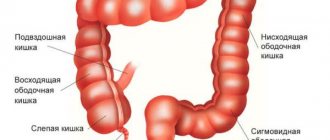
Proctosigmoiditis is an inflammatory disease of the sigmoid and rectum with predominant damage to the mucous membrane, submucosal layer and dysfunction of the intestine. Pathology occurs at any age, equally often in men and women. Without treatment, proctosigmoiditis progresses and leads to severe complications.
Classification
According to the course of the disease
- acute – clinical signs are pronounced, occur unexpectedly or against the background of another pathological process;
- chronic relapsing – periods of exacerbation and remission (improvement of well-being) alternate;
- chronic continuous - the disease proceeds without clearly defined episodes of deterioration and improvement of the condition.
By severity
- mild – symptoms of proctosigmoiditis occur periodically, are mild, general health does not suffer;
- average – complaints are constantly present, working capacity and quality of life decrease;
- severe - other parts of the intestine are involved in the process, complications develop.
According to the nature of changes in the intestinal mucosa
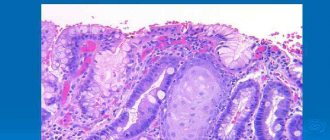
- catarrhal - redness, pinpoint hemorrhages, pronounced vascular pattern;
- erosive – single or multiple surface defects;
- ulcerative - ulcers of various shapes and sizes, covered with a coating of fibrin;
- atrophic – thinning and smoothness of the mucous membrane that occurs during a long process;
- mixed – there are erosions, ulcers, and areas of atrophy.
Causes of the disease
The most common cause of this pathology is poor nutrition. Also, with proctitis and sigmoiditis, the following factors are identified:
- damage to the mucous layer by solid fragments of feces;
- helminthic infestation;
- frequent constipation;
- drinking alcohol in large quantities and smoking;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- aggravated hemorrhoids;
- infectious diseases;
- frequent enemas;
- post-radiation and chemical burns;
- long-term antibacterial therapy;
- chronic intoxication;
- allergic factor;
- proctitis or sigmoiditis;
- pregnancy;
- tumor neoplasms;
- the appearance of dysbacteriosis;
- venereal diseases.
Return to contents
Causes
Under the influence of damaging factors, defects in the mucous membrane of the rectum and sigmoid colon occur, the production of immunoglobulins and lysozyme is disrupted, and autoimmune and allergic reactions develop.
Etiological factors
- Intestinal infections. The causative agents of dysentery and yersiniosis lead first to acute, then chronic inflammation. With intestinal dysbiosis, changes in the mucous membrane occur under the influence of opportunistic flora: staphylococci, pathogenic E. coli, yeast fungi, etc.
- Worm infestation. Long-term mechanical and toxic effects of helminths on the intestinal wall lead to an inflammatory process.
- Autoimmune intestinal pathology : nonspecific ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease. Damage to the rectum and sigmoid colon is accompanied by typical symptoms of proctosigmoiditis.
- Food allergies. Intolerance to certain foods leads to damage to the mucous membrane and increased permeability.
- Intoxication . The toxic effect of medications (antibiotics, laxatives, salicylates), industrial factors, and alcohol causes chronic inflammation and dystrophy.
- Atherosclerosis of mesenteric vessels . Impaired blood supply to the sigmoid and rectum leads to changes in the mucosa. The pathology is typical for older people.
- Cancer of the sigmoid or rectum. Tumor cells release toxic substances that irritate intestinal tissues, causing autoimmune reactions.
- Radiation damage . During radiation therapy for oncological diseases of the colon and pelvic organs, “radiation” proctosigmoiditis develops.
- Chronic constipation. Fecal masses stretch the intestinal walls, and blood supply deteriorates. Hard feces during defecation damage the anal canal.
- Other diseases of the digestive system : pancreatitis, cholecystitis, liver cirrhosis, hepatitis. Due to a lack of enzymes, food digestion in the small intestine is disrupted. Unprocessed substances enter the lower intestines, irritate the mucous membrane, and an inflammatory process develops.
