What is hepatomegaly
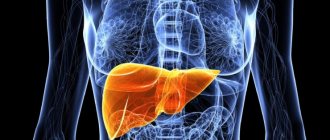
Hepatomegaly is a secondary disease, which is accompanied by an increase in the hepatic lobes. Normally, the parenchyma (liver tissue) has a soft consistency. During palpation, it is felt in the area of the costal arch only on the right side.
Hepatomegaly syndrome is diagnosed with liver hypertrophy and palpable compaction of the parenchyma. Structural changes in the organ are caused by:
- tumors;
- dystrophy of hepatocytes (liver cells);
- replacement of parenchyma with fibrous tissue;
- stagnation of blood in the portal vein;
- purulent inflammation, etc.
Pathological enlargement of an organ is always secondary, that is, it is not an independent disease and occurs against the background of others. If the size of the gland along the midclavicular line exceeds 12 cm, and its left lobe is palpable in the epigastrium, hepatomegaly is diagnosed. Symptoms are most pronounced in blood cancer (leukemia, hemoblastosis). Due to infiltration by leukemia cells, the weight of the organ sometimes reaches 15-20 kg - ten times more than normal.
Diagnostics
The first step is a DIF diagnosis for hepatomegaly, that is, the root cause is established by exclusion. If signs are pronounced, the doctor feels the organ to obtain information about its size, examines external signs and collects anamnesis. To establish an accurate diagnosis, you may also need:
- general and extended blood tests;
- PCR is the most informative and reliable analysis;
- virological and immunological blood tests;
- biochemistry of urine - allows you to identify infectious agents;
- puncture biopsy - a piece of the organ is taken for extensive examination;
- Ultrasound of the abdomen - provides information about the condition of the parenchyma, the diameter of the vessels of the spleen;
- Dopplerography - examination of the veins supplying the liver;
- coagulogram - tests for blood clotting;
- CT, MRI - due to their high cost, they are usually prescribed only when cancer is suspected.
Usually limited to ultrasound and tests. Other methods are used if it is not possible to identify the exact cause of the pathology.
Causes of hepatomegaly
Liver hepatomegaly is a nonspecific symptom that accompanies many cardiovascular, endocrine, and infectious pathologies.
The principles of treatment depend on the provoking factors. Therefore, before prescribing a course of therapy, the cause of the change in the structure of the organ is determined.
Liver pathology
In most cases, damage to the liver tissue is caused by disturbances in the hepatobiliary system, which includes the liver, bile ducts and bladder. Hepatomegaly in adults is one of the symptoms of such diseases:
- nonspecific cholangitis – infectious inflammation of the bile ducts;
- enzymopathy is a pathology that is accompanied by a violation of the synthesis of enzymes by liver tissue;
- fatty liver hepatosis is a metabolic disorder in hepatocytes caused by fatty degeneration of the parenchyma;
- Gaucher disease is a congenital disorder of lipid metabolism, leading to the accumulation of lipids in hepatocytes;
- viral hepatitis is an infectious inflammation of the parenchyma, which is most often caused by hepatitis viruses types A, B and C.
Diseases entail changes in the structure of the organ, due to which it greatly increases in size.
Blood diseases and oncology
The growth of malignant tumors in the liver parenchyma, as well as its infiltration by cancer cells, leads to hypertrophy.
With oncology and blood diseases, the liver sometimes reaches gigantic sizes.
Diseases that lead to liver enlargement:
- hepatocellular carcinoma – liver cancer caused by malignant degeneration of hepatocytes;
- adenoma is a benign tumor that is formed from parenchymal tissue;
- hemangioma - benign neoplasms in the parenchyma, which are formed from blood capillaries;
- leukemia is a malignant pathology characterized by an increase in the number of immature blood cells in the systemic circulation;
- hemoblastosis is an oncological disease accompanied by the accumulation of tumor lymphocytes in the lymph nodes and liver parenchyma.
In the early stages, the enlargement of the organ occurs mainly due to the left lobe. When infiltrated by malignant cells, severe hypertrophy of the gland is observed. Typically, oncology diagnoses a diffuse form of hepatomegaly.
Infectious and parasitic diseases
Many parasitic and infectious diseases are accompanied by enlargement of the hepatic lobes. Hepatomegaly is observed in the following diseases:
- toxoplasmosis;
- fascioliasis;
- malaria;
- amoebic abscess;
- mononucleosis;
- clonorchiasis;
- echinococcosis;
- streptococcal infection.
Moderate hepatomegaly is caused by helminths and roundworms, which are easily treatable. When flukes (fascioliasis, opisthorchiasis) penetrate into the gallbladder, cholestasis and cholangitis occur. Pathologies are fraught with impaired liver function and an increase in its size.
Cardiovascular diseases
In older people, hepatomegaly is often a sign of cardiovascular pathologies. Provocateurs of the pathological syndrome include:
- heart failure;
- stagnation of blood in the portal vein;
- constrictive pericarditis;
- heart defects;
- congestion of the venous sinuses;
- Budd-Chiari syndrome.
