Disturbances in the normal functioning of the intestines are a serious problem that can change a person’s usual life activities. Bloating, indigestion, and constant pain can cause a lot of trouble for adults and children.
Often modern people suffer from a disease such as esophagitis. What it is? This is an inflammatory process in the walls of the esophagus. The course of the disease is characterized by varying degrees of severity. At the initial stages, the walls are dotted with small inflamed spots.
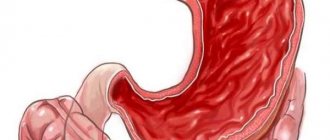
If the disease is in an advanced stage, then erosions and necrotic foci of varying sizes appear.
Types of esophagitis
The following types of esophagitis are distinguished:
- Catarrhal. With it, small spots appear on the walls of the esophagus.
- Hydropic. It is characterized by the formation of edema that interferes with the passage of food.
- Erosive. Erosion forms on the walls of the esophagus.
- Hemorrhagic. Characterized by the presence of hemorrhage.
- Fibrinous. Characterized by the formation of a fibrous film. Most often it occurs with diphtheria and scarlet fever.
- Necrotic. Formation of necrotic foci in the esophagus.
- Phlegmonous. The inflammatory process is more acute, with the formation of pus.
Kinds
The course of esophagitis occurs in acute or chronic form and depends on its origin, such as:
- nutritional, caused by poor quality nutrition, resulting in reflux;
- allergic, caused by hypersensitivity;
- sluggish or stagnant;
- professional, caused by the costs of the profession;
- caused by infection - infectious.
Based on morphological symptoms, the following types of pathology are distinguished:
- catarrhal - inflammation of the inner lining of the esophagus;
- edematous - characterized by edema;
- an erosive disease is caused by the appearance of damage on the internal walls due to chemical burns;
- bleeding caused by infection;
- necrotic – characterized by the death of sections of the shell;
- phlegmonous - purulent-inflammatory.
In all of these forms of the disease, reflux is caused, the release of oxidized food from the stomach, accompanied by damage to the walls of the esophagus.
Fibrinous esophagitis, features
Fibrinous esophagitis is a special form of the inflammatory process in which the formation of a rather dense film is observed in the walls of the esophagus.
If the disease proceeds calmly, then removing this film using medical equipment is not difficult. There are situations when the disease progresses, while the film is pressed against the mucous membrane. Over time, it detaches itself, but erosion remains in its place.
Focal esophagitis is a consequence of infectious diseases - scarlet fever or diphtheria.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
Factors contributing to the development of the disease:
- Infectious diseases (scarlet fever, diphtheria).
- Non-compliance with diet. Eating fatty and too spicy foods.
- Bad habits (smoking and drinking alcohol).
- Esophageal hernia.
- Sedentary work and a predominantly passive lifestyle.
- Consequences of radiation therapy.
- Infections, fungi.
In order not to start the course of the disease and to receive medical help on time, you need to know the symptoms of the disease. With fibrinous esophagitis there is:
- Severe pain in the area behind the sternum. Gets worse when swallowing or eating.
- The patient may feel a gray film appearing in the mouth. These are the remnants of the film that enters the oral cavity directly from the esophagus.
- The swallowing process is impaired.
- The patient may cough up blood. This occurs due to bleeding ulcers on the walls of the esophagus.
- Heartburn often occurs, even after eating regular foods.
- Often there are attacks of severe pain, which can radiate to the heart or back.
- Nausea, vomiting, severe salivation.
- Belching, bad breath.
Causes
The inflammatory process of the inner wall of the esophagus can be caused by many factors affecting the lining of the esophagus.
Conventionally, they can be divided into external and internal. The first include damage to the walls due to excessive alcohol consumption; spicy, hot food; acid; alkali; medications.
Internal ones are caused by the release of oxidized gastric contents - reflux, which is characterized by the erosion of the mucous membrane by acid.
