In this article we will figure out whether hemorrhoids can turn into cancer.
Hemorrhoids are varicose transformations of the vessels of the rectum in the form of their extensions, called hemorrhoids. These formations can be internal and external, and at advanced stages of the pathological process, the nodes begin to fall out and bleed.
The disease usually progresses in waves: chronic periods are replaced by acute ones, and vice versa. The remission period can be almost painless, and the patient does not experience pathological symptoms or complications.
Stages of the disease
Main stages of the disease:
- formation of external and internal hemorrhoids;
- periodic loss of nodes and independent reduction;
- prolapse and return of nodes to their place is carried out with additional medication and is accompanied by periodic bleeding.
Periods of exacerbation of hemorrhoids are characterized by a number of complications, of which the most common are considered to be thrombosis of the hemorrhoid, swelling and inflammation of adjacent tissues and mucous membranes.
Many people wonder whether hemorrhoids can turn into cancer?
Features of oncology
Malignant inflammation of the rectum is an oncological tumor of the mucous membrane. Pathology has causes:
- unbalanced diet;
- abuse of alcohol and tobacco products;
- ulcerative colitis;
- anal fissures;
- inflammatory processes;
- intestinal polyps;
- proctitis;
- thrombosis of the hemorrhoid;
- obstruction of hard feces;
- obesity;
- heredity;
- stressful condition.
The cause of rectal cancer is an insufficient amount of nutrients in the mucous membrane, weakened immunity. An unbalanced diet, bad habits, and pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract are the etiology of the accumulation of solid feces, the toxic substances of which cause the formation of polyps and metabolic disorders.
The first stage of cancer has no obvious signs. The main symptoms of cancer as the pathology progresses are:
- unstable stool: diarrhea followed by constipation;
- false urge to defecate;
- thin feces;
- discomfort during the act of defecation;
- discharge of blood from the anus;
- increased gas formation;
- vomit;
- weight loss;
- pale skin;
- fatigue, lethargy;
- hyperthermia;
- aching joints.
Rectal cancer is characterized by signs of intoxication of the body. This is due to the appearance of atypical cells that secrete pathogenic substances during cancer. An increase in malignant tumor leads to intestinal obstruction, and as a result, constipation, which is accompanied by bloating, flatulence, and intestinal spasms.
Cancer is a factor in changes in the hormonal levels of internal secretion, decreased immunity, and poor blood clotting.
Characteristics of rectal cancer
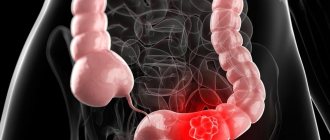
Malignant processes in the rectum are characterized by the development of oncological formations originating from the epithelial tissues of the walls of the rectum. Over time, metastases begin to form - screenings from the main focus of the pathological process, which have the ability to grow and affect other organs. The structure of metastases is similar to the main tumor.
How to distinguish colon cancer from hemorrhoids? More on this below.
Initially, metastases develop around the lymph nodes, and as the disease becomes more complicated, they develop in the lymph nodes themselves. In this case, the lesion affects most of the intestine. The next stage is the spread of cancer to neighboring organs, which significantly impairs their functions. The lungs, pelvic bones, bladder, and uterus have the highest probability of metastases settling. At the last stage of its development, cancer is incurable and leads to death.
So, can hemorrhoids turn into cancer? What are the signs of this?
Symptoms
The clinical manifestations of these two diseases, although relatively similar, have a number of fundamental differences. Let's compare them.
Manifestations of hemorrhoids
The severity of the patient's condition correlates with the clinical manifestations of hemorrhoids. It is considered a chronic pathology that periodically worsens, so the division occurs as follows:
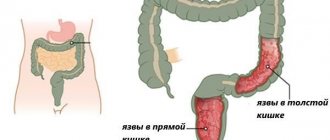
Stage I – traces of blood appear without prolapse of internal nodes;- Stage II - dilated venous structures fall out only with straining, retracting on their own;
- Stage III - nodes after prolapse have to be reset manually (with the help of hands);
- Stage IV - the affected nodes fall out at rest, they cannot be set back in any way.
