What are diffuse changes?
Since the ultrasound specialist does not make a diagnosis, his terminology has names to describe the picture he sees on the monitor. These data are then deciphered by the attending physician and used to make a diagnosis. Diffusion is the transfer of a pathological process to neighboring cells, due to which it spreads to a certain area.
Diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the liver, pancreas and other organs can be:
- increase in size;
- blurring of boundaries;
- changes in the lumen of blood vessels or bile ducts.
Diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas are a uniform deviation from one of the normal indicators over the entire surface of the organ. They can be either minor or indicate dangerous diseases. All data is entered into the form during the examination. The information on it is presented not for the patient, but for his attending physician. He will be able to determine what the ultrasound specialist’s instructions mean, compare them with the data of the anamnesis, laboratory and instrumental studies, and then make a final diagnosis.
Ultrasound signs of hepatomegaly
The main method that makes it possible to determine the level of diffuse changes is ultrasound. The symptoms by which the doctor identifies them can be severe or moderate.
Ultrasound makes it possible to determine:
- All dangerous diseases that were once suffered or developing now. They leave a pronounced mark on the organ, so a specialist will be able to see these symptoms.
- Moderate symptoms do not cause serious damage, but are visible on ultrasound, and are sometimes provoked by a virus or poor nutrition.
- Ultrasound also makes it possible to determine the dimensions of the lobes, echogenicity, outlines of the boundaries and homogeneity of the structure.
A qualified doctor will notice diffuse changes, which include:
- Fabric characterized by heterogeneity of structure.
- Parenchyma with high echo density.
- Increasing dimensions.
- Damaged pattern of blood vessels of the circulatory system.
- Degrees of echogenicity in both lobes.
- Rapid attenuation of ultrasound.
How can you determine pathology on ultrasound - echo signs
Normally, the liver does not protrude beyond the edges of the costal arch and is poorly visible during examination. It has a uniform hypoechoic (low density) structure and clear edges. The bile ducts should not be clearly visible on ultrasound.
The pancreas is conventionally divided into head, body and tail. This organ is located behind the stomach and partially extends into the left hypochondrium. Ultrasound diagnosis of the gland is complicated by the fact that it is closed by the stomach and intestines, which may contain gases. The examination takes into account the size and shape of the organ, the clarity of its boundaries, and the presence of pathological contents. This is a mixed secretion gland. It actively participates in the digestive process and the production of gastric juice, and also forms two important hormones for humans (insulin and glucagon).
When examining the abdominal organs using ultrasound, all echo signs are taken into account. They can manifest themselves in the following forms:
- an increase or decrease in parenchyma density, which may be a sign of inflammatory or degenerative changes in tissues;
- increase in organ volume - a symptom indicates the development of acute inflammation;
- the appearance of inclusions of adipose tissue, connective tissue scars or any other pathological inclusions.
Pathological changes in the structure of organs do not depend on the gender or age of the patients. In children, they are most often associated with congenital developmental anomalies, and in adults, with an unhealthy lifestyle and consumption of junk food.
An increase in the density (echogenicity) of the parenchyma of an organ is a sign of its inflammation. Such changes are characteristic of hepatitis or pancreatitis, as well as inflammatory diseases of other parenchymal organs. The tissues acquire a light shade and are clearly visible on ultrasound. The size of the organ most often increases, but may remain within normal limits.
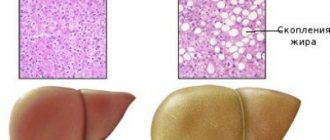
In some cases, pathological inclusions can be found in the thickness of the parenchyma. Most often they are adipose tissue located together with normal healthy cells. In the liver, this phenomenon is called hepatosis (fatty degeneration). In the pancreas, such changes can become a sign of diabetes mellitus, especially in old age.
Symptoms of diffuse organ changes
Signs of hepatomegaly, diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas can be detected during an ultrasound examination. However, without a clinical picture of the disease that accompanies them, patients do not seek help. The consultation usually involves patients with pronounced clinical signs of dysfunction of the liver and hepatobiliary tract, as well as the pancreas.
Symptoms that most often cause examination and detection of pathologies of these organs:
- painful sensations that are localized in the right or left hypochondrium can radiate to the back, shoulder blade or neck;
- nausea and vomiting;
- general weakness and increased body temperature;
- heartburn;
- a feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- bowel disorders;
- headaches and dizziness.
