general information
Recently, this diagnosis has been made more and more often. It is quite natural that ordinary people want to know the answer to the question: intestinal pneumatization - what is it? After all, the ability to identify pathology in a timely manner and seek help affects the duration and effectiveness of treatment.
Nowadays, this diagnosis is given to almost every third patient who comes to the clinic to check the gastrointestinal tract. If you find yourself in such a situation, first of all check with your doctors how to restore intestinal motility. This will help avoid complications.
Is intestinal pneumatization dangerous? What does this name hide behind it? The diagnosis usually does not involve serious risks. Nevertheless, the present disorders significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life. The most unpleasant symptoms are diarrhea, gas, bloating. With this disease, changes are observed in the structure of the intestinal walls. Often, the affected areas become the site of the formation of cavities in which air accumulates. In addition, there is a risk of developing a cyst.
Associated symptoms
Since pneumatosis is more of a symptom or a complication, its symptoms are directly related to the clinical picture of the underlying disease.
Nonspecific manifestations of pneumatosis include:
- periodic cramping pain in the abdomen without clear localization;
- nausea, vomiting;
- belching with an unpleasant (rotten) odor;
- feeling of heaviness and discomfort;
- violation of the act of defecation in the form of constipation;
- the appearance of mucus in the stool.
Be sure to read: In detail about intestinal colonoscopy: preparation and progress of the procedure
Diffuse distribution of gases leads to a deterioration in the general condition of the patient: weakness, pale skin appears, systemic pressure decreases and at the same time the pulse increases.
Note!
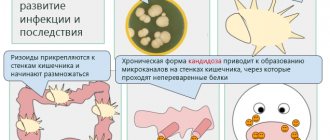
Why does increased intestinal pneumatization occur? Medicine knows many reasons, but the most common is stomach diseases. And sometimes it’s all about tissue infection.
The disease is often accompanied by spasms, and in some patients they are quite painful. Abnormal bowel movements are observed in an adult patient.
The disease often manifests itself in very young children. The risk group is children who have had intestinal infectious diseases.
Classification
Doctors distinguish two subtypes of the disease:
- widespread (extensive);
- limited (local).
More common is the limited type, in which the pathological process is localized in the wall of the small intestine. But in the second form, the disease covers the entire intestine.
The areas most susceptible to the disease are:
- ileum;
- ileocecal zone.
In both types of diseases, changes occur in the intestinal mucosa, causing the appearance of cysts. Such neoplasms can accumulate in one area or be evenly distributed throughout the entire intestinal wall.
Causes of the disease
The following reasons for the development of this gastrointestinal pathology are identified:
- intestinal obstruction;
- spasms;
- increased pressure in the abdominal cavity;
- impaired peristalsis and associated increased flatulence;
- infection with pathogens of intestinal diseases;
- penetration of air through the intestinal wall;
- sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work;
- disruption of the functioning of intestinal lymphatic capillaries.
Medical practice shows that treating the disease is not easy, so prevention is much more effective in preventing the development of pathology.
How to suspect something is wrong?
In what cases should you visit a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination? If a person notices increased flatulence, then this is a serious reason to think about whether everything is in order in the body. As a rule, this symptom appears suddenly and sharply.
Another obvious manifestation of pathology is constipation. How strongly it is expressed is determined by the degree of intestinal damage. Which part of the gastrointestinal tract is under attack also plays a role.
Since the disease is characterized by disorders such as bloating and gas formation, the intestinal walls stretch over time, which becomes the cause of a cramping pain syndrome that comes without warning, suddenly. The patient also regularly notes discomfort, unpleasant, even painful sensations in the intestinal area.
The list of symptoms includes diarrhea. Some patients complain of colic.
Signs and manifestation
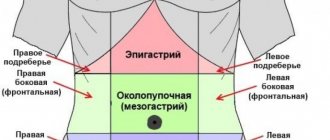
A striking symptom of pneumatosis of the stomach and intestines is increased persistent gas formation and flatulence. The intensity of the sensations depends entirely on the degree of filling of the cavities with gas bubbles, on the number of cystic components and air cavities inside the digestive system. The main symptoms of pneumatosis are:
- discomfort in the rectal area (feeling of stretching of the walls, distension);
- vomiting and constant nausea;
- pale skin;
- cramping pain (sometimes of unclear localization);
- constipation along with diarrhea;
- belching.
