General rules
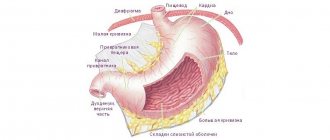
Gastroduodenitis is a combined inflammation of the mucous membrane of the lower part (pyloric section) of the stomach and the upper part of the duodenum. It is the anatomical proximity of these organs, and often the commonality of etiological factors (the presence of Helicobacter ), that contributes to the secondary involvement of the duodenal mucosa in the pathological process. This disease is a type of chronic gastritis .
There are acute and chronic forms of the disease, but at the everyday level, most people by gastroduodenitis mean a chronic form of the disease, which lasts for a long time with alternating periods of remissions and exacerbations, which are perceived as “acute gastroduodenitis”.
Diet for gastroduodenitis is the most important component of the treatment process and depends on the form and type of the disease (superficial “catarrhal”, erythematous, erosive gastroduodenitis), as well as gastric pH-metry . The general principles of nutrition for gastritis and duodenitis are: maximum sparing of the mucous membrane of the compromised organ from any type of damaging factors. This is achieved by excluding from the diet foods that require long-term digestion; food is served in a homogenized state (boiled, ground, mushy), and it is also necessary to chew food thoroughly.
It is not allowed to serve food in an excessively hot/cold state. Foods that cause chemical irritation (fatty and fried foods, smoked meats, marinades, spices and sauces, canned food, raw vegetables, alcohol) are excluded from the diet; salt intake is limited.
Dietary recommendations
One of the main roles in the proper treatment of such a disease is played by adherence to a special diet, with the help of which a person can normalize his condition and make the course of the pathology more stable.
Thus, if this disease is detected, a person needs to adhere to the following medical recommendations for proper nutrition:
- Do not eat too hot or cold foods, as they will only irritate the digestive system and aggravate the inflammatory process. All food must be served at the optimal temperature. Thus, the patient needs to forget about cold ice cream and other similar products for a long time.
- Chew solid foods thoroughly. In general, during an exacerbation of gastroduodenitis, it is advisable for a person to eat food that has been crushed in a blender or grated. This will make it much easier for the gastrointestinal tract to digest it.
- You should eat frequently (5-6 times a day), but portions should be no more than a full handful. Thus, the patient will feel full, but at the same time, will not overload the digestive system.
- You should completely limit your intake of foods that can irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa.
- You should give preference to boiled or steamed foods. As an alternative, stewed dishes will also be allowed, but without the top crust.
- If the dish is prepared in a slow cooker, then adding oil or any other fats to it is prohibited.
- It is important to properly plan your diet and combine light and hard-to-digest foods.
- It is recommended to create your own diet and eat at the same time.
- The break between meals should not be longer than three hours, because then the person will begin to produce gastric juice, which will further worsen inflammation and lead to pain.
- The last meal should not be later than two hours before bedtime. As for night meals, then, naturally, you need to completely abandon them.
Important! Not all patients can correctly create a dietary menu for themselves and strictly follow it. For this reason, this question should be addressed to an experienced nutritionist or gastroenterologist, who will describe in detail not only the recommended foods and dishes, but also the frequency of their intake, portions, etc.
In complex treatment, one should not forget about folk remedies for gastritis.
Varieties
Nutrition for chronic gastroduodenitis is prescribed according to certain schemes, sequentially depending on the form and phase of the disease, the acidity of gastric juice.
Diet for gastroduodenitis in the acute stage
Exacerbation of gastroduodenitis against the background of increased or normal acidity requires the prescription of Diet No. 1 and its varieties. On the first day, complete fasting with small amounts of liquid (boiled water, tea without sugar) is indicated. On days 2-3, the patient is transferred to Table No. 1A .
The energy value of the diet is 1800 kcal. The reduction in calorie content is carried out mainly by reducing the consumption of carbohydrates and, to a small extent, proteins and fats.
Dishes and foods that stimulate secretion and irritate the gastric mucosa are prohibited. Food is steamed or boiled, served pureed or mushy; too hot/cold dishes are not allowed. Salt intake is limited to 6-8 grams.
Meals during bed rest are fractional. Drink about 1.5 liters of liquid. On days 6-8, in order to stimulate regeneration of the gastric/pancreatic mucosa, the patient is transferred to Diet 1B .
