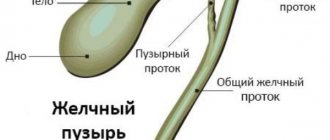
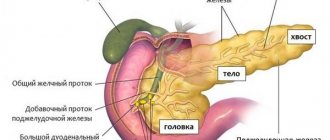
Chronic cholecystitis is characterized by the occurrence of a long-term inflammatory process affecting the gallbladder. The occurrence of inflammation is associated with the activity of pathogenic flora of bacterial and viral origin.
Chronic cholecystitis is a sluggish disease. The disease has a paroxysmal course. Exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis can be triggered by a number of reasons and factors, so patients suffering from this pathology should know what to do in case of exacerbation of cholecystitis.
What provokes exacerbation of cholecystitis?
Chronic cholecystitis can be of two types - calculous, accompanied by the formation of stones, and acalculous.
The main reasons for the appearance of a chronic form of pathology are the development of an infectious process and stagnation of bile. These factors are interrelated; any of them can become the impetus for the formation of the disease.
The accumulation of bile secretion leads to an increased risk of an infectious process, and infection and the inflammatory process contribute to a narrowing of the excretory duct and a decrease in the rate of release of bile secretion into the intestinal lumen.
Exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis is provoked by the presence of the following factors:
- the presence of overweight and obesity, an increased amount of cholesterol in bile is one of the reasons for the development of cholelithiasis;
- diabetes;
- starvation;
- the presence of a hereditary predisposition;
- period of bearing a child;
- taking hormonal contraceptives, certain antibiotics and other medications;
- rare meals, when meals are taken 1-2 times a day.
In addition, exacerbation of cholecystitis of the calculous form can be provoked by:
- Strong shaking when driving.
- Excessive physical exertion, especially after prolonged physical inactivity.
- Sudden changes in body position after a heavy meal.
Exacerbation during the acalculous form of chronic cholecystitis can provoke:
- consumption of large amounts of fatty, smoked and pickled foods;
- binge eating;
- drinking excessive amounts of alcohol;
- effects of stress on the body;
- development of an allergic reaction, especially to food;
- a diet in which there were no fiber-containing foods for a long time.
The pathology can worsen in a person who is exposed to hypothermia, has abnormalities in the development of the biliary tract, or suffers from dyskinesia.
Cholecystitis can worsen from once a month to 3-4 times a year, the exacerbation stage can last a different amount of time, so doctors distinguish between mild, moderate and severe exacerbations. Depending on the course of the pathology, different treatment tactics should be used.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for chronic cholecystitis is generally favorable unless a phlegmonous or gangrenous complication develops. However, the disease greatly impairs the patient's quality of life.
Prevention of cholecystitis can be primary and secondary. Primary prevention consists of a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and timely treatment of gastrointestinal diseases. Secondary prevention, that is, prevention of exacerbations of cholecystitis, consists of following the prescribed diet, avoiding both physical inactivity and excessive physical activity and stress.
[1] Zmachinskaya, I. M. Chronic cholecystitis: educational method. manual Minsk, 2021.
The main signs of exacerbation of pathology
The main symptoms of an attack of the disease are abdominal pain, gastrointestinal disorders, weakness and fever.
The first symptom indicating the presence of an exacerbation of cholecystitis and the need for treatment is the appearance of severe pain in the abdominal area.
The area of localization of pain, its intensity and duration depend on a large number of individual characteristics of the adult’s body.
The main features of the patient’s body that influence the intensity and localization of pain are the following:
- A type of biliary dyskinesia.
- The presence of complications accompanying the inflammatory process in the gallbladder.
- The presence of concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The last of these features can have a significant impact on the choice of therapy used. This feature has a significant influence on the choice of diet when exacerbations of chronic cholecystitis occur.
Most often, pain during exacerbation of the disease is localized in the area of the right hypochondrium; it can be constant and not severe. The pain may be aching in nature, in some cases it may feel like heaviness under the right rib. Such pain is characteristic of a situation in which there is a decrease in the tone of the walls of the gallbladder.
If the tone is higher than normal or the stone moves in the bladder, the pain is of the nature of biliary colic.
Characteristic signs in such a situation are:
- severe pain in the right hypochondrium;
- the pain is paroxysmal in nature;
- the pain radiates to the area of the right shoulder blade, collarbone or shoulder.
The pain is relieved by applying a warm heating pad. If vomiting occurs, after its completion the pain increases significantly.
When the inflammatory process spreads to adjacent tissues, the pain becomes constant and intensifies when making movements with the right hand, as well as when bending and turning the body.
Signs of the development of dyspeptic disorders are:
- The appearance of bitterness in the mouth.
- Vomiting with an admixture of bitterness.
- Attacks of nausea.
- Bitter belching.
- The appearance of bloating.
- The appearance of diarrhea.
The patient develops a feeling of itching; if bile stagnates in the excretory tract, this leads to an increase in its pressure and partially bile acids enter the bloodstream. The feeling of itching can spread both to the entire body and to individual areas.
