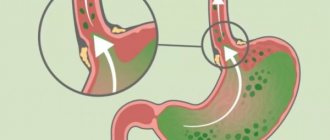
Why does heartburn hurt?
The reflux of gastric juice with a food bolus into the esophagus, where normally there should be an alkaline environment, leads to irritation of the mucous membrane. The epithelium of the esophagus does not have a special protective layer from the aggressive effects of acid, which is located in the stomach. Therefore, the mucous membrane is damaged6. Erosion is formed - surface defects that do not affect the muscular layer of the esophagus. These wounds are additionally exposed to acid, which causes pain.
Heartburn is characterized by pain behind the sternum and in the epigastric region. It is quite easy to confuse it with the heart. A specific condition for pain in the esophagus is a direct connection with food intake7. In addition, heartburn and stomach pain worsen when bending over or in a horizontal position.
List of main reasons
Heartburn and the accompanying heaviness in the stomach can occur due to problems with the stomach and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
Bad habits and poor nutrition affect the appearance of symptoms. Heartburn often appears simultaneously with a feeling of heaviness in pregnant women, and can also be caused by stress.
Gastrointestinal diseases
The list of main problems begins with common diseases:
- A hiatal hernia in the muscle that separates the abdominal and thoracic cavities - the diaphragm. Its increase to a certain size leads to protrusion of part of the stomach beyond its usual location. Because of this, heartburn often appears - especially during sleep, after exercise and eating.
- Chronic gastritis with high acidity. The reason for the increased pH level can be an unhealthy diet (including fatty, salty or fried foods), and heartburn in this case usually appears after eating.
- Ulcers of the stomach or duodenum. Due to these diseases, food enters the intestines later than usual. Distension of the stomach leads to increased pressure inside it and the appearance of additional digestive problems. One of the signs of pathology is heartburn.
The causes of symptoms are also considered to be achlorhydria and achylia. Due to these pathologies, not only the acidity in the gastric juice decreases, but also the content of a special enzyme for breaking down the proteins eaten - pepsin. And heartburn is caused by the reflux of lactic and butyric acids into the esophagus, formed during the fermentation of digested food.
Errors in nutrition
Patients who do not follow basic nutritional rules also suffer from heartburn:
- those who abuse food that is unsuitable for their health – high in fat, salt and spices, as well as food prepared by frying or smoking;
- those who violate the diet - first of all, overeating or eating rarely, but in large volumes (whereas it would be correct to eat more often, but in small portions);
- those who incorrectly consume fresh fruits or vegetables, which it is advisable to consume no earlier than half an hour after a meal.
Carbonated water, especially sweet water, can also cause heaviness in the stomach with a burning sensation. Lively conversations while eating and poor chewing of food are not recommended for people suffering from stomach problems. It has an adverse effect on the stomach, leading to heartburn and a stressful state for the patient. Due to stress, the digestion process is disrupted, and the likelihood of unpleasant symptoms increases.
Pregnancy
Heartburn and heaviness in the gastrointestinal tract often accompany pregnancy, especially in the later stages. One of the main reasons is increased levels of a hormone called progesterone, which causes poor gastric motility. Food is digested more slowly and unpleasant symptoms occur.
The longer the period, the more pressure the growing uterus puts on the stomach and intestines. This increases the risk of reflux and heartburn in the third trimester of pregnancy. And, although there is an opinion that such symptoms almost always accompany pregnancy, in fact, if they appear, it is advisable to immediately consult a doctor.
Bad habits
Overeating, which often causes heartburn, is often accompanied by another bad habit - drinking alcohol. Alcohol has an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa. The discomfort is accompanied by other symptoms, including bouts of nausea, vomiting and stomach pain.
The list of factors that increase the risk of heartburn includes smoking. This habit is dangerous for people who smoke more than 15–20 cigarettes during the day. Irritation of the mucous membrane leads to problems with the stomach and a burning sensation in this organ, as well as the intestines and chest area.
