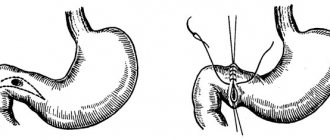
How is scar deformation formed?
During the healing process of an ulcer of the duodenal bulb, a scar is formed. Just as scars form on the skin after a wound, so after an ulcer the completely normal structure of the tissue is never restored, being replaced by a dense connecting “tie” - a scar. If you treat a wound poorly, let it fester, and do not resort to modern medical care, instead of a wound you will soon have a disfiguring
surface scar. And the larger the wound, the worse the consequences will be. The same is true for the duodenal bulb - the worse the ulcer is treated, relapses, failure to follow a diet, and failure to take medications, the greater the chance of forgetting about the normal function of this organ in the future. In the most severe cases, cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb leads to complete closure of its lumen, making it impossible for food to exit the stomach. In such a situation, mutilation surgery - cutting out this area and creating an unnatural connection of the intestines - cannot be avoided.
What are the dangers of cicatricial-ulcerative deformity?
If a peptic ulcer is treated well, then only a small linear connective tissue defect forms at the site of the ulcer, which has practically no effect on the function of the organ. With large, poorly treated, multiple, repeated ulcers, the deformation can range from slight contraction of the wall to obstruction. Most often, after a few months or years, the duodenal bulb gradually returns to its original shape, but with a severe form of peptic ulcer and the person’s reluctance to follow a diet and take medications, this does not happen.
Deformation threatens primarily by dysfunction of the digestive system. The fact is that, together with the bulb, the pylorus of the stomach also disrupts its function. As a result, large quantities of acid from the stomach are thrown into the intestines, and bile and pancreatic juice from the intestines are thrown into the stomach. Neither one nor the other should happen. The consequences of this are digestive disorders, diarrhea and constipation, pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen, and bitter belching. The most severe consequence is cicatricial narrowing of the lumen with the formation of intestinal obstruction. Intestinal obstruction in this case can be compensated or decompensated. In the case of compensated obstruction of the duodenal bulb 12, a pronounced narrowing occurs, but the remaining hole is enough to at least somehow, with problems, perform its function. With decompensated obstruction, it becomes impossible to carry out food gruel in sufficient quantities, food stagnation and fermentation occur. These changes are accompanied by pain in the upper abdomen, a feeling of fullness in the stomach, rotten breath, massive vomiting of semi-digested food, and foul-smelling belching. Treatment in this case is only surgical.
Cicatricial deformity of the duodenal bulb, causes, symptoms, treatment
A dangerous complication of peptic ulcer disease is cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb. Occurs in patients with a history of a long course of the disease with occasional exacerbations. Let's consider the pathogenesis of the disease, clinical picture, main complaints, diagnostic methods and choice of treatment tactics.
Causes
The duodenal bulb is topographically located near the pyloric section of the stomach.
Therefore, if the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract organs is disrupted (in this case we are talking about the final section of the stomach and the initial section of the intestine), acidic contents may be thrown into the duodenum, where pH is alkaline.
The aggressive effect of gastric juice irritates the intestinal wall, causing a violation of its integrity.
In addition to local factors, bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse) and stressful situations also play a significant role in the pathogenesis of the disease. Detection of Helicobacter pylori in the body increases the risk of peptic ulcer disease.
Pathogenesis
Erosion affects the surface layers, regeneration processes take place without scarring. An ulcer eats away at the wall of the organ down to the muscle tissue (with perforation, the muscle layer also becomes completely thin), so during the recovery stage it is not possible to avoid the development of a connective tissue scar.
The more often a person experiences exacerbations of peptic ulcer disease, the more severe the morphological and functional changes are experienced by the initial section of the intestine, represented by the duodenum.
In the development of scar deformity, experts distinguish the following stages: compensation, subcompensation, decompensation. Let's see what the difference is.
- The compensatory and subcompensatory stages are characterized by the presence of a lumen in the area of the duodenal bulb of at least 0.5 cm.
- The process is said to be decompensated when the degree of narrowing is significant (lumen diameter
In the initial phases of the disease, due to hypertrophy of the muscle tissue of the stomach, increased peristalsis, and increased pressure of gastric contents on the area of narrowing, the food bolus passes through the altered zone.
In the decompensation phase, when muscle tissue atrophies, motor skills and tone decrease, the stomach looks like an expanded, stretched bag. His body shifts downwards, which further enhances evacuation dysfunction.
Clinic
Patients with deformation of the duodenal bulb are people with a long history of the disease. Clinically, each of the 3 stages described above is characterized by certain symptoms. Let's take a closer look at them.
Compensation phase. The movement of the food bolus through the gastrointestinal tract is slightly disturbed. Retention of gastric contents occurs for 6-8 hours.
Patients complain of:
- feeling of heaviness in the epigastric area after eating;
- nausea;
- periodic vomiting;
- belching (there is a feeling of acid in the mouth).
With a pronounced concomitant inflammatory process, periodic pain is also observed. There is deep, enhanced peristalsis.
The subcompensation phase is characterized by signs of motor-evacuation failure, the food bolus lingers in the stomach for up to 24 hours, peristalsis is weakened. The following symptoms are expressed:
- Constant feeling of heaviness localized in the epigastrium.
- The belching intensifies, acquiring a “rotten” character.
- Copious, frequent vomiting. Perhaps even in the morning, when the patient has not yet had breakfast. In this case, a large amount of eaten food leaves the stomach with signs of fermentation. People often induce vomiting because it provides temporary relief.
- Bad breath occurs due to stagnation and rotting of proteins.
In the decompensation phase, signs of intoxication increase. Due to the lack of lumen in the area of scar deformation, symptoms of complete intestinal obstruction develop.
Observed:
- Weakness, obvious deterioration in general condition.
- Progressive loss of body weight.
- The presence of symptoms of dehydration: dry skin, sallow color, pointed facial features.
- Feeling of increased dryness in the mouth.
- Diuresis decreases.
- Tachycardia increases.
Increased disturbances in water-electrolyte metabolism lead to severe hypochloremia and hypocalcemia. And this in turn causes the appearance of signs of convulsive syndrome.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of “cicatricial deformity of the duodenal bulb” is made on the basis of the described symptom complex, gastroscopy data, X-ray results, and when studying the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract. A mandatory component of diagnostic measures is a comprehensive laboratory examination.
