Many people are interested in what HPV is and how the diseases it causes develop. Human papillomavirus is the general name for a family of viruses that cause papillomas, dysplasia, or cancerous growths on the skin and mucous membranes in humans. This is the most common viral infection. It is quite difficult to avoid infection, since the infection does not always enter the body through the fault of the infected person.
Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus is very dangerous, since such a neoplasm provokes various kinds of complications and can gradually develop into a malignant tumor.
Features of the disease
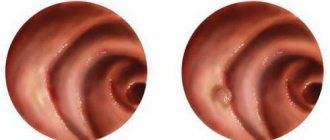
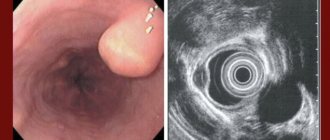
Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus is dangerous because such a neoplasm is detected only during a diagnostic examination using an endoscope. Visually, it is a small flat growth with an uneven surface.
It forms in the middle or lower part of the esophagus and may consist of one such growth, or may include several formations. In this case, with the help of an endoscopic examination, you can see something like a bush with very thin processes of the epithelium.
Papilloma can be of various sizes. Often its diameter does not exceed 3 mm, but there are known cases of growth of the formation up to 20 mm. The color of such a neoplasm is no different from the color of the mucous membrane. The first sign of an expanded papilloma may be short-term pain, which is similar in sensations to those that occur with gastritis.
Causes
It is very important to understand exactly what HPV is, why the disease occurs, what the symptoms may be, and how treatment is carried out. The exact causes of growths in the esophagus have not yet been fully studied, but it is known that the provoking factor is the effect of papilloma viruses on the human body.
The virus can remain latent in the body for a long time and only appears when the immune system weakens. There are a number of factors that contribute to the development of esophageal papilloma. Among them it is necessary to highlight:
- constant consumption of spicy, fried, salty foods;
- habit of consuming too hot foods or drinks;
- alcohol or tobacco abuse;
- presence of burns of the esophagus;
- chronic esophagitis;
- pathologies of the digestive organs.
After a long period of inactivity of the virus in the body, it can suddenly become more active, as a result of which squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus begins to sharply increase in size. This is facilitated by the presence of some favorable factors, namely:
- improper diet;
- nervous breakdowns, frequent stress;
- excessive physical activity;
- following strict diets.
The main reasons for the activation of the virus are exhaustion of the body and weakened immunity.
Causes of papilloma in the esophagus
The causative agent of growths is papillomavirus, which has many strains. In this case it is the 52nd type. Every carrier of the virus is at risk of developing cancer, but HPV may never appear, remaining in the inactive stage in the human body until the end of life.
A connection has been established between decreased immunity and the appearance of tumors. Some factors also influence their growth:
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages,
- smoking,
- abuse of spicy and fatty foods,
- chronic heartburn,
- recurrent gastritis.
All this creates microtraumas of the esophagus, which creates a favorable environment for the development of tumors.
How does infection occur?
Often, infection with the virus occurs through contact with a sick person. This can be the transfer of the disease from mother to fetus during pregnancy, through poorly sterilized instruments in manicure and dental offices, during sexual contact, and even through the skin.
Even if the patient has undergone treatment and the esophageal squamous cell papilloma has been removed, there is no guarantee that a relapse will not occur.
Regardless of the method of infection, in all cases the human mucous membrane is damaged. Penetrating into the esophagus, the virus is literally instantly absorbed into the walls, provoking the formation of a neoplasm.
Symptoms of neoplasms
This pathology can develop without manifestations for several years. If a large papilloma has formed in the esophagus, a person may feel the following ailments:
- sensation of a foreign object in the esophagus;
- painful sensations are felt at the moment of swallowing;
- the passage of food through the esophagus causes severe discomfort;
- sudden and causeless pain in the chest area;
- unreasonable urge to vomit;
- excessive salivation;
- belching.
Important to remember! People who are at risk need to be examined periodically! Since a tumor that stays in the esophagus for a long time can develop into a malignant tumor.
