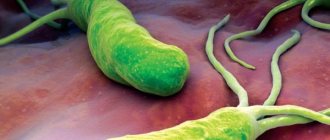
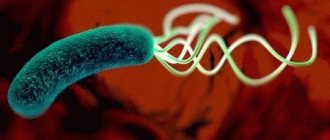
Helicobacter pylori is a pathogenic microorganism from the category of gram-negative bacteria.
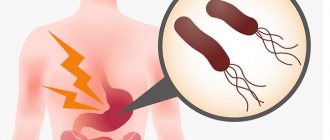
Its main habitat is the human stomach. The bacterium can be present in the digestive system for a long time without symptoms. Under the influence of certain factors, Helicobacter pylori begins active life. The bacterium is toxic and causes serious abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract. This microorganism is the main causative agent of gastritis and peptic ulcers. Early identification of the bacterium can shorten the duration of therapy and speed up the trend toward recovery. Late diagnosis and lack of adequate treatment increases the risk of complications. In case of severe damage to the digestive tract, antibiotics must be used.
Is it necessary to treat Helicobacter pylori?
Helicobacter pylori may not cause harm to the body if it is in “sleep” mode. As soon as symptoms of abnormalities in the digestive tract appear, treatment should begin immediately, but antibiotics are used only as directed by a doctor. The pathogenic microorganism has a destructive effect on the mucous membranes of the digestive organs, causing the formation of ulcers and erosions. If certain factors are present, therapy should begin as quickly as possible.
Indications for mandatory treatment of Helicobacter pylori:
- atrophic type gastritis and intense atrophic changes in the digestive tract;
- progression of inflammatory processes in the abdominal organs;
- peptic ulcer of the duodenum and stomach;
- lack of results from treatment of gastrointestinal disorders;
- oncological pathologies of the digestive system;
- regular causeless vomiting;
- progressive gastroesophageal reflux;
- constant deviations in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- intestinal spasms that occur at night;
- detection of cancer of the digestive system in close relatives.
Start of treatment
Before the doctor selects a treatment regimen for Helicobacter, he is obliged to prescribe a test that determines the sensitivity of the bacterium to antibacterial agents. This will help you choose the right drugs to kill the bacteria.
Principles of effective antibiotic treatment for Helicobacter pylori:
- Initially, you should undergo examinations to identify bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract.
- It is advisable that not only patients, but also their loved ones and relatives living with the patient undergo H. Pylori therapy. In this case, it is not at all necessary to examine household members.
- After drug therapy, control diagnostics are carried out. If a pathogenic microorganism is newly detected, it is recommended to re-administer antibiotics for 3-5 days. The duration of the course is determined by the doctor.
- Today, the most effective is to take three or even four drugs at once.
How to cure Helicobacter pylori if drug therapy does not work? American scientists were puzzled by this question. They conducted an experiment on 18 patients, during which they found out that the culprit of many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is vulnerable to light. Phototherapy has shown high effectiveness, however, scientists need to conduct a number of additional studies. After them, it will become clear whether it is possible to replace antibacterial therapy with laser.
Antibiotics are mainly taken for gastritis and the presence of Helicobacter in the gastrointestinal tract.
However, there are other indications:
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- maltoma and gastrectomy;
- gastrointestinal tumors;
- lack of iron in the body;
- development of anemia.
No matter how strange it may sound, drug therapy is not carried out in all cases. It is only necessary if there is a risk of developing an ulcer or if there are nonspecific symptoms.
Several drugs are prescribed simultaneously to treat the infection. There are different lines of medications against Helicobacter pylori.
Their choice depends on the following factors:
- Age of the patient with H. Pylori.
- The body's reaction to antibiotics (for this it is necessary to conduct a drug sensitivity test).
- Contraindications to taking certain groups of medications. For example, some cannot be taken if you have kidney failure.
The doctor should also select a remedy, taking into account:
- Its ability to kill colonies of bacteria in an acidic environment created by exposure to hydrochloric acid.
- The bioavailability of the antibiotic must be high.
- Minimal number of side effects (this is especially important for the treatment of children and pregnant women).
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori
If infection with pathogenic bacteria is suspected, the patient should undergo a comprehensive examination. There are special techniques that allow you to most accurately determine the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body. After confirming the diagnosis, the specialist prescribes therapy. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection can be carried out in several ways - using antibiotics, chemotherapy methods, without the use of antibacterial drugs. Completion of each stage of therapy involves a follow-up examination.
Features of Helicobacter pylori therapy:
- identification of a bacterium implies urgent treatment not only of the patient, but also of his relatives;
- if infection is detected in more family members, then everyone is prescribed a course of azithromycin-based medications (regardless of whether there is infection or not);
- lack of treatment effectiveness within six weeks implies the mandatory use of eradication;
- determining the duration of the therapeutic course and the set of necessary medications is the doctor’s task (self-medication is excluded).
Actions after completion of treatment
Once the basic treatment regimen for Helicobacter pylori has been completed, you should not relax. Next, you need to support your body with the help of medications for a certain period of time:
- Five weeks, if we are talking about duodenal localization of the microorganism.
- Seven weeks, if its localization is gastric.
