Any deviations in the functioning of the human body lead to unpleasant consequences. The reflux of bile into the stomach (bile reflux) is a pathological process that can also lead to serious, sometimes irreversible consequences.
Duodeno-gastric reflux is the root cause of bile in the stomach. This disease is rarely classified as a separate disease, but it is a companion to many diseases. The appearance of vomiting, diarrhea, severe pain – all this may indicate that the body is not functioning properly.
Only a specialized gastroenterologist can remove bile from the stomach permanently.
Functions of bile
Bile activates the gastric glands and is also necessary for processing food in the intestines. Its release occurs in the liver. Bile accumulates in the gallbladder, after which it is transported to the intestines using the bile ducts.
Bile has the following range of functions:
- Production of micelles;
- Formation of feces;
- Antiseptic effect on the intestines;
- Emulsification of fats;
- Synthesis of intestinal hormones and mucus.
Diagnostic methods
The following tests can help determine what is causing excessive bile production:
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS, gastroscopy) is an endoscopic examination of the mucous membranes with the possibility of cell biopsy.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the gallbladder, liver and ducts in particular and the abdominal cavity in general.
- Contrast fluoroscopy - shows the real picture of bile release.
- Morphological study of biopsied cells of the stomach and duodenum.
- Intragastric pH-metry - changes in the acid level of gastric juice.
How bile gets into the stomach: reasons
The human body is designed in such a way that food can move exclusively from top to bottom. However, vomiting does not follow this rule, which makes it possible to get rid of toxic substances. The sphincter plays the role of a kind of lock that prevents food from moving in another direction. The presence of bile in the stomach indicates a deviation in the functioning of this organ.
Duodeno-gastric reflux provokes the passage of bile from the duodenum into the stomach. Once in it, the liquid can move upward - into the esophagus and oral cavity.
Biliary reflux is a particular companion to many diseases: gastritis, ulcers, GERD. There is no need to worry if this pathology rarely bothers a person. However, the persistent nature of the problem may indicate serious health problems.
Causes of bile reflux in the stomach:
- Deterioration of the intestines and digestive system;
- Improper functioning of the intestinal sphincter;
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure (which may be a consequence of pregnancy);
- Increased thickness of bile, causing its stagnation;
- Improper functioning of the digestive organs;
- Activity of parasites;
- Absent gallbladder;
- Gallbladder diseases;
- Tumors, including cancer.
The appearance of bile in the stomach in healthy people
Experts assure that isolated cases of bile reflux can also occur in a healthy person.
The following factors lead to this:
- Binge eating.
- Poor nutrition, abuse of foods high in fat.
- Poisoning.
- Excessive amount of physical activity. Sometimes this leads to a pathological increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
- Hangover.
- Constant fasting.
- Tablets that impair the functioning of the intestinal sphincter. These include some types of anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Stress that has a long-term negative effect on the body.
- Obesity.
In women, bile reflux sometimes occurs during pregnancy. The embryo puts strong pressure on the internal organs, after which the contents of the duodenum are thrown into the stomach, which leads to a deterioration in the woman’s well-being.
Main reasons
According to experts, the reflux of bile from the duodenum into the stomach periodically occurs in every tenth healthy person. This happens at night and is not considered a pathological condition if the acidity of gastric juice is within normal limits.
In this case, the pathology can be provoked by:
- eating in large quantities;
- the predominance of spicy, fatty, fried foods in the diet;
- intense physical activity;
- sudden movements;
- late dinner;
- eating stale food;
- drinking large amounts of drinks during meals;
- hangover after drinking alcohol;
- the fetus puts pressure on a woman’s internal organs during pregnancy;
- uncontrolled use of antispasmodics;
- stressful condition.
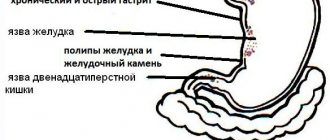
If bile appears in the stomach, the reasons may not only be physiological. It is likely that this condition is one of the symptoms of the following diseases:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- cholelithiasis;
- pathologies accompanied by cholestasis (stagnation of bile);
- duodenostasis – obstruction of the duodenum;
- gastritis;
- acute cholecystitis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- spastic condition of the gallbladder;
- biliary dyskinesia of the liver;
- duodenitis, accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane of the duodenum;
- injuries in the epigastric region;
- insufficient production of protective mucus;
- impaired motility of the initial part of the small intestine.