Source: https://GastroMedic.ru/yazvennaya-bolezn/12-perstnoj-kishki/rubtsovaya-deformatsiya-lukovitsy.html
How to avoid this disease?
This condition is a complication of bulb ulcer. Accordingly, the best way to avoid it is to avoid ulcers and peptic ulcers. Read about this in the corresponding section of our website. If an ulcerative lesion occurs, it is necessary to treat it adequately and follow all the instructions of the attending physician. Do not break your diet or skip medications under any circumstances. And then, most likely, severe post-ulcer deformation will be avoided.
0 out of 9 tasks completed
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
TAKE THE FREE TEST! Thanks to detailed answers to all questions at the end of the test, you can REDUCE the likelihood of disease by several times!
You have already taken the test before. You can't start it again.
You must log in or register in order to begin the test.
You must complete the following tests to start this one:
- No category 0%
1.Can cancer be prevented? The occurrence of a disease such as cancer depends on many factors. No person can ensure complete safety for himself. But everyone can significantly reduce the chances of developing a malignant tumor.
2.How does smoking affect the development of cancer? Absolutely, categorically forbid yourself from smoking. Everyone is already tired of this truth. But quitting smoking reduces the risk of developing all types of cancer. Smoking is associated with 30% of deaths from cancer. In Russia, lung tumors kill more people than tumors of all other organs. Eliminating tobacco from your life is the best prevention. Even if you smoke not a pack a day, but only half a day, the risk of lung cancer is already reduced by 27%, as the American Medical Association found.
3.Does excess weight affect the development of cancer? Look at the scales more often! Extra pounds will affect more than just your waist. The American Institute for Cancer Research has found that obesity promotes the development of tumors of the esophagus, kidneys and gallbladder. The fact is that adipose tissue not only serves to preserve energy reserves, it also has a secretory function: fat produces proteins that affect the development of a chronic inflammatory process in the body. And oncological diseases appear against the background of inflammation. In Russia, WHO associates 26% of all cancer cases with obesity.
Formation of scar deformation
As already mentioned, the duodenal ulcer appears first. When a duodenal bulb ulcer begins to heal, there are no symptoms, and a scar gradually forms in its place. This is a kind of scar, like after deep wounds, if the injury is neglected and infection is allowed to cause inflammation.
The same process occurs with ulcers. If you do not pay attention to it, do not treat it and do not follow a diet for ulcers, then there is a risk of complications that will forever deprive the organ of the ability to function normally, like a healthy person.
Relapses can be deadly: in the most severe cases, the bulb can become deformed, reach large sizes and close the intestinal passage. As a result, digested food cannot pass into the intestines. Stagnating, it provokes the process of decay and intoxication of the body. In this case, urgent surgical intervention is simply necessary to cut out the inflammation and connect the sections of the intestine properly.
That is why bulb ulcer must be cured immediately. With the right approach, not a trace will remain at the site of the ulcer; in extreme cases, a small linear scar that does not create discomfort and does not pose a threat to health.
In order not to provoke a relapse, you need to ensure complete rest of the intestinal tract, follow a diet and avoid stress. Of course, taking medications is also a mandatory measure.
When acute ulcerative deformation of the duodenal bulb becomes large and blocks the passage, the pylorus of the stomach, where hydrochloric acid is located, also begins to perform its job worse. This leads to stomach acid entering the intestines, and bile and pancreatic fluid migrate from the intestines to the stomach, and this is a pathology. All this contributes to diarrhea, constipation, pain in the upper abdomen, belching, nausea, and sometimes vomiting.
Cicatricial deformity of the duodenal bulb – Medicine – great!
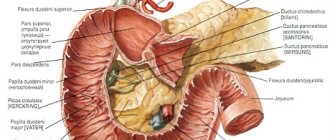
The duodenum, which is the initial section of the small intestine and located after the pylorus of the stomach, consists of several elements. The key is a bulb or ampoule that has longitudinal folding.
As part of various pathological processes and the formation of an inflammatory reaction on the mucous membranes of the organ, a partial change in the structure of the epithelium occurs, resulting in the creation of preconditions for the formation of scars.
Such deformations usually clearly indicate a partially or completely healed ulcer, but may also indicate other causes of pathology. The most famous:
- Incoming deformation against the background of severe edema due to the inflammatory process of the entire duodenum,
- Physical compression of the bulb due to the influence of external or internal factors - injuries, features of the anatomical structure of the patient’s neighboring organs, and so on,
- Systemic pathological processes affecting the gastrointestinal tract complex. In the latter case, scarring of the duodenal bulb is a secondary complication.
Main reasons
Peptic ulcer of the duodenal bulb appears due to the fact that the amount of hydrochloric acid increases. Hydrochloric acid begins to corrode both the stomach and the onion, which should change the pH of semi-digested food, making it alkaline. Therefore, the main reason is an increase in acidity, which can be caused by a number of factors:
- the patient did not eat properly, ate a lot of salty, bitter or sour foods, as well as fatty and fried foods, canned food, pickles and marinades, and often replaced a full breakfast or lunch with dry snacks;
- took certain medications, anti-inflammatory drugs or hormonal pills for a long time;
- The functioning of the gastrointestinal tract can also be affected by a person’s bad habits, namely smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Stress also plays a big role in the development of the disease, no matter whether it is chronic or isolated stressful situations. This reason is considered one of the main ones.
Additional reasons
Our site is dedicated primarily to chronic gastritis, but we consider ourselves obligated to talk about bulbitis. These diseases often develop together, significantly complicating each other.
This page of the website gastrit-yazva.ru talks about the manifestations of bulbitis, as well as its origin.
Clinical picture characteristic of the disease
First, let's define the concept of illness.
Patients—and some doctors, too—confidently use the expression “stomach gurgles.” At its core, it is wrong.
The disease we are interested in is localized not in the stomach itself, but in the intestinal bulb immediately adjacent to the latter (in the so-called proximal duodenum - duodenum). The ducts of the pancreas and gall bladder open into the mentioned bulb; It also contains digestive enzymes.
Bulbit should be considered rather as a type of duodenitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the duodenum, accompanied by its pathological structural restructuring.
Symptoms of scar deformation of the duodenum
The symptoms of scar deformation of the duodenum are not specific and depend on the severity of scarring and its type, the presence of secondary provoking circumstances that form the prerequisites for exacerbation of the process.
In general, during the remission stage, the problem practically does not manifest itself, especially if the scarring is minor.