The subsequent treatment regimen for Helicobacter pylori with antibiotics includes the use of one of the following drugs:
- Proton pump inhibitors - drugs "Omez", "Rabeprazole". You need to take these medications 1-2 times a day.
- Histamine H2 receptor blockers. These may be drugs such as Ranitidine, Famotidine. Taken twice a day.
- Antibiotic "Amcosiclav" - 2 times a day.
Effective methods of treating Helicobacter pylori
One of the methods of treating Helicobacter is eradication therapy. Eradication involves the use of a combination of several types of drugs with different pharmacological properties. There are three lines of eradication therapy. The indication for such treatment regimens is the lack of results from the use of medication courses. Eradication should be applied in stages. First, the first line of treatment is used, then (if there is no effect) - the second, and only as a radical measure - the third.
First line eradication therapy
The first line of eradication therapy is presented in two versions.
According to the classical scheme, a combination of Clarithromycin and penicillin antibacterial agents is used. As a supplement, drugs are prescribed whose action is aimed at regulating the secretory function of the digestive organs. Antibiotics belong to the category of potent drugs. To reduce their negative impact on the body, eradication is supplemented with Enterol. The drug well compensates for the aggressive properties of antibacterial medications.
If there is no result of therapy with the standard regimen, the second option is prescribed:
- Tetracycline;
- Omeprazole;
- Metronidazole;
- De-Nol.
Second line eradication therapy
The failure of treatment with the first line of eradication is the basis for the use of second line of therapy. The combination of drugs is changing. The basis of therapy is a penicillin antibiotic (Amoxicillin). The medication is supplemented with Omeprazole and De-Nol. To reduce the aggressive effect of the antibiotic on the body, Levofloxacin is used.
Third line eradication therapy
The indication for the third line of eradication is not only the failure of therapy by other methods, but also the presence of severe dyspeptic disorders in the patient that arose during long-term use of antibiotics. The main set of drugs is selected from the first or second line, but drugs based on bifidobacteria are a mandatory addition. Medicines reduce the load on the digestive tract, restore microflora and protect the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Examples of drugs:
- Linux;
- Normobact;
- Bifiform.
How to take de Nol for Helicobacter pylori
The occurrence of gastritis and peptic ulcers is associated with many factors: poor diet, stress, smoking and alcohol abuse, long-term use of medications (non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory, anti-tuberculosis, antibacterial or hormonal therapy). However, the leading role in the etiology of these diseases is occupied by the infectious nature of inflammation associated with Helicobacter pylori, a gram-negative spiral-shaped bacterium.
Is it possible to treat Helicobacter pylori without antibiotics?
Eradication of the pathogen without antimicrobial therapy is impossible.
However, eliminating concomitant factors that contribute to the development of ulcerative defects of the mucous membrane (alcoholic drinks, smoking, spicy, fried foods, stress, etc.) helps reduce the risk of relapses and accelerates the process of scarring of the ulcer.
The diet during an exacerbation should be as gentle as possible. It is preferable to consume all dishes in pureed, slimy form. Marinades, smoked meats, spicy and salty foods are completely excluded. Carbonated drinks, coffee, strong tea and alcohol are also prohibited.
During therapy with De-Nol, a dairy-free diet is indicated.
What is the difference between an ulcer and gastritis?
The term gastritis refers to an inflammatory process that affects the gastric mucosa and leads to atrophic changes in its structure, decreased regenerative capacity, impaired secretion and motility functions, as well as the evacuation of food. Just like peptic ulcers, gastritis has a chronic course, with periodic relapses (periods of exacerbation of the disease). Unlike gastric and duodenal ulcers, it is not accompanied by the formation of a defect in the wall of the organ.
Antibiotics for gastritis and stomach ulcers are prescribed precisely when infection with this pathogen is confirmed. You can become infected with Helicobacter directly from another person (kissing, sharing utensils) or by drinking low-quality water.
What antibiotics are used to treat Helicobacter pylori?
To eradicate the pathogen, use:
- amoxicillin (Flemoxin Solutab ® );
- metronidazole (Trichopol ® );
- tinidazole;
- clarithromycin (Klacin ® , Fromilid ® );
- levofloxacin (Levolet R ® , Glevo ® , Tavanik ® , Hyleflox ® );
- ciprofloxacin (Tsiprolet ®, Tsiprobay ®, Tsifran ®);
- tetracycline ® .
For first-line therapy use:
- proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole ® , the use of Lansoprazole ® or Esomeprazole ® is indicated if it is impossible to use the first drug);
- amoxicillin preparations and 5-nitroimidazole derivatives (metronidazole ® or tinidazole ® ).
A combination of inhibitors, amoxicillin ® and clarithromycin ® is also possible.
Treatment regimen (three-component) with first-line drugs
The most effective combination is Omeprazole ® twenty milligrams twice a day, clarithromycin 0.5 grams every twelve hours and metronidazole ® 400-500 mg, or amoxicillin ® 1 gram twice a day.
A regimen containing amoxicillin for peptic ulcer disease is currently considered ineffective due to the high resistance of the pathogen.
First-line therapy was previously prescribed for seven days, but recent studies suggest that a two-week course of treatment is more effective.
This is due to a decrease in the sensitivity of Helicobacter to the drugs used. Antibiotics for gastritis and ulcers in a 4-component treatment regimen are also used from 10 to 14 days. Quadruple therapy is prescribed if there is no effect from first-line treatment!
