general description
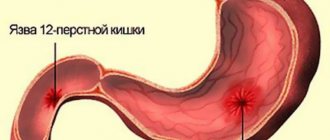
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum is a chronic seasonal recurrent disease of the stomach and duodenum, manifested by a defect in the mucous membrane (ulcers).
These disorders occur against the background of destabilization of the nervous and humoral mechanisms in the human body, which regulate secretory-reparative processes in the stomach and duodenum. Peptic ulcer disease is characterized by periods of exacerbation (spring and autumn) and remission. The result of ulcer healing is the formation of a scar. The prevalence of the disease in all countries is about 4-6% of the adult population. With full medical screening of patients, this percentage increases to 20-25%.
The peak incidence occurs at the age of 30-45 years. Mostly in men aged 35-50 years, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum is 3-4 times more common.
Symptoms
Symptoms of stomach and duodenal ulcers are generally similar. The most common complaint is burning pain in the stomach.
Duodenal ulcers can also cause abdominal pain several hours after eating.
This pain tends to respond well to medications or foods that reduce stomach acid levels, but as their effects wear off, the pain usually returns.
Abdominal pain from a duodenal ulcer may be worse when the stomach is empty, such as between meals, at night, or first thing in the morning.
Other common symptoms of peptic ulcers include stomach ulcers:
- heartburn or indigestion
- feeling full even when your stomach is empty.
- bloating
- gas
- nausea
Some people with these ulcers develop intolerance to certain foods. These foods may make a person feel sick or worsen symptoms associated with peptic ulcers.
Less common and more severe symptoms include:
- feeling of frivolity
- weight loss
- blood in stool
- vomit
- vomit blood
- labored breathing
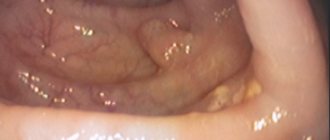
Some people with stomach ulcers have no symptoms. A doctor may only detect an ulcer when checking for another digestive disorder.
Anyone who has symptoms of a stomach ulcer should see a doctor. If symptoms are severe, seek immediate medical attention.
Causes of peptic ulcer
- The presence of Helicobacter pylori in the stomach and duodenum, which is the main etiological factor in the occurrence of ulcers. The influence of other bacteria has not been proven
- Eating disorder
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse
- Long-term use of drugs that affect the gastric mucosa, the main ones: NSAIDs and glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone)
- Emotional overstrain, stress
- Genetic predisposition
- Metabolic disorders
- Hypovitaminosis
Complications
The appearance of defects in the gastrointestinal mucosa is an unfavorable sign. Lack of quality treatment leads to adverse consequences. Possible complications of peptic ulcer and duodenal ulcer are presented:
- Bleeding. Occurs when tissue necrosis involves blood vessels.
- Penetration is a condition in which the process spreads beyond the stomach and duodenum to neighboring organs, causing their damage.
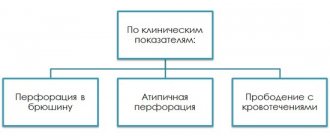
- Perforation is characterized by the formation of a through defect through which gastric contents penetrate into the free abdominal cavity with the development of progressive inflammation of the peritoneum.
- Pyloric stenosis. It is noted when the ulcer is localized in the area of physiological narrowing and the transition of one digestive zone to another.
- Malignancy is caused by the degeneration of cellular structures due to prolonged aggressive exposure to unfavorable factors.
Important!
Symptoms of complications that require emergency surgery: severe pain and weakness, pale skin, sweating, loss of consciousness, vomiting blood.
Symptoms of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
- Aching or cramping pain, low intensity in the epigastric region, often occurs on an empty stomach or immediately after eating
- Constant heartburn, especially at night and in the morning, sour belching
- Nausea
- Belching with air, sour or bitter taste
- Heaviness in the epigastric region after eating, a feeling of rapid filling of the stomach
- Decreased appetite
- When bleeding from ulcers, vomiting appears like “coffee grounds”, dark stools (melena)
- With perforation of ulcers - severe, dagger-like pain in the epigastric region, nausea, vomiting, painful tension in the abdominal muscles
Causes
Food soaked in gastric juice enters the duodenum. Hydrochloric acid and enzymes have a powerful irritating effect. Normally, substances are produced that protect the mucous membrane: mucus, prostaglandins, endorphins. Damaged cells are renewed every 3-5 days. When the balance between the factors of aggression and defense is disturbed, ulcerative defects are formed.