Diseases accompanied by heartburn and pain
Diseases whose symptoms may include heartburn:
- GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease). Persistent relaxation of the esophageal sphincter, which is accompanied by frequent reflux of a bolus of food covered with gastric juice into the esophagus. A person does not necessarily feel every reflux. There can be several dozen of them per day.
- Gastritis. Chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which in most cases is associated with the active proliferation of Helicobacter Pylori. There is also atrophy of the mucosa or, conversely, its excessive growth. The main symptom of gastritis: pain in the epigastric (upper) abdomen 20-30 minutes after eating. Additionally, signs of dyspepsia may be present: nausea, vomiting, belching, increased gas production.
- Peptic ulcer disease. The disease is characterized by the appearance of an ulcer on the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum. A characteristic sign: severe pain about half an hour after eating when located in the stomach and pain 1.5-2 hours after eating when localized in the duodenum. In the latter case, so-called “hunger” pain may occur.3
An isolated burning condition is characteristic only of GERD. For stomach diseases, heartburn is not a key symptom. But if a burning sensation behind the sternum is accompanied by pain in the right or left side of the abdomen, near the navel, then one may suspect diseases of the stomach or pancreas.
Diseases that cause heartburn
In addition to external causes, there are internal factors that provoke the appearance of corresponding symptoms - these are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), often associated with excess acidity of the stomach and duodenum.
Gastritis
Gastritis is a disease that develops as a result of a violation of the integrity of the gastric mucosa. The classification of gastritis is quite complex - it can be acute and chronic and is divided into several types, which differ in etiology, course and methods of treatment. The disease appears against the background of hereditary predisposition, bad habits, poor diet, frequent nervous shock, infection of the stomach and other gastrointestinal organs with the bacterium helicobacter pylori.
In addition to heartburn, gastritis is manifested by sharp or aching pain in the stomach, bouts of vomiting, and lack of regular bowel movements. To treat gastritis, medications are used that envelop the surface of the mucous membrane and restore it, and the patient must also adhere to a special diet.
Stomach and duodenal ulcers
Gastric and duodenal ulcers can occur as a complication of gastritis or as an independent ailment. When the disease occurs, defects form in the mucous membrane of the digestive organs in the form of ulcers, which, depending on the type of ulcer, may begin to bleed from time to time. In addition to poor nutrition and Helicobacter pylori infection, intoxication with alcohol, medications, and various chemicals can accelerate the appearance of ulcers. Characteristic signs of the disease are “hunger pain” (a cutting sensation in the stomach area that occurs on an empty stomach), night pain in the stomach and increased appetite. In addition to heartburn, the disease is characterized by symptoms such as sour belching, nausea, and indigestion.
Duodenitis
Duodenitis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the duodenum. It is characterized by pain in the pit of the stomach, intensifying some time after eating, and night pain in the stomach. Duodenitis is also characterized by symptoms such as periodic vomiting (bile may be present in the vomit from time to time), constipation, loss of appetite, weight loss, belching, heartburn, a feeling of “fullness” after eating, increased body temperature, and general weakness.
The causes of the disease are most often pathologies of intestinal development, food, medication, chemical poisoning, addiction to spicy foods and alcoholic beverages, and helicobacter pylori. Duodenitis is treated inpatiently, the treatment method is determined by the doctor depending on the factors that provoked it, the severity and form of the disease.
Hiatal hernia
A hiatal hernia (HH) is a relaxation of the muscles of the ligamentous apparatus of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm. The hiatal hernia leads to displacement of the lower part of the esophagus, the upper part of the stomach, and intestinal loops into the chest cavity. The pathology can be caused by old age, uterine pressure during pregnancy, trauma, tumors, frequent hysterical cough, constipation, chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms of hiatal hernia include pain that worsens after eating, when lifting heavy objects, during physical activity, difficulty swallowing food, reflux esophagitis, and frequent and severe heartburn.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (reflux esophagitis, GERD) is a disorder of the digestive process in which the contents of the stomach are regularly released into the esophagus. The process contributes to irritation of the walls of the esophagus (less commonly, the larynx), causing a rapid feeling of satiety, burning in the chest area, heartburn and belching. GERD is most often diagnosed in people who are prone to obesity, those employed in hazardous industries, those exposed to constant physical activity, and pregnant women. Additional symptoms that help diagnose GERD are shortness of breath, dry throat, change in voice tone, chronic cough of non-infectious origin.