To potentiate the anti-Helicobacter action of antimicrobial agents, cytoprotectors (bismuth salts) are added. Fluoroquinolone or tetracycline antibiotics for stomach ulcers are used if the pathogen is resistant to metronidazole ® , clarithromycin ® or amoxicillin ® .
The combination of metronidazole ® , De-Nol ® , Omeprazole ® and tetracycline (0.5 grams every six hours) is effective in more than 95% of cases.
If eradication has not been achieved, a ten-day regimen is used that combines: a proton pump inhibitor, amoxicillin ® and levofloxacin ® (0.25 grams every 12 hours).
Antibiotics for gastritis and stomach ulcers in a sequential therapy scheme
Therapy is carried out in a course of ten days. At the beginning, proton pump inhibitors and amoxicillin drugs are prescribed for five days, then for another five - inhibitors, clarithromycin and tinidazole ® (500 mg twice a day).
The use of a combination of clarithromycin and Pilorid ® is also effective.
Pilobact ®
The Pilobact ® package contains seven blisters with a daily dose of omeprazole ® , tinidazole ® and clarithromycin ® (two tablets of each).
Not prescribed for pregnant and breastfeeding women, patients with intolerance to components, blood diseases, and severe renal impairment.
Children over sixteen years of age may be prescribed Pilobact-Neo ® .
Omeprazole ®
A proton pump inhibitor that suppresses the secretion of hydrochloric acid by blocking the last stage of its formation.
The effect of use occurs quickly (within an hour) and lasts for 24 hours after a single use.
Not prescribed for children (can be used from the age of five as prescribed by the attending physician for a short course as part of complex therapy), pregnant and breastfeeding women, and those with impaired kidney and liver function.
Tinidazole ®
A 5-nitroimidazole derivative that inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis.
It has high bioavailability and rapid absorption. Maximum therapeutic concentrations are achieved within two hours after administration. It is excreted from the body with bile and urine.
Able to penetrate the placental barrier. Strictly prohibited in the first trimester of pregnancy. In the second and third cases, it can be used only for health reasons in the absence of an alternative, due to the risk to the fetus. Also, Tinidazole passes into breast milk and is excreted within three days after administration.
Not prescribed for pathologies of the central nervous system, blood diseases and individual intolerance.
Clarithromycin ®
A semi-synthetic antimicrobial agent from the macrolide group, which is a derivative of erythromycin with improved oral bioavailability. The drug has good acid resistance and an extended spectrum of antimicrobial activity.
Cmax after administration is achieved within two hours. The antimicrobial effect is determined by the ability of clarithromycin ® to inhibit the synthesis of structural components of the bacterial cell wall.
The digestibility of the drug and the rate of absorption from the gastrointestinal tract do not depend on food intake.
The tablet form is not used until the age of twelve. If antibiotics against Helicobacter pylori are prescribed to young children, it is recommended to use a suspension.
Clarithromycin ® is contraindicated in case of porphyria, in the first trimester of pregnancy, during breastfeeding, in case of renal and liver failure.
Side effects may include dyspeptic disorders, diarrhea, colitis, candidiasis, disruption of the normal intestinal microflora, heart rhythm disturbances, anxiety and insomnia, allergies, hypoglycemia, and a decrease in the number of platelets and leukocytes.
Pilorid ®
An antiulcer drug that is a combination of ranitidine ® (a histamine receptor H2 blocker and bismuth citrate.
The mechanism of action is due to the gastrocytoprotective and bactericidal effect of bismuth, as well as the ability of ranitidine ® to suppress the secretion of gastric juice.
Not prescribed for pregnant women, children, patients with porphyria and patients with renal failure.
Treatment regimen for Helicobacter with antibiotics with de-nol ®
The most common treatment option is a combination of bismuth salts, amoxicillin and metronidazole ® .
Source: https://tsitologiya.su/zheludok/kak-prinimat-de-nol-pri-helikobakter-pilori
Antibiotics for Helicobcter pylori and their effectiveness
Helicobacter pylori belongs to the category of bacteria that are quite difficult to get rid of. The microorganism may be resistant to some types of antibacterial drugs. Not all medications in this group have the ability to penetrate the mucous membranes of the digestive tract (the main habitat of Helicobacter pylori). In addition, the effect of certain types of antibiotics is partially neutralized by the increased acidity of gastric juice. Selecting a treatment regimen is a specialist task, for which a comprehensive and step-by-step examination of the patient should be carried out.
Treatment regimen with denol
De-Nol has bactericidal activity only in combination with antimicrobial agents. Taking the medication alone for Helicobacter pylori will not lead to the desired result.
The drug does not have the property of destroying pathogenic bacteria. Its main effect is to create protection for the mucous membranes of the digestive tract. However, in combination therapy, De-Nol is able to enhance not only its properties, but also the effect of antibacterial agents.
Amoxicillin (Flemoxin) - tablets for Helicobacter pylori
Amoxicillin is included in the first and second line of Helicobacter pylori eradication. This drug belongs to the category of synthetic penicillin antibiotics. The main feature of the drug is the ability to destroy only dividing pathogenic bacteria. The drug should not be prescribed for colitis, a tendency to leukemoid reactions and mononucleosis. An absolute contraindication is hypersensitivity to penicillin.
