What is mucus in stool
The wisely designed human body constantly secretes mucus to protect tissues and organs. An oily, jelly-like substance of white or transparent color is formed by the secretion produced by the intestinal glands. Part of it consists of epithelial cells, leukocytes on the surface of the mucous membrane. This secret plays an important role:
- protects against the influence of toxic components of feces;
- protects the intestinal lining from the mechanical effects of coarse food fibers;
- prevents chronic constipation due to difficult passage of stool.
The adult body constantly produces and eliminates viscous contents - this is normal. Thanks to mucus, stool can easily move through the intestinal tract and exit through the anus. With inflammatory changes in the intestines, serious problems arise with the release of lubrication. As a result:
- in the absence of cracks, damage to the mucous membrane, bleeding, and development of hemorrhoids;
- Serious pathologies are possible with excessive secretion production;
- A change in the color of the discharge indicates the presence of problems that require treatment.
Causes of stool mucus with gastritis that does not pose a threat to life
The mucous membrane is exposed to the irritating effects of coarse fibers, which, due to improper nutrition, leads to its depletion and, as a result, disruption of digestive processes and an increase in secretions. In some cases, the appearance of stool mixed with mucus in adults with gastritis is caused by reasons that are not as serious as diseases that pose a threat to health.
Such phenomena occur:
- when consuming large amounts of cottage cheese, bananas, watermelons, oatmeal and rice porridge;
- due to starvation diets or during the absorption of large quantities of vegetables and fruits;
- due to a lack of protein in the diet.
What does it look like
The norm is that transparent mucus in the stool of an adult comes out in small quantities and consists of dead epithelial cells. With pathological lesions of the intestines, changes in the stomach, a protective reaction to the irritation process occurs. A lubricant begins to be intensively produced, protecting the mucous membrane and helping to remove foreign substances and pathogenic microorganisms.
Depending on the pathology, the viscous contents may differ in color and shape:
- white or transparent – problems of the distal intestines;
- yellow – provoked by antibiotics, polyps, hemorrhoids;
- grayish flakes on the surface of the stool are evidence of damage to the rectum and descending colon;
- green – bacterial infection;
- pink – processes with the release of pus;
- small flakes mixed with feces - problems of the small intestine;
- with an admixture of blood - ulcers, cracks, hemorrhagic inflammations;
- black – cancerous tumors.
Symptoms of the disease
Usually people detect mucus in their stool not by chance, but in cases where something bothers them. That is, a large amount of mucus is one of the symptoms that signal the development of the disease.
In addition, patients usually feel:
Blood in stool
- severe abdominal pain, cramps;
- bloating and excessive gas formation;
- abdominal tightness, constipation or diarrhea;
- in severe cases, vomiting or other signs of intoxication;
- pain during defecation;
- blood or pus in the stool, possibly undigested food debris;
- change in the shape and consistency of feces, its nonspecific smell;
- mucus or bloody substance may remain on the patient's toilet paper or underwear;
- for respiratory diseases, characteristic symptoms of cough, nasal congestion, rhinitis and more;
- headaches and fatigue.
If you find these symptoms, as well as ichor or white discharge with feces, you should immediately consult a doctor and get tested to determine the cause of this phenomenon.
What it is and how to treat it can only be told by a competent specialist, and there is no need to self-medicate.
Causes
There are many reasons for the appearance of mucus in the stool of an adult. Some of them are related to lifestyle, for others the provoking factor is diseases. Typical reasons for the formation of mucous discharge:
- poor quality water;
- the presence of coarse dietary fiber;
- prolonged fasting;
- hypothermia of the pelvic organs;
- taking medications;
- swimming in a pond with cold water;
- alcohol abuse;
- frequent dieting;
- stressful situations;
- eating unwashed vegetables and fruits
- smoking;
- unbalanced diet.
Feces with mucus in an adult are a signal of the presence of pathological changes. Discharge causes diseases:
- irritable bowel syndrome, accompanied by diarrhea, vomiting, constipation;
- dysbacteriosis – imbalance of microflora;
- tumors in the stomach, intestines;
- Crohn's disease;
- allergies to substances entering the stomach;
- infectious intestinal lesions - typhoid fever, dysentery, colitis, enteritis.
It is not uncommon for a jelly-like secretion to appear in an adult’s stool as a result of:
- helminthic infestations;
- infections of viral origin;
- respiratory diseases;
- hemorrhoids with cracks and ulcers;
- ulcers of the stomach, duodenum;
- polyps;
- pancreatitis;
- inflammation of the colon;
- spastic colitis;
- intestinal diverticulosis;
- proctitis;
- cystic fibrosis.
White mucus in stool
What causes white, jelly-like discharge to appear in an adult? These symptoms in stool indicate the presence of stomach diseases and intestinal pathologies. The reasons for the appearance of symptoms are:
- inflammation of the rectum, as well as the sigmoid and descending;
- protective reaction to irritation by pathogenic organisms;
- fungal infection of the anus;
- poor nutrition;
- lack of beneficial microorganisms – dysbacteriosis.
