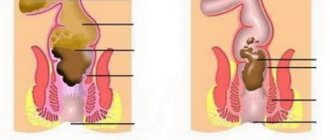
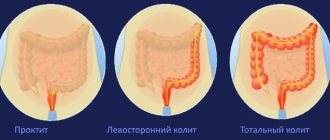
Colitis is an inflammatory lesion that varies in course, as well as clinical signs and the degree of damage to the mucous membrane. Medicines to eliminate intestinal diseases are selected by a medical specialist according to an individual plan based on the results of tests and examinations. The focus of treatment is to neutralize the inflammatory lesion, as well as stabilize the functioning of the organ and alleviate the signs of the disease.
When selecting a medicine for intestinal colitis, the doctor relies on test results and the cause that provoked the onset of the disease. Without eliminating the root cause, effective treatment is not possible. For example, if the disease is caused by worms, then therapy will be aimed at eliminating these pests.
What drugs to use for colitis
Medicines are selected by a doctor; self-medication is not recommended, as this can lead to serious complications. The choice of drug is determined by certain factors:
- To eliminate abdominal distension and flatulence, medications that contain activated carbon, for example, Polysorb, as well as fennel extract, are used.
- Restoring microflora in the intestines is the task of biologically active additives.
- If there is difficulty in emptying, a laxative is used.
- When a person has an intestinal disorder, he is recommended to take antidiarrheal drugs.
- To reduce the lesion and relieve the inflammatory process, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs.
Complex therapy helps eliminate problems and return to your previous lifestyle.
Antimicrobials
The prescription of antibiotics for intestinal colitis is very controversial; most doctors have their own opinion on this matter. Sometimes such components eliminate beneficial microorganisms, causing dysbacteriosis and aggravating the course of colitis. The intestinal microflora is affected, and treatment is delayed. But it happens that without the prescription of antibacterial agents, recovery does not occur.
If spastic colitis is diagnosed, then it is better to treat it without antimicrobial drugs. In rare situations, antibiotics may be prescribed by a medical professional.
When a harmful environment spreads quickly, you have to resort to antibacterial drugs. They are used strictly according to the scheme prescribed by the gastroenterologist. Depending on the patient’s condition and the stage of the disease, the medical specialist selects the appropriate treatment.
These may be drugs from the sulfonamide group, for example, Fthalazol or Sulgin. Their use is carried out strictly as prescribed by a gastroenterologist according to the following scheme:
- For intensive treatment of the inflammatory process, the medicine is used six times a day. The duration of therapy is determined by the severity of the disease.
- The second stage is the suppression of residual pathogens. It lasts two days, application is carried out four times a day.
- The third stage is consolidation of positive action. Two days are allotted for it, with the use of medications three times a day.
Based on the results of a study of the patient’s microflora, a medical specialist can recommend an antimicrobial drug, the action of which is aimed at eliminating a specific type of pathogen.
Antibacterial drugs with hydroxyquinoline (Intestopan and Enteroseptol) are also used to eliminate colitis. These are more severe drugs, their use is justified when pathogens have developed resistance to many antibiotics. The treatment regimen depends on the stage and severity of the disease. The duration of treatment with medications that contain hydroxyquinoline is approximately ten days.
Antimicrobial agents for colitis
Treatment of intestinal colitis with medications begins with the prescription of antimicrobial drugs. Doctors have an extensive list of remedies for colitis at their disposal:
- sulfonamides;
- nitrofurans;
- quinolones;
- antibiotics.
Treatment of colitis with medications aims to eliminate the cause of inflammation (pathogenic and opportunistic microbes). Each type of microbe is sensitive to a specific drug. Therefore, to select the most effective remedy, an analysis of the sensitivity of the bacterial flora to medications is carried out.
Sulfonamides
Therapy with Fthalazol, Ftazin, Sulgin is carried out for ulcerative colitis, dysentery, and E. coli contamination. The tablets are slowly absorbed from the intestines when taken orally, creating a high concentration of antimicrobial agent. Sulfonamides are contraindicated for pregnant women, nursing mothers, children under 3 years of age, and people with kidney problems.
Nitrofurans
The antibacterial activity of nitrofurans extends to Giardia, Shigella, Clostridia, Salmonella, and Vibrio cholerae. Enterofuril capsules will help with antibiotic-associated colitis. They suppress the development of clostridia, the causative agents of pseudomembranous colitis. Enterofuril is approved for children from 1 month in the form of a suspension. 200 mg capsules are prescribed to adults 4 times a day for a week. Pregnant and lactating women are recommended to use according to compelling indications.
