Helicobacter pylori appears in children and remains for life. Previously, there were no methods to get rid of the disease. Today antibiotics and other drugs are used. People often go to the doctor after the holidays. The reason is overeating. Examination shows inflammation of the mucous membrane. The cause of the illness was a microbe. Peculiarities in the treatment of children boil down to the undesirability of using proton pump inhibitors.
Bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract
Helicobacter pylori settles in the duodenum and stomach. Several strains are known to medicine, 2 of them are pathogenic and have managed to multiply throughout the planet. Carriage is common in Russia (up to 80% of adults). The condition is asymptomatic; there are no antibodies in the blood that characterize the active phase. Before the start of activities, the diagnosis is clarified: the microbe can be cured with antibiotics. Types of drugs are selected based on the results of bacteriological analysis.
general information
Infection occurs in adolescence - from 14 to 16 years. In countries with a high population density, the percentage of infected people reaches 90-100%. The microbe does not always appear. Gastritis and ulcers are considered different stages of the same disease caused by bacteria.
The presence of antibodies in the blood cannot be considered a sufficient sign of diagnosis. We have to turn to other methods. Antibodies indicate a collision between the body's immune system and a microbe. If a high titer is detected, an additional endoscope examination is prescribed. The goal is an external examination of the epithelium of the stomach and duodenum. The mucous membrane becomes covered with nodes, polyps, and ulcers.
Often the situation is not limited to a specific degree of inflammation. Sometimes it comes to the development of a tumor disease. Therefore, Helicobacter cannot be treated without endoscopic examination at the preliminary stage. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the gastroenterologist chooses an acceptable treatment. When the course of antibiotics is completed, a repeat analysis is carried out to assess the success of the measures taken. After 3 years, the examination is repeated.
The problem is extraordinary survivability. The bacterium dies when heated to 95 degrees Celsius for five minutes. It is difficult to destroy during pasteurization. All it takes is a patient's saliva getting into fruit juice at a food processing plant. The disease has frequent relapses, and it is difficult to identify and exclude the routes of initial infection. Advice to parents: avoid kissing your child on the lips, protect children from unwanted contact with animals and people.
The infection is transmitted in simple ways by humans through kissing and sharing utensils. It is not recommended to drink from the same bottle. If there is a sick person in the family, the rest are under direct threat of infection. If a single case is detected, the next of kin are tested. A sufficient analysis is a biopsy of the gastric epithelium. It is more convenient for doctors to work with blood samples and breath tests - this ensures effective coverage of groups of people.
Helicobacteriosis (Helicobacter pylori, Helicobacter pylori infection, Helicobacter pylori, H. pylori)
Gastritis
Ulcer
Iron deficiency
Vomit
Diarrhea
12510 January 28
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Helicobacteriosis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Helicobacteriosis is an infectious disease that affects the pylorus of the stomach, or pylorus, and duodenum. Its causative agent is a unique pathogenic microaerophilic gram-negative bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). The bacterium got its name from the section of the stomach in which it lives - the pyloric.
As a result of its vital activity, H. pylori forms a “cloud” of alkaline environment around itself, which allows this bacterium to survive in the aggressive acidic environment of the stomach, causing accelerated secretion of hydrochloric acid, as well as a decrease in alkali secretion in the duodenum.
As a result, the microorganism further colonizes the mucous membrane, forms its increased susceptibility to hydrochloric acid and provokes inflammation, leading to the development of ulcerative defects.
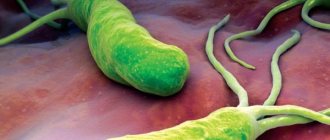
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped bacterium 3.5 microns long and 0.5 microns wide. It has flagella, with the help of which it moves freely along the wall of the stomach or is securely attached to it. The bacterium H. pylori is very variable; its strains (varieties) differ from each other in their ability to attach to the gastric mucosa, cause an inflammatory process, and have varying degrees of pathogenicity.
Helicobacter pylori, which colonizes the gastric mucosa, is a common cause of its inflammatory changes; it is recognized as the etiological factor of gastritis, and gastritis itself is an infectious disease. Depending on the state of the protective factors of the stomach, the resulting infectious process can occur latently or with severe clinical symptoms of inflammation. According to modern concepts, H. pylori causes chronic gastritis in all infected individuals. This can lead to peptic ulcer disease, atrophic gastritis, gastric adenocarcinoma or low-grade gastric lymphoma. H. pylori is a first-order carcinogen.