Diagnosis of pathology
It is not possible to visually determine the appearance of a growth in the esophagus. If papilloma is suspected, the patient is referred for the following hardware tests:
- computed tomogram;
- contrast fluoroscopy;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
The results of the studies help to accurately determine the presence of a growth in the digestive tract.
Main symptoms
For a long time, the neoplasm in the lumen of the esophagus does not manifest itself in any way. Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus is a growth that looks like a wart, has a heterogeneous surface and a papillary structure. Its hue is practically no different from the mucous membrane of the esophagus, and at the initial stages the neoplasm does not rise above the surface of healthy tissue.
Mostly, papillomas are single and localized in the lower third of the esophagus. However, sometimes they can be multiple, grouped in the form of a bush-like growth, and then a narrowing of the esophagus may even be observed. As the tumor increases in size, the patient experiences unpleasant symptoms, namely:
- frequent belching;
- burning and soreness in the solar plexus area;
- fatigue and severe weakness;
- nausea and vomiting.
In addition, there is often a sensation of a foreign body in the throat, which gives the impression of something stuck to the walls of the organ. Associated symptoms may also occur. A person sometimes feels as if food is stuck in the esophagus.
If these signs occur, you should definitely visit a doctor who will prescribe the appropriate diagnosis and subsequent treatment. In some cases, such a neoplasm can cause severe salivation, but few people pay attention to all these signs.
Symptoms and signs of development
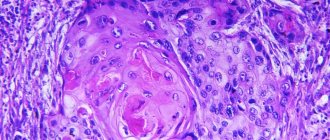
Identification of papillomas in the early stages of development occurs only during the diagnostic process. But if squamous cell papilloma develops in the body long enough, it leads to deformation or narrowing of the esophagus and causes the patient the following symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- difficulty passing food;
- epigastrium;
- increased salivation;
- weakness, sweating;
- constant feeling of a “lump” in the throat.
The problem with diagnosing the virus is that all these symptoms are episodic in nature and pass as quickly as they appear.
To date, virologists have identified more than 100 varieties of papilloma virus strains. Most of them are non-oncogenic (with a low risk of malignant tumors).
Carrying out diagnostics
Esophageal papillomas can be diagnosed by conducting a comprehensive examination, as well as taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s condition. Initially, the doctor examines the patient's esophagus using an esophagoscope. This procedure is safe and almost painless. To identify neoplasms, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- X-ray of the esophagus;
- performing endoscopy;
- tomography;
- laboratory research;
- test for the presence of hidden HPV.
It is worth noting that the faster pathology is detected, the faster treatment can be carried out, preventing the occurrence of dangerous complications. If a patient is prescribed fibrogastroduodenoscopy, then it is imperative to know how FGS is done and how to prepare for this procedure.
This method helps to examine the stomach and detect tumors even at the initial stage of their growth. Many people are interested in how FGS is done using modern techniques, and whether the procedure can be performed completely painlessly. In many clinics, patients are given anesthesia so that they do not feel discomfort.
Specifics of the FGS procedure
Before starting the procedure, the doctor numbs the oropharynx with a local anesthetic solution. Thanks to this, this manipulation causes virtually no discomfort and is well tolerated. The patient assumes a position - lying on the left side. To simplify the insertion of an endosocope (a special tube with a miniature camera and a compact illuminator), a ring - a mouthpiece - is placed between the patient's teeth. The device is passed through it. The patient then makes one swallowing movement, which helps the doctor guide the fiberscope into the esophagus. And the specialist begins to carefully examine the cavity of the esophagus.
Feature of treatment
Once the doctor has made a diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a comprehensive treatment, which includes measures such as:
- drug therapy;
- traditional medicine;
- carrying out the operation.
Treatment is carried out in stages, since this type of neoplasm belongs to a high-risk group and has certain characteristics. The operation can be performed with complete or partial excision of the growth. Complete removal of the esophagus is very rare and is prescribed only if a malignant neoplasm is present. After this, a course of chemotherapy is carried out, as well as maintenance treatment with medications.
