Treatment of Helicobacter pylori with antibiotics
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is widespread, known as a dangerous microorganism that is not afraid of hydrochloric acid. It provokes the appearance of gastroduodenitis. It was revealed that control measures are based on different drugs. But, most antibacterial drugs do not bring much benefit. Not all of them penetrate under the mucous layer in which the bacterium is located. With advanced disease, oncology may develop. For this reason, it is important to find out which antibiotics to treat Helicobacter.
Clarithromycin for Helicobacter pylori
This drug is a 14-membered macropid derivative of erythromycin, corresponding to the level of activity and method of use. But, compared to erythromycin, it is more resistant to the effects of acid. A drug with a long elimination period. There is a triple antibiotic treatment regimen.
Clarithromycin is prescribed for adults - 250 mg (1 capsule) twice a day. Take tablets for 6 to 14 days. If a severe form of the disease is present, the dose is increased to 2 capsules twice a day. Take the medicine with water, regardless of meals.
Azithromycin for Helicobacter pylori
The drug has a wide spectrum of action and is bacteriostatic. It reduces and inhibits peptide translocase and protein synthesis even at the stage of translation. It also slows down the growth of bacteria, prevents their reproduction, and has a bactericidal effect. It acts on pathogens both intracellular and extracellular, which are caused by sensitive pathogens of duodenal ulcer, which is associated with Helicobacter pylori.
It is necessary to take the medicine with caution. Pregnant women can only take it if the benefits of treatment outweigh the risks. It is not recommended for use in children who have severe dysfunction of organs such as the kidneys or liver. Swallow regardless
Tinidazole: effective against Helicobacter
The drug is active against anaerobic bacteria, microaerophilic Helicobacter pylori or mixed aerobic-anaerobic infections. Antibiotics from Helicobacter are combined with it.
Not recommended in the first trimester of pregnancy. It is possible only if it is impossible to do without taking medications and the positive result outweighs the risk to the child. Children under 12 years of age are not allowed to take the medicine. Adults – 4 tablets (500 mg) 1 time per day. Children – 50 mg/kg once a day.
Levofloxacin
Prescribed for acute sinusitis, Helicobacter pylori, infections caused by pathogens sensitive to levofloxacin. The dose is determined by the attending physician.
Duration of therapy is from a week to two. Take orally – 250 – 750 mg once a day before or between meals. The solution is administered intravenously, slowly. Within an hour up to 500 mg, and 750 mg up to an hour and a half.
Tetracycline
This drug stops protein biosynthesis and combines in an unusual way with the 30‑S subunit of the ribosome. It has proven to be effective against H. Pylori. Intensity is maintained even at low pH levels. The medicine is included in the second-line treatment system.
Acts as a bactericidal drug, increases the level of resistance of the stomach lining to negative effects. The protective functions are reconstructed, preventing relapses of the disease. While taking it, it is better not to drink juices or milk. The course of treatment is up to two weeks. To enhance the effect, antisecretory tablets are added. But such treatment is not enough; only combined treatment can achieve a cure in 980% of cases. Therefore, a special treatment regimen for Helicobacter with antibiotics + denol is being drawn up.
Amoxicillin for Helicobacter
This is an antibiotic belonging to the series of penicillins; its dynamics are very similar to ampicillin. It behaves stably in an acidic environment. It acts locally as well as systemically. Helicobacter pylori shows sensitivity to the drug, but an integrated approach is required for quality treatment.
Use the medicine 4 times a day at 500 mg, or 2 times at 1000 mg. Available in tablet or suspension form, it is absorbed quickly and almost completely. Food intake does not depend on the use of medication.
Metronidazole
Helicobacter is sensitive to the drug. After use, a high concentration of the drug is formed in the stomach acid. This allows you to achieve a good therapeutic effect. During the metabolic process, “metronidazole” undergoes activation by nitroreductase, which leads to the elimination of the DNA structure of the bacteria, after which they die. Dissolves quickly and well, in about 1 hour.