Be sure to read: Gastroenterocolitis: symptoms and treatment methods (diet, medications)
Provoking factors
By themselves, they do not cause proctosigmoiditis, but they enhance the effect of damaging factors and increase the risk of developing pathology:
- Eating disorders : frequent consumption of spicy, fried foods, monotonous meager diet, irregular food intake, alcohol abuse.
- Hypothermia – a decrease in the body’s defenses leads to the activation of opportunistic bacteria and the exacerbation of chronic diseases.
- Immunodeficiency states - develop against the background of frequent infections, taking antibiotics, immunosuppressants.
- Stressful situations lead to disruptions in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system and impaired intestinal motility.
Proctosigmoiditis
Proctitis (proctitis: proktos - rectum, itis - inflammation) - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum. If proctitis is accompanied by inflammatory changes in the sigmoid colon, it is called proctosigmoiditis. Proctitis and proctosigmoiditis can be part of a general inflammation of the colon mucosa - colitis, including such well-known forms as ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, ischemic colitis. These diseases are described on the corresponding pages of our website, and this article discusses only cases of isolated damage to the rectum (including part of the sigmoid colon, which is very common, taking into account the unclear, conventional boundaries of the sections of the colon).
Classification
With the flow:
- spicy
- chronic
According to morphological changes in the intestinal wall:
- atrophic
- hypertrophic
- catarrhal
- purulent
- ulcerative
- ulcerative-necrotic
- fibrinous
- hemorrhagic
Due to the occurrence:
- nutritional
- infectious
- parasitic
- toxic
- stagnant
- ischemic
- ray
The cause of proctosigmoiditis cannot always be determined. The most common factors that cause a mild chronic form of the disease without obvious reasons are: poor diet, with regular and excessive consumption of spicy and salty foods, spices, alcohol (alimentary proctosigmoiditis); chronic constipation, which is accompanied by venous stagnation in the wall of the rectum and injuries to its mucous membrane with dense feces (congestive proctosigmoiditis); age factor, when atherosclerotic changes can also affect the vessels supplying the colon and rectum (ischemic proctosigmoiditis).
Acute proctosigmoiditis most often has an infectious nature. The infectious agent can enter the rectum in various ways: through the mouth (dysentery, cholera, etc., although in this case, as a rule, the entire colon is affected), through the anus, during anal sexual intercourse or anal masturbation (in this case it is possible specific damage to the rectum with gonorrhea, syphilis, etc.), hematogenously with other inflammatory diseases of the rectum and neighboring organs (hemorrhoids, paraproctitis, polyps and rectal cancer, prostatitis, cystitis, vaginitis). Separately, it is worth highlighting parasitic proctitis, when inflammation of the intestinal wall is caused by the presence in the lumen of the small and large intestines of parietal parasites and helminths (dysenteric amoebas, lamblia, trichomonas, balantidia, roundworms, pinworms).
In addition, acute forms of procosigmoiditis can be the result of poisoning with various poisons and fungi (toxic proctitis) or as a result of long-term use of antibiotics. In the latter case, the balance of the intestinal microflora is significantly disturbed, which can cause damage to its mucous membrane by pathogenic microflora, including mycotic damage. Separately, it is necessary to highlight long-lasting and difficult to treat radiation proctitis, which is often observed after radiation therapy for malignant tumors of the pelvic organs.
Clinical picture
Acute proctitis is manifested by constant pain in the rectum, an imperative urge to defecate, often with involuntary discharge from the anus of purulent, serous, mucous or sanguineous discharge. A rise in body temperature to 37.5-38° is often noted. Less commonly, weakness or spasticity of the anal sphincter is noted. The outcome of acute proctosigmoiditis can be either complete recovery or transition to the chronic stage. In especially severe cases, after recovery, cicatricial narrowing of the rectum is possible.
Chronic proctitis occurs with periodic moderate pain in the left iliac region, upset stool, and the presence of mucus in it. Quite often, chronic proctitis occurs without pronounced symptoms. In such cases, the patient is concerned about indirect signs of the disease - periodic discharge of mucus with feces, itching in the anus.