When hepatomegaly is caused by blood stagnation, this is indicated by tachycardia, lethargy, and increased sweating. Also, obstruction (narrowing) of the portal vein is caused by long-term use of medications and dietary supplements. In case of circulatory disorders, unexpressed hepatomegaly is more common, which is characterized by an increase in the organ by only 1-2 cm.
Other reasons
The causes of liver hypertrophy are varied. They are not always associated with pathologies of the organ itself, oncology or disturbances in the functioning of the heart.
There are often cases when hepatomegaly is provoked by prolonged and excessive use of medications, regular use of dietary supplements.
Causes of hepatomegaly include:
- focal hyperplasia;
- hepatic cirrhosis;
- Wilson's disease;
- amyloidosis;
- diabetes;
- alcohol intoxication;
- protein metabolism disorder;
- chronic toxic poisoning;
- endocrinopathy during pregnancy;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Liver hypertrophy due to trauma cannot be ruled out. Degeneration of hepatocytes due to autoimmune disorders and common infectious diseases is also possible.
Therapy methods
Treatment of hepatomegaly is most often carried out with the help of medications; in exceptional cases, surgical intervention is possible. To enhance the effect of traditional therapy, it is recommended to use folk recipes based on herbs.
The duration of therapy depends on the stage of the disease and the nature of liver damage. It is important to prevent relapse of the disease if the disease is viral.
The use of medications in the treatment process depends on the type of underlying disease:
- if the body is affected by hepatitis A or B, the use of antiviral medications is necessary;
- antibiotics are used to treat listeriosis and other infectious diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria;
- if echinococcosis is detected, anthelmintic drugs are used;
- if the cause of changes in liver size is a neoplasm, chemotherapy is required;
- for heart failure, drugs from the group of glycosides are used;
- To protect and regenerate damaged liver tissue, hepatoprotectors and essential phospholipids are used, and taking vitamin complexes is also recommended.
In order for drug therapy to have a beneficial effect on the body, the symptoms of hepatomegaly are eliminated based on a preliminary diagnosis of the disease.
Complete restoration of the functionality and normal size of the liver is possible with timely detection of the pathology and in the initial stages of the development of the disease.
Severe forms of liver damage can be dangerous to human health, and when the disease enters the chronic stage, complete regeneration of the organ cells does not occur. In medicine, it is believed that such manifestations most often lead to cirrhosis.
Hepatomegaly can be treated with surgery for the following diseases:
- if purulent ulcers are detected on the liver tissue, it is necessary to open them and install drainage;
- for oncological benign liver lesions, surgical removal of the tumor is recommended;
- if tissue integrity is compromised as a result of liver injuries and heavy bleeding, it is necessary to ligate the vessels;
- in case of acute thrombosis, an organ transplant may be required.
For successful therapy, the patient is recommended to use a special diet and give up certain foods in his diet.
Most often, the doctor prescribes diet No. 5 according to Pevzner. It is used for diseases of the liver, spleen and gallbladder pathologies. The main principles of gentle nutrition are the following rules:
- food must correspond to physiological completeness in terms of macro- and micronutrients;
- the nature of the diet should be observed in a gentle manner;
- It is recommended to eat small meals 5 to 6 times a day.
Recommended foods:
- porridge (barley, rice, oatmeal, buckwheat);
- vermicelli;
- low-fat steamed fish;
- low-fat dairy products;
- milk soups with noodles or cereals;
- boiled lean meat;
- vegetables (carrots, beets, zucchini, pumpkin) fresh, steamed or baked;
- dried fruits;
- cold pressed vegetable oil;
- dried bread;
- honey.
Foods that should be excluded from the patient’s diet:
- legumes;
- fatty meats, including waterfowl;
- fatty fish;
- salo;
- pastries, cakes and pastries;
- pastry products;
- cooking and animal fats;
- smoked products;
- conservation;
- spices and hot seasonings;
- fatty types of dairy products, including cheese and ice cream;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- strong tea and coffee;
- soups with rich broth.
Traditional methods of treatment help supplement medical means of combating the disease. An effective means of speeding up the recovery process after treatment for liver disease is a honey-based drink.
A remedy made from honey and lemon helps with hepatomegaly
To prepare this remedy you will need two tablespoons of honey, a glass of warm water and the juice of half a medium lemon. All ingredients must be mixed thoroughly and consumed on an empty stomach up to three times a day.
A decoction of medicinal herbs helps a lot. You will need: motherwort, sage, dandelion and peony roots, 20 grams each. All ingredients are poured into a container, pour 0.5 liters of water and bring to a boil over low heat. After cooling and straining, this product is consumed twice a day before meals.
