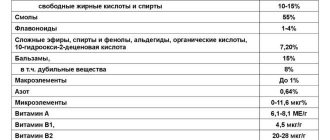
According to the instructions, De-Nol is a popular gastroprotective agent. While it provides protection, it is not effective enough alone to cure the disease. The bismuth-containing drug De-Nol with antiulcer effect is produced in the Netherlands in the form of tablets. Promotes a moderate anti-inflammatory effect, reduces acidity, improves the tone of the muscle wall of the stomach, and reduces the activity of Helicobacter pylori infection.
The main property of the medicine is, through the interaction of bismuth salts and mucus proteins, to form a colloidal substance that covers the inner surface of the stomach with a film. Erosions, ulcers, and foci of inflammation are protected from the effects of food and medications. Conditions are created for tissue regeneration, healing, and scar formation.
Antiulcer drugs: joint treatment with De-Nol
For complete treatment of peptic ulcer, drugs with targeted pathogenetic effects are needed. They are prescribed simultaneously with De-Nol, expecting an enhanced joint effect.
Why is complex treatment necessary?
The formation of an ulcer goes through several stages: from hyperacid and erosive gastritis to the formation of a deep defect in the mucous and submucosal layer. In severe cases, the bottom of the ulcer is located on the muscular wall of the stomach. The reasons include the following:
- high acidity with irritating effect and corrosion of own tissues,
- disruption of hormone production (pepsin, gastrin),
- changes in the nervous regulation of muscle tone under the influence of stress,
- unhealthy diet with constant consumption of hard-to-digest foods, spicy seasonings, alcohol, carbonated water,
- focal deterioration of the nutritional conditions (blood supply) of the stomach,
- insufficient mucus production for protection.
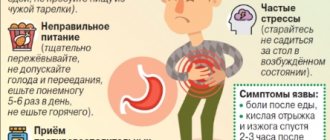
As a result, the patient experiences severe attacks of pain in the upper “floor” of the abdomen with irradiation to the back and sides, vomiting mixed with blood, a tendency to diarrhea, heartburn due to reflux (reverse) reflux of acid into the esophagus, belching, and bloating. Dyspeptic symptoms are explained by the entry into the intestines of insufficiently processed and crushed food mass.
To cope with such diverse symptoms, potent drugs are needed, therefore, in the treatment of ulcers, the following are used together:
- antibiotics to suppress and get rid of Helicobacter,
- antibacterial nitro drugs that have a pronounced bacteriostatic effect,
- antacids (acid reducers),
- H2-histamine receptor blockers to reduce the effect of histamine in the inflammatory response,
- painkillers, antispasmodics,
- prokinetic drugs that restore sphincter tone and help stop vomiting,
- stimulators of cell regeneration through increased blood circulation, activation of metabolic processes and immunity,
- sedatives (calming agents).
For each medicine, the doctor selects the optimal dosage, sets the duration of use, takes into account contraindications and compatibility with De-Nol.
What antibiotics are the most effective?
Among the huge arsenal of antibiotics, those to which the bacterium that lives in the stomach and causes peptic ulcers are most sensitive were selected. This has been proven both through scientific laboratory studies and many years of clinical practice. Such antibiotics are Amoxicillin , Amoxiclav , Clarithromycin , Tetracycline and the complex antibacterial agent metronidazole.
Characteristics of the antibacterial agents used
Amoxicillin
The drug belongs to the group of semi-synthetic penicillins, has a bacteriostatic effect - it inhibits the growth and stops the reproduction of bacteria. The tablets are taken on an empty stomach, the action time is up to 8 hours, so amoxicillin is taken for stomach ulcers three times a day for 8-14 days.
Amoxiclav
A combination drug containing amoxicillin in combination with clavulonic acid or its salt - potassium clavulonate, which inhibit the enzymes of bacterial membranes and make them more vulnerable to the effects of the antibiotic, enhancing its effect. It is used in tablets or in the form of a suspension prepared from powder. Prescribed before meals in 3 doses per day, treatment duration is 5-14 days.
Clarithromycin
Belongs to the group of broad-spectrum antibiotics – macrolides. In fact, it is semi-synthetic erythromycin. It has greater antibacterial activity than penicillin drugs and is more resistant to gastric acid. However, it is poorly compatible with other medications, so it is prescribed with great caution and taken under the supervision of a doctor. It has a longer effect, so it is taken every 12 hours - morning and evening on an empty stomach, the course of treatment is 5-10 days.
Tetracycline
A popular antibiotic with a wide spectrum of action, it is good because bacteria rarely develop resistance to it. It is effective for 6 hours, so it is prescribed in 4 doses per day before meals. The disadvantage is high toxicity, which limits its use.