Achalasia cardia
Achalasia cardia is a disease characterized by a violation of the tone of the opening located between the esophagus and the stomach (cardia). As a result, it loses the ability to open in time when swallowing, and, conversely, can open when it is not necessary. Signs of the disease are difficulty swallowing food, regurgitation, belching, vomiting, and increased salivation.
Additional Information! The disease is dangerous because the hole between the stomach can open at night, during sleep, which will lead to vomiting in an unconscious state.
The situation is fraught with suffocation and even death, so patients diagnosed with achalasia cardia are strongly recommended to sleep exclusively on their sides.
Digestive problems (dyspepsia)
Quite often, patients of different ages complain of various functional disorders of the digestive process in the absence of morphological signs of a particular disease. In this case, the patient is diagnosed with dyspepsia and prescribed treatment aimed at eliminating specific symptoms.
Dyspepsia may include:
- chronic constipation;
- satiety too quickly, feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- frequent diarrhea in the absence of objective reasons;
- bloating;
- heartburn;
- burping;
- periodic abdominal pain.
Sometimes dyspepsia signals the early stage of gastritis or ulcers, and its manifestations can also be a consequence of a heavy feast. Most patients with complaints of digestive problems come to the gastroenterologist’s office after popular holidays - New Year, Easter, etc.
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder, most often having an acute development, but over time developing into a chronic condition, which is characterized by heartburn with pain. Factors contributing to the inflammatory process in the gallbladder are blockage of the bile ducts, impaired flow of bile. Cholecystitis occurs primarily as a consequence of cholelithiasis and is characterized by paroxysmal dull pain in the right hypochondrium, sometimes radiating to the area of the stomach. During periods of exacerbation, the patient may notice yellowing of the skin, darkening of the urine, and lightening of the stool. Antibiotics, antispasmodics, and choleretic drugs are used to treat cholecystitis. If conservative treatment does not produce results for a long time, and the patient suffers from constant pain and other unpleasant sensations, the problem is solved surgically.
Other reasons
In addition to the listed pathologies, the following conditions can cause discomfort:
- Pregnancy. In the first trimester, a sharp hormonal change in the body can lead to indigestion, including heartburn accompanied by stomach pain. In the second and third trimester, the cause of attacks is the growing uterus and increased intragastric pressure. Unpleasant symptoms usually go away after childbirth.
- Recent operations in the epigastric region (removal of tumors, hernias).
- Obesity. In people who are prone to excess weight, the digestion process is almost never healthy. A distended stomach, excess food in it, slow metabolism and other disorders - all these problems cause various manifestations of dyspepsia.
Diet for heartburn and stomach pain
Therapy for burning sensation behind the sternum begins with lifestyle changes, including nutrition. Features of the diet to prevent weakening of the esophageal sphincter5:
- Products not recommended for consumption: carbonated drinks, coffee, strong tea, chocolate, baked goods, fast food, fatty foods, canned food, smoked meats, fruit juices, tomatoes and their derivatives, seeds, nuts, cabbage, sour fruits, black bread, pasta, radish, onion.
- It is recommended to drink enough water per day.
- It is recommended to enrich the diet with vegetable fats, such as legumes, and limit animal fats.
- The diet should be enriched with various vegetables, steamed or baked.
- The use of large quantities of spices is not recommended. Spicy foods will be especially harmful.
Additional recommendations regarding diet:
- Meals should be regular (3-4 times a day in the absence of other recommendations from a doctor).
- Portions should be small.
- After eating, a short walk in the fresh air is recommended.
- After eating, it is not recommended to bend over or lie down.
- It is recommended to sleep with the upper half of the body elevated.