If the liver is damaged, it is recommended to drink pumpkin juice and prepare porridge from it. The remedy for restoring liver functionality consists of two types of natural products. It is necessary to mix the juice of raw beets and carrots in a ratio of 3:10 and consume three times a day.
Symptoms of hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly always occurs against the background of other diseases. To understand what this diagnosis means, it is necessary to determine the cause of liver hypertrophy. With mild and moderate hepatomegaly, a person often does not experience any discomfort. As the size of the organ increases, pain is felt in the right side, which intensifies while walking or doing physical work.
The main signs of hepatomegaly:
- nausea;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- flatulence;
- frequent constipation;
- bad breath;
- heartburn;
- yellowness of the skin.
With viral hepatitis, there are complaints of fever, headache, and early satiety. If the pathology is caused by cirrhosis, the skin becomes sallow in color, tingling in the epigastrium, weakness and fatigue are a concern. With fatty infiltration of the liver, symptoms of intoxication appear - headache, fever, high temperature, loss of appetite.
In the case of toxic damage to the parenchyma, hepatomegaly is often the only manifestation of the disease. Sometimes combined with yellowing of the sclera of the eyes, moderate skin itching. When palpating the organ under the ribs, pain and nausea worsen.
How to diagnose
The above reasons for the increase in liver size indicate the difficulty of finding the underlying disease and the importance of differential diagnosis. This means that, in addition to identifying hepatomegaly, all possible types of research are used: blood and urine tests, general tests, bilirubin, sugar, protein, liver function testing using biochemical tests for basic enzymes.
Monitoring of the blood coagulation system and enzyme immunoassay are prescribed for viral and bacterial infections. The doctor determines the estimated growth of the organ using percussion and palpation methods.
Hardware methods are much more accurate and objective: ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, radiography is less informative, scanning with preliminary administration of hepatotropic radioactive substances gives a complete picture of cell damage, and the proportion of remaining undamaged tissue can be calculated.
Modern equipment makes it possible to detect not only changes in size, but also to accurately contrast the boundaries, tissue structure, and the nature of the changes (focal, diffuse). Morphological changes can be definitively judged by examining a biopsy.
Ultrasound allows you to compare the structure of the liver in all zones, identify denser foci and the size of the lobes. Echoscopic observation can be thought of as a visual examination on a screen without recording. It is more important when monitoring a contracting organ (heart). The liver is examined using echographic criteria, and images are printed in different projections.
Echo signs of hepatomegaly not only make it possible to determine the possible root cause of the pathology, but also the degree of its development.
Diagnostic methods
Palpation and percussion (tapping the abdomen) accurately determine moderate and severe hepatomegaly. To identify the causes, hardware methods of visualization of the abdominal organs are used:
- Ultrasound – ultrasound examination of the echostructure of the liver tissue;
- static scintigraphy is a radioisotope examination of the liver when a contrast agent accumulates in it.
Echo signs of organ hypertrophy are of great importance in determining the underlying disease. If it is caused by cardiovascular, parasitic or viral pathologies, the parenchyma does not become denser. In case of fatty hepatosis, sluggish hepatitis and fibrosis, echo signs in 96% of cases are focal in nature.
Treatment of hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly does not require therapy; it is necessary to treat the disease that led to the enlargement of the liver.
For liver diseases (depending on the specific diagnosis), antiviral, detoxification, and restorative therapy may be recommended. As a rule, hepatoprotectors based on ursodeoxycholic acid are prescribed. UDCA helps to increase the resistance of hepatocytes to external influences and thus prevents the death of liver cells. UDCA preparations (Ursosan) help restore the normal flow of bile, as well as reduce the toxic effect of bile acids and bilirubin on the central nervous system.
For fatty hepatosis (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease), the Table No. 5 diet, weight loss, increased physical activity and ursodeoxycholic acid preparations are recommended.
Therapy for storage diseases comes down to selecting an antidote to remove pathological metabolic products. If there is no antidote, dynamic observation and symptomatic therapy are prescribed; in severe cases, liver transplantation may be recommended.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system that result in liver enlargement should be treated by a cardiologist.
How to treat liver hepatomegaly
Treatment of hepatomegaly depends on the type of underlying disease. Therapy includes several areas:
- dietary nutrition;
- pharmacotherapy;
- operation.
For oncology, chemotherapy and radiation techniques are prescribed. Benign tumors in the liver are simply removed surgically.
Diet and lifestyle
People with liver pathologies are recommended to follow the Pevzner diet, table No. 5.
To reduce the load on the affected organ and improve digestion, it is recommended:
- eat small meals, up to 7 times a day;
- completely give up alcohol;
- limit confectionery products on the menu;
- include boiled and stewed vegetables in your diet;
- eat only lean fish and meat.
In case of hepatomegaly, legumes, canned food, seasonings, and whole milk are strictly prohibited. You should also give up coffee and hot chocolate in favor of natural juices and herbal tea.