In operated patients, duodenogastric bile reflux is often observed after removal of the gallbladder or suturing of a duodenal ulcer. In addition, if there is a lot of bile in the stomach, the cause of reflux may be:
- congenital defect of the biliary sphincter;
- smooth muscle dystrophy;
- surgical interventions during which the integrity of the pylorus (sphincter) was damaged.
According to observations, bile is thrown into the stomach in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, but in every third patient this phenomenon exists as a separate pathology. In this case, men and women are affected with equal frequency.
How does bile reflux occur?
For the proper course of the digestive process, a special secret is required, which is produced by liver cells and is called bile. This biological fluid has a sharp unpleasant odor, bitter taste, and tends to accumulate in the gallbladder.
When the initial section of the intestine is filled with food, which undergoes primary processing in the stomach, the active digestive phase begins. At this moment, the required amount of bile from the liver enters the duodenum to break down lipids, activate the contraction of the smooth muscles of the small intestine, eliminate the effect of pepsin, stimulate the production of mucus and hormones.
Normally, fatty food enters the stomach, its primary processing begins, and a food bolus is formed, which enters the duodenum. At this moment, the gallbladder contracts, and bile is released through the ducts into the intestinal lumen.
In this case, the bile should stop in the intestinal lumen and not enter the stomach or esophagus. Backflow of bile can be prevented using a valve device. But due to some disorders, an excess of cloudy, foamy bile enters the stomach, and sometimes into the lumen of the esophagus, reaching the oral cavity.
The root cause of reflux is a dysfunction of the sphincter, which is located on the border of the stomach and intestines. Additional provoking factors for reflux may be:
- insufficient contractility;
- increased pressure in the initial parts of the small intestine;
- irritation of the mucous membrane with aggressive duodenal contents.
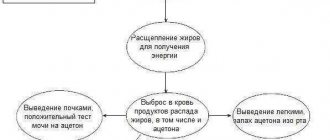
Frequent reflux of bile secretions leads to the development of toxic-chemical gastritis. The fact is that bile and pancreatic enzymes destroy the protective layer of the mucous membrane.
Due to reflux and chemical reactions, the environment in the stomach becomes acidic. This leads to increased irritation and sensitivity of cells to gastric juice and bile. In addition, if bile contents are thrown back into the stomach, the pressure inside its cavity increases.
With insufficient contractility of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract, overflow of the stomach and duodenum occurs. Stagnation of food masses causes obstruction, as well as the return of excess into the stomach.
Symptoms and signs of bile in the stomach
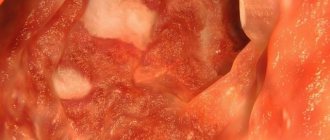
This is what the reflux of bile into the stomach looks like on video gastroscopy.
Bile reflux in some cases does not manifest itself in the initial stages of the disease. This may prevent correct diagnosis and timely resolution of the problem.
Bile in the stomach has many negative consequences. This leads to inflammation in the stomach, gastritis, and esophagitis. Symptoms of the pathological process depend on the severity of the disease and the duration of the problem.
The presence of this pathology is indicated by the following manifestations:
- Bitter taste in the mouth;
- Discomfort in the upper abdomen associated with food consumption;
- Rapid loss of body weight;
- Deterioration of hair and nails;
- The coating on the tongue is yellow;
- Heartburn, chest pain;
- Periodic aversion to food;
- Alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- Cough;
- Bloating in the abdominal area.
Sometimes an adult may vomit bile. After a binge or heavy overeating associated with alcohol abuse, the digestive organs may not be able to withstand the load. Vomiting usually begins with a hangover.
At night, bile may be released into the oral cavity. During sleep, a full gallbladder and its ducts relax, provoking negative consequences. Belching with a feeling of bitterness and an unpleasant odor may indicate serious abnormalities of the gallbladder, which requires emergency medical attention.
The sudden appearance of acne is one of the manifestations of improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Purulent inflammations on the skin are a consequence of uncontrolled releases of bile. Proper hygiene does not help to completely overcome the problem; it is necessary to completely get rid of the root cause.
Children often suffer from bile problems. In a child, bile reflux occurs due to a weakened sphincter.
Expressed by the following list of symptoms:
- Constant crying;
- Frequent regurgitation;
- Vomit. May occur after feeding or during meals, as well as at night;
- Inability to sleep;
- Restlessness and capricious behavior;
- Frequent belching.