In the last three stages, bleeding may or may not be present at all, which does not mean regression of the disease. During exacerbation, thrombosis of nodes occurs with the possible addition of an inflammatory process up to necrosis of soft tissues.
Oncology examines the appearance of neoplasms in the body, which, in the worst case scenario, may be malignant in nature. This implies, first of all, the tendency of the tumor to metastasize, infiltrate (violates the integrity of surrounding tissues) and autonomous growth. The main danger of a cancerous tumor is that it quickly becomes a state of competition with normal tissues of the body for nutrients and space. In this case, abnormal blood supply to such a neoplasm is often possible.
Clinic for rectal oncology
With widespread cancer, the following pathogenetic types of symptoms will predominate in the patient:
- Primary (local);
- Secondary (differing in functional disorders caused by tumor growth);
- General (symptoms of cancer intoxication).
The first stage of cancer can proceed covertly, without showing itself in any way, so screening is of great importance - early detection using specific methods in people at risk.
Only an experienced doctor can distinguish rectal cancer from hemorrhoids after conducting appropriate research.
Similarity of symptoms
In the early stages of the development of such diseases, the symptoms of the pathological process are quite similar. Their list includes:
- bleeding from the rectum or blood-stained stool;
- false urge to defecate;
- discomfort or pain in the anorectal area.
If such signals appear, you should immediately consult a doctor to diagnose the pathology in order to determine whether it is hemorrhoids or cancer.
How often do hemorrhoids turn into cancer? Let's figure it out.
What are hemorrhoids
The disease is characterized by an abnormal increase in the size of cavernous bodies, which occurs against the background of an equally common pathology - varicose veins. Impaired blood flow, changes in blood density and the formation of blood clots in the lumens of the veins lead to the formation of hemorrhoids in the rectum.
Localization of nodular neoplasms is inside the rectum (internal hemorrhoids) or in the anus (external hemorrhoids). Upon palpation and visualization, hemorrhoids resemble small tumor formations, but, in fact, they are not such, since the nature of their origin has nothing to do with the formation of cancerous tumors.
Hemorrhoids can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- Itching, burning in the anus.
- Discomfort, feeling of heaviness, sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the rectum.
- Inflammation, swelling of the tissues around the anus.
- Pain when sitting or walking.
- Painful bowel movement.
- False urge to defecate.
- Minor blood spots in the stool.
- Rectal bleeding.
- Pain on palpation, prolapse of hemorrhoids.
One of the symptoms of hemorrhoids is a frequent and false urge to defecate.
The course of the disease is wavy. During periods of regression (resting state), the nodes decrease in size and fall off. With aggravation, straining, tension, they swell and become larger. Chronic hemorrhoids are characterized by mild symptoms and are not accompanied by pain. The acute phase of the disease is characterized by: noticeable discomfort in the anus, severe pain, prolapse of hemorrhoids, anal bleeding.
Causes of hemorrhoids:
- Sedentary work.
- Physical inactivity.
- Poor nutrition.
- Abuse of tobacco products and alcoholic beverages.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (chronic constipation).
- Hereditary predisposition.
One of the fundamental factors in the formation of hemorrhoids in the rectum is congenital or acquired weakness of the walls of blood vessels. That is why the disease can often accompany or develop simultaneously with varicose veins of the lower extremities.
For women, the likelihood of hemorrhoids increases during pregnancy and childbirth. This factor is due to changes in the functioning of the body, increased stress on internal organs, in particular the intestines, during pregnancy and childbirth.
Pregnancy and childbirth are a common cause of hemorrhoids.
Differences in symptoms
Hemorrhoids and rectal cancer have significant differences, and they lie mainly in symptoms.
Differences between cancer and hemorrhoids:
- The nature of the bleeding. With the development of hemorrhoids, the blood has a bright red (scarlet) color and is released, as a rule, at the end of the act of defecation, which can be visually determined by the feces - the blood is most often on the surface and often looks like a clearly defined strip. In case of malignant processes in the rectum, the blood is predominantly dark in color and mixes evenly with feces. How often do hemorrhoids turn into cancer? We will answer this question.