For patients with severe liver hypertrophy, smoking, excessive physical activity, and working in hazardous industries are contraindicated. To prevent congestion in the abdominal organs, take daily walks in the fresh air.
Drug therapy
Pharmacotherapy involves taking medications that combat the manifestations of the underlying pathology. To prevent liver enlargement, take:
- hepatoprotectors (Heptral, Artichol) – protect liver cells from the negative effects of toxins;
- cardiac glycosides (Korglikon, Digoxin) – stimulate contraction of the myocardial muscle, eliminate symptoms of circulatory failure;
- antibiotics (Augmentin, Doxycycline) – destroy bacteria that cause intoxication of the body and inflammation of the parenchyma;
- choleretic agents (Allohol, Hofitol) – stimulate the removal of bile into the intestines, restore digestion;
- cytostatics (Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin) – disrupt the growth and division of cancer cells in oncological pathologies.
Painkillers, antiemetics and other drugs are used to relieve symptoms.
Surgery
If surgical intervention is necessary, the following is performed:
- drainage of abscesses in the liver;
- removal of tumors;
- ligation of blood vessels.
Patients with acute thrombosis, hepatocellular carcinoma and severe hepatomegaly are indicated for organ transplantation. Untimely surgery can lead to liver failure and death.
Other methods
Hepatomegaly due to cancer is treated with chemotherapy and ionizing radiation. When eliminating provoking factors, physiotherapeutic procedures (magnetic therapy, plasmapheresis, ultraviolet radiation) are indicated. They cleanse the blood of toxins, accelerate the restoration of normal liver size, and prevent complications. The choice of treatment method depends on the cause of the disease and the presence of contraindications.
DIAGNOSIS OF HEPATOMEGALY
The presence of hepatomegaly is determined by the doctor after examination, questioning and a thorough physical (without the use of instruments) examination of the patient. A significant diagnostic method in this case is palpation, during which the density and degree of enlargement of the liver is determined.
However, the mere statement of liver enlargement does not give anything - it is necessary to establish the cause, identify the disease, the development of which led to the occurrence of this syndrome. For this purpose, a number of additional examination methods are carried out - instrumental and laboratory:
- General and biochemical blood test with determination of the renal-hepatic complex;
- Serological blood test with determination of antibodies to the hepatitis virus and;
- Survey radiography of the abdominal organs;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- CT and MRI of the abdominal organs;
- Coagulogram - determination of blood clotting.
If these studies do not help determine the cause of hepatomegaly, doctors decide to perform diagnostic laparoscopy - surgery to identify the primary disease. But this happens extremely rarely.
Why is pathology dangerous?
Hepatomegaly is only a consequence of underlying diseases. With inadequate treatment of infections, helminthic infestations, and tumors, life-threatening complications arise:
- hepatic cirrhosis;
- portal hypertension;
- liver failure;
- encephalopathy;
- cysts in the parenchyma;
- abscesses;
- hepatic coma.
Against the background of an enlarged liver, accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum (ascites, or abdominal dropsy) is possible. Its formation leads to compression of internal organs. Iron also performs a neutralizing function in the body. Violations in its work are fraught with poisoning, toxic shock, and death.
Causes
Liver hepatomegaly
It is diagnosed for many diseases of the gland, internal organs and body systems. In most clinical cases, it occurs due to the following pathologies.
For ease of understanding, they can be divided into five groups:
- Infections and parasites
- — Infectious diseases of the body (hepatitis, mononucleosis, leptospirosis)
- — Parasitic lesions (opisthorchiasis, toxocariasis, echinococcosis, liver fluke)
Intoxication
— Drug-induced or toxic hepatitis
- — Chronic disturbance of intestinal microflora, constipation
- — Alcohol intoxication of the liver.
Metabolic disease
- — Amyloidosis (protein metabolism disorder)
- - Diabetes
- — Wilson's disease (copper metabolism disorder)
- — Gaucher disease (accumulation of glucocerebroside in the liver and other organs)
- — Gilbert's syndrome (disorder of bilirubin metabolism)
Tumors
- – Malignant or benign tumors in the human body
- Influence of other organs and systems
- — Impaired patency of the bile ducts and intrahepatic stagnation
- — Cardiovascular failure
The most common diagnoses that are accompanied by hepatomegaly:
— Cirrhosis (including fibrosis)
— Fatty degeneration of the gland (steatosis, fatty hepatosis, fatty liver).
It is important to know! Experiencing enormous loads every day and protecting the body from intoxication, the liver needs protection and cleansing.
If a cause such as infection, parasitosis or tumor has not been established, then you can use natural remedies for deep comprehensive cleansing of the body and maintaining liver function.
The idea of detoxing according to the Sokolinsky System is that you don’t just need to drink hepatoprotectors for a month. Studies of the activity of the ingredients that we use in our formulas (omega-3 acids, herbal extracts, sulfur) indicate that the course of hepatocyte restoration should last from 2-12 months. To reduce it to a minimum of 60 days, it makes sense to take a comprehensive approach.