Diagnostics
The main instrumental method for diagnosing the disease is rectoscopy. When carrying out the procedure in non-specialized institutions, the diagnosis of proctosigmoiditis is made very often, since the rectal mucosa reacts to the very process of preparing it with enemas, which creates the appearance of inflammatory changes. So if you have been diagnosed with this, there is no need to be scared. It may just be worth repeating the study after some time and using other methods of bowel preparation. Additionally, to clarify the diagnosis, cytological examination of intestinal contents, stool culture to determine the composition of the intestinal microflora, and biopsy of the intestinal mucosa are used.
Treatment
The main methods of treating proctitis:
- diet
- antibiotic therapy
- microenemas
- candles
Diet is an important condition for achieving good treatment results. Food should be mechanically gentle. The consumption of foods containing large amounts of fiber is limited, fried, spicy, smoked foods, and alcoholic beverages are excluded.
In cases of acute proctitis and proctosigmoiditis with pronounced changes in the intestinal mucosa, antibiotics and sulfonamide drugs are actively used. In mild chronic forms there is no need to prescribe them.
For mild forms of the disease, microenemas (30-50 ml) with collargol solution, chamomile decoction, oils (sea buckthorn, rose hips), and fish oil are prescribed. Rectal suppositories provide a good therapeutic effect, especially when proctitis is combined with other diseases of the anorectal area (hemorrhoids, anal fissures, cryptitis, papillitis, etc.). The choice of drugs is quite large; among those that have proven themselves well in our institution, we can mention Proctosan (multicomponent suppositories containing bufexamak, which has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect) and the domestic drug Natalsid, obtained from brown seaweed.
In cases of severe ulcerative proctitis and proctosigmoiditis, hormone therapy is indicated. Microenemas with hydrocortisone, suppositories with prednisolone or sulfasalazine are used.
The prognosis with proper and timely treatment is most often favorable. Prevention of proctitis comes down to timely treatment of diseases that contribute to its occurrence.
We remind you of the importance of obtaining a timely consultation with a proctologist, since early treatment is much more likely to be successful in non-surgical treatment of rectal diseases.
Symptoms
The severity of clinical signs depends on the cause of the disease, the severity of damage to the sigmoid and rectum, and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Intestinal manifestations
- aching or cramping pain in the lower abdomen on the left;
- pain in the anal area, radiating to the tailbone, lower back, genitals, intensifies during bowel movements;
- painful false urge to defecate
- burning and itching of the anus, sensation of a foreign body in the rectum;
- stool disorder: fragmented dense feces or diarrhea, alternating constipation and loose stools;
- pathological impurities in the stool: mucus, streaks or blood clots, pus;
- involuntary discharge of mucus from the anus, wetting of the perianal area.
Extraintestinal manifestations
- increase in body temperature to 37-37.2 °C for moderate disease and to 38-38.5 °C for severe disease;
- weakness;
- chills;
- weight loss;
- decreased or lack of appetite;
- psychoneurological disorders: anxiety, tearfulness, sleep disturbance, obsessive thoughts.
Causes
Having studied the classification of proctosigmoiditis according to the etiological factor, one can be convinced of the variety of causes and contributing factors.
The following main causes of the development of the disease are identified::
- anomalies of development and anatomy of the intestinal tract;
- regular consumption of food that is aggressive to the gastrointestinal tract, including alcohol;
- chronic dysbacteriosis;
- secondary infection in the postoperative period, with hemorrhoids;
- venereal diseases;
- intoxication of any nature;
- enzyme deficiency.
An important role in the development of the inflammatory process is played by a woman’s pregnancy , compression of the intestinal loops by the growing fetus. Compression may be a consequence of a tumor of the internal genital organs.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of proctosigmoiditis is carried out by a gastroenterologist together with a proctologist. The task of the gastroenterologist is to suspect the disease and refer the patient for examination. The proctologist identifies complications requiring surgical intervention.
Diagnostic methods:
- History taking and examination . The doctor finds out characteristic complaints, their duration, conditions of occurrence, and conducts an examination of organs and systems. A characteristic sign of the pathology: painful palpation of the left parts of the abdomen, compaction and rumbling in the projection of the sigmoid colon. When examining the anus and anal canal, anal fissures and enlarged hemorrhoids are revealed.