Meals while observing semi-bed rest. The energy value is reduced mainly by limiting the amount of carbohydrates, with a normal content of proteins and fats. Soups with mucous broth. Solid, stimulating foods, cold and hot dishes are excluded.
Food is steamed or boiled and served in a homogenized state. Salt is limited. The duration of Diets 1 and 1B is determined by many factors, including the form of gastroduodenitis. Thus, with superficial gastroduodenitis, given that only the mucous membrane is involved in the inflammatory process, and the remaining structures of the stomach and intestines are functionally sufficient and not affected, the period of fasting and dietary nutrition can be relatively short.
With erosive gastroduodenitis , in which there are already defects ( erosions ) on the surface of the mucous membrane, both the duration of fasting and the length of time spent on Diets No. 1A , 1B and No. 1 . In this regard, with gastritis and erosive duodenitis, which is considered a pre-ulcerative condition, it is necessary to more strictly comply with all the requirements of therapeutic nutrition.
Next, Table No. 1 . An energetically and physiologically complete diet without pronounced mechanical sparing. Food is not wiped. The menu includes dishes with various heat treatments - boiled, stewed, baked without crust and degree of grinding. Table salt is limited slightly. Meals are fractional, in reduced portions. As the patient's condition improves, the menu expands.
Salads from boiled vegetables, mild varieties of cheese, doctor's sausage and milk sausage are allowed. Only yesterday's white bread. Among the fats, preference is given to refined olive, sunflower and flaxseed oil. For porridges, rice, oatmeal and buckwheat are recommended. You should avoid pasta. Only dietary meat (chicken, rabbit, turkey). Eggs - in the form of a steam omelet.
A small amount of low-fat cottage cheese is allowed from dairy products. The advisability of including whole milk and cream in the diet is questionable. It is useful to include vegetable juices in your diet. Eating fruits and berries raw is undesirable. New dishes are gradually introduced into the diet, portions are increased, and soon the patient is transferred to Table No. 15 .
Gastroduodenitis in the vast majority of cases occurs against the background of normal/high acidity. In cases of gastroduodenitis in patients with low acidity in the recovery stage, the patient's treatment is adjusted by prescribing Diet No. 2 . In addition to providing the patient with adequate nutrition, its task includes moderate stimulation of the secretory function of the gastrointestinal tract and normalization of the motor function of the intestinal tract. To do this, the diet increases the content of foods rich in fiber and connective tissue, and also expands the types of heat treatment of foods - baked, boiled, stewed, fried without forming a crust.
Rich mushroom, meat and fish broths are allowed. The diet includes sweet and sour vegetables and berries (strawberries, currants, raspberries, lingonberries), citrus fruits, sour dairy products, sauces based on vegetable decoctions (white sauce with lemon, sour cream, mushroom) and spices, parsley, dill, celery. The consumption of butter and refined vegetable oils is increasing. Physiologically, the diet is complete (3000 Kcal). Diet: 4-5 times without overeating. The nutrition menu for hypoacid gastroduodenitis is given in the corresponding section.
What can you eat if you have gastroduodenitis?
For patients with a diagnosis such as gastroduodenitis, a diet designated as table No. 1 (with high acidity), diet No. 2 (with low acidity) and diet No. 5 is provided.
Table No. 5 normalizes the functioning of the liver and bile ducts, promotes bile secretion. If you have severe pain due to gastroduodenitis in the first week, the doctor will prescribe you a diet with severe restrictions. During this period, baked goods, raw vegetables and fruits are completely excluded. All dishes are only in ground form.
For gastroduodenitis with increased acidity of gastric juice, use table recipe No. 1.
In this case, you need to adhere to the following rules:
- Cooking boiled, steamed and pureed dishes. Fried foods and smoked foods are prohibited;
- The white bread you eat should not be fresh. It's better to eat crackers. Buy only biscuits;
- During an exacerbation, soups made from well-cooked, pureed cereals and vegetables are allowed (an exception is made for cabbage). Cereals include rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, and semolina. Vermicelli choose small ones. You can eat baked or boiled potato, pumpkin, beet and carrot dishes. Green peas are subject to restrictions. The food must be pureed;
- You can introduce low-fat fermented milk products and low-fat cottage cheese into your daily diet;
- Lightly brewed tea and cocoa are allowed as drinks;
- Using unsalted butter;
- Meat is selected from low-fat varieties. It can be beef, veal, rabbit, chicken (without skin), turkey. Fish should also be low-fat varieties - pike perch, perch, carp. It is recommended to cook meat and fish by steaming or in the form of a soufflé;
- Fruits and berries cannot be eaten raw. Make compotes, decoctions, jellies, and mousses from them.