- The nature of discharge during defecation. In case of cancer, before bowel movement, mucus or pus is sometimes released from the rectum, and in some cases, particles of the malignant neoplasm itself when it is damaged. In addition, there may be a change in the shape of feces - the development of a tumor often leads to the formation of ribbon feces. With hemorrhoids, such symptoms are not observed.
- Nature of constipation. Oncological disease is often accompanied by longer-term constipation than with hemorrhoids. The patient may not have a bowel movement for more than two days.
- General condition of the patient. Sudden weight loss, loss of appetite, pale skin, constant pain in the abdomen, fever, constant feeling of fatigue, shortness of breath and weakness - such symptoms can only occur with oncology and are rarely observed with hemorrhoids.
- The nature of the formations. Hemorrhoids, unlike a malignant tumor, prolapse from the rectum.
In addition, in cases where polyps were previously identified in the patient (which should be recorded in the medical history), the likelihood of developing cancer pathologies increases. Many people think that hemorrhoids can develop into cancer, how can this be detected?
Disguised symptoms: distinguishing signs of rectal cancer from hemorrhoids
The course of hemorrhoidal disease has similar symptoms to the appearance of malignant formations in the rectum. However, there are a number of details that make it possible to distinguish between the symptoms of oncology and hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids and cancer: differences in symptoms
- Type of feces. With hemorrhoids, the stool looks unchanged, but a growing tumor will affect its shape - it will become ribbon-like and thin.
- Patients with hemorrhoidal disease may deliberately stop eating if they fear painful bowel movements. But this is the only symptom that is similar to cancer intoxication. There should be no other symptoms. Abdominal pain, weight loss, painfully pale skin, elevated body temperature no longer indicate hemorrhoids, but the possible development of oncology.
- With hemorrhoids, the patient finds traces of scarlet blood on linen, toilet paper, and in stripes on stool. Rectal bleeding from hemorrhoids is observed immediately after visiting the toilet or during the process. In the case of cancer, the blood is dark, it can be seen inside the stool, or it is detected during an occult blood test.
- Another symptom is mucus discharge from the anus. If the patient has hemorrhoidal disease, mucus will be detected during bowel movements. If the disease is at a late stage, mucus can be found on underwear throughout the day. In the case of cancer, mucous discharge may contain traces of blood, pus and even tumor particles, which will be observed immediately before bowel movement. The discharge may smell unpleasant.
Hemorrhoids do not develop into cancer. However, in its advanced form it can cause disability or provoke the development of serious complications that can lead to death.
This is interesting: How to eat properly with erosive gastritis of the stomach
Can hemorrhoids turn into cancer?
The answer to this question is quite clear: hemorrhoids do not turn into cancer. But this does not exclude the concomitant development of both pathological processes, which, as a rule, occurs extremely rarely.
It is a misconception that hemorrhoids lead to cancer.
Similar symptoms in the early stages of disease development are only an indication for contacting a specialist. Neither oncology nor hemorrhoids go away without a trace, however, rectal cancer can lead to death if this pathology is not diagnosed in a timely manner and treatment is not started.
What to do if such symptoms appear?
Only a doctor can understand what kind of disease a person is developing, hemorrhoids or cancer. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a laboratory test of urine and feces for occult blood and determine the level of hemoglobin.
It is also mandatory to donate blood for tumor markers. If the analysis shows an increase in the concentration of biological compounds indicating inflammatory processes and cell degeneration, further examination is prescribed, which includes colonoscopy and CT.
Colonoscopy is the most effective method for diagnosing cancer of the rectum and the entire intestine in general.
Drug treatment
These activities are characterized by taking prescribed medications: ointments, tablets and suppositories for a hemostatic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory and venotonic effect.
This type of therapy in most cases is complex and is prescribed to the patient for a certain period of time: for chronic forms of hemorrhoids up to two months, for exacerbation of the disease - from 7 to 14 days.
The most popular medications for hemorrhoids are phlebotonics, combined anesthetic and anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, which are also used in the treatment of oncology.
Treatment
Treatment tactics for cancer always depend on the size of the tumor, its exact location, and the process of metastasis. If the malignant tumor is operable, it is excised along with part of the adjacent tissue. The rest of the therapy is prescribed to reduce the size of the formation and destroy the resulting metastases.