Cystic cavity
Important! Pneumatosis is a gastrointestinal pathology that can lead to serious complications such as peritonitis and intestinal obstruction as a result of cysts blocking the intestinal lumen. With ordinary flatulence, the patient does not experience a general deterioration in his condition. The mistake of many patients is that they separate bloating, nausea and flatulence from weakness and general deterioration of the condition.
Severe cases
The most difficult situation is the occurrence of intestinal obstruction associated with a cyst in the anal area. In some patients, due to pathology, the intestinal lumen is completely blocked.
Another severe scenario is a rupture of the intestine, caused by increased pressure of gases accumulated inside. In this case, the contents of the intestine are poured into the abdominal cavity, which leads to inflammation.
Without knowing how to restore intestinal motility, by delaying contacting a doctor, you can lead to peritonitis. And the treatment of this inflammatory disease is complex and does not always give positive results even with timely initiation of therapy.
Diagnosis of pneumatosis
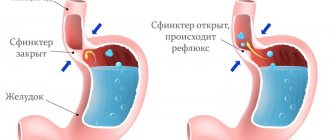
How to detect pneumatosis of the colon and small intestine? Unfortunately, the diagnosis of diverticulosis is difficult due to the nonspecificity of the symptoms of the pathology. The disease is mainly caused by other problems of the gastrointestinal tract. Diagnostic methods include: X-ray, ultrasound, endoscopy (colonoscopy), palpation. What is the best way to diagnose pathology? The most effective method is considered to be an endoscopic examination, which can be performed by doctors to confirm the diagnosis of intestinal emphysema after an X-ray with a contrast agent.
Pneumatosis intestinalis on ultrasound
One method for detecting diverticulosis is ultrasound. By chance, a doctor may detect an accumulation of gases of various etiologies on an ultrasound of the small or large intestine. Intestinal pneumatosis is diagnosed on ultrasound by examining the gastrointestinal tract or abdominal cavity. Ultrasound examination is carried out on an empty stomach, 2 days before the procedure you need to exclude foods that lead to gas formation: raw vegetables, beans, milk, brown bread.
Intestinal palpation
In some cases, a gastroenterologist will be able to detect diverticulosis in a patient without laboratory testing, by palpation of the abdomen. This happens rarely, but it is possible: air bubbles in the intestinal area can be felt. Active palpation of the intestine reveals a cyst-pouch. Such cysts are arranged in rows; when palpated, you can hear the sound of bursting gas and air bubbles.
- How to choose a private detective - hire, prices for services and activities
- Homemade cream for sour cream cake. Sour cream recipes with photos
- Lipoma - what is it, removal surgery. Treatment of lipoma with folk remedies
Treatment methods
If the diagnosis shows that there is pneumatization of the intestine, then complex treatment is practiced. First of all, a special diet is prescribed, and concomitant diseases are identified. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the primary causes of the disease.
Antibiotics and antiseptics are prescribed if an intestinal infection can be identified. If pneumatization is suspected, taking such medications on your own is strictly prohibited, as this can provoke an aggravation of the situation, including the need for urgent hospitalization.
In case of intestinal obstruction, surgery is prescribed. For constipation, it is recommended to use laxatives and monitor your meal schedule.
The greatest effectiveness is shown by a combination of medications and diet. The patient should remember that a number of popular foods are difficult for the intestines to tolerate even in a healthy state - such foods should be avoided.
Diet for pneumatosis intestinalis
Is there a special diet for pneumatosis intestinalis ? There is no clear description or nutrition plan. The diet is prepared by the doctor and is individual for each patient. However, general recommendations are aimed at maintaining a balanced diet (diets No. 46 and 4c). Diet for pain in the intestines No. 46 limits the consumption of certain foods, but necessarily contains all the nutrients:
- Carbohydrates.
- Fats.
- Squirrels.
- Vitamins.
- Macro- and microelements.
Only if you follow a balanced diet for gastrointestinal diseases will nutritional deficiencies in the body be prevented.
During the active phase of poisoning or diarrhea, the body weakens and becomes dehydrated. And if the diet for inflammatory bowel disease does not provide the body with enough nutrients, it will worsen the symptoms.
Healthy eating habits should be a way of life for people with sensitive guts. Inappropriate nutrition is the main cause of symptoms.