Factors contributing to this are:
- hiatal hernia;
- damage to the muscular valve of the stomach;
- cholelithiasis;
- ulcer of the digestive organs;
- compaction of organ tissue;
- peritoneal tumors;
- overweight;
- pregnancy;
- ejection of gastric food through the mouth.
Interesting! Terminal esophagitis - what is it and how to cope with it
In addition to the above, this disease is caused by tuberculosis, diphtheria, and viral infections.
How to identify the disease
If the patient notices changes in his body that are similar to the first signs of the disease, he should immediately consult a doctor. The following activities will help to make a correct diagnosis:
- General blood and urine tests will determine the stage of the inflammatory process.
- Radiography allows you to track changes in the esophagus and detect a hernia or ulcer.
- Daily pH-metry. The procedure lasts 24 hours. Helps determine the level of gastric oxidation.
- Endoscopy. Determines the degree of the disease, the presence of erosions and edema.
- Biopsy. This is a test that requires taking a tissue sample.
- Diagnosis may consist of an initial examination of the oral cavity and palpation of the abdomen.
Possible complications due to untimely treatment:
- Heavy bleeding.
- Stomach ulcer.
- Scarring.
- Cancer.
Esophagitis 1st degree, symptoms and treatment
Esophagitis, an inflammatory disease of the digestive system associated with malfunction of the valve connecting the esophagus to the stomach, has several degrees of manifestation.
They depend on the stage in which the disease is located, as well as on the area affected by this pathology of the esophageal mucosa. Stage 1 is considered the easiest and most treatable. It is expressed by the intense red color of the esophagus, indicating the presence of an inflammatory process in it and the presence of small defects on the mucous membrane in the form of scratches or cracks.
Drug treatment
The first step to a cure is to determine the cause that led to the disease. Most often, the doctor prescribes one of the following medications to the patient:
- Almagel, Phosphalugel. They act as protection for the mucous membrane and relieve inflammation.
- Omeprazole, Pantoprazole. These drugs help reduce the acidity of the esophagus.
- Raglan, Cerucal. Helps normalize esophageal motility.
- Vikasol, Ditsinon. These drugs are prescribed in cases where there is hemoptysis. They help stop bleeding from the mucous membrane.
In severe cases, when medications do not help, urgent surgery is necessary.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease, you need to contact a gastroenterologist. He will give directions for examination of the esophagus, after which the whole picture will become clear.
The examination is carried out using an endoscope. At the first stage of the disease, slightly smoothed, sometimes loose walls of the esophagus are visible. An X-ray examination is also prescribed; it determines changes in the contours of the mucous membrane and the volume of mucus.
If esophagitis has several pronounced symptoms and there is pain, it will not be difficult to make a diagnosis during a routine examination. Treatment in this case will be short-lived and effective.
The first step in treatment should be to eliminate the underlying cause. The inflammatory process that provoked the occurrence of reflux esophagitis should be identified in a timely manner. These include diseases such as gastritis, ulcers or even neurosis.
It is also important to correctly select the right medications that will not only alleviate symptoms, but also eliminate third-party inflammatory processes.
Diet is an important point in the treatment of esophagitis. Its erosive type tends to “listen” to food. Prohibited foods may aggravate the situation and increase the severity of symptoms. Coffee, alcoholic drinks, chocolate and citrus fruits should be excluded from the diet.
Lifestyle and diet for fibrinous esophagitis
If we are talking about the initial stage of the disease, then you can get by with a diet and certain innovations in a person’s lifestyle.
- In the first couple of days, this may be fasting combined with taking certain medications.
- The patient should sleep in such a position that the head is elevated. This is done in order to prevent reflux (belching, heartburn) back into the esophagus.
- You can’t carry heavy objects, you need to bend over less often.
- Meals should be no later than an hour and a half before bedtime.