In this context, during instrumental examination, asymmetry of the bulb is observed, caused by partial shortening of one of its contours, but the lumens of the organ are open, and the evacuation of the contents proceeds normally.
Primary, externally diagnosed signs are characteristic of moderate and severe deformities with the formation of diverticulum-like protrusions, “trefoils” within the framework of cicatricial convergence with a narrowing of the lumen up to 50% or more, a parallel slowdown in the function of evacuation of biological contents up to 1 day or more.
In this context, the following manifestations are possible:
- Pain in the upper abdomen radiating to the back and neighboring organs. The pain syndrome intensifies with prolonged fasting and at night,
- The appearance of belching , nausea, increased gas formation and intestinal discomfort, and other broad-spectrum dyspeptic disorders,
- Staining of vomit and feces with bloody inclusions, indicating the start of internal bleeding - such a symptom directly threatens the patient’s life and requires his immediate hospitalization in a hospital and intensive care unit.
In addition, a relapse of the ulcerative pathological process against the background of organ structures weakened by cicatricial deformations sometimes leads to partial or complete blocking of the passage to the pylorus, where hydrochloric acid for the stomach is located.
Ultimately, this causes the substance to enter the intestine with subsequent migration of pancreatic bile fluids through various parts of the gastrointestinal tract, contributing to the development of a complex pathological acute process.
Diagnosis of pathology
Determination of the primary and final diagnosis of cicatricial and ulcerative deformation of the duodenal bulb 12 is carried out comprehensively based on the results of laboratory instrumental studies. The main activities include the following procedures:
- X-ray examination with the introduction of barium-based contrast to assess the degree of evacuation function,
- Ultrasound of the duodenum. Allows you to assess the condition of the bulb in general terms,
- Penetrating fibrogastroduodenoscopy. The most informative, but invasive endoscopic technique,
- Other activities as necessary.
In parallel with the implementation of basic instrumental procedures, laboratory diagnostics are prescribed:
- General analysis of stool and blood,
- Blood biochemistry,
- Gregersen analysis,
- Other studies as necessary.
The main specialized specialist who makes the appropriate diagnosis based on anamnesis and objective data is a gastroenterologist.
Treatment of scar deformity of the duodenal bulb
After determining the main diagnosis, the gastroenterologist prescribes individual treatment, including complex measures:
- Drug therapy,
- Diet,
- Preventive actions.
After the main inflammatory process has been removed, the rationality of performing surgical intervention to eliminate scar structures within the framework of classical surgery is considered.
Such measures are relevant in case of relapses of the pathological process, advanced forms of scar deformities, and the presence of a number of complications.
Source: https://ndkbsmp.ru/bolezni/ulcerogennaya-deformaciya-lukovicy-dpk.html
Diagnosis of bulb ulcer and scar deformity
The most effective diagnostic method is invasive. With its help, you can certainly detect the slightest deformed bulbous area and scar, as well as an acute ulcer of the duodenal bulb. It is necessary to do a penetrating examination already at the first degree of duodenal ulcer. At the stage when the duodenal bulb begins to deform.
Very often, such a medical mistake is made as neglecting invasive diagnostics. Many limit themselves to an external examination of the patient, which leads to incorrect conclusions. Therefore, the patient should insist on a penetrating examination, even if the doctor says that this is not necessary and there is nothing to worry about.
Penetrating diagnostics is a set of measures carried out using fibrogastroduodenoscopy. Briefly it is called FGDS.
The above method is the main one. However, there are other ways to make a diagnosis with more detailed research:
- Blood analysis.
- Blood chemistry.
- Gregersen test (stool is studied). Helps detect the presence of blood.
- General stool analysis.
How to reduce the risk of cicatricial deformation of the bulb and ulcers to a minimum? These two diseases are related to each other. Deformation of a chronic ulcer of the duodenal bulb appears against the background of an intestinal defect. Therefore, to avoid scar formation, ulcers must be avoided.
Peptic ulcer disease should be treated competently with the help of a specialist. You should not neglect taking medications or violate your diet.
Duodenal bulb ulcer
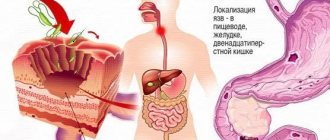
One of the most common types of erosive formations of the gastrointestinal tract is an ulcer of the duodenal bulb.
The disease is common. According to official data, up to 10% of the planet's population is sick. Deformation develops due to a failure in the chemical processing of food. The anatomy of erosive formations is different, but most often they form on a bulb shaped like a ball. The duodenal bulb is located at the very beginning of the intestine, at the exit from the stomach. Treatment is long and complex. It can be deformed on the front and back walls (kissing ulcers). The ulcer of the duodenal bulb also has a special location - at the end or at the beginning (mirror). Specular erosions are treated like other forms. Negative factors affecting the functioning of the stomach and intestines provoke the appearance of ulcers of various forms. The risk group includes middle-aged people and those who are forced to work night shifts.
If the stomach fails to process food, an ulcer of the duodenal bulb may occur.
- 1 Causes of duodenal ulcer
- 2 Symptoms
- 3 Stages
- 4 Diagnosis of the disease
- 5 Treatment
- 6 Forecast
- 7 Prevention
Causes of duodenal bulb ulcer
Most often, inflammation of the duodenum occurs due to the aggressive action of acid. In the absence of therapy, the development of a perforated ulcer and bleeding is possible. There could be a number of reasons:
- disordered diet (a lot of fatty foods, spicy foods, diet abuse, carbonated drinks);
- The Helicobacter bacterium is the cause of ulcerative formations in most cases;
- smoking, alcohol;
- severe stress or systematic stay in a state of emotional tension;
- hereditary predisposition;
- long-term use of certain anti-inflammatory drugs;
- incorrectly prescribed treatment at the initial stage of the disease.
Kissing ulcers in the intestines can appear due to concomitant causes: HIV infection, liver cancer, hypercalcemia, renal failure, Crohn's disease, etc.
Return to contents
Symptoms
Symptoms of duodenal bulb ulcers are also characteristic of other types of gastrointestinal ulcers, and they appear depending on the stage of the disease:
- heartburn;
- nausea in the morning or after eating;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- pain in the stomach at night;
- flatulence;
- the appearance of a feeling of hunger a short period of time after eating;
- if the disease is in an advanced form, bleeding may occur;
- vomit;
- pain localized in the lumbar region or chest area.