The diet for intestinal pneumatosis should contain food products of the main groups:
- Cereals.
- Fruits and vegetables.
- Lean poultry and fish.
- Vegetable oils (linseed, olive).
- Dairy products (excluded in case of lactase deficiency or contraindications).
It is important to remember the drinking regime, especially at the time of severe poisoning. With prolonged vomiting or diarrhea, the water-salt balance in the body is disturbed and the risk of dehydration increases. Inflammation of the intestines with constipation is often caused by a lack of water in the body. To prevent this, you need to drink 2 liters of purified water daily. The consumption of tea and other drinks is not taken into account. If attempts at bowel movement do not improve, in this case, a diet for intestinal atony is recommended.
To some extent, the diet for pneumatosis intestinalis is compiled by the doctor and the patient by trial and error. Depending on the characteristics of the disease, some foods, despite the fact that they have a beneficial effect on intestinal functions, cause food intolerance in the patient. Therefore, they are excluded from the diet. Over time, the doctor may make adjustments to the diet.
Having felt cramping and bursting pain in the abdomen, accompanied by a gag reflex, nausea, belching and stool upset, a person turns to a gastroenterologist, who, after carrying out diagnostic measures, determines the patient’s disappointing diagnosis of pneumatosis intestinalis. Further treatment of gastrointestinal disease is carried out depending on the prevailing symptomatic signs.
What does pneumatosis intestinalis mean, what are the causes, symptoms and treatment of the disease, will be discussed in this article.
Diet features
With increased gas formation, doctors recommend monitoring your diet very carefully. In particular, the following foods should be completely or almost completely excluded:
- peas;
- legumes
All their subspecies, including lentils, are rich in complex proteins that the body absorbs with great difficulty. In addition, these products stimulate the formation of gases in the intestines.
Due to the increased concentration of fiber and the abundance of extractive components, the following should be excluded from the daily menu:
- apples;
- radish;
- cabbage
For the same reason, it is not recommended to eat kiwi and garlic.
Bloating and gas formation are the result of fermentation processes in the intestines. Therefore, you should avoid these products:
- kvass;
- bread;
- beer.
You should not get carried away with raisins, as they also provoke increased fermentation, which turns into a problem when intestinal motility is disrupted.
Meat products you should exclude from your diet:
- goose;
- pork meat.
You should not overuse mushrooms, as these products are difficult to digest in the stomach and begin to rot before the enzymes have time to break them down. Nutritionists also recommend avoiding carbonated drinks and all foods rich in carbohydrates.
What is allowed?
Because of the list of restrictions listed above, you may get the impression that you can’t eat anything at all. In fact, this is not so - the variety of foods and dishes allowed and even recommended for intestinal motility disorders is great.
Cereal porridges boiled in water are extremely useful:
- buckwheat;
- millet
It is recommended to either steam or cook any food before eating. You can simmer. But you shouldn't eat fried food. Only those flour products that were made from coarsely ground raw materials can be eaten.
To achieve the maximum positive effect from the diet, you need to eat strictly according to the schedule. This regimen will help normalize the production of gases in the intestines and improve the health of the body. You should eat small portions, but at least six times a day.
Eat slowly, chewing all food thoroughly. Remember that when talking while eating, a person involuntarily swallows air, which only aggravates the situation. It is recommended to eat at the same time every day.
Gastric pneumatosis symptoms and treatment
More and more people are leaving the doctor's office with a diagnosis of gastric pneumatosis. The disease is unpleasant, accompanied by symptoms that can even isolate a person from the outside world. Discomfort, shame and embarrassment - a person with this diagnosis often tries to avoid society. With this disease, a person does not control the occurrence of belching, hence the fear.
What kind of disease is this?
Gastric pneumatosis or aerophagia is excessive swallowing of air.
Usually there is always 200 milliliters of air in the stomach, which is then absorbed by the intestines without any problems. The air that enters the digestive system is the main part of the gas; the remaining gases are produced by microorganisms.
If many times more air enters the stomach than is needed, then a large amount of gas begins to accumulate there, and the excess begins to come out by belching. Loud belching causes a person’s reluctance to communicate with the world; such a patient tries to retire in order to avoid shame.
Scientists who undertook to study aerophagia came to the conclusion that the gas that accumulates in the stomach can enter the lymph, so a person may develop vascular diseases.