The elimination period is 8 – 10 hours. Take for adults 2 tablets per day (500 mg). Children are prescribed the drug depending on body weight (30 mg in 3 doses).
Rifambutin
The antibiotic is active and is located both inside and outside the cells. It is used both for the treatment and prevention of gastrointestinal diseases, for the eradication of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Medicine is often recommended when first- and second-line regimens are ineffective.
It is used regardless of food intake. For adults, 2 capsules (300 mg) once a day. After administration it is well absorbed. It is evenly distributed in other organs and tissues and accumulates in significant concentrations intracellularly.
The fight for recognition
It was not until 1994 that the US National Institutes of Health documented the close association between H. pylori and peptic ulcers and recommended treating it with antibiotics. However, in 1995, most patients with stomach ulcers were still receiving antisecretory therapy, and only 5% of the lucky ones met doctors who prescribed antibiotics.
In the same 1995, the American Health Foundation conducted a large survey among people suffering from peptic ulcers. The results were impressive. More than 10 years after the discovery of H. pylori, 90% of patients had no idea that the true cause of their illness was an infection and blamed stress and weak nerves.
In 1996, the American Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of an antibiotic for the treatment of peptic ulcers for the first time in the world. A year later, in the same United States, a national campaign was launched, the purpose of which was to inform doctors and pharmacists about the connection between gastric ulcers and H. pylori. Soon the news of the absolute curability of the previously quite serious disease spread throughout countries, cities and villages, and a new era in the treatment of peptic ulcer disease began.
Table 3.
Combination drugs for eradication therapy
| International name | Tradename |
| omeprazole+amoxicillin+clarithromycin | Pilobact AM |
| lansoprazole+amoxicillin+clarithromycin | Lancid Keith, Helitrix |
What about the discoverers? They fully felt the sweet burden of glory and continue to bask in its rays to this day. In 2005, at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, Marshall and Robin William received the most prestigious prize, which has been awarded for more than 100 years for outstanding achievements in science and culture. The gold medal, accompanied by a diploma from the Nobel Committee and a very substantial monetary reward, was awarded to Australian scientists for “the discovery of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in the development of gastritis and peptic ulcers.” And eradication therapy, which began back in 1982, continues to save millions of patients, curing ulcers and preventing cancer.
Preparations for Helicobacter pylori eradication
Today, several regimens for Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy have been developed, which are selected individually.
The traditional anti-Helicobacter complex includes: an antibiotic (amoxicillin, clarithromycin or tetracycline); proton pump inhibitor; metronidazole; bismuth preparations.
Amoxicillin
The penicillin antibiotic, amoxicillin, is very close to ampicillin both structurally and in its spectrum of activity. Amoxicillin is stable in an acidic environment. The drug inhibits the synthesis of bacterial cell walls and acts both locally and systemically after absorption into the bloodstream and subsequent penetration into the lumen of the stomach. H. pylori demonstrates good sensitivity to amoxicillin in vitro, but complex therapy is required to eradicate the bacterium.
Clarithromycin
Clarithromycin, a 14-member macrolide, is a derivative of erythromycin with a similar spectrum of activity and indications for use. However, unlike erythromycin, it is more acid resistant and has a longer half-life. The results of studies showing that a triple anti-Helicobacter therapy regimen using clarithromycin gives a positive result in 90% of cases has led to the widespread use of the antibiotic. In this regard, an increase in the prevalence of clarithromycin-resistant strains of H. pylori has been recorded in recent years.
Tetracyclines
The point of application of tetracyclines is the bacterial ribosome. The antibiotic interrupts protein biosynthesis and specifically binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit, eliminating the addition of amino acids to the growing peptide chain. Tetracycline has been shown to be effective in vitro against H. pylori and remains active at low pH.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
PPI therapy has proven effective in various clinical studies. It is assumed that antisecretory drugs of the PPI group may help increase the concentration of antimicrobial agents, in particular metronidazole and clarithromycin, in the gastric lumen. PPIs reduce the volume of gastric juice, as a result of which the leaching of antibiotics from the surface of the mucosa decreases and the concentration, accordingly, increases. In addition, reducing the volume of hydrochloric acid maintains the stability of antimicrobials. Different PPIs do not differ in effectiveness.
