What is mucous membranous colitis
Colitis (colitis, from Latin colon - colon, -itis - inflammation) is an inflammatory lesion of the large intestine .
The inflammatory process affects the mucous membrane and submucosa of the large intestine. In the modern international classification there is no such thing as mucous or membranous colitis . This is a generalized name that clearly demonstrates one of the signs inherent in almost all colitis: the presence of mucus and membranes (constrictions) in the stool during bowel movements.
In ICD-10, colitis is encrypted in several categories and has different designations depending on the cause and the affecting agent (for example, K51 - ulcerative colitis, K51.5 - mucosal proctocolitis, K51.8 - other ulcerative colitis, K52 - other non-infectious gastroenteritis and colitis and etc.).
Etiology and pathogenesis
This type of colitis is called “membranous” because of the presence of mucous films on the evacuated feces. Experts associate the development of the disease with the penetration of sensitizing (allergy-provoking) agents, bacterial and fungal infections. Other reasons have been noted:
- long-term uncontrolled use of medications;
- atherosclerotic changes in the blood vessels supplying the colon;
- exposure to toxic substances, food poisoning;
- chronic constipation, intestinal atony.
Sometimes the disease is disguised as pancreatitis or inflammation of the appendages (in women), which makes diagnosis difficult. This fact is explained by the proximity of the organs of the genitourinary and digestive systems.
Attacks occur unexpectedly, under the influence of negative emotions or the consumption of food intolerable to the patient. Lasts from several hours to a day or more. They end with the release of loose stool with whitish mucus in the form of plates, shaped like fragments of the intestinal mucosa, which increases the patient’s anxiety.
The disease worsens against the background of psychotraumatic episodes, overwork, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Patients aged 20 to 60 years are most often affected.
Types of pathology
Colitis is divided into acute and chronic forms of the disease . Chronic is divided into two stages: remission and exacerbation.
According to the nature of the course, chronic colitis can be classified into:
- monotone;
- progressive;
- recurrent;
- hidden (latent).
Most often, the disease has a specific localization , affecting the left or right half of the intestine. In extensive forms of colitis (total colitis), the mucous membrane is affected along its entire length.
Depending on the characteristics of the inflammatory process, colitis is divided into:
- catarrhal;
- fibrous;
- necrotic;
- ulcerative.
Colitis is also classified according to the causes of the disease : infectious, parasitic, toxic and medicinal, nutritional, neurotic and neurotrophic, due to mechanical damage to the intestines, mixed origin, radiation, secondary, unknown origin.
Treatment of mucous colitis
When diagnosing this disease, the main method of treatment is diet, which must be followed regardless of the form and type of disease. In this case, the features of the course of the pathology are taken into account, as well as the reasons that provoked its occurrence. If the causative agent is an infection, the patient is prescribed antibiotics.
If mucous colitis and its symptoms were provoked by therapy using medications to eliminate another disease, then their abolition is envisaged.
Treatment of the chronic form involves the use of a complex technique in the form of heat therapy and sessions with a psychotherapist. Treatment in a sanatorium is especially welcome. In order to recognize colitis, and, in addition, to prescribe the necessary medications and treatment methods, you should visit a gastroenterologist or proctologist, who will make the best decision for each specific case.
Causes
The main cause of acute colitis is infection of the body by pathogenic bacteria and protozoa. Allergic reactions, viral diseases (for example, influenza), nutritional disorders, and taking medications can also be a trigger.
Chronic colitis is often the result of illiterate and inadequate treatment of acute colitis. The causes of chronic colitis include :
- helminthiases;
- dysbacteriosis;
- toxic effects of various substances, including medications and endogenous toxins;
- nutritional reasons (diet disorder, monotonous diet, abuse of spicy food and alcohol, enzymatic deficiency);
- allergic reactions;
- reactive responses to inflammatory processes in anatomically related organs (inflammatory processes in the pelvis), inflammation in directly related organs (pancreas, stomach, gall bladder, liver, small intestine).
Very often, the causes are combined to one degree or another , which complicates diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms
The main symptom due to which the name “mucosal colitis” came into use is the presence of mucus in the stool . Mucus may appear in small amounts or be the only result of a bowel movement with little or no stool. Mucoid colic is a prime example of this.
Another recognizable sign is the presence of membranes, constrictions and white ribbons in the stool. It is thanks to this feature that colitis became known as membranous colitis.