Quinolones
Quinolones are a relatively new group of antimicrobial agents. Microorganisms have not yet developed resistance to quinolones. Drug treatment of colitis with this group of drugs eliminates salmonella, shigella, cholera, and staphylococci. Nolicin, Sophasin, Medociprin are used in the treatment of chronic colitis.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics for colitis are needed with a broad spectrum of action. A new generation of drugs is polymyxins. Polymyxin B is taken to eliminate Salmonella, Shigella, Klebsiella, and cholera. Treatment of colitis in adults with Polymyxin B occurs in a hospital setting.
For home antibiotic therapy, the doctor prescribes:
- Levomycetin - helps get rid of acute and chronic inflammation caused by E. coli, salmonella, streptococci, staphylococci. The medicine is taken half an hour before meals 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 8 days. Children under 2 years of age, expectant and nursing mothers are not prescribed.
- Neomycin is a drug from the group of aminoglycosides. When taken orally, it is poorly absorbed, affecting mainly the microflora in the intestines. Neomycin is used by prescription due to the large number of side effects.
- Alpha-Normix - the medicine eliminates the overgrowth of pathogenic bacteria, since almost everything remains in the small and large intestine. It is possible to treat intestinal colitis in women during pregnancy and lactation. Adults and children over 12 years of age are advised to take 1 tablet every 8 hours. An antibiotic is used for a week.
Treatment of colitis with medications, especially antibiotics, occurs under the supervision of a gastroenterologist. The dosage of drugs, the duration of treatment for colitis, and the selection of effective medications are carried out strictly individually. Unsystematic use of antibiotics threatens to complicate the inflammatory process with antibiotic-associated colitis (AAC).
Classification
When eliminating the disease, medical specialists use various medications for intestinal colitis. All of them can be divided into the following types:
- Sulfonamides (“Sulfasalazine”, “Mesacol”). Their influence is aimed at eliminating pests.
- Complex drugs (“Intestopan”, “Mexaza”). They inhibit pathogenic microflora and also contain enzymes.
- Biological medicines with beneficial microorganisms and medicines of the eubiotic class (Bifidumbacterin, Bifiform, Linex). As a rule, they are localized in the intestines, in the form of lacto- and bifidobacteria.
- Medicines that contain enzymes (Pancreatin, Mezim, Festal).
- Medicines from the category of antispasmodics (“No-shpa”, as well as “Papazol” and “Bellasthesin”). These medications effectively neutralize pain.
- Monoclonal antibodies help the body cope with the inflammatory process on its own, giving immune cells the ability to recognize the problem and eliminate it.
Treatment
The therapeutic regimen usually includes a whole range of measures:
- nutrition modification;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- correction of the immune response;
- normalization of intestinal motor function;
- elimination of dysbiosis;
- vitamins;
- physiotherapy.
Diet
Meals for chronic colitis should be divided, and long breaks between meals should be avoided. Foods that are “heavy” for the intestines are excluded from the diet:
- spices;
- raw vegetables with coarse fiber;
- nuts;
- fatty meats and fish.
Of dairy products, only mature cheeses are allowed; whole milk, sour cream, and yoghurts are prohibited. If there are manifestations of food allergies, you will also need to give up strawberries, honey, oranges, lemons, and chocolate.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
These include derivatives of 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA):
- Sulfasalazine;
- Pentasa;
- Salofalk.
One of the new directions in the treatment of chronic colitis is the prescription of Infliximab. The drug is an antibody to one of the components of the inflammatory response - tumor necrosis factor (TNF). In particular, the effectiveness of Infliximab in the treatment of Crohn's disease has been proven.
Less commonly, corticosteroids (Prednisolone) and immunosuppressants (Azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, Cyclosporine A) are included in the therapeutic regimen. They have a number of side effects, so they are prescribed only if there is no effect from 5-ASA derivatives.
Immunomodulators
In people with long-term chronic colitis (more than 10 years), the production of interferons is reduced. This is especially common in cases where the trigger is a viral infection.
In clinical practice, Viferon (recombinant α-2b-interferon) is most often used. Other drugs with an immunomodulatory effect: Lykopid, Kipferon, Polyoxidonium.
Protection of mucous membranes and normalization of motility
To restore and protect the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, gastroprotectors based on rebamipide (Rebagit) are needed: it works throughout the gastrointestinal tract and at all three structural levels of the membrane. This is necessary for both micro- and macro-damages (erosions, ulcers).
Depending on the severity of certain symptoms, prokinetics (Itomed) or antispasmodics (Meteospasmil) are prescribed.
If colitis is accompanied by constipation, laxatives are indicated:
- plant origin: Ramnil, Tisasen;
- diphenylmethane derivatives: Bisacodyl, Isaman;
- increasing the volume of feces: Laminaride, Lactulose.
For one-time use, suppositories (with glycerin, rhubarb) or microenemas (Microlax) are suitable.
Probiotics
The lacto- and bifidobacteria included in their composition reduce the pathogenicity of viruses and bacteria in the intestinal lumen. This provides higher general and local immunity.