The cells of the parenchyma of the liver and pancreas produce secretions necessary for the complete digestion of food. Due to organ dysfunction, the digestive process becomes more complicated and nutrients are less absorbed. Therefore, all signs of diffuse changes most often appear after breaking the diet and eating large amounts of junk food. Soon after consuming fatty, fried foods or alcohol, the patient begins to feel a sharp or dull pain in the abdomen, which may be evidence of hepatitis or cholangitis.
Possible forms of pathology Echo signs of diffuse changes in the structure of the liver and pancreas may differ in nature and severity. In this regard, a special classification has been developed. It allows the doctor to understand how pronounced the symptoms of the disease are. There are several forms of damage to these organs:
- minor - often found among the adult population with poor nutrition, may indicate inflammatory diseases in the initial stages;
- moderate diffuse changes - appear in chronic damage to the liver and pancreas caused by junk food or alcohol, certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- strong changes are a symptom of diabetes mellitus, hepatosis or hepatitis, obesity or oncological processes.
Liver hepatoma
Hepatoma is a primary liver cancer; it begins to develop as a result of a DNA malfunction, which gives a negative impetus to uncontrolled cell growth. The tumor develops against the background of liver cirrhosis, hepatitis B and C, which are characterized by diffuse changes in organs. Primary liver cancer can also occur with metastasis of malignant neoplasms developing in the lungs and mammary gland.
Successful treatment of hepatoma is possible only if it is detected at the initial stage. In later periods, hepatoma has a negative prognosis, even if intensive treatment with chemotherapy, radiation and surgical removal of the tumor was used. Therefore, the most important task is timely diagnosis of the disease.
Causes of hepatoma
The risk group for hepatoma consists of patients who have the following diseases:
- hepatitis B and C,
- cirrhosis of the liver,
- alcoholism,
- cholecystitopancreatitis;
- alcoholism, smoking,
- diabetes.
In addition, those who eat moldy food and expose themselves to the risk of ingesting aflatoxins, which cause hepatoma, are at risk of developing primary liver cancer. A signal for a thorough examination of the liver should be hepatomegaly or detected diffuse changes and enlargement of the liver and pancreas, as a border organ.
How are changes in the liver and pancreas diagnosed?
The most common diagnostic method for determining hepatomegaly is palpation of the liver by a doctor. When an organ enlarges, the doctor assumes diffuse changes in it and informs the patient that he has hepatomegaly. At the same time, you need to know that hepatomegaly is not a disease, but a formidable sign that there may be dangerous diffuse changes in the liver and walls of the pancreas. That is, changes in tissue structure, which may involve obesity or the growth of cancer cells. Thus, hepatomegaly is a signal of a serious illness and that it is necessary to begin its treatment.
The next stage will be the appointment of ultrasound, MRI, CT and examination of samples for bilirubin, protein in the blood, stercobilin in feces, examination of the biliary tract, radioisotope examination and biopsy of liver tissue. Only after this will it be possible to confirm that diffuse changes in the liver and hepatomegaly are of a threatening nature.
At the same time as the liver, the pancreas is examined, since hepatomegaly also affects this organ, and treatment, as a rule, is complex. Diffuse changes in the pancreas occur for the same reasons as changes in the liver. Symptoms are characterized by pain not only in the right hypochondrium, but also on the left, often taking on a girdling character. With these signs, treatment begins immediately in order to reduce the patient's suffering.
Treatment methods and diet
Treatment of the liver and pancreas for serious changes that cause painful symptoms is medicinal in nature. If there are no pronounced symptoms and no hepatoma or other severe disorders are detected, then a diet and a gentle exercise regimen are prescribed. It should be said that the diet for diseases of the liver and pancreas is used not only as treatment during an exacerbation, but constantly.
For patients suffering from liver diseases and pancreatitis, diet becomes a way of life. They are prohibited from consuming the following types of foods:
- fatty,
- roast,
- spicy,
- alcohol,
- preservatives,
- smoked meats.
It does not matter whether there are currently symptoms of the disease or not. Non-drastic diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas can be eliminated with the help of proper nutrition; in this regard, diet and the use of medicinal decoctions become the most important element of healing. Traditional medicine recommends taking infusions of chokeberry and rose hips. At home, you can treat with mineral waters, which will be prescribed to you by your doctor.