- Complete blood count – increased number of leukocytes, ESR; with bleeding – decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells.
- Blood biochemistry - signs of an inflammatory process: increased levels of fibrinogen, sialic acids, seromucoid, CRP.
- Scatological analysis - stool is liquid or mushy, with mucus; microscopy reveals a large number of leukocytes, epithelial cells, parasite eggs, vegetative forms and protozoan cysts.
- Bacteriological seeding of feces - the relationship between beneficial and opportunistic flora is disrupted, pathogenic microorganisms appear. Determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics.
- Digital examination of the rectum - assesses the tone of the anal sphincter, intestinal mobility, and the condition of the peri-intestinal tissue. A characteristic sign of proctosigmoiditis is sphincter spasm. Up to 80% of all rectal neoplasms are diagnosed using digital examination.
- Inspection using a rectal speculum – visualization of the rectal mucosa over 8-10 cm.
- Sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the rectum and lower part of the sigmoid colon, allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane, identify inflammation, ulcers, neoplasms, and take a biopsy from the affected areas.
- Fibercolonoscopy is an examination of the entire colon using fiber optics, carried out if an intestinal ulcer is suspected to determine the extent of the process.
Be sure to read:
Function of absorption of substances in the intestines
Treatment methods
Treatment of proctosigmoiditis with drugs involves taking anti-inflammatory medications. The doctor may also prescribe enemas using various herbs, such as chamomile or sea buckthorn oil. The prescription of medications depends on the factors that caused the disease. When infections enter the body, antibiotics are prescribed. If the disease is caused by parasites, the doctor prescribes anthelmintic medications. Based on the symptoms of the pathology, other drugs are prescribed, which is reflected in the table.
| For pain | From temperature | For constipation | For diarrhea |
| Painkillers Antispasmodics | Antipyretics | Laxatives | Detoxification Enterosorbents |
Chronic proctosigmoiditis is treated mainly in sanatoriums. In this case, patients drink special alkaline water and use various procedures, for example, mud therapy.
Treatment of the disease is usually medicinal
Treatment of proctosigmoiditis with folk remedies involves the use of infusions and decoctions of herbs. Use licorice, belladonna or calendula root. Sometimes herbs are used in different combinations. If some symptoms of proctosigmoiditis occur, treatment with candles prepared independently at home is also used. To do this, take a tampon and soak it in anti-inflammatory oil (sea buckthorn oil is most often used). You can also use pharmaceutical products. There are many names used for suppositories for proctosigmoiditis. If the medicine has not been prescribed by a doctor, the pharmacy staff will help you choose the right medicine.
Herbal medicines are used externally and in case of severe itching. For example, take a bath with chamomile or calendula added to it. However, you need to know that before using folk remedies, you must consult with your doctor. He will advise which herbs are more effective and in what dosages it is best to use them.
The main goal of treating erosive proctosigmoiditis is to eliminate the causes that caused inflammation and prevent this type from developing into an ulcerative lesion.
The video provides more information about identifying and treating the disease:
Treatment
Mild forms of proctosigmoiditis are treated on an outpatient basis, moderate and severe forms are treated in an inpatient setting. First of all, they find out the cause of the disease and try to eliminate it, then prescribe complex therapy to relieve inflammation and regenerate the mucous membrane.
Nutrition
Dietary nutrition is necessary for healing defects of the intestinal wall, restoring the functioning of the sigmoid and rectum, and normalizing stool.
Basic Rules:
- exclude foods that irritate the gastrointestinal tract;
- They recommend split meals - 5-6 times a day in small portions;
- the products are boiled in water or steamed; in case of severe exacerbation, pureed dishes are prepared: mousses, soufflés, liquid porridges.
Grocery list
| Allowed | Prohibited |
|
|
The list of products is adjusted depending on the type of bowel disorder. For constipation, increase the amount of boiled vegetables; for diarrhea, introduce foods with a strengthening effect: rice, blueberries, bananas. If you have a food allergy, avoid foods that cause a pathological reaction. As you feel better, the diet is gradually expanded, avoiding prohibited foods.