Prevention of hepatomegaly means eliminating the effect on the liver of internal intoxication, sluggish infections, and stagnation of bile. To do this, not only the liver is cleansed, but also those organs that affect it - the intestines, blood, and the normalization of the microbiota (microflora).
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis depends on the provoking factors, the degree of parenchymal damage, and the reversibility of pathological processes. The likelihood of a complete cure is low for cirrhosis and cancer. If the disease is caused by infection or helminthic infestations, after treatment it quickly regresses.
An important role in the prevention of pathological enlargement of the liver is played by timely treatment of various diseases that can provoke a disorder.
There is no specific prevention, since hepatomegaly is caused by many reasons. To reduce the risk of liver enlargement, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right and treat other pathologies in a timely manner.
Prevention
As for the prevention of the syndrome, a person must understand the importance of simple and accessible measures to everyone - a proper diet, giving up bad habits such as smoking, alcohol abuse. What works most is what happens regularly.
Self-medication of any disease with medications is prohibited. Attempts to get rid of hidden infections, Helicobacter and even acne with the help of antibiotics lead to an enlarged liver.
Therefore, with a dosage form, the best prevention of hepatomegaly is to restore the microflora and immunity, to make sure that you do not need to take antibiotics again.
If you live in a region with an unfavorable environmental situation, are prone to smoking and drinking alcohol, work in hazardous industries, have previously taken potent drugs or suffered from hepatitis - carry out a prophylactic detox course 2 times a year and use omega-3 acids (Megapolynol) in winter, essential phospholipids (LecithinUM).
Maintain adequate levels of vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and plant fibers in your diet to correct carbohydrate and fat metabolism. The easiest way is to add 1/3 teaspoon of NutriDetox with a high content of spirulina, chlorella, and psyllium fibers to smoothies or drink with plain water 3-4 times a week.
An ultrasound showed an enlarged liver - what does this mean?
Hepatomegaly, in itself, is not a serious disease. The ability to increase is a natural property of the organ. Inside the liver there can be up to 2 liters of blood at the same time, as well as water, bile acids, secreted hormones and other substances.
The result of an ultrasound examination indicating an enlarged gland is not always evidence of disease. In order to make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary, first of all, to pay attention to the general condition of the body. All possible symptoms and signs of disease are taken into account. In addition, a comprehensive diagnosis is required, which includes laboratory and instrumental methods.
Pathological hepatomegaly means that the lobes of the liver are affected negatively. Tissues can increase due to the inflammatory process, tissue replacement due to cirrhosis or hepatosis, due to the accumulation of bile due to obstruction of the biliary tract.
This is interesting: How can you determine if your liver is enlarged at home?
What causes the pathology?
The causes of hepatomegaly are very diverse. They are associated both with diseases of the liver itself and with other pathologies. Most often, organ enlargement is caused by the following liver diseases:
- viral and non-viral hepatitis;
- hepatosis (fatty hepatosis is a common pathology in obese people), alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty degeneration;
- tumors (adenoma, hemangioma, carcinoma, cancer metastases from other organs, focal hyperplasia);
- formed cysts;
- amyloidosis;
- liver enzymopathy (with lysosomal lipase deficiency, hepatomegaly appears in 87% of cases);
- Gaucher disease, which causes fat accumulation;
- cirrhosis with irreversible fibrotic disorders with necrosis of hepatocytes;
- thrombosis of the hepatic veins, blockage of the bile ducts due to inflammation of the bladder.
Hepatomegaly is caused by chronic infections and intoxications. The liver ensures the neutralization of toxic substances and poisons; some pathogens “settle” directly inside the organ: with malaria, echinococcosis, granulomatous hepatitis develops with tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, cytomegalovirus infection, mononucleosis, septic pericarditis.
With decompensation of cardiac activity in the liver, venous blood of the inferior vena cava system is retained, the organ swells, a long process causes compression of hepatocytes and their necrosis, followed by replacement with fibrous tissue, cardiac cirrhosis of the liver is formed
Since the liver suffers from pathology associated with metabolic disorders, hepatomegaly is found in hemochromatosis (iron deposition in cells), Wilson-Konovalov disease (copper particles are found in hepatocytes).
Decompensation of cardiac activity caused by right ventricular failure contributes to overflow and increased pressure in the inferior vena cava and its basin. A congestive type of hepatomegaly is observed:
- with the consequences of acute myocardial infarction;
- myocardial dystrophy;
- cardiomyopathies;
- heart defects.
Hepatomegaly is most pronounced in malignant tumors of the lymphatic system (leukemia, leukemia). In this case, foci of additional extramarrow hematopoiesis are formed in the liver or the tissue is saturated with lymphoblastic cells. The liver reaches enormous sizes, occupies most of the abdominal cavity, and its weight reaches 20 kg.