Metronidazole
H. pylori is generally very sensitive to metronidazole, the effectiveness of which is independent of pH. After oral or infusion use, high concentrations of the drug are achieved in the gastric juice, which makes it possible to achieve the maximum therapeutic effect. Metronidazole causes H. pylori to lose its helical DNA structure, causing DNA damage and killing the bacterium.
Bismuth preparations
Bismuth was one of the first drugs to eradicate H. pylori. There is evidence that bismuth has a direct bactericidal effect, although its minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC - the smallest amount of drug that inhibits the growth of a pathogen) against H. pylori is too high. Like other heavy metals such as zinc and nickel, bismuth compounds reduce the activity of the enzyme urease, which is involved in the life cycle of H. pylori. In addition, bismuth preparations have local antimicrobial activity, acting directly on the bacterial cell wall and disrupting its integrity.
What other drugs are needed to treat Helicobacter?
Treatment is done with antibiotics. They are attributed with the intention of having the least negative impact on the body. Sometimes drugs cause more harm than the bacteria itself. In this case, medications are not prescribed. If there are ulcers, as well as various erosions, treatment without an antibiotic will not be beneficial. The effect will be minimal, and the healing will not be of high quality, even if you take additional medications to restore the walls of the digestive organ. All existing regimens include medications, two antibiotics, and an additional proton pump inhibitor. Treatment is prescribed for two weeks. Already on the first day, an improvement in the condition is felt. But it is important to complete the course of treatment. Otherwise, the bacteria will get used to this type of antibiotic and you will have to select a different drug.
Drugs to protect the stomach walls
To protect the lining of the stomach, antacids are prescribed, protecting against the negative reaction of hydrochloric acid after irritation with food. The remedy is simple and effective, but antacids (1st generation) do not last long. The presence of aluminum leads to constipation. Modern drugs work better, those that are not absorbed, they do not affect peristalsis. The dose is prescribed after meals, 1 to 2 hours later.
Bismuths are effective remedies for inflammation and heartburn. They protect the mucous membrane by forming a film that has a bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effect. These drugs, used in combination, eliminate the symptoms and the cause. Take after meals. Quickly and without negative consequences normalizes the gastrointestinal tract.
Myotropic series are antispasmodics used to relieve stomach pain. Affects smooth muscles, reducing spasm. Among them:
- Drotaverine (Nosh Pa);
- Spasmalgon;
- Combispasm;
- Renalgan.
Enzymes cope with heaviness, bloating and flatulence. The appointment is scheduled after a hearty lunch. Accelerate digestion, improve peristalsis, break down proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
Probiotics to restore microflora
It is imperative that after antibiotics have been used for Helicobacter, medications containing beneficial bacteria are prescribed. Each species plays its role. Once inside the body, probiotics restore the microflora, trigger the mechanism of revival, as well as the formation of their lactobacilli.
Probiotics are ready-made preparations containing the necessary bacteria. But, when the state is weakened, their action is not effective. The appointment is carried out in the case when there are not enough native Latobacteria. The prescription must be made by a doctor, describing on what day to start taking it and dosage.
The most popular in pharmacies:
- Linux;
- Hilak-Forte;
- Bifiform.
Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy regimen
When a doctor chooses an eradication therapy regimen in each specific case, the following factors must be taken into account:
- Treatment regimen;
- Predicted duration of treatment;
- Clinical picture of this case of heliobacteriosis;
- Cost of drugs included in the treatment regimen.
The Russian Gastroenterological Association and the Russian Group for the Study of Helicobacter pylori recommends taking as a basis a combined three-component treatment regimen that satisfies the following principles:
- The ability to eradicate bacteria in at least 80% of cases;
- The absence of side effects that force the attending physician to cancel the treatment regimen, or provoke the patient to stop taking medications (up to 5% of such cases are allowed);
- effectiveness even with a short course does not last longer than 1-2 weeks.