The inflammatory lymphofollicular form of the duodenum has a different type of pain: stabbing pain, sharp or aching. Sometimes it goes away after a person has eaten. Hunger pains usually occur at night, and to eliminate the discomfort it is recommended to drink a glass of milk or eat a little. Night pain is caused by a sharp increase in acidity levels.
Return to contents
Stages
The intestinal healing process is divided into 4 main stages:
- Stage 1 - initial healing, characterized by creeping layers of epithelium;
- Stage 2 - proliferative healing, in which protrusions in the form of papillomas appear on the surface; these formations are covered with regenerating epithelium;
- Stage 3 - the appearance of a polysadic scar - the ulcer on the mucous membrane is no longer visible; upon closer examination, many new capillaries are visible;
- Stage 4 - scar formation - the bottom of the ulcer is completely covered with new epithelium.
Erosive kissing formations on the duodenum heal after therapy. Multiple ulcers in a small area of the intestine result in multiple scars. The result of such healing is cicatricial and ulcerative deformation of the duodenal bulb. The appearance of fresh scars leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the bulbous sector. Inflammatory cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb has negative consequences, for example, stagnation of food and malfunctions of the entire gastrointestinal tract.
There is also a distribution by stage: exacerbation, scarring, remission.
One form of intestinal ulcer is lymphoid hyperplasia of the duodenal bulb, which is characterized by inflammation due to a disturbance in the outflow of lymph. The causes are exactly the same as for duodenal ulcers. There are also similar symptoms. Lymphofollicular dysplasia is a pathology in the mucous membrane of the intestines or stomach. It is characterized by the appearance of round-shaped formations on a wide base. Lymphofollicular dysplasia is deformed and has a dense consistency and point size. Lymphofollicular mucosa is infiltrated. Stages of development:
- acute;
- chronic.
Return to contents
Diagnosis of the disease
The FGDS method (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) will help to accurately diagnose the presence of a duodenal ulcer. Using a special probe with a camera, the intestinal surface is examined. It is this diagnostic method that will allow us to determine the location of the ulcer, its size and stage of the disease. Inflammation is usually observed, or the surface is hyperemic, covered with point erosions of a dark red color. The intestinal area is inflamed at the mouth, and the mucous membrane is hyperemic.
Tests are required to determine the Helicobacter bacteria. Not only blood and feces are used as testing material, but also vomit and material after a biopsy. Ancillary diagnostic methods include x-rays, palpation in the stomach area, and a general blood test.
Return to contents
Treatment
After a diagnosis of “inflammation of the duodenal bulb” is made, treatment must begin immediately, as serious complications may develop. Kissing ulcers are treated mainly with medications. During an exacerbation, hospitalization is necessary.
The doctor selects medications and physical procedures individually for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of the body and stage. For example, the chronic or lymphofollicular stage is treated differently than during an exacerbation. This regimen usually includes the following medications:
- bismuth-based medications, if Helicobacter bacteria are detected; such drugs have a depressing effect on pathogenic microflora;
- drugs that reduce the amount of gastric juice produced: blockers, inhibitors, anticholinergics;
- prokinetics - improve intestinal motility;
- unpleasant pain is eliminated with the help of antacids;
- To combat the bacterial cause of lymphofollicular ulcers, antibiotics are prescribed;
- Gastroprotectors will help prevent the negative effects of hydrochloric acid on the affected area;
- inflammation is relieved by analgesics and antispasmodics.
The combination of medication and physiotherapy promotes faster recovery of the body. These techniques include: electrophoresis, ultrasound, the use of microwaves, modulated current therapy for pain relief. Special physical therapy will help normalize gastric motility. Gymnastics is a good preventative against stagnation in the intestines and stomach.
In addition to generally accepted methods of healing intestinal ulcers, traditional medicine has long proven its effectiveness. The first place for ulcerative lesions is freshly squeezed potato juice. It must be drunk three times a day, and only freshly squeezed. First, the potatoes are peeled, grated, and squeezed through cheesecloth. The first few days the dosage is one tablespoon. Gradually it can be increased to half a glass. You need to drink before eating.
Other equally effective remedies include honey, medicinal herbs (calendula, St. John's wort, plantain), olive and sea buckthorn oils.
During the acute period, bed rest is mandatory. After the exacerbation passes, you can take short walks. Heavy physical activity and exercise are prohibited. The army is contraindicated for those who have ulcers. In order not to provoke new attacks, it is important to avoid stress and take care of the nervous system.
Diet is one of the important factors on the path to recovery and reduction of inflammatory processes. General dietary recommendations are as follows:
- small portions;
- chew each piece thoroughly;
- temporarily exclude foods that provoke active production of gastric juice (vegetable soups, fish and meat broths);
- in order not to further irritate the mucous membrane, food should be ground;
- fruit juices should be diluted with water;
- drink milk more often;
- do not use spices in dishes;
- prepare ground porridge;
- eat food at the optimal temperature, not too hot and not too cold;
- meals are fractional, up to 5 times a day.
Food should be prepared by steaming or in the oven. The diet must include non-acidic fruits, kefir, milk, cottage cheese, boiled or steamed vegetables. It is necessary to stop drinking alcohol and smoking, as this can lead to the development of serious complications.
Return to contents
Forecast
A favorable prognosis for recovery can be achieved if treatment is carried out on time and the correct diet is followed. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner or if medications are prescribed incorrectly, serious complications can develop: lymphofollicular ulcer, bleeding (vomiting blood), ulcer perforation (acute pain under the sternum) and penetration (due to adhesions, intestinal contents enter neighboring organs). In each of these cases, the only option is surgery.
Duodenal stenosis is a complication. After healing, there are scar changes, which can subsequently cause swelling and spasm. Stenosis usually manifests itself during the acute form or after therapy. Stenosis occurs in those patients whose ulcer does not heal for a long time. Stenosis is accompanied by impaired intestinal and gastric motility.
Return to contents
Prevention
The main methods for preventing duodenal ulcers are regular and proper nutrition, a healthy lifestyle (complete abstinence from alcohol and nicotine). After taking medications or in the postoperative period, sanatorium-resort rehabilitation is recommended. To prevent ulcers, you should regularly undergo examination by a gastroenterologist and take tests. The emotional state plays an important role in the prevention of erosive manifestations of the gastrointestinal tract, so it is better to avoid stressful situations.
med.gastrit-i-yazva.ru
Since childhood, I have been bothered by abdominal pain, often hunger pains, bloating, and constipation, which began about 7 years ago.