It is important to remember that if you have painful symptoms in the right hypochondrium and pain on the left, radiating to the back or pain of a girdling nature, you must immediately consult a doctor and do not start self-medication. This is dangerous because hepatomegaly, especially in children, often indicates primary liver cancer. No one needs such a result, therefore, take care of yourself and your children and monitor the health of your family.
Causes of diffuse pathologies of the liver and pancreas
Despite the difference in diagnoses, the causes of pathologies of the liver and pancreas may be similar. These organs are interconnected both functionally and anatomically, so their diseases often manifest themselves in a complex. These may be pancreatitis, hepatitis, fatty degeneration and other deviations from the norm.
The causes of such changes may be congenital or acquired. The most common of them:
- eating disorders, abuse of fatty and fried foods;
- alcohol dependence - regular consumption of even small doses of alcohol affects the condition of the liver and pancreas;
- any intoxication and poisoning - food, medication, chemical vapors, this also includes bites of poisonous animals and insects;
- viral, bacterial, parasitic diseases;
- formation of stones in the hepatobiliary and urinary systems.
Diseases can be acute or chronic. Acute inflammation that accompanies recent poisoning is less dangerous because it does not have time to damage a large surface of functional tissue. As it enters the chronic stage, the number of healthy cells decreases, so you can notice a decrease in the density of organ parenchyma. First of all, you need to make sure that there are no tumors - for this, ultrasound diagnostics may not be enough.
Other diagnostic methods for detecting diffuse changes
The liver and pancreas are not completely accessible to the ultrasound probe. They are hidden by other internal organs: the liver is located behind the costal wall, the pancreas is behind the stomach and intestines. However, there are additional ways to study them that will provide a more complete picture of their condition:
- general blood test - will indicate the presence of inflammatory processes in the body;
- biochemical blood test - will determine the activity of specific enzymes, which are a diagnostic criterion for evaluating the liver and pancreas;
- x-ray - as needed;
- MRI, CT - mainly for suspected neoplasms;
- liver biopsy examination.
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are the two most informative ways to study internal organs. During the procedure, rays are exposed that allow them to be visualized regardless of their location. For minor inflammation, these methods are not used, but if more serious diseases are suspected, they will detect pathological foci even in hard-to-reach areas.
Methods of treatment and prevention
Treatment of diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas is prescribed individually. The course of therapy may include diet and taking certain groups of medications, and for serious diagnoses - surgery. During the treatment period, it is necessary to completely avoid fatty and fried foods, alcohol and other foods that can provoke another exacerbation. You may also need to take the following groups of drugs:
- analgesics - for severe pain;
- antispasmodics - to eliminate spasmodic pain;
- antibiotics - if a bacterial infection is suspected or for its prevention;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- specific antiviral drugs - for viral hepatitis.
Diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas are a set of abnormalities that can be noted during an ultrasound examination. These data are used to make a diagnosis together with the results of other studies. Treatment will vary depending on the type of organ damage, its severity, the patient's age and associated symptoms.
Unfortunately, there are quite a lot of patients who have had to deal with such an unpleasant diagnosis as diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas (hepatomegaly). At the same time, few people know what hepatomegaly is and how it is treated.
Doctors characterize this disease with the term hypertrophy, which means an increase in the size of cells and entire organs, which is often caused by the consequences of inflammatory processes occurring in the body. The result of such a moderate diffuse change in the liver is the replacement of functional tissues with connective ones, as well as dysfunction of both this organ and the thyroid gland.
Medical experts define an anomaly such as hepatomegaly, diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas as a syndrome, and not a separate type of disease. Moreover, its manifestations indicate the unsatisfactory condition of the previously mentioned organs, which leads to the need for timely conservative therapy.
Additional diagnostics
Signs of hepatomegaly and diffuse changes in the liver are confirmed using the following studies:
- Examination of the abdominal organs using ultrasound. Ultrasound examination determines the structure of the organ. This procedure is also necessary to determine the size of the gland. In pathology, the localization of the affected areas is visible.
- Urine and blood tests to identify the characteristics of the biochemical composition of fluids.
To confirm the diagnosis, computer or magnetic resonance imaging and radiography are recommended. If cancer is suspected, a biopsy is performed with further examination of the section in the laboratory.
REASONS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF DIFFUSE CHANGE
In the case of a patient with signs of diffuse changes in the liver, doctors distinguish destructive processes in hepatocyte cells, which are subsequently replaced by non-functional connective tissue. Such connective tissue tends to grow.