- Clothes should be loose, without tight belts.
Also, to successfully combat a burning sensation in the chest, you need to stop smoking, drinking alcohol, and increase physical activity.
How to avoid unpleasant sensations?
When you are concerned about regular stomach pain and a burning sensation in the chest, the first thing you should notice is what happens after that. When provoking factors have been identified, you should simply avoid them. If this is due to acute or chronic illnesses, then you should not self-medicate and delay visiting a doctor.
To avoid discomfort in the stomach and esophagus, you should take care of this in advance. Every person's morning should begin with exercise 15 minutes before breakfast. The first meal should be complete in order to give the body a charge of energy and strength for the whole day. It is important to lead an active lifestyle and take more walks, which is especially welcome after meals. Stress and conflict situations negatively affect the digestive system, so you should try to avoid them. Smoking often provokes heartburn, nausea and other associated symptoms; nicotine is especially dangerous on an empty stomach.
Medicines for heartburn and pain
A common method for treating heartburn is to drink a baking soda solution, which reacts with the acid in the esophagus, neutralizing it. This method does temporarily relieve discomfort, but only for a short period of time. In addition, constant use of soda only aggravates the condition and is not recommended by any doctor.
Proven remedies for the treatment of heartburn and stomach pain:
- Proton pump inhibitors. Powerful antisecretory drugs that suppress the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach and affect the mechanism of heartburn formation. The basic drug from this group is Omeprazole, which is the active ingredient of Omez® 10 mg. The recommended dose of Omez® 10 mg is 2 capsules per day. The effect of the drug can last for 24 hours. This is a convenient way to combat heartburn: capsules are taken 1 time 30 minutes before meals in the morning. The maximum possible duration of a course of the drug without a doctor’s prescription is 14 days4.
- H2 histamine blockers. Antisecretory drugs that are inferior in power to PPI7. Drugs rarely cause side effects when used in small doses7. Currently, proton pump inhibitors are preferred in medicine4.
- Antacids. The mechanism of action of antacids is to neutralize hydrochloric acid. In this way they relieve the symptoms of reflux, but do not have any effect on the formation of excessive amounts of acid in the stomach. Antacids1 act quickly and are often used as an emergency treatment. However, the duration of the effect of these drugs is short – a few hours1.
- Alginates. The principle of action of alginates is somewhat similar to the effect of antacids. Only they do not completely neutralize the acid, but form a layer of neutral medium between the mucous membrane and gastric juice3.
Treatment of heartburn accompanied by pain includes therapy for the underlying disease. A disease of the gastrointestinal tract can be suspected if taking the listed medications does not have a lasting effect within 2 weeks1. Changing your lifestyle along with timely treatment will help you avoid the complications of frequent acid reflux into the esophagus and prevent the occurrence of heartburn and abdominal pain.
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, YOU MUST READ THE INSTRUCTIONS FOR MEDICAL USE OR CONSULT A DOCTOR.
Treatment
The doctor should select a remedy for heartburn depending on the provoking factor. It is not recommended to take any medications on your own, otherwise you can only worsen the course of the disease. To eliminate the symptom, medications, folk remedies and diet are used.
Medicines
Medicines for heartburn and stomach pain:
- Proton pump inhibitors . To eliminate a burning sensation in the abdomen, Omez, Nolpaza, Emanera and other similar medications are often prescribed. Such medications act on the cells of the mucous membrane that produce hydrochloric acid, resulting in a decrease in the production of gastric juice. This line of products is effective for gastritis and ulcers, because... does not cause withdrawal syndrome. 1 tablet is effective for almost 24 hours.
- Antacids . For treatment, Rennie, Gastal, Phosphalugel and Almagel are prescribed for heartburn and stomach pain. Such drugs are produced in the form of tablets and suspensions, which quickly envelop the mucous membrane, forming a protective barrier on it and neutralizing hydrochloric acid. This group of medications is effective for no more than 2-3 hours. The drugs are prescribed for heartburn in pregnant women, gastritis, ulcers and gallbladder diseases as symptomatic therapy.