I didn’t contact the doctors. At the age of 28, after eating pickled mushrooms, I developed nausea and black, mushy stools. A week later, I found out that I was pregnant. The entire pregnancy period went well, sometimes I felt nauseous if I ate a little sweets, the stool continued to be black and mushy, I drank Elevit vitamins throughout the pregnancy. After stopping the vitamins, the stool did not change. At the age of 29, after the birth of a child, 10 months later, severe pain suddenly appeared in the stomach area, which went away after eating. EGDS was done. 05/15/09 Conclusion: G.p.o.d.. Chr. gastritis in st. exacerbations, “kissing” ulcers of the 12th intestine (1.2 cm and 0.7 cm) Bulbit, Duodenitis. Dyskinizia of the intestine and 12p. Treatment was prescribed: Pariet 20 mg, 4 weeks, plus de-nol 112 tablets. The pain stopped. Next prescription: Omez for 1 year and mezim for 2 weeks. No additional studies were conducted. The pain periodically bothered me. I did an endoscopy on April 8, 2011. Esophagus: The esophagus is freely passable, its lumen is of normal size. The folds are longitudinal. The mucous membrane is pale pink. Stomach: The stomach is hook-shaped and of normal size. It expands completely with air, Contains an excess amount of liquid and mucus with traces of bile. The walls are convoluted and standard in height and relief. Peristalsis is moderate and can be seen in all parts of the stomach. The pale pink mucosa in the lower 1/3 of the body and antrum is hyperemic. The pylorus does not close, gapes widely, and there is a small portion of bile reflux from the intestine. The urease test for Helicobacter pilori is positive. -duodenum: Bulb 12p.k.. deformed, does not close, reflux. The mucous membrane of the bulb and postbulbar part of the intestine is clearly hyperemic, with bile deposits. In other parts of the duodenum: the intestinal lumen is oval, the folds are circular. mucous membrane is pale pink. Conclusion: Deformation of the bulb 12p. k.. Reflux gastroduodenitis DGR.HP++. Dyskinizia. Prescription of treatment: Nexium 20 mg - 2 times a day before meals. Klacid 500 mg - 2 times a day before meals, Flemoxime salutabpo 1000 mg - 2 times a day before meals, De-nol 2 tablets - 2 times a day for 30 minutes . before meals and at night. I took all medications together for 14 days. From the 15th day - Nolplaza 20 mg 2 times a day before meals for 15 days, Ganaton 50 mg 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals, 15 days Bifiform 1 capsule 2 times a day with meals for 15 days. Diet: drink plenty of fluids. On August 1, 2011, I did an endoscopy. Esophagus: The esophagus is freely passable, its lumen and size are normal. The folds are longitudinal, the mucosa is pale pink, the cardia closes. The ZET line is differentiated. Stomach: Hook-shaped, normal size. Expands completely with air. Contains a small amount of liquid and mucus, bile deposits on the walls, the walls are elastic. The folds are tortuous, standard in height and relief. Peristalsis is moderate, can be traced in all parts of the stomach. The mucosa is pale pink in color, viscous bile deposits, barely hyperemic in the pyloric department The pylorus does not close. Urease test for Helicobacter pilori is positive. Duodenum: Bulb 12-p.k. formed, does not close. The intestinal lumen is oval in shape, the folds are circular. The mucosa is hypermic in the bulb and postbulbar section, lined with bile, in the remaining sections it is pale pink in color. Conclusion: Erythematous gastroduodenitis. DGR.HP++. Deformation of the bulb 12 p.k.. Dyskinizia. Treatment: Phosphalugel 1 pack - 3 times a day after meals and at night, 10 days. Ursosan 250 mg 1 drop at night for 2 weeks, Trimedat 200 mg 3 times 20 minutes before meals. 2-3 weeks Next stage: Meteospasmil 1 tablet 30 minutes before meals 3 times a day for 2 weeks, Lancid 15 mg 1 tablet. in the morning before meals 2 weeks., Bifiform. 2 months passed after treatment, pain and heartburn reappeared. I don’t eat anything fried, salty or spicy, I only eat sweet fruits, I don’t drink, I don’t smoke, I lead a healthy lifestyle. Tell me what to do next? Why is Helicobacter pilori positive? Do I need to treat HP again? How to prevent bile from refluxing into the stomach?
www.consmed.ru
Ulcer of the duodenal bulb: treatment
There are many ways to prevent duodenal ulcers and treatment options. In the simplest cases of this disease, the following treatment regimen is used:
- Drug therapy is prescribed.
- A diet for ulcers is being developed.
- Preventive measures are being taken.
If the patient has a more complex stage of development of an ulcer of the intestinal bulb (for example, kissing ulcers), then complex treatment is resorted to. It usually consists of several methods combined together according to the individual condition of the patient.
The following methods are found:
- Pharmaceutical treatment (painkillers, antimicrobials, improve peristalsis, to restore mucous membranes).
- Dietary food for ulcer patients (you can’t eat fatty, fried, salty, spicy, smoked foods, drink alcohol and coffee).
- Physiotherapeutic method. It does not bring any noticeable benefit on its own. Used to increase the effect of medications.
- Medicines for diarrhea, constipation, malaise and other symptoms of ulcers and scarring.
- Surgery.
- Preventive measures (it is recommended to introduce a large amount of vegetables and fruits into the diet, as well as take medications for inflammation of the gastrointestinal mucosa).
Proper nutrition and diet in the presence of scar deformity
If an ulcer of the 12pk bulb or cicatricial deformation of the dpk bulb is detected, the first thing you need to do is adjust your diet and create a healthy menu. The latter must be done so that you don’t have to think about dishes for lunch or dinner and don’t resort to some tasty but unhealthy food.
Healthy eating can also be tasty, contrary to popular belief. So, it is forbidden to use the following for ulcers and deformities of the duodenal bulb:
- Alcohol.
- Fatty, fried.
- Smoked meats, pickles.
- Meat, fish.
- Canned food.
- Rich broths.
- Rye bread.
Mild irritants to the gastrointestinal tract are mineral waters, milk and dairy products, boiled lean meat, pureed vegetables, cereal soups, boiled vegetables, berries and fruits. All these foods can be eaten, but not very often.