Medicines block the subsequent development of the virus, and this method of therapy refers to preventive measures against relapses.
Classification of degrees of Barrett's esophagus
Esophageal polyp ICD 10: diagnosis code D13.0
This neoplasm of the esophagus is classified in medicine by origin:
- Hyperplastic polyp of the esophagus - is formed due to the proliferation of normal, healthy tissue. This species is practically not prone to degeneration into a malignant formation. Hyperplastic polyps often occur in people who lead an unhealthy lifestyle, neglect proper nutrition, and prefer fast food and smoking.
- A neoplastic polyp of the esophagus (what causes polyps to arise is already clear) develops from pathological cells. This type of esophageal polyp can be either benign or cancerous.
- Inflammatory is localized directly at the site of inflammation, where the integrity of the organ tissues is compromised. There is a high probability of an inflammatory growth occurring against the background of esophagitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the esophageal tube.
Polyps on the esophagus are not dangerous as long as they are small in size and not numerous in number. These compacted growths can be multiple and spread to neighboring internal organs; this phenomenon is called polyposis. The process of polyp spread is considered to be started if the neoplasms begin to systematically increase in size.
Not only the frequency of observation during the year in a medical institution, but also the treatment of the disease depends on the stage and degree of development of the disease. Even practically incurable disease processes that are little known to science, scientists try to break them down into variants of their course to make it easier to work with them.
Is there any classification of Barrett's esophagus or is the disease only in one of the initial stages of development? Yes, there are several classifications that were developed taking into account the location, distribution and structure of the process.
Drug therapy
Patients diagnosed with papilloma of the food tract are prescribed a course of antiviral drugs. You can reduce the activity of the virus and activate the body’s defenses using medications such as:
- "Viferon";
- "Interferon";
- "Acyclovir";
- "Amiksin".
The doctor selects the medications strictly individually. In addition, a course of vitamins is required.
Surgical intervention
To avoid complications, if there is severe narrowing of the esophagus, surgery is indicated. Several methods can be used for this, namely:
- laparoscopy;
- endoscopy;
- esophagotomy.
When performing endoscopy, access to the pathological growth is through the mouth or nose. This intervention method is used for small papilloma sizes.
Laparoscopy is considered a low-traumatic procedure, since removal is performed through a small incision. Within a day, the patient can return to normal life. Esophagotomy is an abdominal operation, which is performed when the tumor is large.
In some situations, it is necessary to remove a piece of the esophagus, and in this case, plastic surgery is needed after the procedure.
Traditional medicine
If you have esophageal papilloma, replacing medications with folk remedies is strictly prohibited; they can only be used as an auxiliary therapy. The most effective home remedies are:
- infusions of medicinal herbs;
- propolis;
- garlic infusion.
To make a medicinal infusion, you need to take the roots of elecampane, licorice, and calamus in equal proportions. Then 1 tbsp. l. Pour 1 cup of boiling water over the finished collection and leave to brew until it cools completely. Filter the finished drink and take ¼ glass 3 times a day.
Instead of tea, you can consume an infusion of raspberries, nettles and currants. This is a good general strengthening remedy that should be taken several times a day. To do this, mix all components in equal proportions, then 1 tsp. Pour 1 cup of boiling water over the finished mixture. Leave to infuse for 30 minutes. Drink the finished infusion as tea in small sips.
Garlic infusion will be no less effective. To do this, pass 3 cloves of garlic through a press and pour 1 cup of boiling water. To do this, crushed cloves are filled with water and left for 2 days. You need to take 10 g of the finished product before bedtime. You can add freshly squeezed vegetable juice to the infusion.
Propolis has good antiviral properties. To strengthen the immune system, a mixture made from dried fruits, nuts, honey and lemon will be very useful. You need to take this medicine daily for 1 month, 1 tbsp. l. on an empty stomach.
Potato juice helps a lot. To do this, grate the raw potato tuber. Squeeze the juice out of it, and then consume 1 tbsp every morning. l. on an empty stomach. The duration of therapy is 1 month.