Mucus in the stool of an adult, white in color, is formed as a result of:
- bacterial infection of anal fissures;
- inflammatory diseases of the large intestine;
- irritation of the intestinal walls due to allergic reactions, lactose intolerance, atopic dermatitis;
- damage to the intestinal mucosa;
- use of antibacterial drugs;
- inflammation of the rectal mucosa;
- candidiasis;
- disturbances of normal microflora;
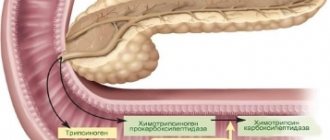
- diseases of the pancreas, liver, gall bladder.
Mucus instead of feces in an adult
When a patient comes out of the anus instead of feces with a viscous secretion that resembles snot or mucus, this means that the person is unable to retain the contents of the rectum. In this condition, pain in the lower abdomen and fever are observed. They provoke the appearance of the following symptoms:
- prolonged constipation;
- intestinal obstruction;
- helminthic infestations;
- volvulus;
- bacterial infections;
- rectal ulcer;
- neoplasms;
- polyps;
- foreign object in the intestine.
With blood
A very serious situation - the release of bloody viscous contents. This is a sign of dangerous diseases. Mucus with blood in the stool of an adult has specific features in appearance, depending on the diagnosis. Experts note:
- pathological impurities - veins with lumps of mucus - Crohn's disease, oncology;
- inclusions of blood clots in the stool indicate bleeding due to hemorrhoids, rectal cancer (mucus can be found on toilet paper after defecation);
- jelly-like mass – proctitis, polyps, stomach ulcer.
It is urgent to undergo an examination and begin treatment when mucous discharge with blood first appears during bowel movements. Symptoms, depending on the nature of secretion, indicate pathologies:
- the presence of an admixture of mucus with blood of a watery consistency - respiratory, intestinal infection;
- scarlet mucous contents – liver cirrhosis, intestinal varicose veins, ulcer or stomach cancer;
- copious discharge in the stool – rectal diverticulosis, ischemic colitis.
Yellow slime
When an adult has stool with mucus, the yellow color of the discharge may indicate the presence of polyps, symptoms of hemorrhoids. The viscous secretion protects the mucous membranes from damage. The appearance of stool with yellow mucus indicates the following problems:
- bacterial inflammation of the intestines;
- impaired absorption of products;
- taking antibiotics that affect healthy intestinal microflora;
- hypothermia of the pelvic area;
- intestinal infections;
- cancerous tumors.
Transparent slime
There are many reasons for the appearance of jelly-like discharge in the stool of an adult. Mucus that looks like a transparent dense film is evidence of membranous colitis. Viscous contents may envelop feces or be in the form of mucous impurities. Provoke the phenomenon:
- smoking;
- taking antibiotics;
- drinking coffee;
- remedies for flatulence, gases;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- haemorrhoids;
- infectious intestinal diseases;
- spastic constipation;
- colitis;
- colds with runny nose.
- Barley porridge - benefits and harms for the human body. Properties of barley porridge for children, pregnant women and weight loss
- Shellac lamps - which one is better to choose. How much does a shellac lamp cost, price
- Aevit for eyelashes - vitamins for growth. Eyelashes before and after using Aevit, photo
Pink slime
The formation of pink mucous discharge in the stool of an adult indicates the emergence of serious problems. The situation requires accurate diagnosis and immediate treatment. Pink mucus during bowel movements may indicate the presence of:
- liver cirrhosis;
- stomach ulcers;
- allergic colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- varicose veins in the intestines;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
- colon polyp;
- enterocolitis;
- intestinal diverticulum;
- capillary bleeding in the upper parts of the colon.
Black slime
Feces and mucous secretions may turn black after taking medications and vitamins. You need to know that the appearance of such jelly-like discharge in an adult can be a dangerous symptom. An urgent visit to the doctor and tests will clarify the situation. A change in the color of mucus in the stool is associated with a strong darkening of the blood that accompanies pathologies:
- bleeding in the small intestine, esophagus, stomach;
- growth of malignant neoplasm.
Brown slime
The appearance of brown mucus in the stool of an adult may indicate insufficient pancreatic function and hypotonicity of the colon. Liquid discharge accompanies intestinal dysbiosis. These conditions require the intervention of a gastroenterologist. Doctors note that brown discharge does not always indicate dangerous syndromes. There is no need to worry if the cause is mucous secretion from the nose entering the esophagus and intestines. This happens in diseases accompanied by a runny nose:
- rhinitis;
- allergy;
- acute respiratory disease;
- polyps;
- flu.
Mucus secretion
Discharge from the anus does not always indicate pathology. They appear with a strict diet, drinking poor-quality water, and prolonged constipation. Transparent mucus occurs with dysbacteriosis and intolerance to certain foods.
If there is a lot of discharge, hemorrhoids must be ruled out. It is accompanied by burning, itching, and discomfort during bowel movements. Transparent mucus occurs with functional disorders. Irritable bowel syndrome can be suspected if symptoms appear during stress and are not associated with food intake, loose stools, abdominal discomfort, or loss of appetite.