Authorized Products
The first courses are prepared mainly slimy and pureed. You can cook it in vegetable or weak meat/fish broth, after which the contents are rubbed through a sieve. Butter is added to prepared soups. Lean beef, chicken, rabbit, lean fish (carp, pike perch) are steamed, boiled or stewed with the addition of water.
Cereals (buckwheat, semolina, rice), as well as turkey and noodles are used as a side dish. Vegetables (cauliflower, potatoes, beets, pumpkin, zucchini, carrots) are served boiled or stewed.
Butter and vegetable oils are added to prepared dishes. Only dried wheat bread and white crackers are allowed. Only steam omelette or soft-boiled eggs.
Sweet fruits can only be in the form of jelly, jellies or compotes. Low-fat cottage cheese can be eaten in its natural form, as well as in the form of soufflés and casseroles. Desserts and drinks include marshmallows, biscuits, jam (non-sour), honey, weak tea with milk, fermented milk products.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| boiled cauliflower | 1,8 | 0,3 | 4,0 | 29 |
| boiled potatoes | 2,0 | 0,4 | 16,7 | 82 |
| boiled carrots | 0,8 | 0,3 | 5,0 | 25 |
| boiled beets | 1,8 | 0,0 | 10,8 | 49 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat porridge with milk | 4,2 | 2,3 | 21,6 | 118 |
| semolina porridge with milk | 3,0 | 3,2 | 15,3 | 98 |
| oatmeal with water | 3,0 | 1,7 | 15,0 | 88 |
| white boiled rice | 2,2 | 0,5 | 24,9 | 116 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 3.2% | 2,9 | 3,2 | 4,7 | 59 |
| condensed milk | 7,2 | 8,5 | 56,0 | 320 |
| cream 15% (low fat) | 2,3 | 15,0 | 3,6 | 161 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| beef stew | 16,8 | 18,3 | 0,0 | 232 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled chicken drumstick | 27,0 | 5,6 | 0,0 | 158 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
Eggs | ||||
| omelette | 9,6 | 15,4 | 1,9 | 184 |
| soft-boiled chicken eggs | 12,8 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 159 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| boiled fish | 17,3 | 5,0 | 0,0 | 116 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| vegetable oil | 0,0 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 899 |
| peasant unsalted butter | 1,0 | 72,5 | 1,4 | 662 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| black tea with milk and sugar | 0,7 | 0,8 | 8,2 | 43 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| compote | 0,5 | 0,0 | 19,5 | 81 |
| juice | 0,3 | 0,1 | 9,2 | 40 |
| jelly | 0,2 | 0,0 | 16,7 | 68 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Basic principles of the diet
Depending on the stage and condition of the patient, the diet is prescribed taking into account individual characteristics and the presence of additional pathologies.
There are general rules of nutrition that will allow you to quickly feel noticeable improvements.
Nutrition rules
- Products that increase acidity are excluded from the menu for gastroduodenitis; consumption is prohibited not only in acute cases, restrictions apply for a long period.
- Products can be stewed, boiled, steamed; such processing can reduce the amount of irritating enzymes produced. Also, if you have gastroduodenitis, it is forbidden to bake until a crust appears.
- In case of high acidity, the diet is based on porridge, non-rich vegetable and meat broths, soups, dairy products, vegetables and fruits, also consumed after heat treatment.
- Preferred dishes in pureed form. Restrictions also apply to the size of servings; this helps facilitate the digestion process; additional synthesis of fermenting substances is not required.
- At the stage of exacerbation of gastroduodenitis, high acidity can be normalized by adhering to table No. 1. This is a strict diet that includes:
- lean, soft-textured meats, fish, poultry;
- semolina, oatmeal, buckwheat;
- low fat dairy products;
- ripe, sweet grated or baked fruits and vegetables are used in the form of puree.
- The diet includes drinks such as weak tea, cocoa, compotes, fruit drinks made from sweet berries and fruits, and clean water. Alcohol, coffee, carbonated water, including mineral water, kvass, juices and fruit drinks made from citrus or sour berries are prohibited.