The main reasons for the development of the syndrome
The main reasons for the development of diffuse changes in the liver include environmental factors that negatively affect the human body, namely:
- Poisonous substances or toxins present in the environment;
- Harmful medicinal components found in some drugs;
- harmful substances that enter the patient’s body due to smoking and excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Diseases that provoke diffuse changes in the liver
Diseases that can also provoke minor diffuse changes in the liver include:
- Liver diseases such as cirrhosis , hepatitis, cholangitis and others, accompanied by inflammatory processes;
- Ailments associated with the presence of parasites or worms , such as giardiasis and opisthorchiasis.
- Diseases of neighboring organs, which can lead to the development of an increase in liver and pancreas tissue cells
Diseases of other organs that can provoke the formation of diffuse changes include the following:
- Intestinal and other infectious diseases that occur in severe form, such as yersineosis, malaria, mononucleosis ;
- HIV infections;
- Diseases related to autoimmune diseases , such as lupus erythematosus;
- tumors in the affected organs , for example hemangioma and adenoma;
- Cancer diseases accompanied by the formation of malignant tumors and metastases in the affected organs;
- The presence of obstruction of the bile ducts and hepatic veins;
- A disease such as leukemia;
- When excessive abnormal amounts of protein accumulate in the liver, called amyloidosis;
- Development of fatty degeneration in a patient.
At the same time, people with echosigns include patients in the older age category (over 50 years).
Reasons for the development of diffuse entrainments of the pancreas
Experts identify possible causative agents for the development of diffuse enlargement of the pancreas among diseases related to endocrine, inflammatory or metabolic functional , namely:
- Disturbances due to the development of pancreatitis;
- consequences of diabetes;
- manifestations of cystic fibrosis.
Doctors often include dysfunction of the organs themselves (liver, bile ducts) in the presence of blood stagnation in the affected areas.
Changes in the pancreas
The pancreatic diffuse process, as in the case of the liver, is the transformation of healthy cells and their loss of functionality, followed by death under the influence of endogenous and exogenous causes. Diffuse changes appear in the hepato-biliary system, endocrine gland, with metabolic disorders, systemic disorders, hormonal imbalances, and pathologies of the endocrine system. But poisoning, abuse of bad habits, and eating disorders also cause healthy pancreatocytes to die, and this naturally leads to replacement with fat and connective cells and hepatomegaly:
- With moderate damage, diffuse changes are distributed evenly on the pancreatic parenchyma and can be provoked not only by the organ’s own pathologies, but also by disorders of liver functionality, cholelithiasis, stones in the common bile duct and cholecystitis.
- Unexpressed changes are associated with poor nutrition and permanently experienced stressful situations, inflammation during the recovery stages and disorders of the nervous system. Depression can depress the pancreas, and poor nutrition can be its consequence, but when negative factors are corrected, no special pathologies are found during examination.
- One of the forms of pronounced diffuse changes is pancreatitis, but this disease does not develop without cause. It becomes a consequence of metabolic disorders, diseases of the digestive system, poisoning and inflammation of various etiologies. Pronounced diffuse changes are most often associated with diseases of the gallbladder and liver. This is understandable because they are interconnected by joint processes, and a failure in one part inevitably leads to the development of another disorder.
Chronic pancreatitis inevitably leads to enlargement of the pancreas due to the swelling and hemorrhages present. Then the number of cells decreases, and the connective tissue begins to grow and gradually displaces the pancreases involved in the production of enzymes. The production of hormones also stops.
Lipomatosis develops - when fat cells predominate, or fibrosis, in which connective tissue is predominantly involved. The more pancreatic cells die, the less hormones and enzymes are produced. This leads to irreversible disorders, and not only in the gland itself, but throughout the entire digestive system.
SYMPTOMATICS OBSERVED DURING THE DEVELOPMENT OF HEPATOMEGALY
Symptoms accompanying hepatomegaly, echo signs of diffuse changes in the liver, are determined mainly based on the causative agents of the development of the syndrome.
When studying the initial stage of the disease (moderate diffuse increases), signs of diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma can mainly be characterized by the absence of corresponding systems. Although, with the development of an increase in organ size in a pronounced form, the patient experiences certain symptoms.