The methodology for prescribing eradication therapy is based on recommendations developed by the global community of gastroenterologists in Maastricht in 1996 and updated in 2000.
Recommendations of the Second Maastricht Agreement on anti-Helicobacter therapy:
- In uncomplicated cases of peptic ulcer after a course of eradication therapy, the use of antisecretory drugs is not required.
- Indications for eradication therapy other than peptic ulcer: MALT lymphoma, atrophic gastritis, close family relations with a patient with gastric cancer, condition after resection for gastric cancer, the patient's desire.
- Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection should take into account the possibility of failure of the first line of eradication therapy and the need to use a second line if the bacterium persists in the body. It is proposed to include 2 antibiotics in the first-line eradication regimen (triple therapy): Clarithromycin + Amoxicillin (or Metronidazole) and a proton pump inhibitor (or Ranitidine). It lasts no more than 7 days. If failure occurs, it is recommended to use a second-line regimen (quadruple therapy), which includes 2 antibiotics: Tetracycline + Metronidazole, bismuth preparations and a proton pump inhibitor. The duration of use of quadruple therapy is 7 days.
- Currently, specific antibacterial drugs, probiotics and vaccines directed exclusively against Helicobacter pylori are not used in practice; they are still under development.
The developers of the Maastricht recommendations excluded the usual combination for Russia from the treatment regimen: Amoxicillin + Metronidazole + proton pump blocker due to increased resistance of Helicobacter pylori to nitroimidazole derivatives. Research by Russian scientists has confirmed the low effectiveness of this combination (only 30%). Russian gastroenterologists in first-line eradication therapy often use affordable and effective triple therapy, including bismuth drugs + Amoxicillin + Furazolidone. Improvement of anti-Helicobacter therapy continues. In 2005, modern first-, second-, and third-line eradication therapy regimens were developed in the Netherlands.
Effective treatment regimens for Helicobacter pylori
Each row contains at least three medications. The course of treatment is more than 14 days. It is important to drink everything to the end. When determining the Helicobacter bacteria, it is necessary to control nutrition and lead a healthy lifestyle. It is recommended to completely give up smoking and alcohol. Stress is contraindicated, and smoked, fried, and also too spicy foods are excluded from the diet.
With low acidity
This type of gastritis is difficult to treat. Enzymes, bismuth preparations, and prokinetics are used for this. Gastritis caused by Helicobacter pylori is eliminated using a three-component system. It includes antibiotics, bismuths, inhibitors. The duration of taking the drugs is 10 days. Additionally, nitrofuran derivatives are prescribed for strain resistance. Diagnostics, as well as a list of medications, are prescribed by the attending physician. Self-medication is not acceptable. This can cause a deterioration in health and the overall clinical picture. After purchasing medications, it is important to read the instructions, find out the side effects and whether there are any contraindications.
With increased acidity
When a stomach disease becomes chronic, as well as before prescribing medications, you should first check the acidity of the stomach. An elevated level indicates a high content of hydrochloric acid. The drugs are prescribed with antacids and proton pump inhibitors. They neutralize and also reduce the production of hydrochloric acid, protecting the walls of the stomach.
Four-day treatment regimen
The second row of the treatment regimen is called four-component. What antibiotics for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori are prescribed by doctors in this case? First, one type of proton pump inhibitor, as well as the calming effects of two pyloric antibiotics. Tetracycline and Metronidazole are used if they were not prescribed in the first stage.
It is good if drugs are used that have not yet been prescribed for treatment, so that the given strain is sensitive to the drug. The second method is the use of medications based on Amoxicillin. Products containing tripotassium dicitrate act as a bactericidal drug. They stimulate cytoprotective mechanisms and make the mucous membrane resistant to negative influences. They normalize the functions of the gastrointestinal tract, preventing relapses of the disease. It is important to ensure that while taking bismuth-based tablets, your diet does not include juices, fresh milk and fruits.