Fully or partially limited products
Borscht, okroshka, cabbage soup, and mushroom soup are completely excluded. Raw vegetables (cabbage, onions, turnips, spinach, sorrel, radishes, cucumbers), pickled and pickled vegetables, mushrooms, and canned vegetables are not allowed.
You need to give up fatty meats, smoked meats, canned meat and fish. It is forbidden to serve pasta, millet, pearl barley, corn, and barley porridge, as well as legumes as a side dish. You should not eat hot and fatty sauces, mustard, pepper, horseradish, fried or hard-boiled eggs.
Fresh white bread, rye bread and any flour products are prohibited. Avoid unripe and sour fruits and berries, dried fruits, and nuts. Salty cheeses, fatty cottage cheese, sour cream and cream are not allowed. Desserts and drinks include all confectionery, butter dough, chocolate, ice cream, kvass, carbonated drinks, coffee, alcohol. The diet is limited to greens (dill, basil, parsley).
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| celery (root) | 1,3 | 0,3 | 6,5 | 32 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| dried fruits | 2,3 | 0,6 | 68,2 | 286 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| pancakes | 6,1 | 12,3 | 26,0 | 233 |
| vareniki | 7,6 | 2,3 | 18,7 | 155 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| seasonings | 7,0 | 1,9 | 26,0 | 149 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| dairy products | 3,2 | 6,5 | 4,1 | 117 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| fried chicken | 26,0 | 12,0 | 0,0 | 210 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| dry white wine | 0,1 | 0,0 | 0,6 | 66 |
| dry red wine | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 68 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| cognac | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 239 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
What foods are excluded from the diet?
Table No. 1 is quite strict; all prohibitions must be followed. The patient is contraindicated:
- rich fish and meat broths, soups;
- any dishes made from cabbage and mushrooms;
- lard, sausages;
- canned food;
- fatty meat and fish products, fried dishes from them;
- raw vegetables;
- sour fruits and berries, juices;
- gooseberries, grapes;
- hot seasonings, sauces, mayonnaise, spices, ketchup;
- onions, any greens, garlic,
- rich bread, fresh pastries, rye flour products;
- sparkling water;
- coffee;
- alcoholic drinks;
- chocolate;
- ice cream.
Menu (Power Mode)
Several options for diet table menu No. 1
First option
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Before bedtime |
|
Second option
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Before bedtime |
|
Third option
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Before bedtime |
|
Dietary nutrition during exacerbation of gastroduodenitis is prescribed for 21 days, but depending on the patient’s complaints, individual characteristics of the body and objective examination data, it may vary. The length of time spent on a specific type of diet is determined in each specific case.
Sample menu for exacerbation of hypoacid gastroduodenitis (table No. 2)
Therapeutic nutrition for hypoacid gastroduodenitis is more expanded: the menu includes first courses that are prepared in richer meat/fish, mushroom, vegetable broth (soup, pickle, borscht) with the inclusion of various vegetables, potatoes, and cereals.
Second courses can be prepared using various technologies (boil, fry, bake) in the form of pieces of meat, fish or meatballs and cutlets, vegetables - in the form of casseroles and purees (white cabbage, potatoes, beets, carrots, zucchini, pumpkin, green peas. cauliflower).
The diet includes cottage cheese, various fermented milk products, vegetable and fruit juices diluted with water, bran decoctions, pureed sweet and sour fruits and berries.
Diet for gastroduodenitis in the acute stage
Start the diet from table No. 1a with the transition to menu No. 1b. Nutrition for gastroduodenitis in the acute stage restores tolerance to food, normalizes the secretion of gastric juice and motor function. To ensure optimal digestive process, eat every 2 hours. Portions are reduced to half the volume. Thanks to this, chyme is thoroughly processed and does not linger in the digestive tract.
They start with liquid and semi-liquid porridges, soups and jelly. The menu is dominated by carbohydrates. When the symptoms subside, expand the diet to include protein and fat components. Meat and fish are added, which are mechanically processed. Prepared in the form of puree and soufflé, as the condition improves, steamed cutlets and meatballs are added. Fats are allowed in the form of olive and sunflower oil.
Recipes
Here are recipes for preparing some dishes at home.