The disease develops due to a combination of several reasons:
- Heredity . Relatives of patients with duodenal ulcers get sick 5-10 times more often than other people.
- Helicobacter pylori infection. These bacteria are present in 100% of patients with duodenal ulcer. They secrete substances that damage the mucous membrane and reduce its protective properties.
- Medicines : Indomethacin, Aspirin, steroid hormones. After stopping these medications, the ulcers heal quickly.
- Nutritional Features . Rough, spicy, too hot and cold food increases the secretion of gastric juice and hydrochloric acid.
- Stressful situations . With psycho-emotional stress, the functioning of the autonomic nervous system is disrupted. Stress provokes exacerbations of the disease.
- Bad habits . Alcohol and nicotine irritate the mucous membrane, stimulate the production of hydrochloric acid, and inhibit protective factors. Nicotine causes vasospasm and impairs blood supply to the intestinal wall.
- Concomitant diseases . With chronic pathology of the heart and respiratory organs, the oxygen content in the blood decreases, and the nutrition of internal organs, including the intestines, deteriorates.
Diagnostics
- General clinical analysis of blood and urine
- Analysis of stool for coprogram
- Fecal occult blood test
- Biochemical blood test (liver tests, cholesterol, alkaline phosphatase)
- ECG
- X-ray of the chest organs in 2 projections and X-ray of the abdominal organs (to exclude perforation of ulcers)
- X-ray of the esophagus, stomach with barium mixture
- Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system
- 24-hour pH monitoring in the lower esophagus and stomach
- EGDS
- Non-invasive tests for the determination of Helicobacter pylori (respiratory)
How is a duodenal ulcer diagnosed?
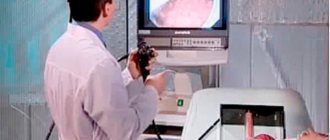
First of all, fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) helps to identify the disease. The doctor inserts an instrument in the form of a flexible thin hose with a light source and a video camera at the end into the stomach and duodenum and examines the mucous membrane. If a pathologically changed area is found on it, a biopsy can be performed.
Tests are prescribed to help detect Helicobacter Pylori infection - stool test, blood test, breath test. To detect bleeding and anemia, they resort to a general blood test and a stool test for occult blood.
The doctor may prescribe a radiocontrast study - radiography or fluoroscopy, before which the patient is given a contrast solution to drink. It helps to examine the contours of the stomach and duodenum.
Sign up for an appointment with the doctor
Forecast
The following factors influence the results of treatment:
- the nature of changes in the mucous membrane - the number, size of ulcers;
- management tactics - selection of the optimal drug therapy regimen, laboratory and FGDS - control; unreasonably low doses of drugs and a short period of treatment contribute to the exacerbation of the disease.
- individual characteristics of the body - in elderly patients with concomitant chronic diseases, ulcers take longer to heal;
- adherence to treatment - following a diet, eliminating risk factors, taking medications accelerates the healing of the ulcer.
When Helicobacter pylori is removed from the body, the risk of relapse does not exceed 7%.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- Rectal fissure: causes, symptoms and treatment of pathology
- Rectal cancer: symptoms, stages, treatment and prognosis for life
- More about Helicobacter pylori: diagnosis and treatment of the pathogen
- Details about the coprogram: preparation, conduct and interpretation of the analysis
- Proton pump inhibitors: generations of drugs and their features
- Diseases of the duodenum: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
- Sigmoiditis (inflammation of the sigmoid colon): symptoms and treatment methods
- Stomach ulcer: how is the pathology manifested and treated?
- Gastroduodenitis: how is the pathology manifested and treated?
- Gastric and duodenal ulcers: signs and treatment methods
Treatment
Treatment of uncomplicated peptic ulcer is carried out in a clinic. The main goals of therapy: elimination of symptoms, suppression of Helicobacter pylori, scarring of the ulcer. In case of severe pain, ineffectiveness of outpatient therapy, or development of complications, hospitalization is indicated.