Metronidazole
The drug is also known as Metrogyl, Trichopolum, Tinidazole, Bacimex, Efloran, which are widely used to treat protozoal infections - trichomoniasis, amoebiasis, gardnerellosis. Its antimicrobial effect was discovered relatively recently. Prescribed in 2 doses, regardless of food, course duration is from 7 to 10 days.
A number of traditional and proven drugs are being replenished with new ones that are successfully used in the treatment of ulcers: Klacid , Macmiror , Helicotsin , Sumamed .
Features of joint use of De-Nol and an antiulcer drug
Creating and using the correct combination of drugs with De-Nol requires knowledge of the characteristics of the medication. The doctor should consider the following:
- it is necessary to drink medications, observing a time interval of 40-60 minutes before taking De-Nol, because the metallopeptide coating slows down the absorption of any drugs,
- if the patient is recommended to take antacids (Maalox, Almagel, Gastrofarm), then the effect of bismuth salts decreases,
- other bismuth-containing medications (Vicalin, Bisal, Vikair) should not be co-prescribed; there is a risk of overdose,
- in any treatment regimen, the maximum duration of the De-Nol course of 2 months and the maximum daily dose should be monitored; an increase contributes to the accumulation of bismuth in the blood and the manifestation of toxic properties.
The drug is contraindicated in therapy:
- pediatric patients up to four years of age,
- pregnant and lactating women (transmitted to the fetus, through milk to the child, increases the risk of gene mutations and abnormalities),
- patients with renal failure,
- if hypersensitivity to components is detected.
You can take De-Nol only if you follow the rules:
- take the tablets with water, do not use juices, tea, coffee,
- It is better to exclude milk from dietary dishes, it reduces the effectiveness of bismuth,
- A complete abstinence from alcohol-containing drinks and tinctures is required.
The dosage for adolescents over 12 years of age and adults is 4 tablets per day. You can drink them one at a time 30 minutes before meals, 4 times or 2 twice. Children from four to 8 years old are prescribed 8 mg per kg of weight per day, at 8-12 two tablets.
Among the most mandatory drugs in a comprehensive antiulcer therapy regimen are proton pump blockers. Their action is to suppress the functioning of parietal cells in the synthesis of hydrochloric acid and pepsin. By reducing acidity, bismuth facilitates the formation of a protective film and a bactericidal effect to destroy Helicobacter.
An important feature of all drugs in the group is the ability to “mask” signs of cancerous degeneration. Therefore, before use, the doctor must fully examine the patient to exclude a tumor.
All products are contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation, hypersensitivity. Let's list some of the drugs in the group.
De Nol in combination with antibiotics
De-Nol is a bismuth-based antiulcer medicine that exhibits antibacterial and gastroprotective properties. The selection of a treatment protocol is carried out by a gastroenterologist after a comprehensive diagnosis.
De-Nol and Amoxicillin are used in complex treatment regimens for diseases whose pathogens are sensitive to the activity of the active ingredients. Bismuth is a drug compatible with other drugs.
It can be taken along with antibiotics and antimicrobial agents for chylactobacteria and stomach ulcers.
Bismuth is also compatible with antibacterial drugs based on azithromycin, clarithromycin, amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid.
Taking Metronidazole (Trichopol)
Taking Metronidazole (Trichopol) is recommended for patients with ulcerative lesions of the intestinal tubes, gastritis, and Helicobacter pylori infection. Metronidazole is not an antibiotic, but is active against Helicobacter. Available in the form of tablets for oral administration, it exhibits antiulcer and antiprotozoal properties.
The question often arises: how to take De-Nol with Trichopolum? Bismuth enhances the antimicrobial activity of metronidazole. The drug is taken during or after a meal for 7-10 days. If the doctor has not prescribed another dosage regimen, use the standard one: 500 mg up to 5 times a day. Additional use of amoxicillin is indicated.
Contraindications to the use of combination therapy
The list of contraindications depends on the medications that are included in the therapy protocol:
- Taking bismuth is contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women, children under 4 years of age, and people with severe liver and kidney dysfunction.
- Clarithromycin is not used for porphyria, during the 1st trimester of pregnancy and breastfeeding, or in the treatment of patients with renal or liver failure.
- An absolute contraindication for all groups of drugs is intolerance to their active substance.
Before using the medicine, you must study the instructions and possible contraindications for its use.
The danger of self-medication for gastrointestinal diseases: the doctor says
Independent selection of medications may not provide the desired therapeutic result. The disease will progress and the likelihood of complications will increase. The symptoms of most gastrointestinal diseases are similar. The selection of a suitable antibiotic therapy regimen, as well as symptomatic drugs, is carried out according to the results of a comprehensive examination.