First meal
Carrot soup
Eggs, carrots, flour, low-fat meat broth, butter.
Boil the carrots in the prepared broth until tender, remove them and grate them on a fine grater. Fry the flour and mix thoroughly with the carrots. Combine the resulting mixture with the broth. Boil, add lightly beaten chicken eggs, add butter.
Vegetable soup with meat broth
Broccoli, carrots, tomatoes, zucchini, meat broth, low-fat sour cream, salt.
Boil vegetables in the prepared broth until tender, add salt and sour cream.
Second courses
Baked fish with mashed potatoes
Any white lean fish, potatoes, butter, salt.
Boil the potatoes, mash, add salt and oil. Bake the condemned pieces of fish in the oven.
Chicken breast with vegetables
Steam the allowed vegetables, cook the chicken breast in a slow cooker, pour in butter.
Desserts and drinks
Berry (fruit) cheesecake
Soft cottage cheese, oatmeal, sweet berries, butter, sweetener egg, gelatin.
Grind the oatmeal in a blender and mix first with the white, and then the yolk and sweetener. Add cottage cheese and mix. Place the resulting mixture in the prepared pan (grease the walls with butter), add the gelatin previously diluted in water, mix and place in the oven for 40 minutes.
Kefir + strawberry drink
Kefir 1%, granulated sugar, strawberries (strawberries).
Rinse the berries thoroughly with water and sort. Cover with sugar for one hour. Pour in kefir and beat with a blender until thick foam. Cool.
Organization of child nutrition
It is better to adhere to the nutritional plan outlined for each day of treatment:
- 1st day: the child should remain unfed, but he must be given plenty and often of warm drinks (weakly brewed tea, herbal decoctions with vitamin C).
- Day 2: Drinking plenty of fluids should also remain. You can supplement your diet with rice water, low-fat vegetable broth with crackers.
- Day 3: rice porridge and oatmeal may be included in the diet, but the cereal must first be ground in a blender. You can add a little butter (about 5 g) to the porridge. A few dry cookies are allowed.
- Day 4: the diet includes vegetable puree soup with a small amount of butter (4-5 g) or unrefined vegetable oil. You can add some crackers to the soup. For dessert, a small baked apple is allowed.
- Day 5: the diet becomes more varied by including various vegetable purees in the child’s diet, for example, potatoes or pumpkin, carrots. Protein foods include steamed meatballs made from lean poultry or fish. Dairy products are also allowed in the form of fermented milk products (ryazhenka, yogurt, low-fat cottage cheese). Dessert consists of dry unsweetened cookies.
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
Diet for erosive gastroduodenitis for a week
It is difficult for a patient diagnosed with erosive gastroduodenitis to get used to a new diet at first. To make the task easier, doctors draw up a sample menu for the week.
On the first day:
- For breakfast - rice porridge with milk and water, baked apple and low-fat cottage cheese.
- For second breakfast - semolina porridge.
- In the daytime - vegetable soup with cream, steamed fish, jelly.
- For an afternoon snack - a grated apple, 2 crackers and fruit juice.
- In the evening - buckwheat porridge, tea with sugar.
- Before going to bed - a glass of fermented baked milk.
On the second day:
- For breakfast - a boiled egg, 2 crackers, tea with milk.
- For second breakfast - curd pudding, chamomile tea.
- In the daytime - buckwheat soup, steamed omelette, apple compote.
- For an afternoon snack - fruit salad.
- In the evening - cheesecakes with sour cream, tea with sugar.
- Before going to bed - a glass of low-fat kefir.
We recommend reading: Chamomile tea: beneficial properties and contraindications
On the third day:
- For breakfast - oatmeal with milk, coffee drink.
- For second breakfast - banana.
- In the daytime - baked meat soufflé, jelly.
- For an afternoon snack - cottage cheese casserole.
- In the evening - steamed fish, mashed potatoes, carrot and apple salad, tea with milk.
- Before going to bed - a glass of vegetable juice.
On the fourth day:
- In the morning - buckwheat porridge with milk, 2 crackers, tea with sugar.
- For second breakfast - a sandwich with butter and juice.
- In the daytime - noodle soup, boiled rice with liver, dried fruit compote.
- For an afternoon snack - low-fat cottage cheese and baked pear.
- In the evening - rice casserole, tea without sugar
- Before going to bed - natural yogurt without additives.