The disease can be accompanied by both diarrhea and constipation in one patient . One of the most striking symptoms is constipative diarrhea. After 1-2 days of constipation, the stool softens a second time; after the dense fecal plug is released, the patient begins to have diarrhea with an unpleasant, putrid odor.
Colitis is accompanied by pain of varying intensity and nature . There may be nagging pain in the lower abdomen localized to the right or left, depending on the location of the inflammation, or cramping attacks.
Increased pain and frequent bowel movements are usually observed in the morning after eating . After defecation or passing gas, the pain subsides, but does not go away. With a widespread inflammatory process, they can cover the entire abdomen and intensify with movement, especially with shaking.
Flatulence is a constant companion of all colitis , as is tenesmus (painful urge to defecate, which is ineffective or ineffective). After going to the toilet, a person often feels that the intestines are not completely cleansed.
The general condition of patients with chronic colitis is little affected; low-grade fever is rarely observed. However, such patients often suffer from disorders of the autonomic and central nervous system :
- reactive responses of the cardiovascular system (tachycardia, cold sweat, weakness, dizziness, drop in blood pressure, fainting, arrhythmia, heart pain);
- vascular dystonia;
- tendency to spasms of smooth muscles;
- increased irritability;
- depression.
The general condition of patients with acute colitis is significantly impaired . The disease is manifested by sudden and continuous diarrhea and vomiting. Abdominal pain is diffuse or cramping in nature. The temperature is elevated, can reach critical values, and convulsions are possible. In severe cases of the disease, signs of dehydration and electrolyte imbalance appear.
Important! If these symptoms occur, especially in children, you should immediately seek medical help.
Membranous colitis and its clinical symptoms
Membranous mucous colitis is an inflammatory process that causes degenerative changes in the walls of the colon. Its acute form can occur in paroxysms. Characteristic symptoms of the pathology are:
- Having severe abdominal pain.
- Inability to release gases, and, in addition, constipation.
- The appearance of a rash on the skin that is allergic in nature.
- Presence of fever and loose stools.
- Presence of headache and rapid heartbeat.
With membranous colitis, people may suffer not only from the digestive system, but also from the nerves. In this condition, patients may experience autonomic dysfunction combined with nervous excitability, drowsiness, weakness and apathy.
Diagnostic features
A correct diagnosis is the first step to recovery . The doctor collects anamnesis: asks the patient about past illnesses, dietary habits, the presence of psycho-emotional problems at home and at work, and the possibility of mechanical damage to the intestines.
The patient is examined and prescribed:
- laboratory tests (general blood and urine analysis, scatological and bacteriological examination of stool);
- endoscopic examinations (colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy);
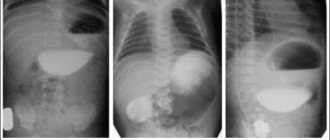
- X-ray examinations (radiography of the abdominal organs, irrigoscopy);
- consultation of related specialists (gynecologist for women, urologist for men).
Based on the data obtained, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Treatment
Therapy for colitis includes both conservative treatment and surgical intervention . The first method includes medication, physiotherapy, herbal and dietary therapy.
Medicines
The following drugs are used in drug treatment::
- antibacterial therapy to eliminate the source of infection (broad-spectrum antibiotics, nitrofuran derivatives, sulfonamide drugs, tetracycline group of antibiotics);
- drugs that normalize intestinal microflora (“Bifikol”, “Bifidumbacterin”);
- antiviral drugs;
- antispasmodics (“Platifillin”, “No-shpa”, “Papaverine”);
- analgesic drugs that enhance the effect of antispasmodics (“Analgin”, “Amidopyrine”).
Microenemas and suppositories play an important role in drug therapy . They facilitate the process of defecation during constipation, have a disinfecting, analgesic, and some have a healing effect. Cleansing enemas are prohibited during an exacerbation of colitis in order to prevent even greater irritation of the mucous membrane. Patients with constipation are prescribed oil enemas.
Traditional methods
In the treatment of colitis, folk remedies are used, water infusions and decoctions recognized by official medicine :
- chamomile;
- St. John's wort;
- alder cones;
- eucalyptus leaves.
These herbal remedies have astringent and antiseptic effects .
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures during an exacerbation to relieve spasm and inflammation are prescribed to patients on a limited basis :
- light warming in the form of heating pads, alcohol, water compresses, compresses with vaseline oil;
- electrophoresis with “Platifillin”, “Novocaine”, calcium chloride;
- irradiation of the abdomen with ultraviolet radiation with a gradual increase in time.