Uncontrolled use of drugs is fraught with:
- incompatibility of medications;
- low efficiency;
- development of resistance of pathogenic microorganisms to the action of active components of drugs;
- development of adverse reactions;
- incorrect selection of dosage: a low dose is ineffective, a high dose is toxic;
- allergic reactions.
Antibacterial drugs are strictly not intended for self-medication. They can only be prescribed by a doctor.
A few weeks after completion of therapy, follow-up diagnostics are recommended. Patients with complications should be under special medical supervision.
People with stomach bleeding and perforation of mucous membranes are at risk. For this category of patients, relapses can be fatal.
The sooner people seek quality medical care, the more favorable the prognosis.
De-Nol and Omez: how to take together?
Omez is the Indian version of the Russian Omeprazole. Due to its blocking effect on the production of hydrochloric acid, it is prescribed for hyperacid gastritis, reflux esophagitis, and peptic ulcers. It relieves heartburn, belching and pain well.
Available in 20 mg capsules. For ulcers, it is recommended to take one 2-4 times a day. The drug should be taken 30-40 minutes before meals (like De-Nol). This is inconvenient for the patient. You will have to think about the interval between taking medications of 30-40 minutes.
The drug is prohibited for children of any age. Has side symptoms such as:
- headaches and dizziness,
- severe sweating,
- disorders of the nervous system (excitability or depression, insomnia, hallucinations),
- blurred vision,
- abdominal pain with stool upset,
- stomatitis, changes in taste sensations,
- pain and weakness in muscles, joints,
- skin allergies.
Combined use with Omeprazole
Omeprazole can be taken only once a day, regardless of food, so it is much easier to draw up a compatibility scheme for taking De-Nol and Omeprazole. It must be borne in mind that after swallowing the drug begins to act within an hour. The effect lasts for a day. Maximum suppression of secretion occurs after 4 days. It is not recommended to immediately discontinue the drug. An analogue is the drug from Slovenia Ultop, also created on the basis of omeprazole.
After stopping taking it for a week, the secretion level reaches normal. The drug is prescribed in a course of 10 days, regardless of the purpose. During eradication, it creates conditions for other drugs to enhance the effect on the infectious pathogen.
De Nol when taking antibiotics
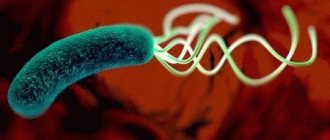
Therapy aimed at expelling Helicobacter rulori from the stomach of a person infected with it is not the easiest task that a doctor sets for himself.
This is due to the fact that pathogenic microorganisms are extremely reluctant to leave their favorite places of existence - the epithelial cells of the inner lining of the stomach or the submucosa, and drug-resistant strains are formed.
Therefore, the effect on the bacterium must be complex: medication, physiotherapy, nutrition, phytotherapeutic. The main point of application is drug therapy.
How and with what to treat Helicobacter pylori - medicinal methods
The expression “treat Helicobacter pylori infection” is not entirely correct from a medical point of view. Doctors treat diseases caused by this microorganism, but the bacterium itself should be gotten rid of.
The main direction in drug therapy is eradication - a method of destroying an infectious agent with the help of drugs.
In addition to eradication therapy, it is important to correct the impaired acidity of gastric juice, restore the motor and evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract, stabilize enzymatic activity, and calm inflammatory processes.
All these functions are assigned to specific drugs, which, in combination with proper nutrition, give positive results. The main groups of drugs, medicines and tablets for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori bacteria:
- Antibacterial
- Preparations of bismuth salts
- Proton pump blockers
- M-anticholinergics
- H2-histamine receptor blockers
- Antacids
- Antispasmodics
- Prokinetics
The most common dosage form of drugs is tablets; antacids can be used in the form of suspensions or powders that require dissolution in water.
Antibacterial drugs are the “heavy artillery” that forces the bacteria to desert and leave the patient’s body.
The standards for the treatment of Helicobacter-associated gastric pathologies indicate at least two antibiotics. With significant contamination of the mucous membrane and pronounced clinical manifestations of the disease, it is impossible to do without them.
What antibiotics are recommended to take for Helicobacter pylori:
- Amoxicillin
- Clarithromycin
- Tetracycline
- Metronidazole
- Rifambutin
- Levofloxacin
Rifambutin and levofloxacin are “reserve” drugs; they are not included in standard treatment regimens, but can be used if pathogenic strains develop resistance to common drugs included in the protocols.
Antibacterial drugs have side effects: allergic reactions, dysbacteriosis, candidiasis, nausea. Patients are often afraid to take antimicrobial drugs precisely for this reason.
If you are infected with Helicobacter and have gastric diseases, you should not do this. Taking antibiotics in this case is justified.