How to reduce adverse reactions during treatment
With any treatment regimen, deterioration of health, weakness, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are possible. In case of diarrhea, we add Loperamide or Enterol; in case of severe headaches, we add analgesics.
What can be done to make the treatment process less difficult? There is only one answer: do not save on the price of drugs. There are expensive and cheaper antibiotics. It all depends on the manufacturer. When purchasing more expensive brand name tablets, there are far fewer adverse reactions. Sometimes they may be completely absent.
Thus, it is better to buy Josamycin as Vilprafen ® Solutab produced by ASTELLAS PHARMA EUROPE BV (Netherlands).
It is better to buy Amoxicillin as Flemoxin Solutab ® produced by ASTELLAS PHARMA EUROPE BV (Netherlands). It is better to dissolve Flemoxin in a small volume of water, the form allows it. More is said about it above.
De-Nol - buy DE-NOL ® produced by ASTELLAS PHARMA EUROPE. If tolerance is poor, De-Nol can be divided into 4 doses of 1 tablet each. Take 20 minutes before meals - this is how long the drug needs to contact the gastric mucosa and form a protective film.
High-quality clarithromycin is CLACID ® tablets, manufacturer: ABBOTT LABORATORIES GmbH (Germany). Pay attention that there is no CP - this is a prolonged form, you need the regular one.
High-quality nifuratel - Macmiror ® Manufacturer: POLICHEM SrL (Italy).
Tablets from the listed manufacturers have better tolerability and bioavailability, cause fewer side effects, which will make it possible to withstand 14-day therapy.
Approximate treatment regimen with good tolerability
Taking into account the nuances described above, a ready-made solution for a regimen with very good tolerability (based on pure original solute forms of antibiotics) looks like this:
- Flemoxin solutab 1000 mg 2 times a day (20 pieces);
- Vilprofen solutab 1000 mg 2 times a day (10 pieces, 2 packs);
- De-nol 2 tablets 2 times a day half an hour before meals (56 tablets, 1 pack) - separately from antibiotics;
- Nolpaza 20 mg 2 times a day (I don’t remember the package size);
Chemotherapy of Helicobcter pylori with antibacterial drugs
Antibacterial drugs used in chemotherapy for Helicobacter pylori have many features that relate to rules of administration, indications, contraindications and drug interactions with other pharmaceuticals. Antibiotics should not be taken during pregnancy and lactation, increased sensitivity of the body to their components, as well as some chronic diseases. Potent medications can cause side symptoms. The treatment regimen should be drawn up only by a doctor.
Metronidazole for helictobacteriosis
The action of Metronidazole is aimed at actively destroying the genetic material of pathogenic microorganisms. The mechanism of action is based on the ability of the drug to introduce toxic metabolites into bacteria at the cellular level. Metronidazole is actively used in chemotherapy for Helicobacter pylori infection. A feature of the medication is the increased risk of side symptoms when the dosage is overestimated or the body is hypersensitive.
Macmiror (Nifuratel) for helictobacteriosis
Nifuratel belongs to the category of nitrofurans. The drug has a pronounced bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect. The medication disrupts the biochemical processes in bacterial cells and prevents their reproduction. Nifuratel is more effective than Metronidazole. In addition, the drug is less toxic.
Bismuth preparations (De-Nol)
De-Nol belongs to the category of antiulcer drugs. The basis of the medication is tripotassium citrate. The action of the drug is aimed at creating protection for the mucous membranes from the effects of waste products of Helicobacter pylori. The components of its composition do not allow gastric juice to penetrate to damaged areas of the tissues of the digestive tract. The additional effect of De-Nol is aimed at accelerating regeneration processes. Bismuth not only penetrates the mucous membranes, but also accumulates inside the cells.
Proton pump inhibitors: Omez, Pariet
Proton pump inhibitors are mandatory drugs in any line of therapy for Helicobacter pylori. Representatives of this group of medications are Pariet and Omez. Medicines reduce the acidity of gastric juice, accelerate tissue regeneration processes, and increase the pharmacological properties of antibiotics. The therapeutic effect of proton pump inhibitors lasts for a long time.
How much to drink de nol
Among gastroprotective drugs, De-nol gained the greatest popularity thanks to television advertising.
As part of complex therapy, it is used for various forms and types of gastritis, ulcers, and also as an adjunct in the treatment of pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and irritable bowel syndrome.
The drug is also active against Helicobacter pylori, an aggressive microorganism that inhabits the human gastrointestinal tract. Let's find the answer to the question in this article - how much de-nol to drink?
De-nol in the treatment of gastritis caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori
De-nol is available without a prescription, so there is a temptation to buy it bypassing the doctor's office and self-medicate.
Many people do this, but instead of the desired positive result, they get side effects in the form of darkening of the gums and tongue, and black stool.
To understand why the product does not work, it is worth understanding its properties.
Does it make sense to take medicine at the first sensation of pain, without knowing the exact diagnosis, or should there be serious indications for its prescription?
In order for a drug to perform its function, its use must correspond to its pharmacological action.
De-nol does not have an antispasmodic effect and is not an enterosorbent, so there is no need to take it for pain caused by acute gastritis or poisoning.