Treatment
Regular entry of bile into the stomach leads to quite serious complications and therefore requires treatment. The main goal of treatment is to create favorable conditions for complete circulation of bile. The attending physician should advise how to treat it after carrying out the necessary diagnostics. There are quite a few treatment methods, the main ones are:
- medicinal,
- surgical,
- prophylactic.
Each of the methods is aimed at eliminating existing problems and preventing them from occurring later. The following will help get rid of bile reflux into the stomach:
- Beta blockers. Drugs that provide relaxation of smooth muscles. Thanks to them, the reflux of bile into the stomach can be stopped.
- Choleretic drugs. Used to relieve symptoms of diseases such as cholecystitis, or after removal of the gallbladder. They help ensure that bile flows through the channels without delay and precisely at those moments when the body needs it. Prevents bile from entering the esophagus from the stomach. The use of biliary medications reduces the risk of bile spreading outside the intestine, and is also an effective way to reduce the load on the gallbladder. In addition, the active use of these medications can protect the organ from the occurrence of kinks and protect a person from complications associated with the occurrence of this pathology.
- Proton pump inhibitors. This type of drug can effectively reduce the level of acidity in the stomach. It, of course, will not cure the disease, but it can actively neutralize bile at certain stages.
There are also surgical treatments that neutralize the reflux of bile into the stomach. One of them is considered to be sabotage surgery . During a surgical operation, if the stomach is full of bile and it is systematically released into it, mechanical cleaning is performed. This method is a direct answer to the question of how to get rid of bile in the stomach that gets there regularly and helps to combat possible consequences.
The second method of surgical treatment is antireflux treatment . The operation is performed to create increased pressure in the esophagus in order to remove stagnant bile in the stomach, as well as reduce its ability to be ejected. This process is carried out by merging a certain part of the stomach with the esophagus. Such surgical intervention protects in cases where bile and accompanying substances are discharged outside the intestine with high regularity, and is highly effective in esophagitis.
The preventive treatment method involves creating favorable conditions for digestion by avoiding fatty foods and bad habits.
There are many ways to remove bile from the stomach, all of them are effective for certain conditions. The medicinal method removes it through the action of drugs on the gallbladder and the muscles of the stomach; using the surgical method, excess bile is removed mechanically, and the preventive method is designed to create the most correct conditions for the full functioning of the entire system. Diagnostic methods will help you choose the right treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
If there is a suspicion of bile reflux into the stomach, the gastroenterologist interviews and examines the patient and refers him for medical examinations. Based on the data obtained, the specialist is able to quickly diagnose this pathology.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- Blood sampling for subsequent tests, liver tests. With their help, you can determine the presence of inflammatory processes in the body and disorders of the liver.
- FGDS . Fibrogastroscopy can indicate excess mucus, increased secretion release, and detect damage to the mucosa.
- Tests for the presence of pathological microorganisms.
- Determination of gastric acidity level.
- Ultrasound may be prescribed to determine the structure and functions of the digestive organs.
- Videogastroscopy (is a very accurate and modern method for diagnosing this disease).
Often, video gastroscopy reveals a large amount of bile in the stomach. Bile is an aggressive environment for the stomach and increases inflammation in it. With prolonged reflux of bile into the stomach, a thick yellow coating is usually visible on the walls of the stomach.
A full gallbladder is indicated schematically in yellow
Diagnostics
To identify pathology, the following research methods are used:
- through ultrasound, tumor formations are detected in the liver, gallbladder, pancreas and bile ducts;
- FGDS is a more detailed examination of the gastrointestinal tract. Any pathologies of the mucous membrane and sphincters are identified. At the same time, a biopsy of all atypical tissue structures is performed, and gastric juice is taken for examination;
- To assess the general condition of the gastrointestinal tract, experts recommend a special x-ray with barium contrast.
FGDS procedure
Attention! Bile reflux is not defined as an independent disease - it is a pronounced symptom of the pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, it is very important to visit a gastroenterologist with subsequent detailed diagnosis of the digestive organs.
If bile is regularly thrown into the gastric area and accumulates, and there are no therapeutic effects, then the risk of developing chronic gastritis or peptic ulcer against the background of a constantly irritated stomach increases.
Bile reflux into the stomach: treatment
A whole range of procedures is used to treat the disease. A competent approach to the problem allows you not only to get rid of it, but also to avoid the recurrence of the disease.
The treatment regimen involves several methods:
- Use of medications;
- Surgical intervention;
- Use of physiotherapy;
- Non-standard methods of treatment.