Signs of enlarged liver or pancreas tissue include the following:
- manifestations of yellowness of the skin; Painful sensations that occur upon palpation of the affected organs;
- discomfort in the liver area;
- rashes may occur;
- patients often suffer from heartburn and/or nausea;
As with any other disease of such important organs as the liver and pancreas, it is important to diagnose their enlargement as early as possible in order to prescribe more effective timely therapy. Although it is quite difficult to determine the signs of parenchyma, because the symptoms in the initial stages of enlargement are quite insignificant. Moreover, with timely detection of the disease, treatment of diffuse liver changes will be more effective and faster.
Complications and consequences
Lack of timely and correct treatment can lead to various complications.
Compression of neighboring organs (intestines, heart, lungs) by the liver can negatively affect their functioning. In the liver there may be:
- Liver failure;
- Liver dysfunction.
Lack of treatment can significantly worsen the disease, which causes the development of diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas.
Consequences of changes in parenchyma
Doctors agree that even a moderate change in the structure of the parenchyma may indicate the development of such dangerous liver diseases:
- Consequences of chronic heart failure;
- Initial stages of development of cirrhosis;
- Consequences of severe intoxication;
- Development of hepatitis, glycogenosis, hemochromatosis.
If we consider changes in the structure of the pancreatic parenchyma, the following ailments can be noted:
- Manifestations of lipomatosis:
- Development of chronic or acute pancreatitis;
- Manifestations of fibrosis;
- Diabetes.
What is hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly is a term meaning an enlarged liver. In medicine, 3 vertical dimensions are measured according to Kurlov, which are normally 9 cm, 8 cm and 7 cm, respectively. The ultrasound method allows us to assess the thickness of the parenchyma, which should also not exceed 9 cm.
When measuring 10 cm or more, they speak of hepatomegaly. It occurs in the following conditions:
- Direct liver diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis, cholestasis).
- Cardiovascular diseases (chronic heart failure, portal hypertension).
- Metabolic disorders, including those of hereditary origin.
- Neoplasms (cysts, cancer).
- Toxic damage.
- Diseases of the pancreas and biliary tract: chronic pancreatitis, cholelithiasis.
In diseases of the pancreas, hepatomegaly develops as follows: due to a violation of the outflow of secretions, stagnation of bile and pancreatic juice occurs in the excretory ducts of the biliary tract. This leads to the fact that bile stagnates in the small collecting ducts of the liver, which contributes to its rapid increase. The resulting metabolic disorders inhibit the normal functioning and blood supply of the organ, which also contributes to the development of hepatomegaly.
Important! Hepatomegaly itself does not require treatment and does not pose a health hazard. This is only a symptom that helps the doctor suspect a pathology of the biliary tract. Hepatomegaly goes away on its own with treatment of the underlying disease that caused it.
Use of medications to treat hepatomegaly
Drugs for the treatment of changes in tissue structure
Classical therapy for the treatment of diffuse changes in the structure of the liver includes the use of the following drugs prescribed by the treating specialist:
- Hepatoprotective drugs, the use of which ensures a reduction in the fat layer and restoration of modified hepatocyte cells of the affected organs;
- Drugs in the form of diuretics - related to diuretic drugs, the use of which provides an effective reduction in fluid content in organs and tissues.
- In addition to the above medications for the treatment of hepatomegaly, treating specialists often prescribe artificial digestive enzymes, the use of which reduces the load on the affected organs.
Drugs aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease that provoked hepatomegaly
For more effective treatment , doctors recommend the use of drugs aimed at eliminating the disease that caused the development of hepatomegaly. These medications include:
- Antiemetic drugs;
- Antispasmodics;
- Painkillers;
- Antibiotics.
If treatment is ineffective using conservative methods of therapy, the attending physician may prescribe surgical methods:
- Portal hypertension;
- removal of cysts or isolation of tumors; ;
- Elimination of metastases.
In severe forms of the disease, a liver transplant may be performed.
An unpleasant diagnosis is diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas (hepatomegaly), which, according to the results of ultrasound, people encounter quite often. What does it mean? This is hypertrophy (increase) in the size of cells and entire organs, which occurs as a result of the inflammatory process. The result is the replacement of functional tissues with connective tissues and disruption of organ function.
Causes
With diffuse changes in the liver, hepatocyte cells are destroyed and replaced with non-functional connective tissue, which can grow over time.
The main reasons are the negative influence of environmental factors:
- Poisoning with poisonous substances or toxins;
- Taking medications;
- Excessive drinking and smoking.
Some liver diseases can also cause diffuse changes in the liver.:
- Inflammatory processes – cirrhosis, hepatitis, cholangitis;
- Damage by parasites and worms – giardiasis, opisthorchiasis.