Regardless of whether colon cancer manifests itself or a tumor arises from hemorrhoids, the patient is required to undergo chemotherapy. Drugs used:
- "Erbitux";
- "Avastin";
- "Irinotecan";
- "Eloxatin";
- "Capecitabine".
The regimen, duration and number of courses are prescribed by an oncologist based on the diagnostic data and studies obtained. Radiation therapy helps reduce the size of the tumor, destroy cancer cells and destroy the structure of the tumor. The doctor’s primary task is to apply radiation directly to the affected area of the body, without affecting healthy tissue, so as not to disrupt the functioning of the body.
To protect yourself from the development of cancerous tumors, at the first suspicious symptoms you should immediately seek medical help
To recover, the patient is recommended to take various vitamin complexes and biological supplements, and to relieve pain in the rectal area, painkillers and anti-inflammatory suppositories are recommended. The use of drugs that irritate the rectum is prohibited.
The prognosis of the disease depends on the stage of development when contacting a specialist. In the absence of metastases and the tumor size is less than 1 cm, the patient in 80 percent of cases has a good chance of survival for more than 5 years. Damage to a third of the rectum with no spread of cancer cells throughout the body gives a favorable prognosis in 50 percent of cases. Metastatic forms of cancer are difficult to treat and provide a guarantee only in 10–20 percent of patients.
Minimally invasive methods
This treatment is a surgical intervention without the use of a scalpel or other cutting medical equipment. Such techniques include:
- infrared coagulation;
- laser coagulation;
- cryotherapy;
- ligation of the hemorrhoid using latex rings;
- sclerotherapy.
These medical procedures are carried out using laser, infrared radiation, liquid nitrogen, sclerosing medications and specialized latex rings. This allows you to remove hemorrhoidal formations with minimal damage to the rectal area and a short recovery period.
Surgery for hemorrhoids
These methods of treating hemorrhoids and colon cancer are quite similar. Surgery for hemorrhoids involves two main operations:
- Hemorrhoidectomy - cutting out all tissues that are affected by hemorrhoidal changes, as well as tissue around the anus. Certain types of surgical intervention distinguish between fixation of the mucous membrane to the underlying tissue, which is a very traumatic and painful operation with a long recovery period. But its implementation is justified in the last stages of disease development, when pathological processes have become advanced.
- Longo's operation is the cutting out of a separate section of mucosal tissue, which involves moving hemorrhoids deep into the canal, disrupting their circulatory processes. As a result, the nodes begin to die off on their own. The Longo method is a safer and faster operation with a minimal recovery period, but it is performed only for internal hemorrhoidal formations.
Features of hemorrhoids
Damage to the venous vessels, leading to the formation of hemorrhoids, is observed in the area of the perianal ring of the rectum.
The causes of the disease are:
- unbalanced diet;
- inactivity;
- heavy loads;
- prolonged constipation;
- pathologies of the digestive system;
- increased pressure inside the abdominal cavity;
- intestinal obstruction;
- pregnancy;
- genetic predisposition.
Inactive life is the cause of hemorrhoids. An incorrect diet, which implies an insufficient amount of consumed vegetables, fruits, herbs, dairy ingredients, the presence of carbonated drinks, alcoholic drinks, coffee, leads to the formation of solid forms of feces. Sedentary work, lack of physical activity, and lifting large objects contribute to tension and compression of the rectum, leading to disruption of natural blood circulation in the venous vessels of the anal area. Chronic pathologies of the digestive system are the cause of fecal obstruction.
Inflammation of external and internal hemorrhoids has four stages of development, differing in the nature of the nodes: size, color, change in location. The first pronounced symptomatic signs of the disease are observed at the second stage of the progression of the pathology.
Manifestations of inflammation include:
- itchy sensation;
- pain in the anus after defecation;
- bleeding during bowel movements;
- stagnation of feces;
- enlargement of hemorrhoids;
- loss of inflamed cones.
Swelling of the nodes is characteristic of the second stage of development. Overcrowding of the venous vessels with blood leads to clogging of the lumen with feces. The loss of cones without the ability to return to the rectum on their own indicates stage 4 of hemorrhoid progression.