Treatment regimen for Helicobacter pylori with antibiotics with De-Nol
There are standard schemes: seven-day, ten-day, and also two-week.
The first line of therapy contains simultaneously prescribed medications for one week, which are taken 2 times a day:
- Omeprazole (20 mg);
- Lanzoprazole (30 mg);
- Rabeprazole (20 mg);
- Esomeprazole (20 mg);
- Ranitidine bismuth citrate;
- Clarithromycin (500 mg);
- Amoxicillin (1000 mg).
Second line of therapy for 10 or 14 days. Appointed:
- Proton pump inhibitor;
- Losek MAPS,
- Lanzoptol,
- Pariet or Esomeprazole 2 times a day;
- Bismuth subcitrate 120 mg 4 times a day;
- Metronidazole 500 mg (3 times);
- Tetracycline hydrochloride (4 times a day).
After such therapy, treatment should be continued for 40 days. For duodenitis and stomach ulcers, one and a half months. For this purpose, one proton pump inhibitor is used. This may be Omeprazole or Lanzoprazole. Drink 1 – 2 times a day. A histamine H2 receptor blocker is also used: Famotidine, Ranitidine 2 times a day.
More about drugs
Features of taking antibiotics for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori:
This is an antibacterial drug from the macrolide group. Included in the first-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. It is successfully used in gastroenterology, it is able to inhibit the synthesis of the cell wall of Helicobacter pylori, and therefore prevent its reproduction. It is acid-resistant, works effectively at normal and high acidity, and is well absorbed.
Some strains of bacteria exhibit resistance to clarithromycin. In this case, the drug must be replaced with another one to achieve a better therapeutic effect.
- Amoxicillin and metronidazole
Metronidazole or trichopolum is a drug that has a destructive or bactericidal effect on H. pylori. Its activity does not depend on the pH level in the stomach; the drug can be used in both hyper- and hypoacid conditions.
Today, resistance of many Helicobacter strains to metronidazole is very common. If the drug is prescribed together with de-nol, resistance to it develops more slowly.
Amoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic that blocks the synthesis of microbial cell walls and is well absorbed by the gastric mucosa. More active in a neutral environment than in an acidic environment. Increasing the pH to 4 increases the pharmacological effect of this drug 10 times.
Metronidazole and amoxicillin are first-line drugs, but can also be prescribed in a 4-component treatment regimen.
Another antimicrobial agent actively used in eradication therapy of helicobacter pylori. The mechanism of action of tetracycline is to inhibit microbial cell protein synthesis.
The medicine is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Eating dairy foods slows down its absorption.
- Proton pump blockers
The most common representative of this group is omeprazole (omez). There are other very effective drugs: lansoprazole, pantoprozole, esomeprazole, rabeprazole).
Medicines suppress the production of hydrochloric acid. Thus, they influence the microbe indirectly: they do not destroy it, but create unfavorable conditions for existence, have a suppressive effect on the infection: they stop bacterial growth and development.
Omeprazole and other representatives of the group, by increasing the pH of the gastric contents, contribute to the better functioning of antibacterial drugs, in particular amoxicillin.
There is evidence that proton pump inhibitors can block the bacterial enzyme urease.
Doctors recommend that after completing the course of treatment with antibiotics, continue taking omeprazole for up to 4-8 weeks. Patients who continue to take proton pump blockers have better mucosal healing processes and a higher percentage of bacterial destruction compared to patients who stopped taking omeprazole after the end of the eradication regimen.
- Antacids and H2 receptor blockers
Most often, the acidity of gastric juice during infection with H. pylori is normal or increased.
In addition to omeprazole, which normalizes pH, antacid drugs (Almagel, phosphalugel, Hefal, Maalox, Rennie) and H2-histamine receptor blockers (famotidine, ranitidine) also have this effect.