Without these medications, the patient runs the risk of developing a stomach ulcer, and by refusing treatment, he exposes the body to the risk of developing oncopathology of the gastrointestinal tract. Stomach cancer is 3-6 times more likely to occur in patients infected with H. pylori who have not received proper therapy.
Today, 3- and 4-component treatment regimens aimed at destroying the bacteria have been developed and are actively used.
If a patient has a microbe in the stomach, there are symptoms of gastrointestinal damage, and the person has not previously received treatment, therapy is always started with a three-component regimen, which includes:
- Proton pump blocker (omeprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, pantoprazole 20 mg) 2 times a day
- Amoxicillin 1000 mg 2 times a day
- Clarithromycin 500 mg 2 times a day
A 3-component regimen is prescribed when a patient first seeks treatment; elderly, debilitated patients can be individually adjusted to the dosage of medications.
This therapy is prescribed for 7 (minimum) to 14 days. Clinical studies have shown that in some cases, taking drugs for a week is not enough to ensure eradication, and therapy is ineffective.
After two weeks of taking the drugs, on the contrary, the effect of treatment was an order of magnitude higher: in a much larger number of patients, eradication of the pathogen reached 80% or more.
Four-component treatment regimen
If the effect of the 3-component regimen is not achieved, the destruction of the infectious agent has not occurred, the doctor will recommend continuing therapy after a month and a half, consisting of:
- Proton pump blocker (omeprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, pantoprazole 20 mg) 2 times a day
- Preparations of bismuth salts 120 mg 4 times a day
- Metronidachol 500 mg 3 times a day
- Tetracycline 500 mg 4 times a day
This is a 4-component eradication scheme. It is important to ensure that previously used antibacterial drugs are not repeated. If resistance to the above antibiotics is detected, “reserve” medications can be prescribed: levofloxacin, rifambutin.
Despite the developed standards, the doctor, when carrying out eradication, must approach each case and disease individually, taking into account the patient’s age, concomitant pathologies, possible allergic reactions of the body and the resistance of specific strains of bacteria to drugs.
A 3-component regimen is prescribed by a doctor for a period of 7 to 14 days. It is not advisable to take the drugs for less than a week; there will be no effect from such treatment.
The bacterium is difficult to treat and develops resistance to drugs, so more and more evidence is emerging that even a week is not enough to achieve a positive result and get rid of the pathogen. More and more doctors are inclined to extend antibiotic therapy to 10-14 days.
A weekly course of administration is recommended for elderly and weakened patients who have concomitant multiple organ pathologies and who find it difficult to tolerate a load of two antibiotics.
The 4-component regimen is prescribed for a period of two weeks.
The effectiveness of treatment should be assessed using diagnostic and laboratory methods no earlier than 1-1.5 months from the end of taking the drugs.
If eradication is 80% or more of the initial level, or no bacteria are found in the body at all, we can talk about success in treating the disease associated with this pathogen.
More about drugs
Features of taking antibiotics for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori:
This is an antibacterial drug from the macrolide group. Included in the first-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. It is successfully used in gastroenterology, it is able to inhibit the synthesis of the cell wall of Helicobacter pylori, and therefore prevent its reproduction. It is acid-resistant, works effectively at normal and high acidity, and is well absorbed.
Some strains of bacteria exhibit resistance to clarithromycin. In this case, the drug must be replaced with another one to achieve a better therapeutic effect.
- Amoxicillin and metronidazole
Metronidazole or trichopolum is a drug that has a destructive or bactericidal effect on H. pylori. Its activity does not depend on the pH level in the stomach; the drug can be used in both hyper- and hypoacid conditions.
Today, resistance of many Helicobacter strains to metronidazole is very common. If the drug is prescribed together with de-nol, resistance to it develops more slowly.
Amoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic that blocks the synthesis of microbial cell walls and is well absorbed by the gastric mucosa. More active in a neutral environment than in an acidic environment. Increasing the pH to 4 increases the pharmacological effect of this drug 10 times.
Metronidazole and amoxicillin are first-line drugs, but can also be prescribed in a 4-component treatment regimen.
Another antimicrobial agent actively used in eradication therapy of helicobacter pylori. The mechanism of action of tetracycline is to inhibit microbial cell protein synthesis.
The medicine is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Eating dairy foods slows down its absorption.
- Proton pump blockers
The most common representative of this group is omeprazole (omez). There are other very effective drugs: lansoprazole, pantoprozole, esomeprazole, rabeprazole).
Medicines suppress the production of hydrochloric acid. Thus, they influence the microbe indirectly: they do not destroy it, but create unfavorable conditions for existence, have a suppressive effect on the infection: they stop bacterial growth and development.
Omeprazole and other representatives of the group, by increasing the pH of the gastric contents, contribute to the better functioning of antibacterial drugs, in particular amoxicillin.