- Physical activity should be reduced.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out depending on the nature of the disease, it is important to eliminate the cause of the disease, otherwise complete recovery is impossible. In the acute form, a diet is prescribed that reduces inflammation. Reduce the consumption of foods that negatively affect the mucous membranes, carbonated drinks, and alcohol. If the acute form of the disease is mild, abstinence from food will be required for up to 2 days. For serious inflammation and infection, antibiotics are prescribed.
If the disorder is caused by reflux, it is recommended to reduce physical activity, bending, and abdominal tension. Traditional methods of treatment are used. When sleeping, your body should be elevated. Drugs are prescribed that reduce spasms in the esophagus and envelop.
If the methods are not successful, surgical intervention is indicated, especially in the presence of acute forms and complications. Diet, lifestyle, and diet contribute to recovery from the chronic form of the disease.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is possible to use folk remedies. It cannot be said that such treatment is effective, but it is excellent as a preventive measure. A course of therapy correctly drawn up by the attending physician can be used in parallel with folk remedies. But only after consulting a doctor.
Examples of home therapy:
- Flax seeds. Their mucus envelops the esophagus, thereby preventing the formation of a fibrinous film and erosion, and reduces acidity. To prepare a healing decoction, just boil one teaspoon of seeds in half a glass of water. You need to take the decoction for up to a week .
- Chamomile. Prepare a special herbal mixture of chamomile, lemon balm, and licorice root. You need to take this decoction about 4 times a week. Chamomile will help relieve inflammation and swelling.
- Dill. Pour boiling water over the ground dill and leave for about two hours. Drink the infusion before meals.
Features of 1st degree esophagitis
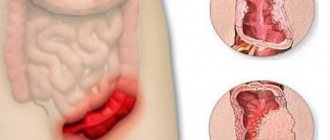
When the disease is at this stage of its development, it is characterized by the fact that the developing inflammatory lesion of the mucous membrane is quite small in size. At this time, it usually does not exceed 5 mm in diameter and is located within one fold.
Stage 1 esophagitis indicates that the sphincter separating the stomach from the esophagus begins to weaken and allows the acidic contents of the main digestive organ to pass through. As a result, the mucous membrane of the walls of the esophagus, which has a neutral environment, receives severe acid burns.
Grade 1 esophagitis or cardial insufficiency occurs due to a number of reasons, which may include acute infectious diseases (diphtheria, scarlet fever, sepsis) and various damage to the mucous membrane.
They are divided depending on the type of substances that caused them: mechanical, chemical and thermal. The most severe ones are those that result from a burn, so you should be very careful when eating very hot foods.
The reason for the development of grade 1 esophagitis in a patient is often surgical intervention performed on the gastrointestinal tract, namely resection of the cardiac sphincter. It also leads to a weakening of the gastric valve, and as a result, the formation of inflammatory lesions on the esophageal mucosa.
Without appropriate treatment, they become increasingly inflamed and erosive defects begin to form in their place.
Symptoms of grade 1 esophagitis
The most common signs of an emerging and developing disease are the following:
- Heartburn. As such, it can occasionally be present in any person after eating. But in the case when the burning sensation in the area of the esophagus becomes permanent and can occur even when harmless foods were eaten, we can talk about the manifestation of a dangerous symptom of the disease;
- Belching, mostly occurring after drinking alcoholic beverages;
- Burning and sore throat, as well as a feeling of irritation in the esophagus;
- After physical exertion, the swallowing reflex becomes difficult, and a feeling of a coma appears in the throat;
- Painful sensations appear behind the sternum, which usually intensify after the person eats.
All these symptoms indicate the possibility of the patient developing stage 1 esophagitis. In addition to them, there may be signs that are completely unrelated to digestion.
Due to the fact that due to esophagitis, which is in the 1st century. development, the stomach, although slightly, moves towards the chest cavity, this affects the functioning of the bronchi and lungs and can cause both a persistent cough and pneumonia.
In addition, due to the release of acidic contents from the stomach, the composition of saliva changes, it becomes more aggressive and negatively affects tooth enamel, causing caries. These symptoms are concomitant with a disease such as grade 1 esophagitis.