When the process subsides and there is no tendency to bleeding , UHF, ultrasound, active thermal treatment (ozokerite, paraffin), thermal baths (coniferous, radon), and mud therapy are prescribed.
Physical activity
Special complexes of physical therapy and gymnastics, walking , skiing and skating, outdoor games are indicated for all patients with chronic colitis during the period of remission.
Important! You should exclude from exercises those in which the main load is directed to the abdominal muscles.
The main rule for all exercises is that physical activity should bring joy, not pain and fatigue.
Diet
Diet therapy has an important therapeutic effect ; neglecting the diet is not only impractical, but also dangerous.
During an exacerbation, the patient is prescribed gentle nutrition for five days. The diet includes :
- white crackers;
- low-fat meat or fish broths with the addition of pureed meat and fish;
- mucous decoctions with pureed porridges;
- steamed diet omelette;
- jelly, unsaturated decoctions of permitted berries and fruits (sweet apples, blueberries, quince, rose hips, bird cherry);
- fresh low-fat cottage cheese.
Important! Milk, fresh vegetables and fruits are strictly prohibited.
As the condition improves, the diet expands . Dairy products are added: mild cheese, kefir, milk porridge with ⅓ milk. Pearl barley and millet porridge are prohibited. Meat and fish dishes are not ground; compotes with pureed berries and fruits, baked apples, marshmallows, marshmallows, and jam are added. Butter is allowed to be added to porridge.
During the period of remission, permitted foods are supplemented with raw vegetables and fruits, lightly salted soaked herring, low-fat ham, salads with sour cream, and diluted juices. Meat and fish can be fried without breading and baked.
When compiling a dietary menu, the doctor always takes into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Nutrition rules
With the onset of an attack of membranous colitis, it is necessary to abstain from food for the first two days. To replenish fluids, drink herbal infusions without sugar. After spasms and pain are relieved, easily digestible food that does not irritate the intestinal mucosa is introduced into the diet. The table shows recommended and prohibited products.
| Featured | Prohibited |
| White bread crackers. | Baking, confectionery. |
| Porridge with water (rice, oatmeal). | Hard cheeses. |
| Vegetable soups without cabbage. | Whole milk. |
| Lean meat (turkey, chicken, lean beef). Boiled sea fish | Fried foods, smoked meats, semi-finished products, spices. Canned food, marinades. |
| Boiled and steamed vegetables. Low-fat cottage cheese. | Fatty meat, lard, rendered fats. |
| Liquid mashed potatoes. | Legumes, nuts. White cabbage. |
| Lactic acid products. | Strong tea and coffee. |
| Peeled, pureed ripe fruits. | Carbonated drinks. |
| Compotes and jelly from fresh berries. | Alcohol. |
It is important to maintain a drinking regime - at least 1.5-2 liters of water per day. It is better to steam, boil or bake food in the oven. You should eat 5-6 times a day, little by little. Serve dishes warm, but not hot.
After recovery, you should adhere to the rules of a healthy diet: do not eat fast food, too salty or spicy foods, limit sweets, exclude foods that cause allergies and fermentation in the intestines.
Constipation should not be allowed. Prunes, boiled beets, carrots, and fresh apple puree will help to establish peristalsis. Food should be high in calories, but not overload the stomach.
Possible complications
Surgical intervention for colitis is practiced to a limited extent, only when a person’s life is threatened. This is mainly due to dangerous complications :
- perforation of the intestine and outflow of its contents, which leads to peritonitis;
- continuous bleeding from the rectum;
- acute intestinal obstruction due to strictures (narrowings) and adhesions.
and following the doctor’s recommendations will help to avoid complications
Prognosis and prevention
With timely and adequate treatment of acute colitis, in most cases, complete recovery occurs without chronicity of the disease.
Chronic colitis, with proper treatment and compliance with all recommendations, goes into a stage of long-term remission and does not bother the patient for a long time.
Preventing a disease is many times easier than treating it. Preventive actions are aimed at preventing acute intestinal infections :
- personal hygiene;
- careful processing of products;
- refusal to purchase questionable products and in places of unauthorized trade.
A balanced diet, giving up bad habits and an active lifestyle are the key to the health of not only the gastrointestinal tract, but also the body as a whole.