The action of the medicine is aimed at protecting stomach tissues that have damage in the form of ulcers and erosions.
To prevent hydrochloric acid from reaching the damaged areas, they need to be protected from its aggressive effects, and also the activity of acidic gastric enzymes must be reduced.
This task is performed by bismuth, the active substance of De-nol. By binding to the proteins of dead tissue, it forms a paste-like mass that seals the ulcers, thereby protecting them from acids.
The causative agent of bacterial gastritis
De-nol treats gastritis of any etiology, including bacterial, which is classified as endogenous (which cannot be influenced by humans).
Its causative agent is Helicobacter pylori, a unique flagellated bacterium that lives in conditions that are lethal to most microorganisms.
The gastric environment has such a high level of acidity that, when pathogenic bacteria enter it, they die, corroded by hydrochloric acid.
And only Helicobacter feels great in these conditions and is even able to reproduce in them. In addition, it creates a barrier on the surface that protects it from many antibacterial agents.
For active life, the microbe does not need a lot of oxygen, so the gastric environment is best suited for it.
Recent scientific evidence suggests that the bacterium inhabits the body of almost 70% of the world's population. But a healthy immune system prevents Helicobacter from multiplying and acting.
When the immune defense is weakened, the microorganism has the opportunity to attach to the cells of the stomach and destroy them.
Helicobacter pylori is of great interest to doctors. New research in the field of gastroenterology is devoted to it, thanks to which it was revealed that the microbe can cause not only gastritis.
The presence of Helicobacter in the body affects the development and progression of diseases of the liver, pancreas, coronary heart disease, bronchial asthma, endocrine disorders, anemia, cholelithiasis.
It was also found that the bacterium has a carcinogenic effect and affects the formation of cancer cells.
The presence of Helicobacter pylori does not mean that a person is sick.
The development of gastritis depends on the immune status of the infected person, the concentration of bacteria in the stomach, and genetic predisposition to the disease.
A strong immune system controls the number of microorganisms, but infectious diseases, stress, bad habits, alcohol abuse, and poor-quality food contribute to the weakening of the defenses.
You can become infected with Helicobacter pylori in several ways:
- using water from untested sources for drinking;
- eating raw, unwashed vegetables;
- in case of non-compliance with hygiene rules;
- while kissing.
Helicobacter gastritis is a sluggish disease, at first asymptomatic, but without treatment it slowly progresses; after the appearance of pronounced symptoms, you need to undergo an examination.
The doctor will order tests to determine the presence of Helicobacter pylori. They do a blood test, general and biochemical, biopsy, gastric juice analysis and a breath test.
The most accurate results are provided by PCR, an analysis that allows you to identify bacteria even in the case of a small concentration.
Since the microorganism is transmitted through close contact, after detecting Helicobacter in one of the family members, doctors recommend that everyone who lives nearby be examined.
You should not ignore these recommendations, since timely treatment or preventive measures can get rid of uninvited guests in a short time.
Treatment of bacterial gastritis
If examinations have shown that the culprit of gastritis is Helicobacter pylori, a standard treatment regimen is prescribed, which gives a positive result if the recommendations are strictly followed in 80% of cases.
The regimen consists of 2 or 3 antibacterial drugs, proton pump blockers, antispasmodics for pain, gastroprotectors.
The use of De-nol is indicated, which accelerates the process of cell restoration, relieves inflammation, and protects damaged areas by creating a film on the mucous membrane.
In addition, the drug acts on Helicobacter, exhibiting a bactericidal effect in several directions:
- prevents bacteria from attaching to the stomach wall;
- interferes with enzymatic processes inside the bacterial cell;
- reduces the speed of movement of the microorganism;
- restores the integrity of the deep layers of the stomach;
- Helicobacter bacteria do not develop resistance to the drug De-nol, which is very important, since the disease does not have the opportunity to take on a resistant form.
De-nol, together with antibiotics, kills bacteria, restores tissue, and heals ulcers. To combat Helicobacter pylori, Clarithromycin and Amoxicillin are used as antibacterial agents.
The medicine must be used separately from antacid drugs; they are used no earlier than an hour after De-nol. At the same time, you should not use other drugs whose active component is bismuth.
Treatment regimens for gastritis with low and high acidity
One of the most common causes of gastritis is infection by Helicobacter pylori. The bacterium penetrates the mucous membranes of the digestive tract, and its waste products become provoking factors for the formation of ulcers and erosions. Gastritis can be accompanied by increased or decreased acidity of gastric juice. Treatment regimens for different types of diseases differ.
With increased stomach acidity
For erosive gastritis with increased acidity of gastric juice, cytoprotective agents are used. Drugs in this group increase the resistance of the gastric mucosa to negative factors and waste products of bacteria. The treatment regimen may also include bismuth nitrate, magnesium oxide and calcium carbonate (in the form of suspensions). The disease requires the mandatory use of antacids, enveloping and adsorbent agents.
For low stomach acidity
Reduced acidity of gastric juice implies the use of medications that increase the production of hydrochloric acid. Liontar or Plantaglucid are used as an addition to the main line of therapy. The first preparation contains citric and succinic acid, the second – plantain juice. Substances stimulate secretory function and restore the functioning of the glands.
Disease prevention
Few people know that a person does not develop immunity to Helicobacter pylori infection, so another infection is possible.