The appearance of itching is characteristic of the calculous form of the pathology, but even with non-calculous chronic cholecystitis, such a symptom may appear, which indicates the need for drug treatment in a hospital setting, and not at home.
Treatment
First of all, a diet is prescribed: table No. 5 according to Pevzner.
If there are no stones in the gall bladder and there are signs of bacterial inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed and the course of treatment lasts at least 8 days.
To reduce pain, antispasmodics (drotaverine, mebeverine, hymecromone, hyoscine butyl bromide) are recommended. To reduce nausea and vomiting, normokinetics (domperidone, trimebutine) are prescribed. To restore the outflow and properties of bile, doctors prescribe ursodeoxycholic acid (ursosan).
If the cause of cholecystitis is gallstones, after the exacerbation subsides, a planned operation to remove the gallbladder is necessary.
Methods of treatment and diagnosis of exacerbations of cholecystitis
When conducting a diagnosis, the doctor studies the patient’s medical history and identifies concomitant diseases that can lead to exacerbation, for example, pancreatitis. When palpating the right side of the body in the hypochondrium area, the patient experiences painful sensations.
To confirm the diagnosis, a complex of laboratory, instrumental and hardware studies is carried out.
Laboratory tests reveal an increased ESR and high levels of activity of liver enzymes such as phosphatase, GGTP, ALT and AST. In the absence of stones, the composition of bile reveals a low content of bile acids and an increased amount of lithocholic acid, cholesterol crystals and an increased amount of bilirubin are also found. In addition, the presence of bacteria that provoked the inflammatory process is detected in the bile.
The following are used as instrumental and hardware diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound;
- cholegraphy;
- scintigraphy;
- duodenal intubation;
- arteriography.
Treatment of exacerbation of cholecystitis
Surgical methods of treatment are used only to treat the calculous form of the pathology, as well as non-calculous in the acute form.
In other cases, treatment with conservative methods is indicated. Conservative treatment involves the use of a whole range of medications.
Antibacterial agents are used to sanitize the source of the inflammatory process. Enzyme preparations - Panzinorm, Mezim and Creon are used to normalize digestive processes. NSAIDs and antispasmodics are used to relieve pain and reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process. Means to enhance the flow of bile help normalize the functioning of the organ.
Such drugs are
- Liobil.
- Allohol.
- Holosas.
In addition, you can use a decoction of corn silk to normalize the flow of bile.
To reduce the degree of intoxication of the body, droppers with sodium chloride and glucose are used.
In combination with drug therapy, the use of physiotherapy methods is recommended. According to reviews from doctors and a large number of patients, the use of such techniques as:
- electrophoresis;
- SMT therapy;
- reflexology;
- installation of applications with therapeutic mud.
If there is a need for surgical intervention, but contraindications are identified, shock wave lithotripsy can be used as an alternative. The technique is used to crush stones in the calculous form of pathology.
The disadvantage of the technique is the high probability of re-formation of stones in the biliary tract in the future.
The use of diet in the treatment of exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis
Dietary nutrition in the event of exacerbations of chronic cholecystitis involves the introduction of a number of restrictions in the diet. At the acute stage, it is recommended to adhere to diet No. 5a.
In addition, certain nutritional principles should be followed. You need to switch to fractional meals. There should be 5-6 meals per day, while the single volume of food consumed should be small. It is recommended to eat at the same time.
Doctors advise reducing to a minimum the amount of simple carbohydrates consumed, such as sweets, honey, and sweet baked goods. You need to stop consuming carbonated drinks, alcohol and coffee. It is better to replace the indicated components of the diet with weak tea, compotes, natural juices, herbal decoctions and mineral water.
The consumption of vegetable oils, lean meat, low-fat dairy products, oatmeal and buckwheat, vegetables and fruits is allowed.
During the acute stage, it is prohibited to consume fatty meat and broths prepared on its basis, nuts, fried foods, egg yolks, sour cream, cottage cheese and milk with a high fat content. In addition, you should exclude sausages and ice cream from your diet.
It is recommended to prepare dishes by steaming or by baking and boiling.
Prevention of exacerbations of cholecystitis
The risk of exacerbations is significantly reduced if preventive measures are followed. To prevent exacerbations, it is recommended to follow a dietary diet and strictly follow the recommendations received from the attending physician. The most optimal diet during the period of remission of pathology is dietary table No. 5. The main requirement is to draw up a diet using approved products and methods of preparing dishes.
A patient at risk must monitor his body weight. It is forbidden to overeat and starve. Doctors advise regular rehabilitation using sanatorium-resort treatment. During the period of remission of the pathology, to prevent the occurrence of exacerbations, it is necessary to do therapeutic exercises recommended by the attending physician.
For preventive purposes, you can use Essentuki mineral water No. 4 and 17, Smirnovskaya and Mirgorodskaya. The recommended amount is one glass three times a day.
To improve the health of the body, after consultation with your doctor, you can drink infusions prepared on the basis of herbal infusions, which include corn silk, immortelle and mint. Infusions based on chamomile, rose hips, St. John's wort, tansy, celandine and calendula can be used as antimicrobial agents.