On the fifth day:
- In the morning - oatmeal with diluted milk, chicory.
- For second breakfast - an apple.
- In the daytime - soup with chicken broth, breast with buckwheat. Compote.
- For an afternoon snack - carrot and raisin salad.
- In the evening - steamed cutlets, boiled rice, jelly.
- Before going to bed - a glass of fermented baked milk.
On the sixth day:
- In the morning - cottage cheese casserole, 2 biscuits, tea with sugar.
- For second breakfast - baked apple.
- In the daytime - vegetable soup, beet and raisin salad, jelly.
- For an afternoon snack - low-fat cottage cheese.
- In the evening - baked low-fat fish, stewed vegetables, compote.
- Before going to bed, drink chamomile tea.
We recommend reading: Beetroot: beneficial properties and contraindications
On the seventh day:
- In the morning - steamed omelet, tea with sugar.
- For second breakfast - apple and pear puree, 2 crackers.
- In the daytime - rice porridge, raisin compote.
- For an afternoon snack - a glass of natural yogurt without additives.
- In the evening - boiled beef, pureed vegetables.
- Before going to bed, take a rosehip decoction.
Before going to bed, you need to take a drink that soothes the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine.
Attention! Diets and nutrition for erosive gastroduodenitis should be followed from 6-8 days after the elimination of acute symptoms. In the first days, the patient completely refuses to eat and should only drink liquid.
Comments from nutritionists
For symptoms of gastroduodenitis, treatment with diet is a necessary condition for recovery. During this period, avoid taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( diclofenac , indomethacin , and buprofen , and spirin etc.), which are often prescribed for joint diseases. If there is a need to take them, then it is recommended to take them only after meals.
During an exacerbation, it is mandatory to take aloe and B of nicotinic acid for elderly patients .
Exacerbations of gastroduodenitis in children are often provoked by psycho-emotional factors, therefore, the comprehensive treatment of a child must necessarily include psychotherapy to eliminate stress and nervous overload.
Diet for chronic gastroduodenitis: list of products
Proper nutrition is an important component of complex treatment of the disease. In order for gastroduodenitis to proceed mildly and without complications, it is important to adhere to a special diet, which, together with other methods of therapy, allows for complete recovery.
Advice! In order not to forget what foods are allowed and prohibited, it is recommended to print the list and hang it on the refrigerator.
What can you eat if you have gastroduodenitis?
In chronic cases, table No. 5 is often prescribed. It involves stabilization and normalization of the functioning of the bile ducts and liver. Diet for gastroduodenitis table No. 5 significantly reduces complexly soluble fats. It includes enough carbohydrates and peptides.
Diet No. 1 is recommended for chronic gastroduodenitis during exacerbation, during remission and with high acidity. It is most often used at the last stage of treatment, since it does not contain products that stimulate gastric secretion. For diseases that occur with low acidity, use diet No. 2.
Mushroom puree soup is an excellent solution for lunch with therapeutic nutrition Table No. 2
Semolina porridge is the best product for dietary nutrition. It is allowed to be used for any form of disease.
With increased acidity, the diet for gastroduodenitis should correspond to the principles of table No. 1:
- crackers;
- yesterday's gray and white bread;
- durum wheat pasta;
- olive, sunflower, flaxseed, butter;
- vegetable and fruit juices, green and black tea, rosehip decoction;
- lean meat (rabbit, beef, turkey);
- cereals;
- sweet vegetables and fruits, pre-heat-treated;
- vegetarian puree soups;
- carrots, pumpkin, zucchini, peas, dill and potatoes;
- scrambled eggs).
With low acidity (in addition to the above products) - raw vegetables, meat, mushroom and fish broths, chocolate in small quantities.
The first place on the menu is occupied by cereals: oatmeal, rice, semolina. The natural mucus of oatmeal envelops the gastric mucosa and protects against the action of hydrochloric acid.
On the second - porridge and vegetable soups, puree soups and broths, with finely chopped or chopped vegetables. Lean meat, boiled sea fish, steamed vegetables. Drinks that are allowed include gelatinous dishes, milk, and rosehip decoction.
Attention! The choice of one product or another for the diet depends on the type and severity of the disease.
The diet for superficial chronic gastroduodenitis limits the consumption of too hard and heavy foods and semi-finished products. The menu includes lean meats, seafood, fish, and protein-rich dairy products. Raw vegetables and fruits are allowed.