The results of numerous studies suggest a possible pathogenetic or indirect role of H. pylori infection in the development and/or course of diseases not related to digestion: cardio-, cerebrovascular, autoimmune diseases, diseases of the blood, skin, nervous system and many others.
The pathogen is relatively resistant to the environment: when boiled, Helicobacter bacteria die almost instantly, and when treated with disinfectant compounds, they die within a few minutes.
Causes of helicobacteriosis
You can become infected with the bacteria through contact with contaminated water or food. Infection is possible during endoscopy and when using other poorly sterilized medical instruments that have had direct contact with the patient’s gastric mucosa.
Household transmission (for example, through kisses, personal belongings, etc.) is also possible, as evidenced by the release of bacteria from saliva and dental plaque.
The prevalence of infection varies depending on the geographic region, patient age, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. According to the Moscow Department of Health (2019), the prevalence of this infection in Moscow is 60.7–88%, in St. Petersburg - 63.6%, in Eastern Siberia reaches 90%.
Classification of diseases
Diseases associated with H. pylori:
- gastritis,
- duodenitis,
- gastroduodenitis,
- esophagitis,
- stomach ulcer,
- duodenal ulcer,
- iron deficiency anemia of unknown origin,
- stomach cancer,
- duodenal cancer.
Symptoms of Helicobacteriosis
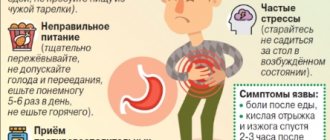
The main manifestation of Helicobacter pylori is chronic inflammation of the stomach. In the case of rapid primary manifestation of the pathogen, the acute period of helicobacteriosis lasts about 10 days. The general condition of patients usually remains satisfactory, sometimes there is a short-term low-grade fever and decreased performance.
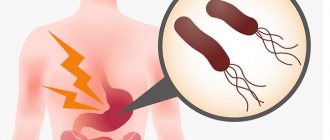
The main complaint with which patients with signs of Helicobacter infection consult a doctor is stomach pain. The localization of the symptom may change and move to the area of the duodenum.
The pain can be sharp, aching, dull, and occurs in the upper abdomen on the left and in the center in the umbilical region. Discomfort can occur during prolonged fasting, on an empty stomach, or after a certain time after eating.
Symptoms of helicobacteriosis depend on the clinical form of the disease and may include:
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- loss of appetite associated with sudden attacks of nausea (if the gastric mucosa is severely injured);
- causeless vomiting against the background of normal body temperature;
- heartburn (burning sensations in the esophagus and even larynx) and belching with an unpleasant sour or bitter taste;
- chronic constipation (lack of bowel movements for three days or more);
- liquefaction of stool, the appearance of a foamy or watery consistency;
- intestinal cramps and bloating.
If there is a strong contamination with Helicobacter, a number of atypical symptoms may occur, which indicate significant infection and progression of the disease:
- loss of appetite to its complete absence;
- nausea may be replaced by vomiting with blood clots;
- a sharp decrease in body weight that is not normal;
- dry mouth and metallic taste;
- the appearance of a white coating on the tongue;
- bad breath in the absence of caries;
- seizures in the corners of the mouth;
- bleeding gums.
In the chronic course of the disease and atrophic damage to the gastric mucosa, signs of iron deficiency anemia appear - frequent headaches and dizziness, pallor of the skin, decreased blood pressure and tachycardia.
Diagnosis of helicobacteriosis
For a long time, helicobacteriosis may not manifest itself in any way, while provoking the development of ulcers, adenocarcinoma or gastric maltoma. People whose relatives have a history of these diseases are at particular risk.
Diagnosis can be invasive (endoscopy followed by biopsy of gastric tissue) and non-invasive (laboratory tests).
According to international recommendations, the methods of choice for diagnosing the bacterium and assessing the effectiveness of treatment for H. pylori are a breath test with 13C-labeled urea and determination of specific H. pylori antigens in stool using an immunochromatographic method.
Signs
Mostly bacteria enter the body through the fecal-oral route. Do not consume unwashed food, dirty water, or expired food. The lack of sanitary conditions guarantees carriage almost 100%.
