Helicobacter pylori - what is it?
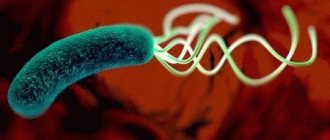
Helicobacter Pylori is a type of harmful bacterium that is present in a certain amount in the human body. With good immunity, microorganisms do not multiply and do not provoke pathological processes.
A decrease in the body’s protective functions and disruption of microflora becomes an ideal environment for the active life of this type of bacteria. Their main action is aimed at damaging the mucous membranes of the digestive tract.
Features of Helicobacter pylori:
- bacteria concentrate in the pyloric region of the stomach;
- microorganisms are resistant to the acidic environment of gastric juice and other factors;
- bacteria easily move along the mucous membranes of the digestive tract and are able to attach to them with special flagella;
- the negative impact of bacteria is aimed at the cells of the digestive tract (microorganisms provoke serious diseases associated with the processes of digestion and assimilation of food);
- a complication of pathologies caused by Helicobacter pylori can be stomach cancer;
- You can become infected with the bacterium during diagnostic procedures (if the instruments have not been fully processed), through the consumption of contaminated food and water, as well as through failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
Locations of Helicobacter
Each reader can imagine how Helicobacter pylori becomes infected by comparing facts from everyday life with the dislocation of the microbe:
- Stomach cavity.
- duodenum.
- Cal.
- Bile.
- Liver tissue.
- Skin.
- Saliva.
- Plaque.
From here, the transmission routes of Helicobacter pylori become obvious. Hypothetically, it is not difficult to catch the infection even on a public beach. However, the microbe is transmitted to humans primarily through the mouth. Although it is not a fact that the air route is excluded, as was found out in relation to salmonella. Simply put, doctors today themselves do not yet know the answer to questions about how to become infected with Helicobacter pylori. Although no one doubts whether the infection is transmitted from person to person.
Of course it is transferable! To avoid getting infected, behave carefully in public places, avoid eating places, and filter your social circle. Which of these postulates will surprise polite society? These are typical rules, following which you will avoid a number of problems. Cook food thoroughly and eat mostly home-cooked meals; avoid animals or maintain hygiene measures.
Symptoms of Helicobacter pylori
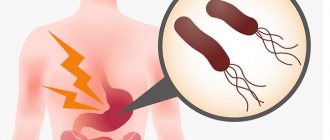
The main symptom of Helicobacter pylori infection is the regular occurrence of pain in the stomach. In most cases, discomfort occurs due to a feeling of hunger. After eating food, the pain syndrome reduces its intensity. Pain can be triggered by fatty, fried or spicy foods. Such food options begin to be difficult to digest. The consequence is regular nausea and heaviness in the stomach.
The presence of other symptoms of infection depends on the degree of progression of the inflammatory process.
Other symptoms:
bloating;- heaviness in the stomach;
- regular burping;
- bad breath;
- loss of appetite;
- flatulence;
- heartburn;
- constant nausea;
- white coating on the tongue;
- intestinal disorders;
- sour taste in the mouth;
- bouts of vomiting;
- regular constipation;
- hunger pains.
Mechanism of appearance of skin symptoms
Violation of the functional state of the digestive tract is directly related to the condition of the skin. This nuance is the cause of various skin reactions when infected with Helicobacter pylori. The provoking factor is toxic damage to the body by bacterial waste products. Skin manifestations can occur in the form of acne, dermatitis, acne and other pathologies accompanied by the formation of pimples and redness of the epidermis.
Mechanism of symptoms:
- disruption of the absorption of nutrients provokes a lack of amino acids and vitamins;
- decrease in the protective properties of the skin;
- sebum secretion increases;
- the body tries to remove toxins through the pores;
- the consequence is the active proliferation of bacteria in the epidermis.
Skin signs of bacterial infection
Common skin manifestations of Helicobacter pylori include acne, rosacea and seborrheic dermatitis. These pathologies have their own symptoms and development mechanisms. The main reason for their manifestation is considered to be the effect of toxic waste products of bacteria on the epidermis.
Rosacea
Localization of skin reactions with rosacea is observed in the forehead, chin and cheeks. Rashes can vary in intensity and appearance. Pimples are small formations with a dense consistency.
In the absence of therapy, the inflammatory process can spread to the mucous membranes of the organs of vision. The patient will be prone to conjunctivitis.
Acne
Acne is a small formation, the development of which begins with a pink spot. As its size increases, a rod with purulent contents is formed. The opening of the abscess occurs spontaneously. A characteristic crust appears at the site of the purulent formation. Acne can cause bluish spots on the skin, which can be extremely difficult to get rid of.
Seborrheic dermatitis
A distinctive feature of seborrheic dermatitis is the formation of characteristic red spots on the skin of the cheekbones, forehead, eyebrows and nasolabial folds. As the pathology progresses, yellow plaques form in their place. The formations cause discomfort with peeling and itching. Seborrheic dermatitis can cause the development of other skin diseases.
Allergic reactions
A tendency to allergic reactions is considered a common complication when infected with Helicobacter pylori. Pathogenic microorganisms can provoke atopic dermatitis, chronic urticaria, and food allergies. This factor is due to the toxicity of bacterial waste products.
