What is atrophic intestinal colitis? more details
Atrophic intestinal colitis (ICD10 code - K51) is a rare disease. It is not known exactly what exactly starts the process of atrophy of the rectal mucosa and the muscle tissue adjacent to it. But in most cases, this disease is hereditary. Pathology can develop in two stages: a period of remission and a period of acute attack.
The course of the disease over a long period of time contributes to its transition to a chronic form. In this case, the intestines atrophy. Both men and women are equally susceptible to this disease.
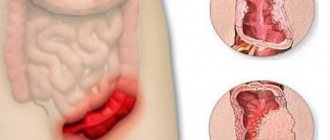
In atrophic colitis, inflammation gradually involves the entire colon. Then destructive transformations are present not only on the mucous membrane, but also in the ligamentous-muscular apparatus.
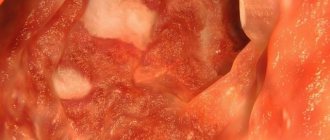
The development of atrophic colitis usually occurs against the background of an inflammatory process in the tissues of the rectum. Upon examination, thinning of the mucosa and signs of dystrophic transformation of tissues are determined.
Forecast
After a course of therapy and restoration of the mucous membranes, the process of establishing proper functioning occurs. The recovery period is long. The mucous membrane can quickly recover. Atrophied muscles take longer to heal.
If all conditions are met, the possibility of full recovery increases. To do this, you need to follow a diet, take pills and medicines on time, and adhere to a schedule of compliance with prescribed procedures.
If symptoms are ignored or treatment and regimen are not followed, colitis leads to complications that disrupt the functioning of neighboring organs and systems, as well as the metabolism of nutrients.
We recommend: How to identify infectious intestinal colitis and how to treat it
Causes of the disease
The following factors influence the appearance of atrophic colitis in a person:
- hereditary predisposition;
- frequent stress or nervous breakdowns;
- non-compliance with the diet and constant consumption of junk food, as well as non-compliance with the diet prescribed for the treatment of other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- poisoning with toxic chemical compounds;
- long-term use of antibiotics or laxatives;
- infectious diseases;
- allergic reactions to certain types of products;
- diseases of the stomach and liver, leading to clinical transformations of the gastrointestinal tract;
- intoxication of the body due to alcohol poisoning;
- use of enemas and rectal suppositories;
- lack of physical activity.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies will help alleviate the patient’s condition with atrophic colitis.
Infusion of mint leaves
Dry raw materials in the amount of two tablespoons pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Let it brew under the lid for 20-30 minutes, after which strain the finished infusion and take a glass a quarter of an hour before meals.
Strawberry leaf infusion
Pour boiling water (250-300 ml) over a tablespoon of dry strawberry leaves. Leave for 30-40 minutes. Strain and take a third of a glass before meals. This remedy remarkably relieves inflammation and normalizes intestinal function, regardless of whether the patient suffers from constipation or has severe diarrhea.
Anti-inflammatory collection
To prepare this healing infusion, take chamomile (flowers), cinquefoil erecta (rhizomes) and peppermint (leaves) - all in equal quantities. Mix thoroughly. Pour 250 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of the mixture, cover with a lid and leave for half an hour. Strain the finished infusion and drink immediately. Brew the mixture twice a day, morning and evening, and take it immediately. You can't cook it for the whole day.
Symptoms of the disease
With atrophic colitis, the symptoms of the disease manifest themselves depending on the stage of the disease. At the first stage (subatrophic colitis), the following symptoms appear:
- the patient begins to lose weight (up to 7 kg);
- intestinal disorders occur;
- moderate pain is observed;
- atrophy of the intestinal muscles occurs.
At stage 2 the following changes occur:
- large weight loss;
- anemia is observed;
- There is a lack of vitamins in the body due to malabsorption.
At the third stage, which is called diffuse atrophic colitis, the following occurs:
- disruption of other organs of the digestive system;
- severe intestinal disorders.
In the chronic course of the disease, acute attacks may occur periodically. In this case, the following symptoms are observed:
- severe bloating;
- painful false urge to defecate;
- sharp pain in different areas of the abdominal cavity;
- belching, heartburn;
- constipation or diarrhea, which is more often observed when the pathology is localized on the right side;
- there may be particles of blood in the stool;
- decreased or lack of appetite;
- fatigue, loss of strength;
- nausea, bitter taste in the mouth.
If treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, the situation may worsen and lead to a direct threat to life.
Classification
There are two forms of the disease:
- acute atrophic colitis – characterized by a sudden onset of symptoms and a significant deterioration in the patient’s condition;
- chronic atrophic colitis - characterized by alternating exacerbation and subsidence of the manifestation of clinical signs. With this course, atrophy occurs not only of the colon mucosa, but also the entire organ, along with all the muscles and ligaments, atrophies.
As the disease progresses, the inflammatory process goes through several stages, which differ in the intensity of symptoms:
- the initial stage is called “subatrophic colitis” and is characterized by the absence of involvement of the muscular system and ligaments in the disease. If the patient seeks qualified help at this stage, then treatment will consist only of following a diet;
- second stage of severity – characterized by deterioration of a person’s condition and progression of symptoms;
- complicated stage - is expressed in the fact that pathological changes in the walls of the affected organ are irreversible. In this case, the disease must be treated surgically.