Treatment of grade 1 esophagitis
At a time when this disease is in the initial stage of its development, no special drug therapy is required, especially since we are not talking about surgical intervention.
At this time, for the treatment of esophagitis, 1 tbsp. It is enough to make adjustments to your diet and also start following an appropriate diet to ease the work of the stomach and prevent additional damage to the mucous membrane. To do this, the following conditions must be observed:
- Avoid overeating by providing split meals (at least 6 times a day in small portions);
- Give up bad habits such as eating at night, drinking alcohol, smoking;
- Get rid of excess weight;
- Stop wearing tight clothes and tight belts;
- Stop uncontrolled use of medications.
Compliance with these conditions makes it possible to cure esophagitis that is in the 1st degree of development without resorting to drug therapy.
Symptoms
The classification of GERD is as follows:
- In grade 1, the area of damage to the esophageal mucosa is small and limited by folds.
- Reflux esophagitis of the 2nd degree is characterized by the presence of several defects or one, but exceeding 5 mm in diameter. All of them are limited by folds.
- The third degree of pathology is characterized by the presence of several lesions, with up to 75% of the surface of the esophagus affected.
- In the fourth degree of the disease, the prevalence of defects exceeds 75% of the esophageal circumference of the esophagus.
- Grade 5 reflux esophagitis was not detected.
In the first stage of reflux esophagitis, the following clinical symptoms occur:
- The entire esophagus seems to be subject to a burning sensation.
- A person often regurgitates stomach contents or air. The belching tastes acidic.
- There is an unpleasant odor in the mouth.
- Diseases often appear inside the oral cavity.
- The patient feels pain and some burning behind the sternum. Sometimes these signs appear on the left.
Signs of chronic gastroesophageal disease:
- Boring cough. This cough rarely causes mucus to be coughed up.
- The voice becomes hoarse.
- There is a constant lump in my throat.
- The headache is concentrated on the surface of the face.
- The nose is often stuffy.
The severity of symptoms is not always comparable to the stages of the disease.
When does the disease occur?
- Inflammation in the distal parts of the esophagus occurs after scarlet fever, diphtheria. The lesion can be primary, that is, it begins in the esophagus, or secondary, that is, it enters the organ through the bloodstream.
- Fungal infections are a risk factor.
- In adults, this condition can occur after radiation therapy, with blood diseases, and malignant neoplasms.
- The presence of reflux (reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus) additionally injures the mucous membrane of the distal section.
Treatment tactics
The doctor’s initial task is to determine the cause of esophagitis. Scarlet fever and diphtheria require specific treatment. Only by coping with the underlying disease can we hope for a speedy recovery.
Diet
It is recommended to eat bland food. All dishes should be pureed and at room temperature. Too cold or hot food injures the mucous membrane in catarrhal fibrinous esophagitis. The optimal serving size is 200-250 g. Avoid fatty, fried foods, spices, marinades, smoked foods, sour apples, citrus fruits, these foods increase reflux.
Complications
- peptic ulcer of the esophagus (often develops with Barrett's disease), characterized by the formation of a deep defect in the wall of the esophagus, which can lead to severe scarring and shortening of the esophagus;
- narrowing (stenosis) of the lumen of the esophagus (leads to disruption of the passage of food into the stomach, loss of body weight);
- perforation of the wall of the esophagus (perforation) is a life-threatening complication that requires urgent surgical intervention;
- purulent complications of esophagitis - abscess, phlegmon (as a rule, are a consequence of damage to the esophagus by a foreign body);
- Barrett's disease (with prolonged reflux esophagitis without adequate treatment, degeneration of the esophageal epithelium develops - metaplasia). Barrett's esophagus is a precancerous condition.