Liquid foods, as well as cereal porridges in boiled or slimy form, irritate the intestines and stomach the least.
Under no circumstances should you eat very hot food if you have a disease of the intestinal bulb. Cold food should also not be eaten, since it goes directly into the intestine without undergoing alkaline treatment, which means that hydrochloric acid enters the intestine. It follows that you need to exclude ice cream, cold drinks, ice, chilled milkshakes and the like from your diet.
If you have ulcers, the body needs a lot of protein to heal the wounds. Protein is a building material, and it also neutralizes excess gastric secretion.
The diet of an ulcer patient should contain proteins in the following quantities: 65% - animal, 35% - plant. It is recommended to eat rabbit meat, as it is digested better than chicken and especially beef, and contains a large amount of protein.
The salt content in dishes should also be kept to a minimum, as it provokes the release of acid in the stomach, and therefore aggravates the disease.
Scar-ulcerative deformation of the duodenal bulb is a consequence of peptic ulcer disease. Any ulceration that occurs on the mucous membrane or on the skin becomes a scar or scar after healing. This leads to deformation of the bulb.
Symptoms and treatment of scar deformation of the duodenal bulb
Cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb is a residual form of the main pathological process associated with a severe form of erosion or ulcer of the corresponding localization of the base organ.
What are the additional reasons for the formation of such a structure? How is it detected and diagnosed? How effective is non-surgical treatment? You will read about this and much more in our article.
Reasons for the development of the pathological process
The duodenum, which is the initial section of the small intestine and located after the pylorus of the stomach, consists of several elements. The key is a bulb or ampoule that has longitudinal folding.
As part of various pathological processes and the formation of an inflammatory reaction on the mucous membranes of the organ, a partial change in the structure of the epithelium occurs, resulting in the creation of preconditions for the formation of scars.
Such deformations usually clearly indicate a partially or completely healed ulcer, but may also indicate other causes of pathology. The most famous:
- Incoming deformation against the background of severe edema due to the inflammatory process of the entire duodenum,
- Physical compression of the bulb due to the influence of external or internal factors - injuries, features of the anatomical structure of the patient’s neighboring organs, and so on,
- Systemic pathological processes affecting the gastrointestinal tract complex. In the latter case, scarring of the duodenal bulb is a secondary complication.
Correction of the power plan
In most cases, in the absence of complications and multiple relapses of the pathological process, diet shows high effectiveness in moderate and advanced forms of cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb (DU). Correction of the diet begins with the exclusion of the heaviest foods that are prohibited for consumption in case of ulcers and deformities of the organ bulb. Completely prohibited:
- Any type of alcohol
- Rye bread,
- Fatty fried foods
- Pickles and smoked meats,
- Canned food and marinades,
- Rich broths.
Spices, sweets, coffee, and tea are consumed with great restriction.
Under additional control are any foods and dishes that can significantly affect the acidity of the stomach, cause intestinal hyperactivity, or, conversely, significantly slow down its work.
The list of general recommendations includes split meals - you need to eat more often, but in small portions.
It is allowed to steam, boil, or, in extreme cases, bake. Food is served only warm. The consistency of the products is small pieces, paste-like and liquid (large pieces are not allowed).
Possible complications
Cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb often causes complications, especially in the presence of predisposing circumstances. The most common problems:
- Relapse of the ulcerative process. Observed on average in a quarter of patients, even when they undergo full-fledged treatment 3-6 months after therapy,
- Blockage of the duodenum. It is formed in the case of advanced forms of scar deformities, with the development of an extreme pathological process. Leads to systemic spillage of bile/hydrochloric acid throughout the gastrointestinal tract, requiring hospitalization,
- Bleeding. Caused by a violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes and epithelial structures in the localization of scars. Requires first aid and qualified treatment in a hospital with hospitalization of the patient.
- Secondary manifestations. Dyspeptic disorders that do not disappear for weeks and months, induction of the development of irritable bowel syndrome, and so on.
Preventive actions
As part of basic preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of scar-ulcerative deformation of the duodenal bulb or the progression of the pathological process after healing of the ulcer, it is recommended to perform the following actions:
- Full completion of the rehabilitation period. It includes drug therapy, physiotherapy, a special regime,
- Dieting. The adaptive nutrition system must be adhered to on an ongoing basis, until the final disappearance of all signs of pathology, including those confirmed by diagnostic measures,
- Rejection of bad habits. First of all, we are talking about alcohol consumption and smoking,
- Moderate physical activity. If there is deformation of the duodenal bulb, active physical activity is contraindicated, however, light cardio training is acceptable and recommended,
- Regular preventive examinations. Includes a visit to a gastroenterologist, laboratory tests, ultrasound, fluoroscopy, and other procedures as necessary.
Source: https://MedTelo.ru/travmy/simptomy-i-lechenie-rubtsovoy-deformatsii-lukovitsy-dpk.html
How does deformation occur?
There are 4 sections of the duodenum (duodenum): upper, descending, lower, ascending. The upper section is a continuation of the pylorus of the stomach. It is clearly demarcated from the next section due to a sharp bend. If you look at x-rays, the upper part looks like a ball. That's why it's called an onion.
Scarring is observed with duodenal ulcer. In the event that there are several ulcers, one continuous scar is formed. As a result, deformation of the organ bulb develops.
What complications can there be?
Scar-ulcerative deformation disrupts digestive function. In this case, there will be a constant reflux of hydrochloric acid, which is part of the gastric juice, from the stomach to the intestinal area, and bile and secretion produced by the pancreas from the intestine to the stomach area. This is unnatural and such processes should not happen. Against this background, stool disorder occurs - diarrhea and constipation, and other unpleasant symptoms.
The most severe consequence of deformation is narrowing of the lumen. This is fraught with intestinal obstruction with stagnation of food and the fermentation process.
The larger the area of scarring, the worse the consequences will be. If you ignore the doctor’s instructions, do not adhere to proper nutrition, and allow relapses of the disease, you can forget about the normal functionality of the duodenum forever. Treatment of bulb deformation in this case is carried out only surgically.
Causes of pathology
Scar-ulcerative deformity is a consequence of multiple ulcers. They develop for one main reason - the effect of hydrochloric acid on the mucous membrane with its subsequent destruction. This happens in the background:
- gastritis;
- long-term use of corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- alcohol abuse;
- repeated stress and nervous strain;
- entry into the body of the Helicobacter bacteria;
- untimely treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Neglect of doctor's instructions for gastritis.