There is evidence that proton pump inhibitors can block the bacterial enzyme urease.
Doctors recommend that after completing the course of treatment with antibiotics, continue taking omeprazole for up to 4-8 weeks. Patients who continue to take proton pump blockers have better mucosal healing processes and a higher percentage of bacterial destruction compared to patients who stopped taking omeprazole after the end of the eradication regimen.
- Antacids and H2 receptor blockers
Source: https://limto.ru/de-nol-pri-prieme-antibiotikov/
De-Nol and Nexium: rules of therapy
Nexium is produced in Sweden in tablets of 20 and 40 mg and in 5 ml bottles with compressed powder for dilution and solution preparation. The active substance is esomeprazole, its isomer in chemical structure.
The medicine combines well with De-Nol, but it is not prescribed:
- children under 12 years old,
- with fructose intolerance,
- during treatment with Atazanavir and Nelfinavir (specific antiviral drugs used for HIV infection).
It is recommended to use cautiously in severe renal failure and epilepsy, but the conditions are not included in the contraindications. For peptic ulcers, a dose of 20 mg is prescribed 2 times, regardless of food intake, for a course of 7 days.
For the purpose of eradication - 40 mg for a month.
To avoid mixing the drug with other antiulcer drugs, it is convenient to carry out treatment by injection (slowly intramuscularly or by drip). This is a big plus in therapy. The antiepileptic drug Phenytoin does not combine well with Nexium.
We treat gastritis and stomach ulcers with De-Nol
Operating principle
Due to the antiseptic properties of bismuth, the drug De-Nol can be used to combat the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Some people mistakenly believe that De-Nol is an antibiotic, but this is not true. If you take only this drug, you can get rid of the bacteria only in 30% of cases. If you additionally use an antibiotic, which is selected by the doctor, then the success of treatment will be up to 90%.
When is it appointed?
Indications for use are quite broad:
- stomach ulcer;
- duodenal ulcer;
- chronic gastroduodenitis;
- gastritis (especially the erosive form);
- dyspepsia;
- IBS is irritable bowel syndrome with a tendency to diarrhea.
So, these tablets can be taken not only for ulcers, but also to prevent its occurrence. They are used in combination with the following means:
- proton pump inhibitor (eg, Omez);
- antibiotic to get rid of Helicobacter;
- a drug for normalizing intestinal microflora and preventing dysbacteriosis.
Treatment regimen and conditions of admission
Combination of drugs
Remember that Omez is a prescription drug and should not be taken without a doctor’s prescription, as this can mask a malignant process in the stomach, which also leads to increased acidity. Before taking any medications, you must undergo a comprehensive examination. Omez is usually prescribed in the morning before meals, sometimes at night.
To restore the microflora, which will certainly be disrupted by the antibiotic, special preparations containing probiotics are used (Bifiform, Acipol and others).
Interaction with other drugs:
Some people believe that you should not drink milk while taking De-Nol. There is no such data in the official literature. Milk, if it is well tolerated, can be drunk with meals, but you should not take pills with it (keep a break of half an hour). For the drug to help, alcohol, strong tea, carbonated drinks, and coffee are prohibited during treatment.
How to use?
Many people have a question: how long should you take the drug? If the disease is detected for the first time, it is usually 10 days. If there are several ulcers, or they reappear, an antibiotic is prescribed for 7-14 days, and De-Nol continues to be taken after that so that it helps consolidate the result. However, the course of treatment should not exceed eight weeks. After this, take a break for the same period, but you cannot take other drugs containing bismuth.
The medicine is prescribed for exacerbation of ulcers, gastritis or gastroduodenitis. If there are no indications, that is, there is no exacerbation, then there is no need to take pills; for prevention, following a diet is enough, and alkaline mineral waters are prescribed at the same time.
Contraindications
Bismuth is almost not absorbed into the blood, but still in some cases it cannot be taken:
- with renal failure (decompensated form);
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- children under 4 years old;
- with individual intolerance.
Side effects and overdose
If you take the tablets for a long time and in large doses, kidney function may be impaired or encephalopathy may develop (extremely rare). After withdrawal, the symptoms disappear.
In case of overdose, kidney failure, vomiting, weakness, and abdominal pain develop. This condition is treated by gastric lavage and taking activated charcoal.
Cost of the drug
Treatment effectiveness
De-Nol, like Omez, is included in all modern treatment regimens for stomach ulcers, and doctors’ reviews of the drug are very positive. However, sometimes you can hear questions about why the drug did not help in treatment. This may be due to various reasons.