These recipes are very good for preventing many other diseases, but do not guarantee complete recovery. That is why doctors recommend complex therapy, which helps to get rid of the existing problem much faster.
Manifestations and treatment of the disease
This pathology is quite rare, so it is difficult to suspect its presence without the help of a specialist. Its symptoms are similar to those of many other diseases, and examination is required to confirm the diagnosis. However, its signs cause considerable discomfort to the patient so that he does not pay attention to them. This disease has the following features:
- nausea;
- frequent belching;
- burning;
- general weakness;
- increased fatigue;
- pain in the solar plexus area;
- excessive salivation;
- sensation of a foreign body inside, which occurs when swallowing.
If such symptoms are detected, you should consult a specialist to identify the causes of these phenomena. The doctor must conduct a diagnosis, during which he can confirm either this diagnosis or establish what other abnormalities caused such manifestations. Diagnostic methods include endoscopy and contrast radiography. A cytological examination will also be required, with the help of which it will be possible to determine the type of neoplasm.
Important addition: Psoriatic psoriasis reviews for psoriasis
Even non-oncogenic papillomas of the esophagus can eventually cause cancer. And the presence of oncogenic neoplasia significantly increases such risks. In addition, if there is a papilloma in the esophagus, many other difficulties arise. The symptoms that appear will only get worse as the patient’s condition worsens, so you need to quickly begin treatment.
Therapeutic actions for such pathology are aimed at eliminating the causes and manifestations. In order to neutralize the traumatic factor, it may be necessary to make certain lifestyle changes:
- normalization of nutrition;
- rejection of bad habits;
- avoiding excessive loads, etc.
In addition, treatment with medications is necessary:
- antiviral (Groprinosin);
- immunomodulatory (Immunal, Interferon), etc.
However, all of these methods are most often carried out after removal of the papilloma to prevent relapse. The fact is that in most cases, only surgery can get rid of the unfavorable symptoms associated with this problem. The intervention is carried out endoscopically or laparoscopically; abdominal surgery is less commonly practiced. With timely removal of the growth and proper postoperative recovery, the prognosis of the disease is favorable.
[poller_master poll_id=»1" extra_class=»opros»]
Forecast
In some cases, papilloma, even without treatment, may not increase in size throughout life and does not cause any concern. The prognosis of such tumors after surgery largely depends on each clinical case, the volume and type of intervention. If the tumor is completely removed and there are no complications, the outcome of the disease is quite favorable.
Even if signs of a tumor becoming malignant are detected at an early stage, its timely removal allows one to achieve good results and survival rates. Relapses are quite rare.
If a malignant tumor is detected at the stage of metastasis and germination into the deep layers of the organ, then the prognosis is quite unfavorable, and complete recovery is no longer possible. If treatment is carried out only by surgery, then the patient's survival rate is no more than 5%.
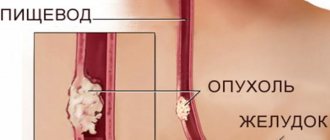
What is esophageal papilloma?
Neoplasms that are found on the walls of the digestive organ are a cluster of benign cells. They form small mastoid processes of the same color as the healthy surface of the mucosa. Their sizes vary from a few millimeters to 3 centimeters.
Most often, single growths occur, but there are cases of papillomatosis, when they take on bush-like forms. Neoplasms are located on the lower or middle sections of the food tube.
So far, this disease has been little studied by specialists. It may not have a clear pattern of symptoms for many years, so it is rarely detected at an early stage. In itself, such a tumor is not dangerous, but it can transform into a malignant one at any time and lead to a serious condition and death.
Carrying out prevention
To prevent the formation of squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus, it is very important to follow the following rules:
- regular visits to the doctor and preventive examinations;
- refusal to drink alcohol and smoke;
- timely treatment of diseases that lead to decreased immunity;
- proper nutrition;
- prevention of overwork and stress.
There are no specific preventive measures, which is why it is very important to be attentive to your health. This will prevent complications from occurring.