Can hepatomegaly develop in only one lobe of the liver?
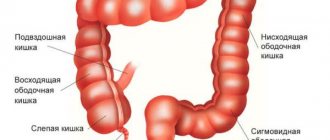
The liver consists of two lobes, each with its own innervation, blood supply, and bile ducts (central artery, vein, bile duct). Isolated hepatomegaly of the right lobe of the liver is observed more often than the left. Functionally, the right lobe is loaded more, performing 60% of the organ’s work, so any violations primarily affect it.
The left lobe is rarely affected; it is located closer to the pancreas; therefore, pancreatic disorders can cause an increase in the lobe. During examination, damage to the gallbladder and ducts, and the spleen is usually revealed.
With uneven enlargement of the organ, they speak of partial hepatomegaly. The lower edge of the liver rarely changes, so ultrasound is necessary for detection. A characteristic echo sign is a change in the homogeneity of the tissue structure. Usually found in tumors, cysts, and abscesses.
Echo signs of hepatomegaly
If signs of the disease occur, a number of diagnostic procedures are performed, the main one of which is ultrasound examination. Using ultrasound, the general condition of an organ is assessed, its size and structure are determined.
When diagnosing, the following echo signs are revealed:
- Homogeneity of echostructure with organ enlargement (indicates parasitic infestation, acute form of hepatitis, heart failure)
- Heterogeneity of the echostructure with organ enlargement (is a sign of cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, fatty infiltration)
- The presence of foci of disturbance of the echostructure (indicates pathological neoplasms, including oncological tumors)
Treatment
Treatment must be approached comprehensively and only after diagnosing the disease. Physicians such as hepatologist , gastroenterologist and general practitioner .
Therapeutic actions are aimed at eliminating the underlying disease:
- For many hepatitis, treatment is carried out by taking antiviral drugs , immunomodulators and interferons .
- If the cause of hepatomegaly is a diseased heart , then appropriate medications .
- Oncology is fought with chemotherapy or surgery .
- Thrombosis is treated with anticoagulant and thrombolytic drugs .
- To restore liver function , hepatoprotectors , such as Ursosan, Essentiale, Karsil, Heptor, Gepabene, etc.
- The load on the liver is reduced with the help of diuretics . They also cleanse blood , which can stagnate in the organ.
Important. If drug therapy does not produce positive results, then surgical intervention is resorted to.
If you contact a specialist in time , the problem can be completely eliminated.
During the period of therapy, a person must adhere to a strict diet , which will reduce the load on the liver. Food is taken often, but in small portions. Spicy and salty foods, smoked foods, fatty and fried foods are prohibited Alcohol and carbonated liquids should not be consumed as drinks
Products that are allowed for consumption :
- Low-fat fish.
- Fermented milk products.
- Soups with vegetables.
- Many cereals are in the form of porridges.
- Certain fruits and vegetables.
How does hepatomegaly occur in pregnant women?
Doctors note that liver problems during pregnancy occur in the third trimester. An enlarged uterus displaces the liver upward to the right. The movements of the diaphragm are limited, which makes it difficult to remove bile and fills the liver with blood.
Hormones influence the functioning of the liver, which is manifested by yellowish spots on a woman’s face and “stars” on the skin. An increase in fatty acids, cholesterol, and triglycerides is detected in the blood of a pregnant woman.
Pathological hepatomegaly can be caused by:
- toxicosis with prolonged vomiting, observed in 2% of pregnant women from the fourth to the tenth week, stops by the twentieth week, due to vomiting, dehydration, electrolyte disturbances can occur, and the woman’s weight decreases;
- intrahepatic stagnation of bile, found in every fifth pregnant woman, the cause is associated with hereditary predisposition.
Hepatomegaly can occur during pregnancy due to exacerbation of existing chronic diseases (heart decompensation, fatty hepatosis, diabetes mellitus, neoplasms, leukemia, hepatitis)
Diet for liver enlargement
The patient's diet has a therapeutic effect on the liver. The basic rules for eating food with hepatomegaly are described below:
1) Eating at least six times a day, in small portions;
2) Refusal of fried, spicy, canned products;
3) Sugar, salt - exclude;
4) Preference should be given to boiled or steamed food.
If all recommendations are followed, the patient’s general condition should improve.
How does hepatomegaly syndrome manifest?
During examination, the doctor identifies signs of hepatomegaly and interprets them in favor of one or another diagnosis. For example,
- the “stony” consistency of the edge of the liver, the bumpiness of the surface indicate the likelihood of cirrhosis or a tumor (new cells grow faster, so bumps form);
- pain on palpation is more typical for hepatitis (inflammation), moderate sensitivity of the edge is observed with steatosis;
- rapid enlargement of the organ is typical for the development of cardiac decompensation, with the capsule stretching, which is accompanied by pain;
- The course of liver abscess and hydatid cyst is distinguished by severe pain.