No specific symptoms of infection were identified in the child’s illness. Sometimes the disease occurs without symptoms. Characteristic manifestations: gastritis, gastroduodenitis, ulcer, dyspepsia. Heartburn is common. Nonspecific signs appear: belching, burning in the upper abdomen. The stool is unstable: hard or turning into diarrhea.
Along the way, deficiencies of vitamins, microelements, and allergic reactions occur. Irritability, fatigue, unstable attention, moodiness, and decreased physical and mental potential appear. In some cases, doctors record growth retardation.
The life process of a microbe
People who are carriers of Helicobacter develop ulcers if they have an unhealthy diet. Doctors say there is a 100% correlation for truck drivers. In other cases, a sick stomach becomes a breeding ground for infection for others. The rod is deposited on the gastric mucosa and remains there for the entire life of the body. When multiplying, the microbe, through special enzymes, digests the lipid membrane of epithelial cells and destroys them. In catering establishments, all conditions have been created for the transmission of Helicobacter to healthy people. The role introduces the wrong lifestyle:
- smoking;
- alcohol;
- stress.
In the USSR, these reasons were named among the predetermining factors in the development of chronic gastritis. Science confirms the conclusions of scientists of the last century. The real reason is the emergence of facts as reasons for the proliferation of a harmful infection. A surgical approach is effective for treating ulcers. It was necessary to open the stomach and remove part of the mucous membrane secreting digestive juices. Acidity decreased sharply - the prerequisites for the occurrence of ulcers were eliminated.
A patient has a stomach ulcer
General information about Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that most often affects the pancreas and pylorus of the stomach. About half of the world's population are carriers of this infection. Often pathogenic microorganisms are detected in a child.
Helicobacter pylori infection is dangerous because it can provoke the development of various gastrointestinal pathologies, including gastritis, ulcers and oncology. For this reason, drug treatment should be started without delay.
Diagnostics
A breath test is used for diagnosis. They give a tablet containing radioactive carbon, and the patient washes it down with orange juice. When urea comes into contact with Helicobacter, carbon dioxide with an increased molecular weight is released. The presence of such a substance is determined using mass spectrometric methods. If the result is positive, but there are no serious complaints, a ten-day treatment is carried out according to the general scheme. The composition of the drug includes proton pump inhibitors and antibiotics in high doses.
A sixth of humanity remains carriers of the microbe after completing the course. The strain in the stomach is not 100% destroyed. If there are serious complaints, an endoscopic examination is performed. If an ulcer is detected, a biopsy is taken to find out whether a microbe is the cause of the disease. The bacteriological study allows doctors to learn about the treatment of the disease. The laboratory is simultaneously conducting studies on the sensitivity of the strain to antibiotics.
Doctors testify that treatment of Helicobacter pylori has sharply reduced the incidence of stomach cancer. Doctors explain: in the last century, the fight was aimed at areas of life that were not scientifically related to the occurrence of the disease:
- Daily regime.
- Rationalization of the diet.
- Treatment of stress.
Therefore, Helicobacter in children is treated and re-infection is avoided. Symptoms of dyspepsia - indications for research. 20 years ago, a conscript with such a diagnosis had no chance of seeing a higher education institution. People with a family history of cancer are at risk. If there is a similar history and a negative breath test for Helicobacter, an additional endoscopic examination is performed. It wouldn't hurt to get a biopsy to get accurate results.
How to accurately determine the presence of bacteria in the body
To check your child for the presence of Helicobacter pylori, you need to seek help from a gastroenterologist.
Diagnostics includes more than one study:
- breath test;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- stool analysis to detect antigen to pathogenic microorganisms.
In addition, it is necessary to take a blood test for antibodies to the infection.
During fibrogastroduodenoscopy, a specialist examines the gastric mucosa and takes a tissue sample, which is subsequently sent to a histology laboratory.
The principle of the breath test is high urease activity. Pathogenic microorganisms are able to break down urea and also synthesize ammonia and carbon dioxide. If a positive test is noted and Helicobacter is detected, then the most appropriate treatment regimen is selected.
Treatment tactics for an infant, a 2-year-old child, a 6-year-old child, and a teenager will have a number of differences.