Before starting treatment, the causes of the disease should be identified. The choice of specific treatment methods depends on many aspects. Some medications are not recommended for patients after gallbladder removal. The essence of treatment then is to reduce the symptoms of the disease.
If cases of reflux occur occasionally, negative manifestations can be dealt with without medical help. To do this, it is enough to drink large amounts of water several times a day - this will help flush out some of the bile.
Drug treatment
Friends, remember, this is extremely important information!!!
Taking any choleretic drugs is started only after consultation with a gastroenterologist, followed by the exclusion of cholelithiasis.
The fact is that these drugs provoke peristalsis of the gallbladder and cause the stones to move, the stones block the passages and the only solution to the problem is surgical intervention.
If severe pain occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In such cases, drugs are used that are aimed at solving several problems:
- Regulation of secretory function (ranitidine, famotidine);
- Normalization of acidity levels (Maalox, Hofitol, Almagel);
- Improving motor skills (Ursosan, Ursofalk);
- Pain relief (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol);
- Elimination of increased density and stagnation of bile (Holosas, Allochol).
If there is no gallbladder, secretions will always accumulate in the duodenum, causing a bitter sensation in the mouth. Before using any medications, you should consult your doctor.
Motilium is actively used in drug treatment. It helps speed up the process of excretion of feces, improves the condition of the gallbladder, and alleviates the course of the disease. The medicine is available in several forms, including as a suspension, making it convenient to treat small children.
One of the important conditions of treatment is control of acidity levels. Proton pump inhibitors reduce the negative effects of cells and stop the release of hydrochloric acid. This has a positive effect on the functioning of the sphincter, stopping pathological processes.
Physiotherapy
Your doctor may decide that physical therapy is necessary. This helps not only to get rid of bile reflux, but also to avoid the development of gastritis. To enhance the effect, specialized devices operating at high frequencies can be used.
Sessions take place in the morning before breakfast. Impact on problem areas is carried out through the skin. Physical therapy can play a crucial role in treating the condition.
It promotes:
- Correction of pathologies of the esophagus and stomach;
- Toning the muscles of internal organs, which has a positive effect on their functions;
- Strengthening immunity;
- Increased blood flow.
Diet. Foods to avoid.
Following a special diet will allow, without pills, to reduce the negative impact on the mucous membrane of all parts of the esophagus and restore the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. A diet for bile reflux is recommended for the entire duration of the disease, as well as during the recovery period.
What diet should you follow?
To remove bile from the stomach, it is recommended to follow some rules:
- Eat small meals several times a day;
- Boil, bake, stew and steam foods;
- Do not eat before bedtime;
- Refrain from drinking alcohol, coffee, carbonated water and juices;
- Do not eat foods that can aggravate the course of the disease;
- Thermally treat and wash any products;
- Chew food longer and snack less;
- Consume more liquid foods.
- Consume more foods containing fiber (usually vegetables and fruits)
The course of the disease can be negatively affected by fried, fatty, smoked and spicy foods, and carbonated drinks.
List of foods to avoid:
- Meat with high fat content. Bacon, smoked meat, lard and rare beef can aggravate the condition.
- Fatty fish (tuna, sprat, mackerel) and canned fish.
- Soft, freshly baked bread.
- Large pasta.
- Food from fast food restaurants.
- Beans (beans, peas, chickpeas).
- Unnatural and spicy seasonings.
- Sweets (chocolate, cakes, pastries).
- Soda. A solution of soda can eliminate the burning sensation in the chest area, but this is a temporary effect. Carbon dioxide, which is produced when drinking soda, can lead to increased discomfort.
- Mint leads to deterioration of the esophageal sphincter. This provokes an increase in the volume of bile released from the intestines.
- Milk is also contraindicated for problems with bile. Microelements contained in milk increase the activity of the stomach. This leads to increased acid formation.
Traditional methods of treatment
Some products can have a positive effect on the treatment process. These include bran, zucchini, watermelon, prunes, carrots and honey.
Traditional methods are used to normalize the functioning of the stomach.
There are several products that are considered useful for the reflux of bile into the stomach:
- Thyme and St. John's wort. The plants should be filled with water and boiled over a fire for a while. The decoction needs to cool, after which it can be consumed internally. This set of herbs can help get rid of belching and heartburn, and also have a positive effect on treatment.
- Celery. Its root juice should be taken several tablespoons per day for a positive effect on the stomach.
- Chicory, barberry and dandelion. Pour hot water over these herbs and leave for a while. Using 100 ml of decoction before meals can have a positive effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal system.