Sometimes complaints that the drug did not help arise because it was taken incorrectly. Remember that you should not drink or eat anything for half an hour before and after taking the medicine. Wash it down only with clean water without carbon. Be sure to read the instructions for use to find out the description and composition, conditions of administration, indications and interactions of all prescribed drugs. If something is unclear, be sure to check with your doctor so you don’t have to wonder why the treatment has no effect.
Combination therapy with De-Nol and Nolpaza
Nolpaza is produced in Slovenia in tablets of 40 and 20 mg. The active substance is pantoprazole, a benzimidazole derivative. The drug belongs to the group of proton pump inhibitors. It is prescribed before meals once a day, so De-Nol and Nolpaza must be “divorced” according to the time of administration. Therapeutic concentration in the blood appears after 2 hours.
Decomposes in the liver. For patients with impaired liver cell function, it is better to choose another drug or adjust the dosage, monitor the tests.
The drug is contraindicated in the following pathologies:
- fructose intolerance,
- severe kidney and liver damage,
- neurogenic dyspepsia.
Caution is required if the peptic ulcer is prone to bleeding and is accompanied by hypovitaminosis B12. In the Helicobacter pylori eradication regimen, 40 mg is recommended in the morning and evening.
We treat gastritis and stomach ulcers with De-Nol
Operating principle
Due to the antiseptic properties of bismuth, the drug De-Nol can be used to combat the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Some people mistakenly believe that De-Nol is an antibiotic, but this is not true. If you take only this drug, you can get rid of the bacteria only in 30% of cases. If you additionally use an antibiotic, which is selected by the doctor, then the success of treatment will be up to 90%.
When is it appointed?
Indications for use are quite broad:
- stomach ulcer;
- duodenal ulcer;
- chronic gastroduodenitis;
- gastritis (especially the erosive form);
- dyspepsia;
- IBS is irritable bowel syndrome with a tendency to diarrhea.
So, these tablets can be taken not only for ulcers, but also to prevent its occurrence. They are used in combination with the following means:
- proton pump inhibitor (eg, Omez);
- antibiotic to get rid of Helicobacter;
- a drug for normalizing intestinal microflora and preventing dysbacteriosis.
Treatment regimen and conditions of admission
Combination of drugs
Remember that Omez is a prescription drug and should not be taken without a doctor’s prescription, as this can mask a malignant process in the stomach, which also leads to increased acidity. Before taking any medications, you must undergo a comprehensive examination. Omez is usually prescribed in the morning before meals, sometimes at night.
To restore the microflora, which will certainly be disrupted by the antibiotic, special preparations containing probiotics are used (Bifiform, Acipol and others).
Interaction with other drugs:
Some people believe that you should not drink milk while taking De-Nol. There is no such data in the official literature. Milk, if it is well tolerated, can be drunk with meals, but you should not take pills with it (keep a break of half an hour). For the drug to help, alcohol, strong tea, carbonated drinks, and coffee are prohibited during treatment.
How to use?
Many people have a question: how long should you take the drug? If the disease is detected for the first time, it is usually 10 days. If there are several ulcers, or they reappear, an antibiotic is prescribed for 7-14 days, and De-Nol continues to be taken after that so that it helps consolidate the result. However, the course of treatment should not exceed eight weeks. After this, take a break for the same period, but you cannot take other drugs containing bismuth.
The medicine is prescribed for exacerbation of ulcers, gastritis or gastroduodenitis. If there are no indications, that is, there is no exacerbation, then there is no need to take pills; for prevention, following a diet is enough, and alkaline mineral waters are prescribed at the same time.
Contraindications
Bismuth is almost not absorbed into the blood, but still in some cases it cannot be taken:
- with renal failure (decompensated form);
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- children under 4 years old;
- with individual intolerance.
Side effects and overdose
If you take the tablets for a long time and in large doses, kidney function may be impaired or encephalopathy may develop (extremely rare). After withdrawal, the symptoms disappear.
In case of overdose, kidney failure, vomiting, weakness, and abdominal pain develop. This condition is treated by gastric lavage and taking activated charcoal.
Cost of the drug
Treatment effectiveness
De-Nol, like Omez, is included in all modern treatment regimens for stomach ulcers, and doctors’ reviews of the drug are very positive. However, sometimes you can hear questions about why the drug did not help in treatment. This may be due to various reasons.
Sometimes complaints that the drug did not help arise because it was taken incorrectly. Remember that you should not drink or eat anything for half an hour before and after taking the medicine. Wash it down only with clean water without carbon. Be sure to read the instructions for use to find out the description and composition, conditions of administration, indications and interactions of all prescribed drugs. If something is unclear, be sure to check with your doctor so you don’t have to wonder why the treatment has no effect.
Doctors and patients who have benefited from the drug note its rapid action, good tolerability and convenient dosage regimen.