Hereditary autoimmune diseases, bronchial asthma and congenital diseases of the digestive system increase the risk of allergies.
Causes of allergies caused by Helicobacter pylori:
- increased release of inflammatory mediators;
- inflammation of the inner lining of the digestive organs under the influence of harmful toxins;
- increasing the permeability of capillaries of the digestive tract;
- strengthening the release of histamine and gastrin.
Results
- there are several ways to determine Helicobacter in stool using a laboratory method;
- each analysis option has its own advantages and disadvantages;
- To obtain the most accurate results, it is recommended to take several tests of different types;
- feces for analysis are collected taking into account a number of rules;
- a few days before the procedure, coarse fiber, fried, fatty foods, hot spices and seasonings, alcohol and any orange or red fruits are excluded from the diet;
- the container for feces must be sterile (pharmacy containers are the best option).
Video on the topic: Why is the Helicobacter pylori bacterium dangerous?
Symptomatic treatment of skin manifestations
Treatment of diseases caused by Helicobacter pylori involves long-term and complex therapy. Relief of symptoms of a pathological process does not confirm the cessation of the vital activity of microorganisms. Bacteria can remain in “sleep mode” for a long time. If the therapy was carried out inadequately, then the slightest provoking factor will cause the restoration of the activity of harmful microorganisms.
Treatment includes taking certain medications and some alternative medicine prescriptions.
Drug treatment
Before starting therapy, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination. There are several generally accepted treatment regimens, each of which has its own nuances. The degree of damage to the digestive tract, the presence of complications, and additional inflammatory processes play an important role.
Examples of medications:
antibacterial agents (Amoxiclav, Clarithromycin, Azithromycin);- proton pump blockers (Nolpaza, Omez, Omeprazole);
- gastrocytoprotectors (Bismol, Bismofalk, Ventrisol);
- histamine blockers (Famotidine);
- antisecretory agents (Zoran, Gistodil, Ranigast);
- products that protect the mucous membranes of the digestive organs (Almagel);
- bismuth preparations (De-Nol).
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine recipes can only be used as a supplement to primary drug therapy. Plant components will help improve the protective functions of the digestive system and the body as a whole.
Before using folk remedies, you should exclude the presence of an allergic reaction to individual components.
Examples of folk remedies:
- flaxseed (boil the ingredient for five minutes, take a minimum amount of water, after boiling the preparation must be filtered, the resulting slimy mass should be taken a tablespoon before each meal);
- infusion from a herbal collection (combine yarrow, St. John's wort, celandine and chamomile in equal proportions, pour four tablespoons of the mixture into 500 ml of boiling water, infuse the product for several hours, take the infusion in small portions before each meal);
- decoction of calamus rhizome (pour boiling water over the dry preparation, 500 ml of water is needed for four tablespoons of the ingredient, leave the product for several hours, take 50 ml thirty minutes before eating).
Video - When is Helicobacter pylori treatment necessary?
Diagnostics
A breath test is used for diagnosis. They give a tablet containing radioactive carbon, and the patient washes it down with orange juice. When urea comes into contact with Helicobacter, carbon dioxide with an increased molecular weight is released. The presence of such a substance is determined using mass spectrometric methods. If the result is positive, but there are no serious complaints, a ten-day treatment is carried out according to the general scheme. The composition of the drug includes proton pump inhibitors and antibiotics in high doses.
A sixth of humanity remains carriers of the microbe after completing the course. The strain in the stomach is not 100% destroyed. If there are serious complaints, an endoscopic examination is performed. If an ulcer is detected, a biopsy is taken to find out whether a microbe is the cause of the disease. The bacteriological study allows doctors to learn about the treatment of the disease. The laboratory is simultaneously conducting studies on the sensitivity of the strain to antibiotics.
Doctors testify that treatment of Helicobacter pylori has sharply reduced the incidence of stomach cancer. Doctors explain: in the last century, the fight was aimed at areas of life that were not scientifically related to the occurrence of the disease:
- Daily regime.
- Rationalization of the diet.
- Treatment of stress.
Therefore, Helicobacter in children is treated and re-infection is avoided. Symptoms of dyspepsia - indications for research. 20 years ago, a conscript with such a diagnosis had no chance of seeing a higher education institution. People with a family history of cancer are at risk. If there is a similar history and a negative breath test for Helicobacter, an additional endoscopic examination is performed. It wouldn't hurt to get a biopsy to get accurate results.
Mechanism of damage to the gastric mucosa
Helicobater pylori disrupts the functional state of the stomach. The protective properties of the mucous membranes are reduced to critical levels. Harmful substances begin to enter the blood in large quantities. The consequence of the vital activity of bacteria is a disturbance in the level of hormones responsible for stimulating the peristalsis of the digestive organs. There is a serious deviation in the motility of the gastrointestinal tract.
Mechanism of damage to the gastric mucosa:
- displacement of beneficial microorganisms from the digestive system;
- provoking dysbacteriosis;
- atrophy of the mucous membranes;
- formation of ulcers on the mucous membranes;
- decreased secretion of gastric juice;
- damage to the digestive organs and the development of chronic diseases (gastritis, peptic ulcer, intestinal or stomach cancer).