Pain in the liver area
If the liver is significantly enlarged, the patient experiences the following symptoms of hepatomegaly:
- heaviness, constant bursting pain under the ribs on the right or in the epigastrium, radiating to the side, right side of the abdomen, intensifying with movements;
- an increase in abdominal volume due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites);
- itchy skin rashes;
- yellowing of the sclera and skin;
- nausea, heartburn;
- bowel dysfunction (alternating diarrhea and constipation);
- small angiomas on the skin of the face, chest, abdomen in the form of “spiders” or spider veins.
Jaundice is one of the possible symptoms of the pathology.
Specific symptoms depend on the cause of hepatomegaly. With hepatitis, the patient's liver enlarges evenly, a thickening appears, which is felt along the lower edge. Palpation is painful. There is yellowness of the skin, signs of general intoxication and inflammation (fever, weakness, headaches, dizziness).
Treatment of hepatomegaly caused by viral hepatitis requires antiviral agents and immunostimulants. With good efficiency, the liver returns to normal size. Cirrhosis differs from hepatitis in the mechanism of destruction of liver tissue. Due to diffuse changes in the liver with areas of necrosis, working hepatocytes are replaced by scar tissue.
Impaired functions are accompanied by a tendency to bleeding, the skin takes on an earthy tint, and ascites grows due to portal hypertension. An expanded venous ring with outgoing vessels in the form of a “jellyfish head” appears around the navel.
In metabolic disorders characteristic of metabolic diseases, fermentopathy, along with hepatomegaly, the following is detected:
- damage to the kidneys and spleen (glycogenosis);
- copper deposits and a colored ring around the iris, hand tremors (Wilson-Konovalov disease);
- yellow-brown spots on the body and xanthelasmas on the eyelids, the connection of clinical manifestations with a period of fasting (pigmented hepatosis in Gilbert's syndrome);
- cough with hemoptysis (hemochromatosis).
In the patient, the signs of heart disease come first: shortness of breath, swelling in the legs, ascites, palpitations and arrhythmia, angina-type pain, cyanosis of the feet, hands, lips, and in children - the nasolabial triangle.
How is an enlarged liver and spleen combined?
An enlarged spleen (splenomegaly) may accompany hepatomegaly. It has been noticed that these two signs of pathology support each other. A simultaneous increase is expressed in hepatolienal syndrome. It is more typical for children, since it is aggravated by the anatomy and physiology of the growing organism.
It is provoked by hereditary diseases, infections, congenital anomalies. The syndrome is observed:
- for vascular diseases of the arteries and veins of the liver, spleen (vasculitis, thrombosis);
- chronic focal and diffuse liver pathology;
- hemochromatosis;
- liver amyloidosis;
- Gaucher's disease;
- hepatocerebral dystrophy.
Chronic parasitic and infectious diseases always, in addition to the liver, affect the spleen (intestinal tuberculosis, alveococcosis, malaria, infectious mononucleosis). Both organs are significantly enlarged with pathology of lymphoid tissue and blood (leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, hemolytic anemia). Heart disease is less likely to promote spleen growth.
The main task of diagnosis is to identify the common cause that caused hepatomegaly and splenomegaly.
Organs have a pronounced functional connection
Kinds
There are different types of hepatomegaly :
- Unexpressed form . With this form, the liver is slightly enlarged , by about 1-2 cm . Signs of the condition practically do not appear . A person may complain of weakness and fatigue . Nausea occasionally bothers . cannot be felt by palpation , so an ultrasound .
- Moderate hepatomegaly . This form is often diagnosed in people who abuse alcohol or eat foods that contain an abundance of salt , spices , fried and fatty foods . The enlargement of the liver is not so pronounced . But now the symptoms are already becoming more active .
- Severe hepatomegaly . The organ is significantly enlarged . Occupies most of the abdominal cavity. There are disruptions in the functioning of the entire body. In particular, this condition is not uncommon with leukemia . Healthy cells are replaced by scar cells, and a tumor process .
- Diffuse type of hepatomegaly . The size of the liver increases to 12 cm . An abscess develops in the organ . Drug therapy does not give a positive result. In this case, surgery will be required .
- Partial view . The enlargement of the liver occurs unevenly . One of the lobes of the organ is enlarged more, or only the edge is enlarged.
Treatment should begin immediately , but first a diagnosis to identify the underlying disease .
Disease prevention
In order to detect the presence of such a syndrome as hepatomegaly, it is recommended to undergo examination at an early stage, this will allow appropriate measures to be taken in a timely manner and prevent its development.
If patients do not see a doctor in time, they may experience various complications, such as liver failure or severe bleeding.
Treatment of the syndrome involves the use of complex methods, which must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. It should be borne in mind that organ enlargement, both in adults and in children, is a manifestation of some disease, so it is recommended to start taking medications only after identifying the causes that provoked the pathology.