Types of disease
Aerophagia (swallowing air) most often occurs in newborns.
There are neurological and organic pneumatosis. The first is typical for people who suffer from neurasthenia and hysteria: they swallow air involuntarily, as if gasping. This often occurs during breakdowns and disorders of nervous activity.
Organic may appear due to excessive swallowing of air along with food, with an abnormal structure of the digestive system.
There is also the concept of functional aerophagia - most often it occurs in newborns, whose digestive system has not yet fully formed.
Reasons for appearance
- Mental imbalance. Nervous shocks and stress are often the causes of hysterics, during which a person may involuntarily swallow air.
- Diseases of the peritoneum.
Gastric pneumatosis often affects people who have hernias in the food canal of the diaphragm. Increased intra-abdominal pressure can also cause gastric pneumatosis. - Respiratory diseases. Difficulty breathing, dry mouth leads to intense swallowing of saliva, and with it air.
- Wrong food intake.
Talking while eating or eating quickly leads to swallowing a lot of air along with food. - Diseases of the cardiovascular system. Aneurysm, damage to the heart vessels, and poor blood circulation can also provoke aerophagia.
- In infants, one of the causes of gastric pneumatosis is low mobility and immaturity of the digestive system.
- Smoking and constant use of chewing gum can also cause aerophagia.
Symptoms
The main symptom is frequent loud belching.
Symptoms of gastric pneumatosis are unpleasant and cause the patient a lot of inconvenience and discomfort:
- The most basic and most unpleasant symptom is frequent loud belching. It may appear suddenly, not necessarily after eating.
- Air accumulated in the stomach gives a feeling of heaviness and bloating. Disappears after the body is freed from air.
- After eating, you may experience palpitations and heart pain after eating. These manifestations should not be confused with angina pectoris, but only a physician can make an accurate diagnosis.
- Hiccups.
- Labored breathing.
Diagnosis of gastric pneumatosis
Gastric pneumatosis can be diagnosed using x-rays. The image will clearly show a gas bubble in the stomach and excessive elevation of the dome of the diaphragm. In addition, endoscopy will also help detect aerophagia.
Additionally, electrocardiography and ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs are prescribed. The earlier pneumatosis is diagnosed, the faster you can get rid of its complications and consequences.
Aerophagia can lead to weakening of the muscle that controls the connection between the esophagus and the stomach; in addition, a hiatal hernia is considered one of the consequences of pneumatosis.
Treatment
If symptoms of gastric pneumatosis appear, you should immediately reconsider your diet.
You need to eat often in small portions, at least 5 times a day.
You should eat at least 5 times a day, portions should be small. You should eat slowly and not talk while eating. Be sure to exclude drinks containing carbon dioxide from your diet.
You can apply a set of measures that will help free the digestive canal from excess air. You should do abdominal massage, breathing exercises, do physical therapy, warm baths will help, but they should be taken while sitting.
If you feel heaviness in your stomach, lie on your left side and lower your head down.
An appointment with a neurologist is also necessary. Pneumatosis can be triggered by a mental disorder, so only a specialist can choose the right course of treatment to save the patient from both nervous disorders and unpleasant aerophagia. The doctor may prescribe sedatives and antidepressants.
Acupuncture is one of the most effective ways to get rid of gastric pneumatosis. Hypnosis is also used to treat aerophagia.
Under no circumstances should you perform gastric lavage, because the gag reflex that accompanies this procedure can further “loose” the diaphragm, which will lead to a hernia.
With pneumatosis, doctors advise not to swallow saliva, but to spit - this will help minimize the swallowing of air.
To minimize the manifestations of aerophagia in young children, you need to do this: stop feeding each time so that the baby burps. And for good removal of gases, give the baby dill water.
You can also try traditional methods of getting rid of belching. There are several methods that alternative medicine recommends:
- Calamus root powder is taken orally in a whisper with water.
- Potato and carrot juice are mixed in equal parts and drunk before meals 3 times a day.
- If belching occurs due to nervousness, then a soothing decoction of hop cones, heather, sweet clover, calamus root and cinquefoil is recommended. Pour boiling water over a pinch of herbs, infuse and take the entire infusion once a day.