Diet
Proper nutrition is the basis for the treatment of duodenal ulcer.
General principles
- a complete diet containing all the necessary nutrients and calories;
- eating in a calm environment, in small portions 5-6 times a day;
- mechanical sparing of the stomach and intestines: products are boiled in water, steamed, crushed using a blender or sieve;
- chemical sparing: exclude dishes that stimulate the production of gastric juice;
- thermal sparing: exclude too hot and cold dishes and drinks. The optimal food temperature is 40 °C.
Be sure to read:
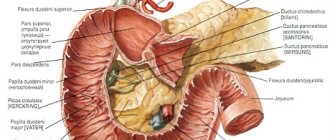
Large duodenal (Vater) papilla: location, functions and diseases of the structure
List of products and dishes
| Allowed | Forbidden |
|
|
Medications
For peptic ulcers, anti-Helicobacter therapy is always prescribed: a combination of several drugs that suppress the activity of the microbe Helicobacter pylori, promoting the healing of the ulcer. The regimen and duration of medication intake are determined individually.
- Antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Metronidazole, Clarithromycin, Doxycycline). Two antibiotics are used simultaneously.
- Bismuth preparations (De-nol, Venter) - coat the intestinal walls, have a healing and antibacterial effect.
- Proton pump blockers (Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Rabeprazole, Pantoprazole) - reduce the production of hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and reduce heartburn.
4-6 weeks after completion of the course of treatment, a control test for Helicobacter is carried out.
Other drugs are also used in the treatment of peptic ulcers:
- Antacids (Rennie, Maalox, Almagel Neo) - contain magnesium and aluminum hydroxide and react chemically with hydrochloric acid. Antacids quickly eliminate heartburn and pain. They are prescribed in addition to the main therapy.
- H2 blockers (ranitidine, famotidine) – duodenal ulcer is combined with high acidity. The drugs suppress the production of hydrochloric acid.
- Antispasmodics (No-shpa, Papaverine, Dicetel, Buscopan) - relieve spasm of the smooth muscles of the intestinal wall, reduce pain.
To monitor the effectiveness of treatment, FGDS is performed once every 2 weeks.
Folk remedies
Use traditional medicine recipes in addition to the main treatment after consulting a doctor.
Potato juice
Potatoes without sprouts and green spots, rinse well, peel, chop in a blender or grate on a fine grater, squeeze out the juice using gauze. Take half a glass half an hour before meals for at least 10 days.
Cabbage juice
Rinse the cabbage leaves well, chop them using a food processor or meat grinder, and squeeze out the juice. Take half a glass three times a day half an hour before meals for a week. Then take a break for 3 weeks and repeat the course.
Surgery
Surgery for peptic ulcer disease is performed routinely or urgently (according to health reasons).
Indications for surgery
Emergency surgery is performed when life-threatening complications develop.
Planned surgery - in the following situations:
- ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, frequent relapses;
- repeated bleeding;
- multiple ulcers;
- drug intolerance;
- narrowing of the duodenum.
Be sure to read:
Gastroenteritis: how is the pathology manifested and treated?
Types of operations
- Suturing an ulcerative defect is performed when the ulcer is perforated, if the patient’s condition or the surgeon’s qualifications do not allow radical surgery to be performed.
- Gastric resection - the lower 2/3 of the stomach is removed, the remaining part is connected to the duodenum end to end (according to Billroth 1) or to the jejunum end to side (according to Billroth 2).
- Trunk vagotomy - the trunk of the vagus nerve is crossed, and pyloric plastic surgery is performed.
- Selective proximal vagotomy - the branches of the vagus nerve are crossed.
Recovery period
To prevent postoperative complications, patients are recommended early activation:
- move your arms and legs and do breathing exercises on the first day after surgery;
- get out of bed on day 2;
- drink no more than half a glass per day on day 2;
- gradually increase the volume of liquid drunk to a liter by day 4; allowed drinks: compote, vegetable broth, jelly;
- from day 5 – pureed semi-liquid food, then gradually expand the diet;
- remove the sutures on the 8th day.
The duration of treatment in hospital is 2 weeks.