the chances of recovery and restoration of organ function. If simple rules are followed, healthy tissues will continue to produce the necessary hormones with enzymes for food digestion and metabolism.
Refusal of the doctor's recommendations can cause severe damage to the tissues of the stomach, liver and intestines. Repeated intoxication of the body with serious consequences is possible.
Pathology of the pancreas is incurable and develops slowly. It will not be possible to completely cure the patient, but it is possible to block further growth of atypical cells and normalize the functioning of the organ. This requires taking prescribed medications and eating right.
Treatment regimen
Therapy for pancreatic lipomatosis is complex. There are 3 types of therapeutic measures, such as:
- Changing diet and lifestyle correction;
- Drug treatment aimed at eliminating the causes and manifestations of pathology;
- A surgical operation, which is prescribed when an advanced form of the disease develops, when more than 60% of the organ is damaged, and conservative methods of therapy do not give the expected result.
Correction of diet and lifestyle
To eliminate the manifestations of pathology and normalize the functioning of the pancreas, it is necessary:
- Stop drinking alcohol;
- Adhere to the rules of fractional nutrition (5-6 meals in small portions);
- Eliminate foods that are difficult to digest from your diet. These are, for example, spicy and fried foods, pickles, foods rich in fat;
- Eating low-calorie foods.
Drug treatment
Depending on the symptoms present, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
- Painkillers;
- Drugs that facilitate the process of digesting food;
- Antidiarrheals;
- Medicines to relieve nausea;
- Antispasmodics.
Expert opinion
Shoshorin Yuri
General practitioner, site expert
These medications should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor, strictly following the recommended dosage and duration of treatment. Otherwise, there is a high risk of developing side effects that only worsen the course of the disease.
Surgery
With the rapid development of pathology, large-scale damage to the organ, surgery is necessary. Depending on the size and location, the degree of its fusion with the tissues of the organ, the following methods of removing adipose tissue are used:
- Husking, when the fatty tumor is carefully separated from the healthy tissue of the organ. This method is less invasive and has a more favorable prognosis for healing;
- Pancreatic resection. This method is used when the tumor is firmly fused with the organs. During the operation, the doctor removes not only pathological fatty tissue, but also partially pancreatic tissue. This operation is considered more complex and requires a longer recovery period.
Prevention
Pancreatic lipomatosis is quite difficult to treat. Often the patient has to constantly adhere to a diet, a special lifestyle and take medications. Therefore, if there are risk factors for the development of this pathology, it is better to take measures to prevent it. They are simple and will help maintain the health of all organs, not just the pancreas. This means giving up bad habits, eliminating fatty and fried foods from the diet, and controlling your weight. If you have any pathologies of the digestive organs, you must be examined in a timely manner and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Despite the fact that lipomatosis develops very slowly and does not cause any trouble at first, you need to start treating it as early as possible. After all, this disease is constantly progressing, albeit slowly. Without treatment, this process can lead to serious consequences.
Treatment
Treatment of glandular lipomatosis is carried out conservatively or surgically. If the tumor does not exceed 3 cm in size, it is treated conservatively. Otherwise, they resort to surgical intervention. In many cases, Diprospan
, a drug that is injected directly into a patient's pancreatic tumor.
Important! Regarding surgical tactics for treating lipomatosis, laser exposure or endoscopy of the gland is used. However, such treatment does not always provide complete recovery, since small lipomas remain after the operation. Under unfavorable factors, they can be activated and lead to irreversible consequences in the gland.
To relieve unpleasant symptoms, the patient is prescribed:
- painkillers for the gland - No-shpa
,
Ibuprofen
,
Nemesil
,
Advil, Solpaflex; - improve the digestive process Pancreatin
,
Creon
,
Penzital
,
Mezim
; - antiemetic drugs - Reglan
,
Emetizan
,
Nauzifar
; - to restore stool, Imodium
,
Enterol
,
Loperamide
.