If you want to avoid repeated therapy, experts recommend:
- Have personal hygiene products and your own cutlery and plates. Since most often people become infected with the infection through household means.
- Observe hygiene rules. Teach your child to wash their hands too.
- Remember that bacteria are transmitted through saliva. Therefore, kissing people whose health you are not sure about can cause infection. Children should not be allowed to share fruit on the “let me take a bite” principle, and girls are not recommended to share lipstick with a friend.
- A passion for alcohol leads to the active functioning of the microorganism. The same applies to smoking (including passive smoking).
- Teach children not to eat unwashed vegetables and fruits.
- Take your pet to the veterinarian for regular checkups. Until recently, there was no information that you can get the infection from animals. However, there is now every reason to believe that cats, dogs, monkeys and pigs carry the pathogenic bacterium.
- When you first notice symptoms of infection, consult a doctor immediately.
Helicobacter is transmitted from mother to child not through the placenta, as pregnant women sometimes think, but only by airborne droplets. Therefore, it is necessary for a mother with Helicobacter pylori infection to avoid trying food and feeding the baby with the same spoon.
There is no other correct way out other than to treat Helicobacter pylori. For such an infection, drug therapy with antibiotics is carried out. Remember that the drug should be prescribed only by the attending physician, who also controls the process of eradication of the pathogenic organism. Remember to eat a balanced diet and do not ignore taking a repeat breath test.
How to do without antibiotics?
There is no need to use antibacterial drugs for Helicobacter pylori only if the concentration of bacteria in the stomach is minimal. If the patient does not have a peptic ulcer, anemia or atopic dermatitis, then Helicobacter is present in the body in “sleep mode” or is just beginning its life activity. Treatment can be carried out in a simplified form, without antibiotics. When these pathologies are identified, antibacterial agents become a mandatory part of therapy.
Lightweight regimen without the use of antibiotics:
- drugs to improve the immune system;
- means for restoring the microflora of the digestive tract.
Nutrition for infection
In order not to think about how many days to take antibiotics during the second course of treatment for Helicobacter pylori, we recommend that you stick to the basics of a balanced diet and eat small meals 5-6 times a day.
In addition, experts advise remembering the principles of diet:
- Chew food thoroughly. If this is difficult for the patient, it is recommended to eat ground food.
- Limit the use of salt in food (no more than 2 teaspoons per day). To control, it is advisable to season the dish already on the plate.
- Do not eat too hot or cold food.
- During the treatment of infection, consume at least 2 liters. water per day.
- Avoid fatty, fried foods.
- Not to starve. All newfangled diets lead to irritation of the gastric mucosa.
To achieve stable remission, it is recommended to adhere to these nutritional rules for 1-1.5 years.
Prevention
Primary and secondary prevention of helicobacteriosis have minor differences. The general rules for the two programs are identical. Only the recommendations for therapeutic measures differ. In the second case, the doctor’s recommendations must be strictly followed. If the course of medication is completed prematurely, there is a risk of not only relapse, but also life-threatening complications from the digestive tract.
General preventive measures:
- compliance with the rules of balanced and proper nutrition;
- eating only clean food and water;
- timely treatment of diseases of the digestive tract;
- implementation of measures to strengthen the immune system;
- compliance with personal hygiene standards;
- regular examinations by a gastroenterologist for abnormalities in the digestive system;
- mandatory diagnostic procedures for suspected Helicobacter pylori infection.
Video on the topic: Antibiotics against Helicobacter pylori.
Helicobacter pylori symptoms and treatment in adults and children. Eradication schemes
A number of medical consensus conferences have been devoted to the diagnosis, symptoms and treatment of Helicobacter pylori (Hp), where effective treatment regimens have been developed. In 2015, the last, 5th conference on the study of H. pylori infection was held.
Maastricht Consensus V (Maastricht V) on Helicobacter
In November 2015, the next consensus conference of the European Group for the Study of Helicobacter pylori (Hp) was held in Florence (Italy), at which the Maastricht Consensus V (Maastricht V), dedicated to modern aspects of the diagnosis and treatment of Hp infection, was adopted.
Particular attention was paid to:
- increased resistance (sustainability) of Hp to previously effective antibacterial treatment regimens, which requires refinement of therapeutic strategies;
- high efficiency of primary and secondary prevention of stomach cancer;
- publication of the new Kyoto Consensus, which resulted in the definition of chronic gastritis as an infectious disease caused by Helicobacter pylori;
- developing treatment recommendations for all infected individuals, regardless of symptoms and complications, unless there are contraindications or competing considerations.
Below, in light of the main provisions of Maastricht V, direct recommendations are given for the treatment of Hp infection and the management of Hp-infected patients.
Treatment depends primarily on the sensitivity of the bacteria to a particular antibiotic. Therefore, there are a number of schemes when, instead of one antibiotic, another or a scheme without it is used.
The Maastricht Consensus-5 contains 5 sections corresponding to the 5 working groups that developed them. Let us dwell on one of them - the treatment of helicobacteriosis according to Maastricht V.
The effectiveness of treatment for Hp infection depends on:
- resistance (resistance) of bacteria to metronidazole, clarithromycin and other antibiotics;
- patient adherence to treatment;
- duration of treatment;
- the presence of concomitant obesity, smoking and some other factors.