Medicines
- Antibiotics are prescribed for infectious diseases. They use drugs from the group of cephalosporins, protected penicillins, and fluoroquinolones. After receiving the results of the bacteriological examination, the treatment is adjusted.
- Antispasmodics - reduce painful contractions of inflamed areas of the intestine (No-shpa, Buscopan, Papaverine).
- Carminatives – drugs to combat bloating, reduce gas formation and pain (Espumizan, Sab Simplex).
- Enzymes - prescribed for chronic enzyme deficiency to improve food digestion (Festal, Creon, Mezim Forte).
- Probiotics – means for restoring intestinal microflora: Linex, Acipol, Enterol.
- Sulfasalazine is a medicine with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activity, prescribed for the treatment of intestinal ulcers.
- Hormonal drugs . Corticosteroids have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, they are used in the treatment of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone, Dexamethasone).
Be sure to read:
Paraproctitis: how is the pathology manifested and treated?
Local treatment
- Microclysters with medicinal solutions . Collargol (a silver preparation) has an antiseptic, healing, anti-inflammatory effect.
- Medicinal rectal suppositories . Methyluracil stimulates the healing of tissue defects. Mesalazine has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects.
- Sea buckthorn oil reduces inflammation and promotes mucosal regeneration.
- Sitz baths with a weak solution of potassium permanganate have an antiseptic effect.
Read on the topic: Herbs for the intestines and features of their use
Treatment of proctosigmoiditis
Help of drugs
Since proctosigmoiditis does not cover the entire area of the large intestine, 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) is the first treatment option. Doctors prescribe it in the form of Mesalazine, an anti-inflammatory drug. Mesalazine is available in several forms: oral, suppository, foam and enema. It is sold under the following brands:
- Lialda;
- Asacol;
- Pentasa;
- Apriso;
- Delzicol.
If using an enema is not possible, then the patient takes Mesalazine.
Severe diarrhea or bleeding may require hospitalization. In hospital, treatment is carried out using intravenous steroids. In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove the affected part of the colon. Since proctosigmoiditis only affects the lower part of the organ, suppositories can be used instead of an enema. Taking oral Mesalazine is indicated if it is not possible to tolerate or administer enemas. Other available medications include:
- oral corticosteroids;
- Infliximab (Remicade), which reduces the immune system response that causes inflammation.
What diet is indicated?
The diet consists of eating semolina, rice porridge, lean soups without fat, heat-treated vegetables, fruits, yogurt with biological additives, and cottage cheese. As a preventive measure, it is recommended to quit smoking, avoid drinking alcohol and spicy foods. If possible, drink at least two liters of fluid per day, lead a healthy lifestyle, and do light exercise. If you suspect an illness, contact a specialist immediately.
Healers' recipes: what is the effect?
While at home, the patient can independently make herbal decoctions, sitz baths with herbs, cleansing or therapeutic enemas. Herbal infusions are a common folk remedy for catarrhal proctosigmoiditis. The following recipes are available:
Chamomile decoction relieves inflammation in the intestines.
- Healing herbs. Infusions prepared from chamomile and calendula flowers, plantain and nettle have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Field horsetail. Use a bath component, it reduces pain.
- Plants for microenemas. Use oregano, lemon balm, chamomile and calendula. This method of treating catarrhal proctosigmoiditis is considered very effective, since the effect occurs directly on the inflamed area. Absorption of the necessary medicinal enzymes occurs much faster - this gives relief to the patient and speeds up the treatment of inflammation. If this procedure is performed correctly, the effect will appear in a few days.
Complications
If the pathological process is severe and there is a delay in seeking medical help, complications develop:
- Hemorrhoids - frequent urge to defecate and straining lead to varicose veins, inflammation, and prolapse of the hemorrhoidal plexus.
- Anal fissures are painful defects in the wall of the anal canal.
- Paraproctitis is the involvement of peri-intestinal tissue in the pathological process.
- Intestinal bleeding - occurs when ulcers are localized in the area of large vessels.
- Intestinal stricture is a narrowing of the lumen and obstruction of patency against the background of severe cicatricial deformation.