The diet for superficial gastroduodenitis includes:
- boiled potatoes;
- beets;
- fruit purees;
- boiled or steamed meat.
We recommend reading: Beetroot: beneficial properties and contraindications
The basic diet for atrophic gastroduodenitis is table No. 2. It allows the consumption of meat and fish dishes, fermented milk and flour products, eggs, rye bread, cereals with milk and unleavened cheese. You can have a small amount of ham without fat.
We recommend reading: What are the benefits of orange, properties and contraindications
During the period of remission of chronic gastroduodenitis, the diet is supplemented with vegetable purees, baked apples, oranges and tangerines. You can add vegetable oils, but only to prepared dishes. Dairy and fermented milk products are consumed in small portions. Tomatoes, lean meat, jam, marmalade, casseroles and soft-boiled eggs are allowed.
Recommended reading: Benefits of tomatoes for the body
What is not allowed in the diet for gastroduodenitis
Prohibited foods should not be consumed even in small quantities. They affect the injured mucosa, which can provoke an exacerbation of chronic gastroduodenitis.
The following foods are included in the diet ban:
- barley, corn, pearl barley and millet porridge;
- spicy, fried and fatty foods;
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- berries with coarse grains (raspberries and currants);
- freshly baked bread and pastries;
- fatty, smoked and canned fish;
- salo;
- melted butter;
- canned food and semi-finished products;
- fatty meats and poultry.
If you prescribe a diet for gastritis, it means you have to forget about desserts, however, tiramisu fits perfectly into table No. 2
A diet for gastroduodenitis with low acidity excludes gooseberries, figs and dates. You cannot drink grape juice, eat sweet peppers and all legumes.
A diet for illness with high acidity prohibits the use of fried and boiled eggs. You cannot eat radishes, radishes, white cabbage, or ice cream.
Results and reviews
Dietary nutrition during gastroduodenitis and during periods of its exacerbation allows you to normalize the function of the gastrointestinal tract in the shortest possible time: pain, nausea, a feeling of heaviness, belching of food disappear, the general condition is normalized, and appetite appears.
- “... I have been suffering from gastroduodenitis with high acidity for many years. Any error in nutrition (alcohol, overeating, spicy foods) causes an exacerbation. I started cooking all my food in a double boiler, eliminating spicy and sour foods. The condition has improved significantly. I’ve already adapted.”
- “... After the holidays, belching, pain and heaviness in the stomach appeared. Doctors diagnosed gastroduodenitis. Treatment of symptoms of gastroduodenitis with diet was carried out at home. A month later everything returned to normal. Now, whenever there is an exacerbation, I immediately go on a diet.”
- “... I have a sad experience. After gastroduodenitis, due to the specifics of my work, I ignored the doctors’ recommendations on dietary nutrition and hoped to get by with medications. The result is a duodenal ulcer two months later. So my advice to everyone is don’t ignore your diet.”
- “... When there is an exacerbation of gastroduodenitis, I always save myself with a diet. Usually 2-3 weeks and everything returns to normal.”
The main objectives of the diet for gastroduodenitis
Nutrition for diseases of the digestive system has general principles. Diet for gastroduodenitis is the foundation of the healing process. It is aimed at reducing the inflammatory process, restoring damaged epithelium, normalizing peristalsis and improving food absorption.
Therefore, it is important to adhere to the following recommendations when drawing up a treatment menu:
- It is necessary to determine what kind of nutrition the patient can eat during an exacerbation and during remission. The main table is diet No. 1 according to Pevzner. In case of severe clinical symptoms, a modification is prescribed - table 1 a, which includes thorough mechanical and thermal processing of products, with a predominance of liquid dishes. As the condition improves, they switch to a diet of 1 b. Recipes in the form of semi-viscous and ground dishes are recommended. Patients with atrophic inflammation are prescribed table No. 2.
- Limit table salt, add foods high in vitamins A, B, C.
- Avoid products that can cause chemical burns to the mucous membranes.
- Observe the temperature regime for serving food, especially in acute conditions.
- Keep breaks between meals for about 2-3 hours to maintain optimal gastrointestinal motility.
- Steam, boil or stew food to preserve the taste and nutritional qualities of food and beneficial chemical elements.