The resistance of H. pylori to key antibiotics is gradually increasing and, accordingly, the effectiveness of eradication regimens is decreasing.
In all cases, the effectiveness and tolerability of treatment can be increased by additional use of probiotics, as well as by increasing acid-lowering therapy. The Maastricht consensus calls for the use for this purpose of those probiotics that have proven effective in clinical studies (Lactobacillus, Saccharomyces boulardii, Bacillus clausii). It is important that the duration of probiotic therapy is sufficient, which should exceed 2 weeks.
Helicobacter pylori eradication for pregnant women . Treatment regimens for children during the treatment of Helicobacter pylorus do not differ from adults (dose adjustment is possible depending on the child’s weight). Sometimes doctors offer children treatment with traditional methods and diet, the use of propolis, garlic, but practice shows that complete eradication cannot be achieved without antibiotics.
True, there has long been a patent for the treatment of H. pylori with an aqueous solution of propolis together with propolis in oil. I will describe the essence of the method in an article about the traditional treatment of Helicobacter.
Modern treatment and its regimens: first line of Helicobacter pylori therapy
There is no single and effective treatment regimen for helicobacteriosis and eradication of the bacterium. Below are a number of drug treatment regimens as recommended by consensus in certain cases.
As a primary treatment, classical triple therapy as the standard of care:
- PPI (Proton Pump Inhibitor - standard dose). One of the inhibitors: omeprazole 20 mg, lansoprazole 30 mg, pantoprazole 40 mg, esomeprazole 20 mg, rabeprazole 20 mg
- clarithromycin (500 mg 2 times a day) or josamycin (1000 mg 2 times a day) or nifuratel (400 mg 2 times a day)
- amoxicillin (1000 mg 2 times a day)
Take all medications 2 times a day for 10-14 days.
Increasing pH = decreasing acidity. Using high doses of PPIs (double dose twice daily) increases the effectiveness of triple therapy.
It is often recommended that after completion of treatment (10-14 days) you take PPIs for another month (for acute gastritis or ulcers). Some gastroenterologists recommend adding De-Nol to classical triple therapy as a coating for the gastric mucosa, which increases the effectiveness of treatment.
An alternative (with prior use of metronidazole or clarithromycin for other indications) is non-bismuth concomitant quadruple therapy:
- amoxicillin (1000 mg)
- clarithromycin (500 mg)
- tinidazole (500 mg) or metronidazole (500 mg)
- PPI (standard dose)
Take all medications 2 times a day for 10-14 days.
For known or established allergies to penicillins, bismuth-based quadruple therapy is recommended:
- bismuth subcitrate (subsalicylate, bismuth tripotassium dicitrate, also known as De-Nol) 120 mg 4 times a day or 240 mg 2 times a day for 10–14 days (the drug darkens the feces and tongue)
- tetracycline hydrochloride (500 mg) 4 times/day
- Metronidazole (500 mg) or tinidazole (500 mg) 3 times a day
- PPI (standard dose) 2 times/day
Duration of therapy is 10-14 days.
Results
- treatment of diseases caused by Helicobacter pylori is carried out according to special schemes;
- if the active activity of a pathogenic microorganism has led to serious deviations in the functioning of the digestive tract, then treatment is carried out using eradication methods;
- Helicobater pylori eradication is based on three lines of therapy (the choice of a specific regimen is made by the doctor);
- without antibiotics, only Helicobacter pylori, which is in an inactive mode, can be treated;
- Lack of timely treatment of Helicobacter pylori will lead to serious complications (progression of peptic ulcers, gastritis, increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding and cancer of the digestive organs).
Gastroenterologist, Therapist
The doctor conducts a general diagnosis of internal organs. Draws conclusions about disorders in the gastrointestinal tract based on the results of the examination and prescribes appropriate treatment. Among the diagnoses that the specialist deals with: stomach and duodenal ulcers, gastritis, dysbiosis, etc. Other authors
Comments for the site Cackl e
When is it necessary to treat a microbe with antibiotics?
People who have encountered the causative agent of most gastrointestinal diseases are often interested in: when should you take antibiotics and in what situations can you do without them? Such questions are not surprising. After all, many medications have a negative effect on the microflora of the stomach, causing allergic reactions, colitis, and indigestion.
Deep therapy is prescribed if:
- atrophic gastritis;
- ulcers of the stomach and duodenum;
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- functional dyspepsia;
- damage to the lymphatic tissue of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ.
In addition, antibacterial drugs are used after eliminating a malignant tumor in the stomach. They are recommended for patients whose relatives include people with cancer of the digestive organs, that is, there is a predisposition to this disease.
How does an antibiotic affect Helicobacter?
Most people think that after swallowing an antibiotic capsule, it enters the stomach through the esophagus and there it begins to destroy colonies of infection. But that's not true.
The accumulation of antimicrobial drugs in the gastric mucosa occurs during the distribution phase from the systemic circulation. Non-local action of the antibiotic. First, absorption occurs and only then distribution from the systemic bloodstream leads the drug to the gastric mucosa.
The concentration of an antimicrobial drug in the gastric mucosa is directly proportional to its concentration in the blood serum, which, in turn, depends on the bioavailability of the drug. That is why Flemoxin Solutab ® (see below) - a soluble form of Amoxicillin, has a good basis and inclinations to be used as part of eradication therapy.