Severity of colitis
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of atrophic colitis includes measures such as:
- stool analysis (to determine the presence of mucus and the level of leukocytes, which indicates an inflammatory process);
- colonoscopy. The condition of the rectum and the pathological changes occurring to it are visually assessed, and tissue is collected during this process for further research;
- X-ray with contrast agent to determine the extent of intestinal damage.
In addition, the doctor conducts a personal examination of the patient and finds out the medical history.
Symptoms and treatment for this pathology in adults are determined only by a doctor. To avoid incorrect prescription of drug treatment, differentiated diagnosis is carried out with diseases such as:
- oncological diseases;
- haemorrhoids;
- peptic ulcer;
- irritable bowel dysphoria.
The doctor should also rule out the possibility of intestinal infections or long-term use of antibiotics.
What it is
Atrophic colitis is called chronic inflammation of the rectum, in which its mucous membrane gradually becomes thinner. Starting in the rectal area, the inflammatory process gradually covers the entire large intestine. At this stage, destructive changes occur not only with the mucous membrane: significant changes also occur with the ligamentous-muscular apparatus.
The greatest danger for the patient is the stage of atrophic change, since at this stage it can be very difficult to make a correct diagnosis due to the similarity of this disease with other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Due to the fact that doctors very rarely encounter diseases like atrophic intestinal colitis, only an experienced gastroenterologist with sufficient qualifications and personally encountered a similar case can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
It is known that about a third of all patients diagnosed with atrophic colitis have had an intestinal infection in the past. Most often, this becomes the starting point for the occurrence of this pathology. However, doctors cannot yet name the exact cause of the disease.
How to treat atrophic colitis
Treatment of intestinal atrophy is complex. Due to the fact that the development of the disease can be caused by a variety of reasons, it is important to determine what caused this reaction. The treatment prescribed will depend on this.
When colitis is the result of a stressful situation, treatment for the disease begins with a consultation with a psychotherapist. In a situation where atrophic colitis appears due to antibacterial drugs, they are canceled or replaced with other drugs.
During an attack, the acute condition is first stopped and painful symptoms are relieved.
The general complex of therapeutic measures for atrophic colitis consists of:
- eliminating the main signs of the disease;
- use of anti-inflammatory drugs;
- use of pain medication;
- carrying out local treatment.
The patient may be prescribed:
- cleansing enemas, for the preparation of which natural ingredients are used: infusions or decoctions of medicinal plants;
- laxatives - Bisacodyl;
- antibiotics – “Fthalazol”, “Intetrix”, “Furazolidone”;
- antispasmodic drugs - “No-shpa”, “Baralgin”;
- sulfonamide drugs to relieve inflammation.
To consolidate the positive results of the treatment, probiotics and prebiotics are prescribed for atrophic colitis to restore the intestinal microflora.
In case of exacerbation of atrophic colitis, the patient is hospitalized, examined, and, if there is diffuse intestinal damage, a surgical intervention is used.
The selection of effective medications, choice of diet, and prescription of additional treatment with folk remedies can only be performed by the attending physician.
Prescribing treatment on your own is strictly prohibited. All the patient can do to help with treatment is to adhere to simple requirements: follow the diet and rules of nutrition, take medications in a timely manner.
Features of treatment of the disease in pregnant women
Symptoms similar to atrophic colitis often occur in pregnant women. What features of the presence of this disease do pregnant women have, and can this affect the health of the unborn child? Atrophic colitis can adversely affect the health of the expectant mother and her child when the pathology is in an advanced state.
During pregnancy, the following medications are allowed:
- sorbents (“Smecta”, activated carbon, “Enterosgel”);
- antispasmodics (“No-shpa”);
- agents that relieve inflammation;
- rectal suppositories (“Natalsid” and others that do not contain antibiotics);
- medicines for restoring intestinal microflora (“Lacidofil”, “Linex”).
In addition to drug treatment, the woman is prescribed a diet that does not create a large burden on the gastrointestinal tract, but fully covers the nutritional needs.
Nutrition for atrophic colitis
In order for the treatment of atrophic colitis to give good results, it is important to follow the Pevzner diet. If you do not establish the right diet, the efforts spent on treating colitis may be ineffective. The diet is selected individually for each patient. It depends on the symptoms of the disease.
For constipation, it is recommended to consume fermented milk products, dishes and drinks that contain dried plums and other dried fruits, for example, jelly.
For patients whose intestines are atrophied, carrots, spinach, celery, bran, and pumpkin are introduced into the menu. It is important that your diet contains foods with a lot of dietary fiber.
You should pay attention not only to the consumption of healthy foods that are included in the daily menu, but also to the size of portions; food should be divided into 5-6 meals.