- Chamomile decoction. For a positive effect, you can drink a decoction of fifteen grams of chamomile several times a day.
To relieve the symptoms of the disease, an infusion of dandelion roots and corn silk doused in boiling water are also used.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle changes can help treat bile problems.
In order to improve your own well-being, adhere to the following rules:
- Avoid alcoholic drinks and tobacco. Alcohol, especially on an empty stomach, leads to relaxation of the sphincter muscles, disrupting the bile circulation mechanism, and smoking increases the amount of gastric juice secreted. Passive smoking can also be harmful, so provide fresh air into the room more often.
- Move more. An active lifestyle improves the digestion process by activating the gastrointestinal tract.
- Avoid stress. Stressful situations can worsen bile problems.
- Avoid wearing tight belts or tight jeans, which can put pressure on your abdomen.
- Spend more time digesting your food. You should not sleep immediately after eating, and dinner can be made more comfortable for the body - consume soups, purees, cereals or other non-solid foods.
Features of diet and lifestyle
Proper nutrition is the basis for treating any problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
In addition, a complete change in the patient’s diet, lifestyle and menu is made. Proper nutrition is fundamental in the treatment of any problems in the gastrointestinal tract. To reduce the number of reflux in the stomach, relieve severe pain and bitterness in the mouth, and prevent the development of serious consequences, it is necessary to remove fatty, smoked and other aggressive foods and dishes from the diet table - such food is harmful. It is better to eat foods that can coat the walls of the stomach and stimulate the production of protective mucus. Such foods include slimy porridges and soups.
In order not to burden the digestive system and to establish proper bile production in accordance with meals, it is important to determine a constant regimen. To do this, you need to eat small portions at the same time every day. It is also important to give up smoking and alcohol, which adversely affect the gastrointestinal tract. Regular physical activity is recommended; it is better to do physical therapy exercises. This will strengthen the muscles and restore gastrointestinal motility.
Complications
the development of complications due to the reflux of bile into the stomach and esophagus.
Lack of timely medical care can lead to serious complications. These include: bile reflux gastritis, various tumors, the development of esophagitis, Barrett's syndrome, cholelithiasis requiring surgical intervention, destruction of the pancreas.
Negative consequences can be avoided if you undergo the necessary examinations on time and follow the instructions of your doctor.
Getting rid of bile reflux occurs most easily in the initial stages of the disease. But diagnosis is complicated by the similarity of symptoms with the manifestations of other diseases, so you should contact an experienced gastroenterologist.
Foamy bile
The consequence of cholecystitis, hepatitis or other inflammations in the liver, bladder, ducts is bile in the stomach. The intensity and nature of the pathology, as well as treatment, depend on the provocateur of the condition.
Provoking factors are weak patency of the gallbladder ducts, incompetence of the duodenal sphincter (DU), in which the symptom appears frequently. If a lot of bile is released into the stomach no more than once a month, there is no need to worry.
But if your stomach hurts regularly, or you experience bitterness on an empty stomach, you should seek medical help.
Advice from a gastroenterologist
The disease causes unpleasant consequences, so it must be treated immediately after detection.
For a quick recovery, doctors recommend following the following rules:
- Follow a diet and avoid foods that aggravate the situation.
- Treat other diseases in a timely manner.
- Pay more attention to physical activity.
- Work on stabilizing your own weight.
- Follow recommendations for the use of medications.
Bile reflux in the modern world can be successfully treated. However, for a complete recovery, do not forget about the recommendations of doctors.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- Rectal fissure: causes, symptoms and treatment of pathology
- Details about the coprogram: preparation, conduct and interpretation of the analysis
- More about hemorrhoids: causes, symptoms and treatment methods
- Rectal cancer: symptoms, stages, treatment and prognosis for life
- Causes of bloating and increased gas formation, treatment methods
- Sigmoiditis (inflammation of the sigmoid colon): symptoms and treatment methods
- Irritable bowel syndrome: symptoms and treatments
- Causes of abdominal pain: pathological and non-pathological cases
- What medications should I use for increased gas formation?
- More about Helicobacter pylori: diagnosis and treatment of the pathogen
Recommendations
To prevent the reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- lie on a raised pillow while sleeping;
- eat healthy, wholesome food;
- do not engage in vigorous activity, do not lift weights after eating;
- wear loose clothing;
- do not take sedatives or antibiotics for a long time;
- monitor body weight;
- visit a medical facility regularly.
We recommend: What is the peculiarity of the transition of the esophagus into the stomach?