Is FGDS done during pregnancy?
Pregnancy is a crucial time in a woman’s life. During this period, you are supposed to take care not only of your own health, but also of your future baby. Difficulties with the stomach are common, and a medical examination is carried out to determine the cause of the disease. Expectant mothers are concerned about the safety of diagnosis using fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
An FGDS examination is indicated if the diagnosis cannot be established by other methods. The procedure is harmless, does not affect the fetus, and is prescribed for serious reasons.
The study using fibrogastroduodenoscopy makes it possible to study:
- Stomach condition.
- Mucous membrane.
- Intestines.
It is recommended to do gastroscopy in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy. In order for the study to proceed without complications and to be informative and accurate, the woman will need to prepare for the procedure. Consultation with a gynecologist is required.
Gastroenterologists say: the examination will not harm the woman. But external influences on the body during pregnancy are stressful. When the question arises about choosing a diagnostic method, the doctor takes into account all factors, the health status of the woman and child, and the course of pregnancy.
Preparation for the procedure
FGDS is considered to be a safe procedure. Carrying a child is not a contraindication to the procedure. However, a woman must carefully prepare for manipulation.
Gastroenterologists recommend conducting the study in the morning. Eating is prohibited 6–8 hours before the intervention. Drinking any liquids is also not allowed. The stomach should be empty. This measure will ensure the reliability of the results. A specialist will use a device to examine all the internal walls of the organ.
Smoking is also prohibited before FGDS. This bad habit should be avoided when carrying a child. Tobacco smoke and tar, entering the esophagus, settle on the mucous membranes. This may distort the results of the study.
Indications for FGDS
An examination using fibrogastroduodenoscopy is performed if there are signs of digestive system disorders. Symptoms of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT):
- Feeling of nausea after eating;
- Heaviness in the stomach;
- Vomiting;
- Acute pain in the abdominal area;
- Increased body temperature;
- Heartburn, belching;
- Deterioration in health, poor appetite.
The listed symptoms are typical for pregnant women. But if the doctor suspects a serious health problem, endoscopy will help refute or confirm the presence of a pathological process in the body. In addition to these symptoms, FGDS is prescribed in the following situations:
- To accurately identify the focus that disrupts the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Ineffectiveness of other diagnostic procedures;
- Ulcerative colitis of the stomach or duodenum;
- A set of symptoms indicating difficulties in the digestive tract;
- Assumption of tumor growth;
- Before a planned operation on the abdominal organs;
- For signs of internal bleeding.
If it is not possible to identify the source of the disease by other methods, the doctor will refer you to an FGDS to diagnose the pathology and determine treatment.
Possible restrictions
Gastroscopy during pregnancy is prescribed if there is a suspicion of stomach problems. It is this technique that allows you to avoid making a mistake with the diagnosis. Determining the disease solely by external symptoms is difficult, since many pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract have similar clinical manifestations.
Before conducting the examination, it is important to consult a gynecologist. Typically, FGDS is recommended to be taken at the end of the first or beginning of the second trimester. At this time, the impact of the device on the fetus is minimal.
It is worth noting that gastroscopy is a safer procedure than radiography. It is better to refuse such diagnostics while expecting a baby.
Gastroenterologists believe that a pregnant woman can safely undergo an FGDS procedure if she has symptoms of an ulcer or gastritis. There are practically no complications or side effects. Many people complain of a sore throat after the test. This involves inserting a tube with a camera into the esophagus.
As a rule, the discomfort goes away on its own within a few days. During this period, a woman should be attentive to her health. The mucous membranes are injured by mechanical stress. This increases the risk of bacteria or viruses entering. A sore throat may develop. The therapist will recommend safe medications for treating the disease.
Preparatory measures
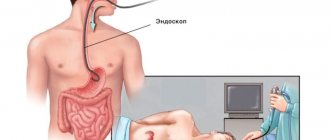
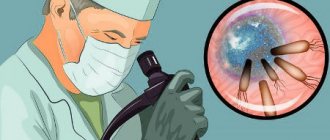
Gastroscopy is an endoscopic examination of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum using a flexible tube with a camera at the end. Fibrogastroduodenoscopy of the stomach is a diagnostic procedure that is also used for biopsy, i.e. sampling tissue for research.
The gastroenterologist referring for FGDS warns of the need to prepare for the procedure. Preparation is carried out according to the following rules:
- Two days before gastroscopy of the stomach, you will have to give up spicy, fatty foods, chocolate, beans, and nuts. This is important if a stomach ulcer is suspected.
- It is prohibited to consume alcoholic beverages and medications containing ethyl alcohol.
- Dinner should be low in fat, exclude meat, fish, cheese, mayonnaise, foods with a lot of fiber (wholemeal bread, cabbage, radishes, beans). You can eat mashed potatoes, buckwheat, oatmeal, cheese, stewed chicken meatballs, soup, juice. It is not advisable to eat more after dinner.
- On the day of gastroscopy, you should not eat or drink.
- Do not smoke before gastroscopy, this leads to the formation of gastric juice and complicates the study.
- On the day of the procedure, the use of tablets, syrups, and capsules of medications is prohibited (aspirin, warfarin and other blood thinners should not be taken 10 days before gastroscopy, they can cause bleeding).
- Tell your doctor if you have a tendency to allergies (especially to painkillers), or about the presence of diseases (heart failure, myocardial infarction, aortic aneurysm, diabetes mellitus, epilepsy, previous operations).