The mechanism of action of antacids is to neutralize gastric acid. The active ingredients in these preparations are aluminum and magnesium hydroskides.
The products effectively eliminate the clinical manifestations of “acidism” – heartburn, sour belching. Take them 1-2 hours after meals and at night. Release form: suspensions, or powders, tablets.
You should not combine the use of antacids with antibacterial drugs or bismuth salts, since aluminum and magnesium hydroxides interfere with the absorption of other substances in the gastrointestinal tract.
New generation H2-histamine receptor blockers (famotidine, ranitidine) have virtually no side effects. Their mechanism of action: they inhibit the production of HCL and the production of pepsin, which causes a decrease in acidity. Prescribe tablets after breakfast and before bed.
This group of drugs, in combination with antibiotics, has a bactericidal effect - it destroys both coccal strains and vegetative forms.
Bismuth salts have many effects that have a positive effect in the complex treatment of diseases caused by Helicobacter:
- Prevents pathogens from attaching to epithelial cells of the gastric mucosa
- Disrupt microbial ATP synthesis
- Block bacteria enzymes
- Promote the destruction of the cell wall of the infectious agent
- Increases the synthesis of protective immunoglobulins, prostaglandins of gastric secretions
- Increases the secretion of bicarbonates and protective mucus
- Reduce the absorption of antibiotics in the gastrointestinal tract, thereby increasing their concentration in the gastric contents
- Provide a reparative, wound-healing effect of the internal gastric wall
- Improves local blood circulation
These pharmacological properties allowed the bismuth drug to occupy its niche in the treatment of helicobacteriosis in combination with two antibiotics. One of the most effective drugs in this group is de-nol.
Does de-nol kill Helicobacter or not?
Only in combination with antimicrobial agents does de-nol have a bactericidal effect. If you take this drug separately as monotherapy, such treatment will not have the desired effect.
But in a combined treatment regimen, de-nol fully reveals its therapeutic effects, while simultaneously enhancing the properties of antibacterial drugs.
The combination “de-nol + 2 antibiotics” is extremely effective, and in the case of Helicobacter sensitivity, it allows the microbe to disappear if the tablets are taken for 10-14 days.
How much to drink de-nol for Helicobacter infection
The drug is prescribed 1 tablet 4 times a day for 30 minutes. before meals and at night for a period of at least 21 days, you can take the medicine for up to 8 weeks as recommended by your doctor. You should know that when the drug is prescribed, the stool turns black.
The tablets should be taken with a glass of boiled water, but not with milk, since dairy products reduce the pharmacological effect of the drug. Tablets cannot be combined with juices either.
Antacids slow down the absorption of de-nol, so you should not drink them together.
If side effects occur: diarrhea, nausea, allergic reactions, vomiting, you should stop taking the medication and consult a doctor.
The occurrence of gastritis and peptic ulcers is associated with many factors: poor diet, stress, smoking and alcohol abuse, long-term use of medications (non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory, anti-tuberculosis, antibacterial or hormonal therapy). However, the leading role in the etiology of these diseases is occupied by the infectious nature of inflammation associated with Helicobacter pylori, a gram-negative spiral-shaped bacterium.
How to diagnose the disease?
The first step to developing a program is a survey. It is carried out primarily for people at increased risk. There are different diagnostic options based on the level of infection activity. The property of Helicobacter is the breakdown of urea with the formation of carbon dioxide and ammonia, this distinguishes it from other microbes. A patient with abdominal pain should first consult a gastroenterologist. If the worsening situation is localized in the upper sections, fibrogastroduodenoscopy is prescribed. This is the main examination method that allows you to see changes in the mucosa, including ulcerative defects.
During this procedure, a biopsy sample is taken. It consists of a histological examination, as well as a urease test, which determines the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. If there is an infection in the biopsy sample, it is determined using the urea splitting reaction using a paper indicator. It contains a complex chemical composition that changes color when bacteria are present.