Currently, the number of patients diagnosed with pneumatosis of the stomach has increased. The disease often progresses in children. What kind of disease is this? What are the reasons for its occurrence? We will try to find answers to these questions in this article.
What is gastric pneumatosis characterized by?
The symptoms of pneumatosis are quite specific
Increased air concentration in the stomach is associated with pneumatosis of the stomach. Usually, with pneumatosis, doctors note the presence of a certain cyst-like cavity that forms between the layers of the stomach or intestinal walls. This cavity can form in infants due to the development of intestinal diseases in their bodies.
The gas formed during pneumatosis is the result of the vital activity of the smallest organisms present in the abdominal cavity. Among these microorganisms there is E. coli. Gas includes an admixture of digestion products with enzymes present in the body.
Scientists around the world are actively studying this disease and believe that the resulting gas can also fill the lymphatic fluid, as a result of which these vascular formations expand in a person. Gastric pneumatosis can affect either a single area or spread to several parts of the body.
The disease can involve the ileocecal and ileal intestinal regions.
By palpation of the abdominal area, the presence of elastic formations is sometimes felt, and in some cases the sound of bursting gas bubbles is even heard. By conducting an endoscopic examination of the stomach cavity, doctors confirm the presence of gas bubbles filling the free cavities of the organs. At the same time, sometimes these bubbles may contain small amounts of blood.
People suffering from the development of pneumatosis in the stomach often experience a feeling of heaviness, severe belching and a feeling of fullness in the epigastrium.
Sometimes a sudden and severe belching becomes the reason for a person’s unwanted exit into society. It is worth remembering that belching is a signal of the development of other pathologies in a person’s abdominal cavity.
Therefore, if you experience frequent belching, you should go to a medical facility and have your body thoroughly examined.
Causes of gastric pneumatosis
Pneumatosis can have different causes of development
Scientists have not yet been able to identify all the causes of this disease in humans. Many of them adhere to the conclusion that pneumatosis is a consequence of the development of diseases in the abdominal organs. For example, it is well established that pneumatosis is present in people who have hernias in the areas of the esophageal canal of the diaphragm.
Gastric pneumatosis affects people suffering from frequent attacks of hysterical psychosis, which can be expressed in nervous belching or neurogenic aerophagia. Pneumatosis occurs in patients with lesions of the phrenic nerve or the development of pathological changes in the left diaphragmatic dome.
Most studies associate pneumatosis with disruptions in the functioning of higher nervous activity in humans.
The cause of the development of pneumatosis is also the low mobility of children at an early age. The disease progresses in people with symptoms of intestinal obstruction and suffering from disruptions in intestinal motility.
Pneumatosis is promoted by impaired removal of generated gases through the anal canal, as well as numerous intestinal spasms. Patients with increased intra-abdominal pressure are also more likely to develop gastric pneumatosis.
All these reasons lead to the development of this disease, so it is worth taking a more responsible approach to their manifestations and treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
When a person develops gastric pneumatosis, a prolonged belching occurs with a characteristic rather loud sound. The occurrence of such a “noisy burp” is always sudden and causeless. Sometimes nervous belching appears, which is a consequence of a violation of the eating pattern.
The disease is accompanied by a constant feeling of fullness in the stomach. In some cases, people complain of pain in the sternum, which feels very similar to angina attacks. Patients with gastric pneumatosis suffer from increased pressure in the intra-abdominal cavity.
In some cases, such patients experience attacks of nausea and vomiting.
What drugs help?
With intestinal pneumatization, antibiotics and some other drugs taken under the supervision of a doctor are beneficial. It is important that the doctor monitors the patient’s condition at all times to avoid additional complications.
The practice of treatment with prebiotics is widespread. This is the common name for drugs that stimulate the growth of colonies of beneficial bacteria in the intestines. Problems with peristalsis are often caused by microflora disturbances, and such medications give good results. Otherwise, all those particles that are not broken down by gastric juice decompose in the intestines with the formation of gases.
Enzyme preparations are another group of medications that are in demand for problems with peristalsis. They improve digestion and normalize the process of digesting foods.
Therapy with choleretic drugs shows remarkable results. If the disease is associated with spasms, drugs based on drotaverine will come to the rescue. But if the appearance of gas is accompanied by the production of foaming mucus, medications that contain simethicone will help. The best results can be achieved by combining drug therapy, proper nutrition and control of work and rest patterns.