- It is recommended to undergo a blood clotting test.
- For fibrogastroduodenoscopy, take a referral, documents, necessary test results, comfortable clothes (robe), and remove jewelry.
How is FGDS performed on pregnant women?
The procedure is carried out in a separate room.
- Before gastroscopy of the stomach, the pharyngeal mucosa is anesthetized (lidocaine is used, suitable for pregnant women).
- You need to lie on the couch on your left side. Doctors advise relaxing and controlling your breathing. When the patient is in a calm state, the procedure is easier and faster.
- You cannot talk, make sudden movements, or try to pull out the probe yourself. You can severely injure the mucous membrane and cause bleeding.
- Listen and follow your doctor's recommendations. The gastroenterologist will explain how the examination is carried out, what you may feel, and how to tell him if your health worsens during gastroscopy.
- The doctor will carefully advance the endoscope through the esophagus and stomach, monitoring the condition of the internal organs through the image of the monitor, which is part of the endoscope camera. Duration is 15 minutes. The procedure cannot be called pleasant, inconvenience is possible, but it is harmless to health.
Gastroscopy reveals pathologies and disorders:
- Hiatal hernia;
- Ulcers in the stomach and intestines, gastritis;
- Perforation of the mucous membrane, esophagitis;
- Enteritis;
- Duodenitis;
- Tumors of the esophagus and stomach;
- Varicose veins
After fibrogastroduodenoscopy, the woman goes home. Based on the examination results, the gastroenterologist makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment. Drugs approved during pregnancy are used.
Before the procedure, the patient should be familiarized with the sequence of the procedure, contraindications and possible complications. The duration and cost of the study are announced. The doctor gives recommendations after the examination.
Tips after the procedure
A pregnant woman may have an unpleasant feeling in the throat after FGDS. The symptom is activated during the insertion of the probe, and the mucous membrane may be slightly injured. After a few days, the damaged tissue is completely regenerated, and the discomfort goes away.
During this period, it is necessary to increase vigilance, monitoring your well-being. Small microtraumas are a good place for a wide range of pathogenic bacteria. It is recommended to follow a number of rules after FGDS:
- Do not eat for 2-3 hours after the procedure.
- The drink is taken warm (hot drinks irritate the mucous membranes and can injure them even more).
- Food should not irritate the damaged mucous membrane.
- For rapid tissue regeneration, it is recommended to eat in small portions.
If you feel severe pain or the feeling of nausea and stomach discomfort does not go away, consult a doctor. The doctor will prescribe painkillers allowed during pregnancy.
Important! Do not take medications on your own; self-medication is dangerous for your health and for your unborn baby. Take pills and other medications carefully.
Recommendations for carrying out
Gastroscopy is considered a not very dangerous procedure for health and life. It is allowed to be performed during pregnancy, as it will not harm the baby.
But you need to know that you should carefully prepare for the study:
- You should not eat food ten hours before the procedure.
- You should avoid any drinks, even water. The stomach should be completely empty.
- The woman should calm down and relax so that the probe can pass through the throat more easily.
During gastroscopy, discomfort may occur that occurs during the insertion of the endoscope into the pharynx. This is due to irritation of the mucous membrane, causing a gag reflex.
This problem can be solved with the help of modern drugs that suppress the gag reflex and relieve pain. Experts prefer to treat the throat with Lidocaine, which is also produced in the form of a spray. After applying the product, a freezing effect occurs, which lasts for several minutes. This helps to avoid discomfort during gastroscopy. In addition, Lidocaine is completely safe and allowed during pregnancy.
In addition to local anesthesia, anesthesia is also used. This allows the woman to fall asleep for the entire period of the study. But before introducing such anesthesia, a specialist must examine the pregnant woman.
All experts claim that FGDS during pregnancy is safe for the process of bearing a baby. But it is worth remembering that any such intervention is stress for the body, which is harmful for the child. Therefore, such a procedure is prescribed to pregnant women in cases of extreme necessity, when the benefit to the mother significantly outweighs the harm to the fetus.
Contraindications
The diagnostic method of gastroscopy does not harm the body and health of a pregnant woman. In some cases, the procedure is postponed or alternative examination methods are used:
- FGDS of the stomach is not done if there is severe pain in the gastrointestinal tract during an exacerbation of a chronic disease. This creates a risk of complications.
- The doctor takes into account the condition of the woman and child, the course of pregnancy, and what week the pregnancy is. If there are prohibitions from the gynecologist, it is better not to conduct an FGDS examination.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy during pregnancy is not an easy procedure. But diagnosing using this method makes it possible to correctly identify the disease and prescribe a course of treatment. Pregnancy is not a contraindication to FGDS. An experienced specialist and a positive attitude of the expectant mother will help carry out the procedure in an informative and painless manner.
After FGDS
What can you do after an FGDS and what can’t you do? Since the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and gastrointestinal tract has been severely irritated, it is not recommended to eat for two to three hours. Half an hour after it ends, you can drink warm water. The doctor will recommend an infusion or solution that will speed up the restoration of pharyngeal tissue. As a rule, the next day the woman does not feel any discomfort.
Gastroscopy during pregnancy is not a simple procedure for a woman. However, it gives the most accurate and reliable result. This allows you to prescribe the correct treatment. Since the baby’s health completely depends on the mother’s health, you need to overcome all fears and concerns and undergo an examination with a positive attitude (the sooner the better). Moreover, pregnancy itself is not a contraindication to FGDS.