Cystic fibrosis also affects the lower intestine. The disease is accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the abdomen, bloating, and increased bowel movements.
Changes in discharge occur in the postoperative period, during resection of the small intestine.
White discharge
White discharge occurs with thrush, which is caused by fungi of the genus candida. The disease is associated with decreased immunity, injuries, chronic infections, and diabetes. In the stool you can find cheesy discharge, blood clots (in the invasive form), and mucus. When examined around the anus, you may see redness and swelling.
Oily discharge
The symptom may indicate a disease of the pancreas, which is involved in the breakdown of fats. If its enzymes are deficient, they are excreted unchanged along with feces. They acquire a grayish color, an unpleasant odor, and are difficult to flush off the toilet.
Oily discharge from the anus occurs after taking fatty foods, medications (dietary supplements, contraceptives, weight loss products).
Bile secretion
Yellow-brown bile-containing discharge occurs with dysbacteriosis, acute intoxication, and cholagenic diarrhea. As a rule, the discharge is liquid and foul-smelling.
Foamy discharge
Discharge from the anus with foam occurs with dysbacteriosis, sexually transmitted infections, infectious enteritis and enterocolitis. With dysbacteriosis, the general condition does not worsen, appetite decreases, and stool becomes frequent.
Infectious diseases accompanied by foamy stools have vivid manifestations: high fever, severe pain along the intestines, nausea and vomiting. Later, signs of dehydration appear.
Discharge of blood and pus
Blood in the stool appears due to infectious and non-infectious causes.
Infectious diseases include diseases whose pathogens penetrate the intestinal wall: salmonella, escherichia, yersinia. An intestinal infection can be suspected if the symptom is combined with hyperthermia, weakness, nausea and vomiting. The discharge may be green.
Non-infectious diseases manifested by blood in the stool: polyposis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, anal fissure, chronic paraproctitis.
Each of the pathologies is accompanied by additional symptoms.
Haemorrhoids
With hemorrhoids, the mucus is clear with blood clots. If it turns red, the hemorrhoid has ruptured. In later stages, nodes may fall out, bleeding, or thrombosis may develop.
Crohn's disease
Transparent mucus with blood occurs in Crohn's disease. The disease is caused by an autoimmune process when your own cells attack the intestinal wall. Over time, ulcers and scars form. The discharge can be mucous and purulent, and there is also pain and false urge to defecate.
Similar symptoms occur in nonspecific ulcerative colitis. You can see mucus and streaks of blood in the stool. Defecation occurs 5-6 times a day, which leads to a gradual decrease in body weight.
Polyp and neoplasms
Mucus streaked with blood is noted with an intestinal polyp. If it becomes infected, pain and discomfort in the abdomen occur. Similar signs are observed in tumor diseases. The neoplasm can be localized in the colon, sigmoid, or rectum.
At the initial stages, streaks are observed in the discharge, then the amount of blood increases. If dark blood appears, it is necessary to exclude bleeding from the upper parts of the digestive system. In the later stages of cancer, the mucus becomes foul-smelling.
Paraproctitis
Purulent discharge occurs in chronic paraproctitis. It is localized in the soft tissues surrounding the rectum. In this case, a fistula is formed, which is filled with pus. The release of contents onto the skin of the perineum is accompanied by the appearance of green mucus with an unpleasant odor.
Diagnostic procedures
When such a delicate problem arises, it is better for an adult to first consult a therapist. The doctor will conduct a survey, find out the nature of the mucus, the consistency of stool, features of lifestyle and nutrition. Important issues include taking hormonal medications, antibiotics, duration of illness, symptoms. Based on the results of the examination, a referral will be given for consultation with specialists:
- gastroenterologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- proctologist;
- surgeon;
- oncologist.
To establish an accurate method of treating diseases, correct diagnosis is necessary. The study of pathology requires special research. Necessary:
- take stool tests for the presence of fungi, viruses, bacteria, parasites, occult blood, leukocytes;
- study the composition of urine;
- do a biochemical blood test;
- perform a colonoscopy - observation of intestinal pathologies using a special probe;
- do an ultrasound examination of organs;
- conduct a computed tomography scan to determine abnormalities in the stomach and intestines.
Treatment
After correct diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment for the adult to prevent the appearance of viscous contents in the stool. One of the first measures is a diet that excludes the consumption of coarse fibers, suggesting a balanced diet. The prescription of the medicine depends on the disease:
- treatment of hemorrhoids - suppositories, tablets to relieve inflammation, stop bleeding;
- for irritable bowels - antispasmodics, medications for constipation;
- to get rid of parasites - tablets for their removal.
If the cause of the appearance of mucous contents is oncology, radiation treatment and chemotherapy are prescribed. Medications that help cope with the problem in adults include:
- Furazolidone – intestinal infections with loose stools;
- Viferon – viral lesions;
- Amphotericin B – fungal pathologies, candidiasis;
- Interferon - ingestion of mucus during the flu;
- Bifiform – dysbacteriosis;
- NO-spa – inflammation, spasms in the rectum;
- Contrical - pancreatitis.