Treatment
Treatment in children involves few specifics. The measures are aimed at reducing toxicity. The use of antibiotics cannot be avoided. When eradicating using traditional methods, they try to reduce the acidity of gastric juice. It came down to removing part of the mucous membrane. The purpose of the procedure is to reduce the number of glands responsible for secretion. Doctors do not recommend prescribing proton pump inhibitors in childhood. This group of drugs is being replaced by histamine blockers (Kvamatel), although the effectiveness is much lower.
Attention should be paid to the diet. Doctors have proven that it is important to change your diet. Israeli doctors say that spicy foods are not the cause of gastrointestinal problems. Onions and garlic are useful.
Children's need for fats, proteins and carbohydrates cannot be called increased. The consequences of a lack of ingredients are catastrophic. The diet certainly includes meat, fish dishes, eggs, fruits, and dairy products. A woman’s ability to intelligently present cooked dishes plays a role. This stimulates the child's appetite.
Features of therapy
As a rule, treatment is carried out with the help of medications. With the right treatment tactics, the problem can be eliminated in the shortest possible time. Traditional medicine can also be used.
Conservative methods
Antibiotic drugs are most effective in fighting infection. Only with their help can it be possible to suppress the activity of bacteria and eliminate them. There are several treatment regimens.
In the first case, the child can only be prescribed a gentle antibacterial drug. In the second, in addition to antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors will also be used.
If the infection does not provoke the development of pathologies, then the use of antibiotics is not resorted to. It is only recommended to adhere to a diet to avoid excessive activity of Helicobacter pylori.
The following drugs can be used by patients to suppress bacterial activity:
- Amoxicillin;
- Omeprazole;
- Noflux;
- Rabeprazole;
- Clarithromycin;
- Pantoprazole.
Traditional methods
At the initial stage of development of pathogenic microorganisms and in the absence of gastrointestinal diseases, it is possible to destroy the infection that has entered the body using folk remedies.
The following are used:
- Beetroot . You need to squeeze the juice out of the root vegetable, leave for about three hours and mix with water. After this, you should give the child a quarter glass of the resulting liquid to drink half an hour before meals. The duration of therapy is two weeks. You need to take the medicine before each meal.
- Egg . You need to drink it a couple of hours after eating and after that you should not eat anything for at least two hours. In total, you should consume no more than three raw eggs per day. Therapy lasts exactly 14 days.
- Cabbage . The juice of this vegetable should be drunk daily half an hour before meals. The course of therapy is only a couple of weeks. It will be enough to drink half a glass of healthy juice at one time.
- Linen . Pour a tablespoon of plant seeds into a glass of just boiled water and leave for about a quarter of an hour. Take the decoction three times a day, 30 minutes before meals. The duration of treatment is at least three weeks.
- Propolis . About 60 grams of raw material should be grated and mixed with a glass of hot water. The resulting mass should be simmered for an hour in a water bath. You need to take the product for three weeks before each meal. At one time, children should drink exactly as many drops as they are currently old. It is allowed to mix the medicine with milk or honey.
Healthy garlic
Dr. Komarovsky remains silent about Helicobacter. In the program, Elena Malysheva invites viewers to answer who is fighting stomach cancer. People think about different products. The answer lies in a Russian proverb: garlic and onions help against seven diseases. Doctors are not surprised at the truth of folk wisdom. We found out that when garlic is chewed, an antibacterial component is formed in the stomach that kills Helicobacter pylori.
Dad and mom figured out how beneficial it is to feed children traditional folk recipes. Allicin kills Helicobacter, but the component cannot be called natural. It is formed from the amino acid cysteine (alliin) under the action of a special enzyme. Compare the component with epoxy glue. While the components are separated, they do not exhibit the properties exhibited by cold welding.
In garlic, the allicin components are separated by cell walls. When garlic is thoroughly chewed with teeth, a bactericidal substance is formed that suppresses the vital activity of Helicobacter pylori. Therefore, the natural product is called prophylactic against cancer, ulcers, and gastritis.
To treat or not to treat
Helicobacter pylori in a child is treated immediately. Especially if your immediate family includes ulcers or cancer sufferers. In developed countries, vaccines against ulcers are being developed. Problems begin with lack of treatment. If there is a need for vaccination, then economists have substantiated the benefits of the event. Patients do not pester doctors with complaints; clinic halls are freed up.
The treatment regimen for children differs little from that for adults. The attention of advanced countries is directed to the creation of vaccines against salmonella and Helicobacter. The time is not far off when the symptoms and treatment of diseases will not be of interest.