Among diseases of other organs, the following are important in the formation of diffuse changes:
- Infectious diseases - severe forms of intestinal diseases, including yersiniosis, malaria, mononucleosis;
- HIV;
- Autoimmune diseases – lupus erythematosus;
- Benign tumors in the liver - hemangioma, adenoma;
- Cancer - malignant neoplasms with metastases to the liver;
- Obstruction of the bile ducts and hepatic veins;
- Leukemia;
- Amyloidosis is the accumulation of abnormal protein in the liver;
- Fatty degeneration;
- Age-related changes (over 50 years old).
The causes of diffuse changes in the pancreas include endocrine, inflammatory or metabolic diseases:
- Pancreatitis;
- Diabetes;
- Cystic fibrosis.
Sometimes tissue changes are detected in case of dysfunction of the liver, biliary tract, or when blood stagnates in the organ.
Related possible symptoms
The symptoms of diffuse changes significantly depend on the cause of the disorders.
At the initial stage (with moderate hepatomegaly), the increase in organ size is asymptomatic. With a pronounced increase in size, the patient can feel.
- Yellowness of the skin;
- Pain on palpation;
- Unpleasant feeling in the right side;
- Rash;
- Nausea;
- Heartburn.
Detecting manifestations of diffuse changes is very important. Often the absence of symptoms leads to a delay in treatment procedures and complications of the disease.
Treatment
Therapy for hepatomegaly is based on the treatment of the disease, which became the root cause of the development of diffuse changes in the pancreas and liver.
Drugs
The following medications are most often used in the treatment of liver diseases:
- Hepatoprotectors – means to reduce the fat layer and restore damaged liver hepatocytes;
- Diuretics are diuretic drugs that can effectively reduce fluid content in organs and tissues of the body:
Essentiale allows you to improve the functions of membranes, hepatocytes, intracellular respiration, and the ability to detoxify. Take 2 capsules 3 times a day with meals.
Heptral - stimulates detoxification, regeneration of hepatocytes, has antioxidant properties. Its dose per day is 800 - 1600 mg.
Hepa-Merz allows for more effective detoxification. 1 packet of the product is dissolved in a glass of liquid, taken orally after meals 2-3 times a day.
To reduce the load on the pancreas, taking artificial digestive enzymes is allowed.
In some cases, depending on the underlying disease - the root cause of diffuse changes in organs - drugs from the following groups are used:
- Antiemetics;
- Antispasmodics;
- Painkillers;
- Antibiotics.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is prescribed in the absence of effectiveness of therapeutic measures or in the most severe cases:
- Portal hypertension;
- Cysts;
- Tumors;
- Metastases.
The most complex operations include liver transplantation.
Folk remedies
To prevent and reduce the symptoms of diffuse changes, folk remedies are often used.
- Mix a tablespoon of honey with lemon in a glass of warm water and drink in the evening before bed and in the morning after waking up;
- Half a beet is cut into half a vegetable, mixed with olive oil and eaten for breakfast and throughout the day;
- Mix half a glass of tomato juice and sauerkraut brine and drink once a day;
- Between meals, eat at least 14 juniper berries every day. You should start with 2 berries, increasing their number daily.
Diet
To help with the main therapeutic treatment, it is necessary to follow a diet that will reduce the load on the liver and pancreas and promote organ recovery.
The basic principle of nutrition is healthy food . The diet must contain sufficient nutrients and vitamins necessary for recovery. You also need:
- Quit smoking completely;
- Refrain from drinking alcohol;
- Exclusion from the diet of fatty foods, spices, and canned food.
Prevention
The formation of diffuse changes is due to various factors. To prevent:
- It is necessary to do regular medical examinations;
- Do not contact with industrial, harmful substances;
- Maintain an active lifestyle;
- Eat a balanced diet.
Eliminate diseases in a timely manner, follow the instructions of a specialist:
- Alcoholism, smoking, unbalanced diet and consumption of fatty foods have a detrimental effect on the functioning of the pancreas.
- Constant use of herbal teas is considered an excellent prevention of diffuse changes. When initial symptoms appear, you need to remove fatty, salty and sweet foods.
- The diet should be varied. Meals should be frequent (5-6 per day), but little by little.
- If you have any gastrointestinal diseases, you need to be constantly examined by a specialist.
Read about why the pancreas can become enlarged in an adult here.