Taking Rabeprazole
Rabeprazole is a Russian-made proton pump blocker. The active substance is rabeprazole sodium. Available in 10 mg capsules. The drug is completely absorbed after 3.5 hours. The intake does not depend on food; De-Nol and Rabeprazole in the regimen do not interfere with each other. The Indian analogue based on rabeprazole is Khairabezol.
May have side effects:
- decreased appetite, nausea, vomiting, persistent diarrhea or constipation,
- stomatitis,
- bloating,
- dizziness with headache,
- lethargy, drowsiness,
- disturbance of taste and vision,
- temperature increase,
- pain in the back, muscles, joints,
- runny nose, cough, sinusitis,
- allergic skin rash.
Blood tests reveal: increased liver tests, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. The drug is not used to treat children due to the lack of reliable research results.
Quadruple eradication therapy (second line)
When previous methods are ineffective, four-component options are used. The duration of the therapeutic course reaches two weeks.
The options are as follows:
- Tripotassium bismuth dicitrate (4 doses of 120 mg daily), PPI, tetracycline (4 doses of 500 mg), metronidazole (500 mg, 3 doses).
- De-nol (240 mg 2 times), amoxicillin (500 mg 4 times), PPI, nitrofuran medicine.
- Amoxicillin (500 mg 4 times), PPI, bismuth subcitrate (120 mg 4 times), rifaximin (400 mg twice).
Other antiulcer drugs
In addition to De-Nol and acid production blockers, the following are used in the treatment of peptic ulcers:
- antacids that eliminate acidity by a chemical reaction with magnesium salts, aluminum hydroxide or phosphate, calcium and silicon compounds (Gastratcid, Phosphalugel, Gaviscon, Maalox, Almagel),
- histamine receptor blockers that reduce sensitivity to inflammatory mediators (Ranitidine, Quatemal, Famotidine),
- antibiotics and nitro drugs to suppress Helicobacter pylori infection (Flemoxina Solutab, Tetracycline, Clarithromycin, Azithromycin, Levofloxacin, their nitro drugs Furazolidone, Metronidazole),
- with the help of antispasmodics, pain relief is provided (Platifillin, No-shpa),
- for frequent vomiting and severe nausea, prokinetics are prescribed (Motilium, Cerucal).
After the acute symptoms are relieved, you will need funds to stimulate the healing process (Solcoseryl, Actovegin, vitamin complex, immunocorrectors).
The combination of De-Nol with antiulcer drugs is used to build a complete therapy for the disease. The effectiveness of complex treatment significantly exceeds the minimum prescription. Gastroenterologists explain to patients the benefits of using a combination of drugs and draw up a dosage schedule. The final decision on indications and contraindications can only be made after a complete examination.
Rules for combination therapy of gastrointestinal diseases
When treating gastritis and ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum, antibacterial drugs with a wide spectrum of action are prescribed. Sometimes it is necessary to use a combination of several components with antibacterial properties, good compatibility and drug interactions. The following recommendations must be followed:
- Medicines are used in the dose recommended by the doctor. If the medicine does not exhibit the expected therapeutic properties, you should not try to adjust the dosage;
- if medications are ineffective, you should consult your doctor and reconsider your treatment regimen;
- It is necessary to maintain an interval of at least an hour between taking bismuth with other groups of drugs. Simultaneous use is contraindicated. Otherwise, De-Nol may neutralize the activity of the active ingredients of antibiotics;
- De-Nol should not be taken with dairy products, juices, fruit drinks, compotes, or smoothies. Only clean, drinking water is suitable.
You should not try to find medications to eliminate symptoms on your own. This can aggravate the course of the underlying disease and provoke complications.
Why are antibiotics or antimicrobials necessary when treating with De-Nol?
When used independently, it eliminates Helicobacter bacteria in 33% of patients. To achieve a more pronounced therapeutic effect, it is recommended to combine it with antibiotic therapy. Antibiotics are a basic element in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases caused by exposure to Helicobacter pylori. Your doctor may recommend using:
- macrolides: Clarithromycin, Josamycin, Azithromycin;
- rifamycins: Rifabutin, Rifaximin;
- fluoroquinolones: Tavanica, Ciprofloxacin, Moxifloxacin;
- nitrofurans: Macmiror, Nifuroxazide;
- Metronidazole (Trichopol), Tinidazole.
When eradicating Helicobacter, therapy must be supplemented with bismuth preparations as antimicrobial agents.
The selection of a suitable treatment regimen is carried out depending on the sensitivity of the pathogen to the active component of the drug and individual tolerance of the antibiotic. Therapy should be properly supplemented with antacids before pH testing is performed.
Drugs by group
If you notice the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor. Only a specialist can carry out competent treatment of Helicobacter pylori. This is due to the fact that symptoms and treatment can vary from person to person. Moreover, the drugs are selected by the doctor based on the characteristics of the identified type of microorganism.