In therapy, we choose Amoxicillin with high bioavailability - Flemoxin Solutab ®. There is another feature of this drug - its high degree of absorption (absorption) in the gastrointestinal tract compared to other forms of Amoxicillin. This makes Solutab safer than other forms of the drug (capsules, tablets). (from the speech of candidate of medical sciences, associate professor T.L. Lapina, broadcast on November 26, 2013).
Drug absorption is a natural process of absorption, namely the penetration of drugs through cell wall membranes directly into the lymph and blood. When assessing the quality of a drug, absorption is the main important indicator of pharmacokinetics.
Does Amoxicillin help get rid of bacteria?
Amoxicillin is an antibacterial drug with a wide spectrum of action, which allows it to be used to treat pathological conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as diseases associated with the presence of pathogenic microorganisms, such as Helicobacter pylori.
Amoxicillin is a drug that is a representative of the semi-synthetic penicillin group - the “successor” of the first antibiotic that became known to the world (Penicillin).
The meaning of Amoxicillin is to fight Helicobacter pylori. But it is worth noting that the drug is active only against actively reproducing bacteria. Also, Amoxicillin for Helicobacter should not be taken simultaneously with those drugs that inhibit the growth of bacteria, because such a combination nullifies the therapy.
As prescribed in the instructions, this medicine, as a rule, does not cause serious side effects. It is even prescribed to pregnant women, but under the close supervision of a doctor.
The dosage of Amoxicillin for Helicobacter pylori depends on the regimen used for therapy, namely the combination of drugs used in tandem. The dose of Amoxicillin for Helicobacter pylori is 500 mg 4 times a day . Also, the dose of the drug can be 1000 mg 2 times / day.
Article verified by Anna Moschovis – family doctor.
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter
We continue the series of articles about such a dangerous microorganism as the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. The article is devoted to the topic: Helicobacter pylori symptoms and treatment. It shows the eradication of Helicobacter according to Maastricht V, presents modern methods of anti-Helicobacter therapy - first, second and third lines, describes which drugs are best used in regimens and why, how to avoid unpleasant side effects. Also, what tests to take to determine the success of therapy.
Symptoms of infection are described in detail in the previous article (link just above). Here we will pay all attention to treatment standards, especially to drug regimens with antibiotics for Helicobacter. Therapy with traditional methods has always been questioned and is only possible as an additional remedy - in parallel with Helicobacter therapy during remission of gastritis or ulcers. Acute conditions are treated only with antibiotics. Which antibiotics are effective are described in generally accepted regimens.
There will be a separate article on nutrition (diet) and traditional methods of therapy. I plan to provide a video of a doctor who uses dietary supplements to eradicate Helicobacter and some folk recipes - when it is not possible to prescribe antibiotics for a number of reasons.
Choosing a treatment regimen
Helicobacter is a dangerous bacterium that requires prompt treatment. Early diagnosis is very important for patients. Do not forget that any antibiotic therapy for Helicobacter pylori should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician. This will help protect yourself from adverse reactions of the body to antibiotics and possible complications that arise from improper eradication of the bacteria.
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori with antibiotics is necessarily indicated for patients with diagnoses:
- dyspepsia;
- gastritis;
- gastroesophageal bacterial reflux;
- malignant tumors of the stomach;
- maltoma;
- gastric resection.
IMPORTANT. Patients who have been prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory therapy by their doctor are also recommended to first eliminate Pilari from the body. Today, the most effective are two active treatment regimens for Helicobacter pylori, both of which are based on the combined use of two types of antibiotics, bismuth-containing agents and medications that reduce the production of digestive juice.
Gastroenterologists are often faced with the problem that antibiotics for Helicobacter pylori of both treatment regimens are ineffective, since the bacterium is very resistant to the constituent components of the drugs.
Common antibiotics used to combat pylori are:
- Amoxicillin (a penicillin drug, prescribed to patients for initial and subsequent preventive treatment, intended to kill Helicobacter only at the reproduction stage, not suitable for all patients);
- Azithromitocin (a mild remedy, ideal at the initial stage of the disease, not accompanied by pronounced symptoms and complications);
- Amoxiclav (contains clavulanic acid, which has a merciless effect on persistent pylori bacteria, as a result of which it can cause dysbiosis in patients);
- Klacid (a new modern drug aimed at quickly destroying Helicobacter in the body, prescribed for stomach ulcers as the most gentle medicine with low toxicity);
- Tetracycline (a strong antibiotic, prescribed in severe complicated situations, has side effects).
Contraindications and side effects
The main contraindications when it is impossible to treat gastritis with Amoxicillin:
- sensitivity to penicillin drugs;
- neurological abnormalities;
- pregnancy and lactation.
Side effects after taking Amoxicillin for gastritis:
- constipation or loose stools;
- weakness, headache;
- an allergic reaction manifested by redness of the skin and/or swelling of the tissues.
Amoxicillin should be prescribed with caution for the treatment of gastritis to people with renal failure, as well as in severe pathological conditions of the liver. Usually, when prescribed and taken correctly, no side effects occur. Most often, such symptoms are characteristic of those patients who used the products without a doctor’s recommendation.