For chronic colitis, the following probiotics are indicated:
- Bifiform;
- Normoflorin;
- Linux;
- Maxilac;
- Atsipol et al.
Preference should be given to probiotics that do not contain milk or lactose. These, for example, include Bifiform and Normoflorin.
Vitamins
Due to a long-term inflammatory process in the intestines, a deficiency of B vitamins and antioxidants (vitamins E, A, C) often occurs. Therefore, it is advisable to take vitamin complexes.
Combination preparations (multivitamins + probiotic) have a good effect. For example, Multitabs Immuno Plus contains the bacteria Lactobacillus rhamnosus, which restore the intestinal biocenosis.
Physiotherapy
During the period of remission or mild exacerbation, physiotherapy is prescribed. These are mainly thermal treatment methods: ozokerite, therapeutic mud, peat mud. Inductothermy, centimeter waves, and mineral baths have a positive effect.
Spa treatment includes drinking mineral water. For chronic colitis with constipation, Essentuki No. 17, Baltinskaya is indicated. For colitis with diarrhea: Berezovskaya, Essentuki No. 4, No. 20.
"Sulfasalazine"
Has a strong anti-inflammatory effect. It is based on the rapid suppression of the source of pathogens by disrupting the metabolism in their cells. The active component does not allow the deoxyribonucleic acid chain to multiply.
According to reviews, “Sulfasalazine” for intestinal colitis is prescribed to people over sixteen years old, one or two grams three times a day. Next - 500 milligrams of the active substance until the end of the maintenance stage. The drug has a number of negative reactions, so it is prescribed only by a doctor.
What does Phthalazol help with?
Experience with the use of the medication shows that it should not be prescribed to children under twelve years of age. But if necessary, the doctor can prescribe this medication to the child, individually calculating the dosage depending on the weight.
What does Phthalazol help with? According to the instructions for this medication, the drug eliminates:
- acute intestinal infections;
- enterocolitis;
- colitis;
- diarrhea.
The medicine can be prescribed in combination with sulfonamide medications and antibacterial agents. The tablets should not be used together with antacid drugs or adsorbents, since in this situation the pharmacological effect of the drug will be reduced. The medication does not affect the functioning of the central nervous system and the speed of psychomotor reactions.
Symptoms of colitis
If a patient experiences paroxysmal abdominal pain or acute diarrhea, these are the first signs of colitis, the intensity of which will only increase in the absence of timely treatment. General symptoms include the following changes in general health:
- feeling of rumbling in the stomach, indigestion, signs of bloating;
- fever (increased body temperature), chills;
- increased urge to defecate;
- symptoms of dehydration, represented by dizziness, general weakness;
- feces mixed with blood, most often caused by hemorrhoids worsened by diarrhea.
Not all symptoms may be present at the same time; their severity and intensity varies depending on the specific clinical picture. Effective treatment of intestinal colitis at home is possible only after a final diagnosis has been made, and this requires knowledge of the classification and distinctive features of each form of this disease.
Articles on the topic
- Diarrhea from antibiotics - why intestinal upset occurs and how to restore its function
- Intestinal diseases - symptoms, manifestations, the most common diseases and their therapy
- Colitis in children - signs and types, how to treat with medications or traditional medicine, complications
"Bifidumbacterin"
The medication is considered a probiotic that stabilizes the intestinal microflora. Due to the huge number of active ingredients and bifidobacteria, the medicine can stimulate the functioning of the stomach and intestines, the digestion process, as well as the body’s nonspecific resistance to various factors, metabolic processes, and the synthesis of vitamins.
According to reviews, “Bifidumbacterin” for intestinal colitis helps to effectively eliminate most pathogenic organisms, including enteropathogenic E. coli, Proteus, as well as staphylococci and some types of yeast-like fungi. The drug is produced in the form of a solution, powder, capsules and suppositories.
Vitamins and medications for stress relief
The long course of colitis and its negative manifestations cause a deterioration in the emotional and physical well-being of the patient. Often he develops an irritated and aggressive state, nervous disorders, and fatigue. These symptoms must be eliminated with the help of sedatives and sedatives. High effectiveness can be achieved by combining these agents with B vitamins. However, due to the pain of intramuscular administration, the doctor often prescribes capsules or tablets.
"Magne-B6"
The drug is prescribed for the treatment of disorders:
- spasms of the stomach and intestines;
- sleep disorders;
- nervous excitability;
- physical or mental fatigue;
- muscle pain;
- anxiety attacks.
The standard dosage is 2 tablets in three doses per day. The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician, taking into account how quickly the symptoms of the disease disappear and the normal concentration of magnesium is restored. Usually the drug is prescribed for a course of therapy, the duration of which is 2-4 weeks. The medication is usually well tolerated, but in some cases it can cause standard symptoms in the form of allergic reactions, nausea, vomiting, stool disorders, and flatulence.