Symptoms of pathology
If a person undergoes treatment on time, the deformed bulb tissue may straighten out over time. The duodenum will function normally. In this case, there will be no unpleasant symptoms.
Pathology appears only at an advanced stage. Symptoms become especially pronounced when the lumen narrows. The deformation process is characterized by the following features:
- paroxysmal pain in the navel and stomach, hunger pain;
- nausea after eating;
- colic;
- gas formation;
- heartburn with an unpleasant sour taste;
- bad breath (especially if the lumen is very narrowed - fermented food can give a foul odor from the oral cavity);
- coating on the tongue;
- vomiting with blood impurities - when bleeding opens.
Stenosis of the pylorus of the stomach and esophagus
The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Determination of pyloric stenosis
Pyloric stenosis (pyloric stenosis) is a complication of gastric ulcer, in which the lumen in this area of the digestive tract narrows and the passage of food into the intestines from the stomach is disrupted. Over time, this pathology leads to the development of severe disorders in the body and changes in homeostasis. Such stenosis occurs in adults and is only acquired.
Causes of development of pyloric stenosis
One of the reasons for the development of gastric stenosis is a scar, consisting of connective tissue and formed during the healing process of a peptic ulcer. It tightens the wall of the stomach, making it inactive.
Another reason for the development of stenosis may be intramural cancer. The neoplasm grows into the tissue, as a result of which the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract narrows. Food moving through the digestive tract cannot reach the intestines in full. It stagnates. To evacuate the contents from the stomach, the muscular layer begins to grow. This compensates for the stenosis to some extent.
However, over time, the hypertrophied muscular layer of the stomach cannot cope with the load, and an increase in the volume of stomach contents leads to its stretching. As a result of stagnation, food under the influence of microbes begins to decompose and ferment.
The disease has the following stages:
1. The first stage is compensated pyloric stenosis. The hole is narrowed slightly. The patient complains of belching with a sour taste and a feeling of a full stomach after eating. Occasionally, vomiting occurs, which brings a feeling of relief for a short time. The patient's condition is generally satisfactory.
2. The second stage is the stage of subcompensation. The patient already has a constant feeling of a full stomach, which is combined with belching and pain. Vomiting occurs after a while or immediately after eating and brings relief. Over time, a person loses weight. When palpating and examining the abdomen, a splashing noise is heard in the navel area.
3. The third stage is the stage of decompensation. Over time, the disease progresses, the stomach is distended. The condition worsens significantly, exhaustion and dehydration develop. Vomiting occurs frequently and does not bring relief. The vomit is in large quantities, foul-smelling, and contains large quantities of the remains of many days' food.
Diagnosis and treatment of pyloric stenosis
Diagnosis of the disease is based on the following studies:
· X-ray examination. In this case, there may be an increase in the size of the stomach, a decrease in peristaltic activity, a narrowing of the canal, and an increase in the time of evacuation of stomach contents;
· Esophagogastroduodenoscopy. It shows narrowing and deformation of the stomach at the exit site, expansion of the stomach;
· Study of motor function (electrogastroenterography method is used). This method makes it possible to learn about the tone, electrical activity, frequency and amplitude of stomach contractions after meals and on an empty stomach;
· Ultrasound. In later stages, it allows visualization of an enlarged stomach.
Treatment of pyloric stenosis (pyloric stenosis) is only surgical. Drug therapy includes treatment of the underlying disease and preoperative preparation. Antiulcer drugs are prescribed, correction of protein and water-electrolyte metabolism disorders, and restoration of body weight are carried out.
Prevention includes timely treatment of peptic ulcer.
Congenital pyloric stenosis
In children, congenital pyloric stenosis can be found. Often the disease is hereditary. With stenosis, there is a proliferation of connective tissue in the area of the excretory section of the stomach. It is the most common cause of gastric obstruction in infants, with boys being affected four times more often than girls.
The disease appears in the second to fourth week of life. The main symptom is frequent and severe “fountain” vomiting some time after feeding. Treatment is only surgical. The prognosis after surgery is favorable provided that treatment is started in a timely manner.
Esophageal stenosis
In congenital esophageal stenosis, the cause is an embryonic malformation. The disease appears immediately from the first days of life when feeding the baby. The baby immediately begins to spit up milk. If the stenosis is mild, symptoms appear with the introduction of solid food.
With acquired stenosis of the esophagus, a narrowing of its lumen also occurs. There are several reasons leading to disruption of the normal patency of the esophagus:
· Scar changes due to inflammatory, infectious diseases, previous peptic ulcers of the stomach, gastroesophageal reflux disease;
· Injuries, burns of the esophagus;
· Neoplasms of the esophagus and surrounding tissue;
· Aortic aneurysm, enlarged lymph nodes, abnormal arrangement of blood vessels.
The main symptoms of stenosis are: pain when eating, along the esophagus, excessive salivation, belching, sometimes vomiting, bleeding. For esophageal stenosis, the following degrees are distinguished:
1. The first degree is characterized by periodic impairment of swallowing solid food.
2. The second degree is characterized by the passage of only semi-liquid food through the esophagus.
3. Third degree - only liquid food passes.
4. Fourth degree of stenosis - it is difficult to swallow water and saliva.
For diagnostic purposes, esophagoscopy and X-ray examination with a barium suspension are performed. Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the disease and will be surgical or conservative. Conservative treatment includes correction of nutritional disorders, drug therapy, and dilation of the esophagus. During surgical treatment, esophageal plasty is performed, scars are dissected, and a gastrostomy tube is applied.
Author of the article:
Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich |
Doctor of Medical Sciences therapist Education: Moscow Medical Institute named after. I. M. Sechenov, specialty - “General Medicine” in 1991, in 1993 “Occupational diseases”, in 1996 “Therapy”. Our authors
Treatment of the disease
Deformation of the bulb is not an independent disease. After the tissue tightens, after a few years with proper treatment, the bulb will recover and return to its normal size. In the event that ulcers appear constantly in healed areas, the scars will tighten the lumen between the stomach and duodenum more and more.
This will make it very difficult for food from the stomach area to enter the duodenum. In this case, surgery is prescribed. There are no other treatments for this condition. The deformed area must be cut off.