How dangerous is the bacterium, how does the mechanism of epithelial damage occur?
Helicobacter pylori can provoke not only pathologies of the digestive system, but also deviations in the functioning of the entire body. Complications include peptic ulcers, the formation of malignant tumors in the digestive organs, sepsis, and gastrointestinal bleeding. In the absence of adequate therapy, the risk of autoimmune disorders (iron deficiency anemia, alopecia, atopic dermatitis) increases.
Bacteria can cause cerebral atherosclerosis, Raynaud's disease and the vascular form of migraine.
Tactics for determining Helicobacter bacteria using stool analysis
The doctor prescribes a specific test for helicobacteriosis. The specialist takes into account the individual clinical picture of the patient’s health status. You can get tested for Helictobacter pylori yourself if you suspect a functional deviation of the digestive tract.
Molecular diagnostics
Molecular analysis reveals the specific DNA of the bacterium. The code is duplicated on a special device. When the bacteria reaches the desired size, it is compared with ethanol. If parts of the DNA match the original, then the test result is positive (Helictobacter pylori infection has been detected). The technique is characterized by a high degree of information content.
Cultural analysis
Bacterial inoculation (or cultural analysis) belongs to the category of microbiological research methods. During the procedure, biological material is placed in an environment that is most favorable for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. After a week, the stool is examined using a microscope.
To identify Helicobacter pylori, the color of the bacteria and their ability to enter into certain reactions are taken into account.
Features of the technique:
- the procedure allows you to identify a pathological antigen;
- in the process of studying biological material, a sensitivity test to antibacterial drugs is carried out;
- The results of the study allow us to select the most effective treatment regimen.
Determination of Helicobacter pylori antigen in feces by immunological method
The main purpose of immunological tests when identifying Helicobacter pylori is to determine antigen + antibody complexes. Labeled antibodies are used for the study. When they react with feces, such substances undergo certain changes. Antibodies are able to detect the presence of not only pathogenic bacteria in the stool, but also their parts, as well as waste products.
Advantages and disadvantages of PCR diagnostics
PCR diagnostics has a number of advantages and disadvantages. Some types of pathogenic bacteria can only be detected using this technique (for example, cytotoxic types of microorganisms). Collecting material for analysis does not imply causing pain or discomfort to the patient. The procedure shows the most reliable results.
Advantages of the technique:
- the procedure allows you to identify various strains of pathogenic bacteria;
- the method has a high degree of sensitivity;
- the analysis is safe for the patient (no medical instruments are used to collect material);
- non-invasiveness and simplicity of the process of collecting biological material;
- high degree of specificity of the test;
- The method allows you to determine not only spiral-shaped, but also coccal types of bacteria.
The high degree of sensitivity of the test is its simultaneous advantage and disadvantage. The analysis accurately determines the presence of bacteria, but if the biological material or container is contaminated, the results of the procedure may be false positive.
To exclude false indicators, you should follow all the rules for collecting stool for testing.
Other disadvantages:
- relatively high price of the procedure;
- inability to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibacterial drugs;
- lower sensitivity compared to the procedure for examining a biopsy of the gastric mucosa.
In vitro stool test for Helicobacter pylori antigen
Procedures for studying feces are carried out outside the patient’s body (“in vitro” - “in glass”, “in vitro”). To detect a microbe, such methods are as accurate and effective as possible. However, the procedures have some disadvantages. Some processes occurring in the human body cannot be recreated artificially.
Tests can show the level of sensitivity of bacteria to certain antibiotics, but such tests do not provide 100% information.
Consequences of ignoring treatment
Lack of adequate treatment for Helicobacter pylori can cause serious complications. The most common consequences of this type of bacteria are stomach cancer, peptic ulcers and a tendency to allergies. Such pathologies take a chronic form, and some of them pose a threat to the patient’s life. For example, the prognosis for malignant tumors in the digestive system in most cases is extremely unfavorable.
Peptic ulcer
Helicobacter pylori is the main provoking factor for peptic ulcer disease. The development of the inflammatory process occurs at an accelerated pace. In the absence of timely treatment, there is a risk of perforated ulcer. The main symptom of the disease is pain in the digestive organs. Seeing a doctor should not be delayed if you experience hunger pains that occur several hours after eating. A characteristic sign of peptic ulcer disease is pain in the stomach area, which manifests itself mainly at night.
Stomach cancer
The most dangerous consequence of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms is stomach cancer. The provoking factor in this case is the lack of treatment for gastritis. The disease becomes chronic and causes metaplasia. In medical practice, such a pathology is considered a precancerous condition. The second cause of intestinal cancer is a complication of peptic ulcer disease. The danger of cancer lies in its long-term asymptomatic development and manifestations that resemble other diseases of the digestive system.
Allergy
Helicobacter pylori significantly reduces the body's protective functions. The patient becomes prone to allergic reactions. Atopic dermatitis is a common consequence. With this disease, rashes appear on any part of the body. Skin reactions are accompanied by itching and suppuration (if the wounds are contaminated).