- Perforation of ulcers is the formation of a through defect in the intestinal wall at the site of deep ulceration.
Complications of the disease require surgical intervention.
Complications of the disease
Complications with proctosigmoiditis develop if the patient goes to the hospital late or the selected medications for treatment are ineffective. In this case, the following diseases develop:
The disease may be complicated by rectal prolapse.
- haemorrhoids;
- fissures in the anus;
- intestinal ulcers become perforated;
- heavy bleeding;
- development of paraproctitis;
- rectum prolapses;
- formation of ulcers in large numbers.
Return to contents
Prognosis and prevention
The results of treatment depend on the cause of the disease, its form, and compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. Acute proctosigmoiditis is cured completely, chronic proctosigmoiditis is not. Eating disorders and stress worsen your well-being. With ulcerative colitis, the risk of severe exacerbation with complications is 15%.
Competent therapy, giving up bad habits, and following a diet for the first 5 years after the onset of pathology reduces the risk of relapse by half.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- Rectal fissure: causes, symptoms and treatment of pathology
- Rectal cancer: symptoms, stages, treatment and prognosis for life
- Diseases of the rectum: symptoms and signs of the disease, treatment
- More about hemorrhoids: causes, symptoms and treatment methods
- Diseases of the sigmoid colon: symptoms and signs of disease, their treatment
- Sigmoiditis (inflammation of the sigmoid colon): symptoms and treatment methods
- Sigmoid colon: location, structure, functions and diseases of the organ
- Details about bowel cancer: stages, symptoms, treatment and prognosis
- Details about the coprogram: preparation, conduct and interpretation of the analysis
- Paraproctitis: how is the pathology manifested and treated?
What complications may arise?
Without treatment, a patient with catarrhal proctosigmoiditis faces the following complications:
- Cancer. A patient with pathology is at risk of developing intestinal cancer, especially if he suffers from ulcerative colitis for several years, in which the pathology is focal and chronic.
- Surgical intervention. Surgical removal of all or part of the damaged organ.
- Toxic megacolon. The colon may expand rapidly when inflammation becomes very severe. Symptoms include fever, abdominal pain and bloating, dehydration and malnutrition. With toxic megacolon, there is a risk of colon rupture.
- Anemia. Blood loss from an inflamed bowel can lead to anemia, which can be treated with iron supplements or blood transfusions.
Treatment includes medications and surgery. In some people, severely inflamed or damaged parts of the organ are removed surgically. This may reduce or eliminate the symptoms of catarrhal proctosigmoiditis, but the disease cannot be eliminated and there is a risk that the disease will return to another area of the colon in the future.
Diet for proctosigmoiditis
Proper nutrition is an important component in the complex treatment of distal colitis. The diet is selected so that the body receives the necessary nutrients, but the intestines are not overloaded. In the first days of an exacerbation, the amount of food is limited. You can eat the following foods:
- vegetable broth soups with boiled cereals;
- water porridge (except pearl barley and millet), steam puddings;
- baked or steamed vegetables, in small pieces or pureed;
- boiled lean meat and fish;
- dried white bread;
- pureed fruits and berries;
- jelly and compotes.
Fresh bread, pastries, confectionery, whole milk, legumes, strong coffee, rich broths, smoked foods, store-bought instant foods, fatty and fried foods, and hot spices should be excluded from the menu. You cannot drink alcohol or any carbonated drinks.
Fractional meals are indicated - you need to eat often, 5-6 times a day, in small portions. Serve the dishes warm, but not hot.
Proctosigmoiditis responds well to treatment - if you follow the rules of nutrition, lead a healthy lifestyle and carefully follow the recommendations of your doctor.
Catarrhal proctosigmoiditis: symptoms
This form of the disease is characterized by the same symptoms that occur in its other forms. The disease occurs due to damage to the large intestine, inflammation of the sigmoid colon is significantly pronounced. As for the reasons, they can be very different, and therefore, to be specific in the diagnosis, first of all, a comprehensive examination should be carried out, aimed at determining the presence of candidiasis, helminthic infestation and dysbiosis.