"Festal"
The medication is approved for long-term use, up to three months. This medication is recommended to be taken 20 milligrams three times a day after eating.
"Festal" helps improve the digestion of food, preventing it from remaining in the intestinal lumen. This is also an enzyme class drug. It is taken with every meal (two tablets). It does not cause side effects and has virtually no contraindications.
Diet for colitis
No medication will cure colitis if you neglect nutritional advice. The diet for colitis consists of pureed vegetarian soups, boiled porridges in water, steamed omelettes, boiled lean meat and fish without skin. Food is prepared in the most gentle way possible - boiling, baking, stewing in water. They eat warm food up to 6 times a day, excluding overeating and limiting hot and cold foods. Fatty, fried, spicy, smoked, and salty foods are removed from the diet. Avoid gas-forming foods - cabbage, radishes, grapes, black bread, sweets. You need to drink clean water, weak tea, mineral water without carbon. It is necessary to completely reject alcohol, smoking and other bad habits.
Medicines for the treatment of intestinal colitis include antimicrobial, anthelmintic, and symptomatic agents. During the treatment, the intestinal microflora is restored and the mucous membrane is regenerated. In parallel with drug treatment, diet therapy is carried out to increase the effectiveness of pharmacological drugs. A well-designed treatment plan will allow you to get rid of colitis or transfer the disease to a stage of long-term remission.
We recommend: How is IBS with diarrhea treated?
"Enterofuril"
The active substance is enterofuryl nifuroxazide, which belongs to the chemical derivatives of 5-nitrofuran. The drug has an antimicrobial effect, which is carried out by disrupting the connection of proteins in the cells of microorganisms. The drug has a wide spectrum of activity. “Enterofuril” is prescribed by specialists for intestinal colitis.
It leads to the elimination of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Despite the increased antimicrobial activity, the drug has virtually no detrimental effect on the state of normal intestinal microflora.
"No-shpa"
Antispasmodic tablets for intestinal colitis, which relax the smooth muscles of the intestine, neutralizing pain. For chronic illness, take two tablets twice a day.
Before starting therapy with No-Spa, you must read the instructions. After all, the medication has its own contraindications and side effects. In pharmacies the medicine is dispensed without a doctor's prescription. If you have any doubts or questions, you should consult a medical specialist.
"Salofalk"
Anti-inflammatory medicine is used to eliminate intestinal diseases. The drug has an effect primarily on the mucous membrane of the organ. "Salofalk" for intestinal colitis is taken orally: adult patients should take 1500 milligrams per day.
If the inflammatory process is severe, you can increase the dosage to 3-4 grams. The duration of treatment with tablets can be carried out for two to three months.
Features of treatment for children
Not all tablet medications are approved for use by young patients, so a pediatrician should be involved in the child’s therapy. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease.
The main treatment measure for the restoration of the mucous membrane is considered to be specialized nutrition. In addition to diet, medications with enzymes, as well as prebiotics and adsorbents are recommended for use. The difference between pediatric therapy and adult therapy is the prescription of antimicrobial drugs only for strict medical indications.
Opinions
According to doctors, the duration of treatment for colitis in the acute stage takes from three days to several weeks. This depends on the method of therapy and the severity of the symptoms. The chronic form of the disease takes longer to treat, but the symptoms do not bother the patient so acutely. To select the right drug, you must consult a doctor. He will prescribe an individual course of treatment, taking into account all the characteristics of the patient’s body.
Patient reviews of drugs on forums are quite controversial. Some patients report that after taking such medications for colitis in the intestines, unpleasant symptoms quickly disappeared. Others note the appearance of side effects after use. Therefore, when treating a disease, it is necessary to consult a doctor in time, as well as undergo an examination and choose the right medications, of which there are a huge number.
Methods for diagnosing intestinal colitis
Thanks to modern clinic equipment and the use of instrumental diagnostic methods, doctors are able to not only determine intestinal inflammation, but also differentiate the type of colitis, depending on which an effective treatment plan will be drawn up.
To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are used:
1. Laboratory:
- UAC;
- coprogram (stool analysis);
- analysis for fecal calprotectin is a study that allows you to diagnose Crohn's disease, against which colitis acts as a secondary symptom.
2. Instrumental:
- Irrigoscopy with the use of a contrast agent - during the procedure, a contrast agent is injected into the patient’s rectum, after which an X-ray is taken. This study allows us to exclude the presence of tumors, perforation, and stenosis of the intestinal walls;
- Colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic examination that allows you to examine the walls of the large intestine from the inside using a special device. During the procedure, the doctor may take a biopsy from suspicious modified areas of the intestine;
- A rectal-digital examination of the patient by a proctologist is carried out in a knee-elbow position to exclude concomitant pathologies (hemorrhoids, proctitis, paraproctitis, deep anal fissures).