- H2 histamine receptor blockers . Ranitidine, Famotidine and Roxatidine are most often used for treatment. Such drugs are not used as often as proton pump inhibitors for the treatment of stomach ulcers, because. after their withdrawal, hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid occurs, which can provoke a relapse. But these medications effectively cope with heartburn.
- Bismuth-containing preparations : De-Nol, Vikalin, Vikair, etc. This line of products forms a protective barrier on the surface of the mucous membrane, protecting it from the damaging effects of gastric juice. At the same time, ulcers, erosions and other defects heal quickly.
Without a gastroenterologist's prescription, you can only use antacids as needed.
Alternative medicine
Folk remedies for stomach pain and burning sensation:
- Pumpkin seeds. To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, it is necessary to consume this product in dried form. As soon as pain occurs, you need to eat 10 seeds.
- Flax seeds. This remedy will help if you take it half an hour before meals, 2 times a day. In this case, you need to eat 1 tsp. flax seeds or pre-soak them in warm water. The course of treatment is 10-15 days.
- Milk with honey. This remedy is best used before bed. It will relieve heartburn and burning in the stomach immediately after taking it. Milk in the amount of 300 ml must be heated to 40°C, then add 1 tsp. honey and mix everything. Drink the contents 2 hours after meals or as needed. The course of treatment is not limited.
- Celery root. It is necessary to take 1 tbsp fresh and crushed. l. 20 minutes before meals for 14 days.
- Potato juice. This remedy quickly and effectively relieves burning and pain, promoting healing of the gastric mucosa. You will need 1 tuber, which must be thoroughly washed, peeled and grated, then squeeze out the juice using gauze and take it 1 hour before meals, 150 ml 2 times a day. Chicken treatment - 10 days.
Traditional methods can be combined with medications only after consultation with a doctor.
Diet for heartburn
Many people are interested in whether it is possible to drink kefir for heartburn and what the risks are. If there is increased secretion of gastric juice, it is not recommended to consume low-fat fermented milk products. The more acidic the kefir, the higher the likelihood of burning.
To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, it is important to exclude from the menu:
- coffee;
- smoked products;
- semi-finished products;
- citrus;
- radishes, tomatoes, onions and garlic;
- fat meat;
- fried foods;
- spicy foods;
- alcohol;
- salty foods;
- carbonated drinks;
- chocolate;
- baking.
Bibliography:
- Practical Manual of Gastroesophgeal Reflux Disease /Ed.by Marcelo F. Vela, Joel E. Richter and Jonh E. Pandolfino, 2013 –RC 815.7.M 368
- Danilov D.V. Modern possibilities for the treatment of erosive esophagitis / Danilov D.V., Shuleshova A.G., Bondareva K.A. // Evidence. gastroenterology. - 2021. - T. 6; No. 1. – pp. 26-30.
- Initial and maintenance therapy in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease / Simanenkov V.I., Tikhonov S.V., Lishchuk N.B. // Med. alphabet. - 2021. - T. 1; No. 9 (306). — P. 8-12.
- INSTRUCTIONS for the use of the medicinal product for medical use OMEZ®10 mg LP 00328 dated 07/11/17 Date of access 11/26/18
- Kardasheva, S. S. Gastroesophageal reflux: new treatment prospects / Kardasheva S. S., Shulpekova Yu O., Leshchenko V. I. // Med. advice. - 2021. - No. 11. - P. 92-99.
- Tarasova, G. N. Pathogenetic features of damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus during gastroesophageal reflux disease / Tarasova G. N., Smirnova E. A. // Consilium Medicum. - 2017. - T. 19; No. 8-2. — P. 7-12.
- Trukhan, D. I. Current aspects of antisecretory therapy of gastroesophageal reflux disease / Trukhan D. I., Grishechkina I. A. // Med. advice. - 2021. - No. 15. - P. 28-35.
How to get rid
Almost every person at least once in his life has wondered how to get rid of heartburn. These days, there are several ways to combat illness. The choice of treatment method depends on the severity of the symptoms.