Organ sizes and types of pathology
To understand that an organ is enlarged, you need to know its normal size. During physical examination, the size of the liver is determined according to Kurlov. First, the upper edge of the liver is found, and then the lower. Available in 3 sizes:
- 9 cm (right lobe);
- 8 cm (oblique right size);
- 7 cm (oblique size, left lobe).
Signs of hepatomegaly
In this case, an error of +1 cm is allowed. The liver is normally not palpable or is determined at the level of the costal arch on the right. With an enlarged organ, the edge of the liver will be dense, sometimes uneven (lumpy).
Hepatomegaly is an enlargement of the entire liver or its lobes. The organ can change size due to damage to hepatocytes.
Liver cells begin to be replaced by connective or fatty tissue, which, growing, lead to an enlargement of the organ. It can also be caused by the growth of cancer or tumor. These processes are sometimes called the general concept of “organ edema.”
The liver, as well as the spleen, can enlarge with increased pressure in the venous system of organs (portal hypertension syndrome). Pathologists distinguish several types: depending on changes in the size of the organ (Table 1) and the localization of the pathological process (Table 2).
Table 1 - Types of hepatomegaly by severity
| Unexpressed | Mild | Expressed |
| An increase in the organ by 1-1.5 cm. Normally it occurs in newborns, as well as children under 5 years of age. The child feels well and there are no symptoms of jaundice. This condition can be classified as physiological hepatomegaly. As the baby grows, the organ becomes smaller. | The organ enlarges by two or more cm. There is no jaundice or other symptoms. With adequate treatment and diet therapy, the liver restores its function and decreases in size. | The organ increases by five or more cm. The size of the abdomen increases, jaundice, dyspepsia, anemia and other manifestations of organ disease appear. |
Table 2 - Types of hepatomegaly depending on the prevalence of the pathological process
| Partial | Diffuse |
| Most often one right lobe is enlarged. It has a greater functional load than the left one. The left lobe may increase due to pathology of nearby organs (pancreas). Separately, the lobes can increase due to the appearance of cysts, tumors, and abscesses. When these formations grow, they push the tissues of the organ apart. | The enlargement of the organ is very strong, more than 10 cm. Surgical intervention is indicated for such patients, since more than 50% of the liver tissue is necrotic. |
Therapy and prognosis
Treatment of the disease, regardless of its cause, includes the use of hepatoprotectors that restore hepatocytes. These medications can improve liver function. There are several groups of hepatoprotectors (Table 4).
Table 4 - Hepatoprotectors
| Essential phospholipids | Plant phospholipids | Amino acid derivatives | Medicines for ursodeoxycholic acid |
| Essentiale forte, Phosphogliv. | Karsil, Gepabene, Hepatofalk Planta. | Heptral, Heptor, Hepa-Merz. | Ursodex, Ursodez, Ursosan, Ursofalk. |
The most commonly used are essential phospholipids (EPL). This group of drugs was one of the first to appear. Medicines have proven themselves in the treatment of liver diseases. They can be used for all types of diseases.
The only limitation for EPL is stagnation of bile. With this pathology, the dosage of injectable EPL is limited to 1 g per day, and tablet forms - to 1.8 g. EPL is often combined with other groups of drugs. Medicines can be used for more than 3 months (up to 2-4 years).
Action of essential phospholipids
Ursodeoxycholic acid medications have an excellent effect on cholestasis. They quickly relieve swelling of the ducts and stimulate the formation of bile secretion. This group of hepatoprotectors is often prescribed together with EPL, amino acid derivatives. Amino acid derivatives help with intracellular bile stagnation. Herbal preparations are more suitable for children.
For viral diseases, therapy is supplemented with antiviral drugs: Ribavirin, Interferon, Viferon. Sofosbuvir is considered very effective against hepatitis C. Autoimmune hepatitis is treated with hepatoprotectors, as well as glucocorticosteroid hormones (Methylprednisolone, Dexamethasone). Toxic hepatitis requires detoxification therapy.
With hepatomegaly, the development of portal hypertension syndrome, encephalopathy, coma, and disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome (especially in pregnant women) is possible. These conditions are very dangerous due to the development of severe kidney and liver dysfunction. Complications arise when treatment is not prescribed in a timely manner or the course of the disease is atypical. After complete liver failure, the patient requires an organ transplant, otherwise the patient may die.
With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable. Liver function is restored after treatment, the size of the organ returns to normal. Changes in the liver, even after therapy, still remain, so the patient should follow a diet.
To avoid the occurrence of hepatomegaly or its relapses, you need to follow simple rules:
- Stop drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Patients should drink at least 2 liters of water per day to prevent the formation of stones inside the bile ducts, as well as thickening of bile.
- Patients need to exclude fried, smoked, fatty foods.
- It is better to steam (boil, bake) lean meats (fish).
- You should not drink very strong tea.
- You need to give up coffee.
- You should eat in small portions so as not to overload the organ.