The selection of medicine is carried out according to the following criteria:
- ability to kill bacteria. Not every product quickly and effectively kills Helicobacter pylori;
- active ingredients. They must definitely get into the blood. Their effectiveness depends on this;
- the ability of the drug to provoke the death of a microorganism or cause inhibition of its development;
- number of side effects;
- whether the bacteria is resistant to a particular drug.
The most common treatment for this disease is antisecretory drugs and antibiotics. Moreover, it needs to be treated comprehensively. How many times and exactly what means should be used is decided only by the doctor.
Antisecretory
Treatment for this bacterium always includes taking antisecretory medications. These drugs help reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid. This therapy is effective when several conditions are combined. In the stomach, pathogenic microflora lives at a pH level of 4.0–6.0. In this case, bacteria multiply at higher pH values. Antisecretory drugs lead to an increase in pH, but make microorganisms more vulnerable to antibiotics.
These drugs have the following mechanism of action:
- reduce the amount of gastric juice produced. This provokes an increase in the concentration of substances with an antimicrobial spectrum of action;
- these drugs have independent activity against the bacterium itself;
- the drug provokes an increase in the viscosity of gastric juice. As a result, it is released from the stomach more slowly. Therefore, the antibiotic may have a negative effect on the pathogen longer.
As a result, we can conclude that antisecretory agents act as amplifiers of the action of antibiotics. Treatment of H. pylori often includes antisecretory drugs such as Omeprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole, etc. Which drug should be taken is determined by the attending physician based on what signs of the disease the patient has, as well as what pathogen calls them.
Antibiotics
The second group of medications that are necessarily prescribed for this disease are antibiotics. They are an important part of therapy.
The following medications are often prescribed by your doctor:
- amoxicillin. This substance destroys the microbial wall, leading to the death of the bacterium. At the same time, H. pylori practically does not develop resistance to it. Included in Amoxiclav and Flemoxin Solutab;
- clarithromycin. The bacteria can develop resistance to it. This is a macrolide antibiotic. Included in “Fromilid” and “Klacida”;
- Levofloxacin. This is a respiratory fluoroquinolone. The bacteria develops resistance to it. Used if a previously taken remedy has proven ineffective. Glevo is often prescribed;
- tetracycline. Not included in the list of drugs that kill the pathogen. However, it prevents the development of bacteria. Resistance to it rarely develops;
- Metronidazole. Causes DNA damage in the microbe. Able to overcome the resistance that has arisen against him. To do this, the dose is increased. Trichopolum is often prescribed on its basis;
- Furazolidone. Treatment with drugs based on this substance inhibits the growth and reproduction of bacteria and also leads to their death.
In addition, you need to drink “De-Nol” (a drug based on bismuth). This medicine has a local effect on the pathogen, leading to its damage. It is worth noting that De-Nol should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. It is “De-Nol” that is most often prescribed when H. pylori is detected, because resistance to it does not develop. That’s why you can often come across the comment “I drink De-Nol and don’t have stomach problems.”
Doctors also often prescribe Bactistatin. This is a dietary supplement. "Bactistatin" is taken to normalize intestinal microflora after taking antibiotics.
Medicines for Helicobacter pylori: treatment with antibiotics
Therapy aimed at expelling Helicobacter rulori from the stomach of a person infected with it is not the easiest task that a doctor sets for himself.
This is due to the fact that pathogenic microorganisms are extremely reluctant to leave their favorite places of existence - the epithelial cells of the inner lining of the stomach or the submucosa, and drug-resistant strains are formed.
Therefore, the effect on the bacterium must be complex: medication, physiotherapy, nutrition, phytotherapeutic. The main point of application is drug therapy.
Peptic ulcer disease in the world of big numbers
Every year more and more new cases of the disease are diagnosed. Doctors attribute this disappointing trend to the widespread use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which significantly increase the vulnerability of the stomach wall. However, the achievements of modern medicine make it possible to give a very favorable prognosis for peptic ulcer disease. But back at the end of the last century, everything was not so clear.
Eradication therapy regimens
| A drug | Dose | Frequency of application |
| 1st line eradication therapy (7–10 days) | ||
| IPP | standard dose | 2 times a day |
| clarithromycin | 500 mg | |
| amoxicillin | 1g | |
| 2nd line therapy (10–14 days) - if first line therapy is ineffective or intolerant | ||
| IPP | standard dose | 2 times a day |
| metronidazole or amoxicillin | 500 mg (amoxicillin - 1 g) | 3 times a day (amoxicillin 2 times a day) |
| tetracycline | 500 mg | 4 times a day |
| bismuth drug | 120 mg | |