Taking medications
Self-administration of medications for heartburn is possible only in one case - if you experience heartburn due to eating foods unusual for your diet or overeating.
Under these circumstances, you can use proven and popular pharmaceutical drugs, including:
- "Renny";
- Gaviscon;
- "Phosphalugel";
- "Maalox";
- "Gastal";
- "Omez";
- "Almagel";
- "Mezim";
- "Vicair";
- "Bellalgin."
By taking these medications according to the instructions, it is easy to cope with the unpleasant sensations of heartburn and belching.
If air belching and heartburn appear twice a week or more often, and are also accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms, this is a serious reason to check your health. It is not recommended to take heartburn medications before visiting a specialist.
The gastroenterologist will conduct an appropriate examination, based on the results of which, using palpation, the doctor will determine the presence of serious diseases accompanied by belching. After this, he may prescribe laboratory tests and instrumental examination of the gastrointestinal tract (endoscopy, ultrasound, etc.).
Based on the results of the examination and research, the specialist will easily make a diagnosis and prescribe a course of medications for heartburn and belching, a special diet and regular consultations with a doctor.
Interesting! Very severe heartburn - what to do, causes of attack
Traditional methods
Over the course of its existence, humanity has come up with several ways to combat illness, for example, for heartburn and belching, it is recommended:
- Chew a small handful of sunflower seeds;
- Eat a medium-sized apple or carrot;
- Use a teaspoon of any vegetable oil;
- Drink warm milk.
Traditional medicine recipes
However, natural remedies are much more reliable in the fight against heartburn. Traditional recipes are based on the correct use of the properties of medicinal plants. Herbs for heartburn have shown effectiveness and are popular; they have virtually no side effects.
To overcome unpleasant sensations, decoctions of the following plants are widely used:
- Yarrow;
- St. John's wort;
- Common dill;
- Pharmaceutical camomile;
- Mint;
- Anise;
- Bobovnik.
Often in folk medicine, freshly prepared potato juice is used for heartburn and belching.
An infusion of flax seeds also has enormous benefits; it is prepared in advance and consumed in the morning.
Calamus root is also an effective remedy. A pinch of the crushed product is dissolved in a glass of warm water and consumed before meals.
Heartburn medications
Gastroenterologists for heartburn prescribe the following groups of medications:
- Antacid drugs. They contain magnesium, calcium, and aluminum salts, which neutralize hydrochloric acid. Now the contents of the stomach, entering the esophagus, do not irritate its mucous membrane.
- Alginates. In the acidic environment of the stomach, alginates form a gel barrier, which reduces the amount of gastric contents reflux into the esophagus.
- Antisecretory drugs. They suppress the formation of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, and the contents thrown into the esophagus are no longer so aggressive.
- Prokinetics. These drugs cause the esophagus to contract more actively, increase the tone of the sphincter (it now well closes the opening between the esophagus and the stomach), and also accelerate the movement of food from the stomach to the intestines.
Folk remedies for heartburn
You can resort to folk remedies only if there are no medicines at hand.
There are many recipes for heartburn, but not all of them are effective. Most often used:
- Milk. It neutralizes hydrochloric acid only for a while, envelops the stomach and creates the impression that everything is fine. But after a lull, milk stimulates the formation of gastric juice, and it only gets worse.
- Soda solution.
Many people immediately drink soda when they have heartburn. Of course there will be an effect, but it will be very short-lived. When soda enters the stomach, a lot of carbon dioxide is formed, which stretches the organ and sharply increases the pressure in it. All this provokes repeated heartburn. Important! You should not regularly take soda if you have heartburn, as this disrupts the ratio of salts and water in the body (the so-called water-salt balance). - Potato. This vegetable is good for heartburn. You can chew raw potato pieces or drink freshly squeezed juice.
- Mint decoction. Mint will not help with heartburn, but will only harm. After all, it relaxes the sphincter between the esophagus and the stomach, and hydrochloric acid rushes into the esophagus even more actively.