This option is very convenient, practical, the result is ready in 2 – 3 minutes. There is also a breath test, using which you can detect the presence of bacteria by exhaled ammonia.
Routes of transmission of Helicobacter pylori, causes, symptoms of gastric pathology
The causative agents of the disease are easily transmitted through household items and personal hygiene products. During a kiss, infection of the body also occurs. Pathogenic bacteria survive in an acidic environment, so they easily attack the gastric mucosa, destroying it. An inflammatory process occurs, against which gastritis and ulcers develop.
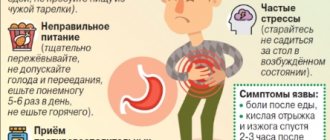
It is recommended to consult a gastroenterologist as soon as characteristic symptoms appear:
- severe nausea;
- pain in the abdomen;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- burning sensation in the esophagus;
- belching with a sour or rotten taste;
- vomit;
- bloating;
- recurring heartburn;
- the swallowing process is disrupted;
- there are problems with bowel movements;
- vomit or stool contains blood.
People who have a low standard of living are at risk of encountering Helicobacter pylori. It is also important to follow simple rules of personal hygiene. Pathogens enter the human body through poorly washed vegetables and fruits. The same goes for dirty water. It is necessary to wash the dishes of an infected person thoroughly
Is gastoscopy necessary for Helicobacter?
To identify diseases of the stomach and duodenum, gastroscopy is used as an informative method. This option allows you to visually assess the condition of the mucous membrane. During the procedure, a piece of tissue is taken to perform an examination. VGDS is used for:
- identifying pathogenic changes;
- obtaining a sample of already changed tissue (biopsy);
- penetration to stop bleeding or remove polyps.
Thanks to VEGDS it is possible to detect:
- inflammation: esophagitis, duodenitis, ulcer;
- neoplasms (benign);
- tumors formed in the esophagus, intestines;
- anatomical defects such as diverticula, stenosis;
- infection with Helicobacter pylori infection.
Pathological changes in the mucous membrane can be detected using the chromoendoscopy method.
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori without antibiotics: is it possible?
Studies have shown that treating Helicobacter without antibiotics will not have a positive effect. Quality treatment consists of three stages. The first row of the diagram is beneficial. But if this method is not effective, doctors prescribe the next series of drugs. When this option does not completely cope with the infection, third-line drugs are used. A treatment regimen without antibiotics will not completely control the bacteria. In some cases, it is necessary to add a fourth component, which has an anti-inflammatory effect. Although they are prescribed at the second stage, the composition of the drug has a positive effect on the walls of the organ, forming a protective film. After this, the pain subsides and inflammation is relieved. But, besides this, it is necessary not only to take pills, but also to lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right.
Possible complications from antibiotic treatment
Treatment regimens for Helicobacter pylori should be strictly followed.
In some situations, patients experience complications for which it is recommended to consult a gastroenterologist:
- severe headache;
- a metallic taste appears in the mouth;
- body temperature rises;
- stool disturbances (diarrhea);
- symptoms of thrush appear;
- pseudomembranous colitis develops;
- rashes appear on the body.
Patients also experience anorexia, neuropathy, severe nausea and vomiting after taking antibacterial drugs.
Diet for Helicobacter pylori
There are dietary guidelines that determine which foods to eat and which to exclude. It is recommended to avoid the following products:
- fatty meats and fish;
- fried food in oil;
- pickles;
- conservation;
- spicy dishes, spices;
- mushrooms;
- soda;
- alcohol;
- bakery;
- vegetables that irritate the mucous membranes;
- legumes;
- grape.
The list of prohibited foods is long, but patients can eat normally and benefit their health. It is advisable to eat white bread, but not fresh. You can have sweet crackers. There is no need to completely exclude meat and fish; the main thing is to select dietary types and steam food. Broths should not be greasy. But, any dairy dishes can be prepared. You can have milk, pasta, nuts (walnuts). The tea is not strong. Healthy honey, bananas are not harmful. Sweet berries and fruits are recommended.