In case of intestinal dysfunction, spicy, smoked, fatty, salty foods, sweets are excluded from the diet, and the amount of raw vegetables, spices, and milk consumed is limited. Fatty meats and fish are replaced with dietary ones. It is better to replace fresh bread with yesterday's bread. It is prohibited to consume foods that increase flatulence, cause constipation, or those that can irritate the mucous membrane of the digestive organs.
In case of atrophic colitis, especially after an acute attack, food should be crushed to a puree state. It is recommended to steam it, you can boil or bake it.
Diet cannot cure atrophic colitis, but with proper nutrition you can reduce the risk of exacerbation and keep the pathology under control.
For atrophic colitis, the following are strictly prohibited:
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol;
- hot and spicy seasonings;
- fatty meats;
- vegetables that irritate the digestive tract;
- fresh fruits and vegetables with small grains (strawberries, wild strawberries, figs, kiwi, tomatoes, cucumbers).
Traditional methods of treatment
As an additional treatment, you can use folk remedies:
- mint infusion. To prepare it, take 2 tbsp. spoons of herbs and pour boiling water (500 ml). Leave for about half an hour, after cooling, take 1 glass 15 minutes before meals;
- infusion of strawberry leaf. 1 tbsp. A spoonful of strawberry leaves must be poured with a glass of boiling water and left for 30-40 minutes. Take a third of a glass before meals;
- anti-inflammatory collection. To prepare it, you should take chamomile flowers, cinquefoil root and peppermint - all in the same quantity. Pour 1 tbsp. spoon the mixture with a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour. The strained infusion is drunk immediately;
- tincture of aloe leaves. It is used to restore microflora. It is recommended to drink 1 teaspoon of the infusion before meals. You can be cured in just 30 days;
- propolis infusion for the treatment of atrophic colitis is taken orally daily, 30 drops. The duration of therapy is at least three weeks;
- Drinking an infusion of mumiyo will help relieve pain. The infusion is consumed 10 ml daily.
Diet
First of all, be sure to follow a diet. Nutrition is organized in the same way as for atrophic gastritis. Its goal is to eliminate mechanical and chemical irritation of the colon mucosa. Food should be nutritious, healthy and easily digestible.
It is preferable to stew, bake, or steam food. It should not have coarse particles that can irritate the intestinal mucosa, and contain coarse dietary fiber. Grind vegetables and meat.
Avoid eating too hot or cold foods. Eat up to six times a day, but do not overload the intestines: portions should be small. It is also important to drink at least 2 liters of fluid per day. If you cannot drink this daily amount, you can switch to drinking melt water. Read how to prepare it at home here.
“Prohibited: rye and fresh bread, rich pastries, pasta, caviar, hard-boiled or fried eggs, legumes, rich broths, fatty meats, fish and poultry, smoked meats, milk, fresh cabbage, raw fruits, honey, sweets, spicy and salty foods, fruit juices that increase gas formation in the intestines, alcoholic and carbonated drinks"
In a special diet, include white fish and lean meats, dairy-free cereals, dried white bread, berry compotes and fruit drinks. To avoid constipation, the menu should include beets, carrots, bran, pumpkin, celery, apricots, kiwi, prunes, dairy products and dried fruits.
As the inflammation subsides, the diet expands: boiled and baked vegetables and vegetable soups are added to it.
Atrophic colitis is a complex disease, and properly selected drug therapy is important for complete recovery. In this case, the doctor must take into account the origin of the inflammatory process, relieve the symptoms, and only then begin to eliminate the provoking root causes of atrophy.
Prevention
To prevent the development of a disease such as atrophic colitis, certain rules should be followed:
- stop drinking alcohol and smoking;
- use medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- follow the principles of healthy eating;
- be careful when working with toxic substances and pesticides;
- if a pathology occurs that can lead to the appearance of atrophic colitis, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor and, if necessary, resort to treatment in a hospital;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- undergo a medical examination regularly for preventive purposes.
Video on the topic:
References: https://www.mosmedic.com/hronicheskij-kolit-kishechnika-neyazvennoj-etiologii.html https://yandex.ru/health/turbo/articles?id=4413 https://www.nrmed.ru /rus/dlya-vzroslykh/proktologiya/kolit-kishechnika/ https://www.kleo.ru/items/zdorovie/kolit-kishechnika-simptomi.shtml https://www.rossimed-clinic.ru/stati-pro- gastroenterologiyu/kolit-kishechnika/ Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/13/2020
Treatment
The complex of treatment procedures for atrophic colitis includes:
- Elimination of the main symptoms of the disease;
- Prescribing analgesic therapy;
- Use of anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Carrying out local treatment.
What is the treatment for atrophic intestinal colitis?
The patient is prescribed:
- Cleansing enemas, for the preparation of which natural ingredients are used: decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants;
- Laxatives - for example, Bisacodyl;
- Antispasmodic drugs - such as Baralgin and No-shpa;
- Antibiotics – Intetrix, Fthalazol, Furazolidone;
- Sulfonamide drugs (to relieve inflammation);
- Physical therapy (to relieve pain and irritation).
In case of exacerbation of atrophic colitis, the patient must be hospitalized, repeated tests are performed, and, if there is diffuse intestinal damage, surgical intervention is performed.