For ulcerative esophagitis with severe pain symptoms, anesthesia is prescribed and gastric lavage is contraindicated. If massive antibiotic treatment of foci of purulent inflammation (phlegmon, abscess) is unsuccessful, surgical debridement is performed. Also, an indication for surgical treatment of esophagitis is the development of severe esophageal stricture that cannot be dilated.
Drug treatment
What is reflux esophagitis in adults, its symptoms and treatment are determined individually. The scheme is established depending on the type of pathology. Patients are often prescribed long-term use of medications Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole, Esomeprazole, Lansoprazole. if taking proton pump inhibitors does not produce results, histamine blockers are prescribed. These include tablets Famotidine, Roxatidine, Nizatidine.
We recommend reading: Pinosol spray: instructions for use. Reviews, children and adults
Equally important is reducing the aggressive effects of Reflux. Doctors often recommend taking prokinetic medications. The list of drugs that normalize natural digestion includes: Domperidone, Cisapride, Metoclopramide. Prokinetics are often recommended for chronic use. To eliminate heartburn and pain in the chest area, antacids are used: Maalox, Rennie, Gaviscon. This group relieves heartburn, but the effect does not last long.
Such funds show their activity instantly. The work is ensured by reducing the acidity of the contents of the gastrointestinal tract. For cardia deficiency, Ranitidine and Omeprazole are used. In some cases, Regidron and strong painkillers are used one-time. It is possible to achieve sustainable results in the treatment of reflux esophagitis through the use of alternative medicine methods, but the possibility of their use must be agreed upon with a gastroenterologist. Drugs that eliminate reflux esophagitis can interact with them.
ethnoscience
Treatment of esophageal esophagitis often requires the use of alternative medicine techniques. The list of popular methods that eliminate negative symptoms and provide treatment for the disease includes:
- To eliminate inflammatory processes, herbs that have a sedative effect are used. The list of popular ones includes: licorice, lemon balm, flax seeds, motherwort.
- To eliminate belching and heartburn, it is advisable to use calamus powder, a decoction of valerian and rose hips.
- First we need to clarify what is the treatment of erosive reflux esophagitis? The main problem is the presence of ulcers on the surface of the mucous membranes, and the main goal is their healing. Plantain juice has a powerful healing effect, but it is prohibited to use it at elevated acidity levels.
- Regular consumption of field chamomile tea is beneficial. This drink will speed up the healing process and relieve inflammation.
- A tablespoon of natural honey should be eaten an hour before meals. The bee product coats the irritated gastric mucosa. During the acute period, the method is not used.
- It is useful to use sea buckthorn oil 1 tbsp per day. It provides an enveloping effect and stops the secretion of gastric juice. Potato juice has the same effect.
Many patients use baking soda as a medicine for reflux esophagitis, believing that it is beneficial. This decision is incorrect, because alkali causes additional harm to the affected mucous membranes. It is more advisable to use antacids; they not only eliminate the symptoms of reflux esophagitis, but also accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues.
Complications of erosive esophagitis
- Formation of a non-healing ulcer and perforation of the esophageal wall.
- Rough scarring of deep erosions, formation of areas of narrowing (stenosis) and dysphagia (difficulty swallowing food).
- Barrett's disease is a change in cell structure with a risk of developing cancer.
- The addition of an infection is a worsening of the pathological process with possible spread to neighboring organs (in children - otitis media, sinusitis, tonsillitis).
We recommend reading: Body temperature in the evening 374
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of the disease include a burning sensation in the chest, belching, nausea, and heartburn, especially after eating and during physical activity in an inclined position.
Esophageal pain is clearly related to food intake. A bitter taste in the mouth is also a characteristic sign of erosive esophagitis of the esophagus.
Moreover, pain occurs regardless of the consistency and composition of food. When eating soft, non-aggressive food for the mucous membrane of the esophagus, the pain is not as severe as after eating spicy or hot food. There is anxiety, general weakness, malaise, and restless sleep. There is also a dry, obsessive cough, which can be very bothersome to the patient, especially at night.