There is no point in treating healed tissue with medications. If the lumen is not very narrowed, then doctors prescribe medications as therapy that will help relieve unpleasant symptoms - pain, heartburn, belching; eliminate the cause of the development of ulcers. Subject to all the rules of treatment and a healthy lifestyle, diet, signs of pathology will eventually cease to bother the person.
Diet is one of the main factors. You should exclude all foods that increase the production of hydrochloric acid. The diet should consist only of healthy foods that have undergone gentle heat treatment. Under no circumstances should you consume alcohol, carbonated drinks, baked goods, spicy foods, fried foods, pickles, marinades and smoked meats. Only in this case will it be possible to prevent negative consequences.
Ulcerogenic deformation of the bulb of the duodenum - what is it?
Scar-ulcerative deformation of the duodenal bulb is a consequence of peptic ulcer disease. Any ulceration that occurs on the mucous membrane or on the skin becomes a scar or scar after healing. This leads to deformation of the bulb.
How does deformation occur?
There are 4 sections of the duodenum (duodenum): upper, descending, lower, ascending. The upper section is a continuation of the pylorus of the stomach. It is clearly demarcated from the next section due to a sharp bend. If you look at x-rays, the upper part looks like a ball. That's why it's called an onion.
Scarring is observed with duodenal ulcer. In the event that there are several ulcers, one continuous scar is formed. As a result, deformation of the organ bulb develops.
In practice, ulcers in the duodenum are always localized in the area of the bulbous region. This is explained by the fact that the bulb is the boundary between the acidic environment of the stomach and the alkaline environment of the intestines.
As soon as the slightest malfunction occurs, an inflammatory process develops, gastric juice enters the area of the bulbous region, and has a destructive effect on the mucous membrane. The consequence is that ulcers form.
After treatment, scarring of the ulcers occurs. Scars are hard and consist of connective tissue. And when there are a lot of them, the connective tissue tightens the upper part of the duodenum, distorting its original physiological forms.
What complications can there be?
Scar-ulcerative deformation disrupts digestive function.
In this case, there will be a constant reflux of hydrochloric acid, which is part of the gastric juice, from the stomach to the intestinal area, and bile and secretion produced by the pancreas from the intestine to the stomach area.
This is unnatural and such processes should not occur. Against this background, stool disorder occurs - diarrhea and constipation, and other unpleasant symptoms.
The most severe consequence of deformation is narrowing of the lumen. This is fraught with intestinal obstruction with stagnation of food and the fermentation process.
The larger the area of scarring, the worse the consequences will be. If you ignore the doctor’s instructions, do not adhere to proper nutrition, and allow relapses of the disease, you can forget about the normal functionality of the duodenum forever. Treatment of bulb deformation in this case is carried out only surgically.
Causes of pathology
Scar-ulcerative deformity is a consequence of multiple ulcers. They develop for one main reason - the effect of hydrochloric acid on the mucous membrane with its subsequent destruction. This happens in the background:
- gastritis;
- long-term use of corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- alcohol abuse;
- repeated stress and nervous strain;
- entry into the body of the Helicobacter bacteria;
- untimely treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Neglect of doctor's instructions for gastritis.
Symptoms of pathology
If a person undergoes treatment on time, the deformed bulb tissue may straighten out over time. The duodenum will function normally. In this case, there will be no unpleasant symptoms.
Pathology appears only at an advanced stage. Symptoms become especially pronounced when the lumen narrows. The deformation process is characterized by the following features:
- paroxysmal pain in the navel and stomach, hunger pain;
- nausea after eating;
- colic;
- gas formation;
- heartburn with an unpleasant sour taste;
- bad breath (especially if the lumen is very narrowed - fermented food can give a foul odor from the oral cavity);
- coating on the tongue;
- vomiting with blood impurities - when bleeding opens.
Treatment of the disease
Deformation of the bulb is not an independent disease. After the tissue tightens, after a few years with proper treatment, the bulb will recover and return to its normal size. In the event that ulcers appear constantly in healed areas, the scars will tighten the lumen between the stomach and duodenum more and more.
This will make it very difficult for food from the stomach area to enter the duodenum. In this case, surgery is prescribed. There are no other treatments for this condition. The deformed area must be cut off.
There is no point in treating healed tissue with medications. If the lumen is not very narrowed, then doctors prescribe medications as therapy that will help relieve unpleasant symptoms - pain, heartburn, belching; eliminate the cause of the development of ulcers. Subject to all the rules of treatment and a healthy lifestyle, diet, signs of pathology will eventually cease to bother the person.
Diet is one of the main factors. You should exclude all foods that increase the production of hydrochloric acid.
The diet should consist only of healthy foods that have undergone gentle heat treatment.
Under no circumstances should you consume alcohol, carbonated drinks, baked goods, spicy foods, fried foods, pickles, marinades and smoked meats. Only in this case will it be possible to prevent negative consequences.
Disease prevention
To avoid narrowing the lumen of the bulb, you should follow fairly simple rules. Since tissue scarring occurs against the background of peptic ulcer disease, it is necessary to prevent recurrence of the disease and the development of ulcers as much as possible. To do this, you need to eat right and take medications that promote the healing of erosions.
Food during meals should be crushed as much as possible. In this case, it will be much easier for both the stomach and duodenum to digest it. Under no circumstances should you starve or overeat. This will all lead to the formation of new ulcers.
If a person experiences everyday stress, it is advisable to take a course of sedatives. A common cause of ulcer formation is the Helicobacter bacterium. Antibiotics are prescribed to destroy foreign infection.
The treatment is long-term. Under no circumstances should you stop taking antibacterial drugs halfway through the course of treatment. The bacterium is insidious in that it can appear again in the future and have a destructive effect on the mucous membrane.
To prevent the development of deformation of the duodenal bulb, people diagnosed with gastritis or peptic ulcer disease need to undergo a diagnostic examination during periods of possible exacerbation (autumn, spring).
Scar-ulcerative deformity is a pathology that can lead to quite serious consequences. We must not forget that an ulcer is the first step in the development of stomach and duodenal cancer.
Source: https://worldwantedperfume.com/ulcerogennaja-deformacija-lukovicy-dpk-chto-jeto-takoe/
Disease prevention
To avoid narrowing the lumen of the bulb, you should follow fairly simple rules. Since tissue scarring occurs against the background of peptic ulcer disease, it is necessary to prevent recurrence of the disease and the development of ulcers as much as possible. To do this, you need to eat right and take medications that promote the healing of erosions.
Food during meals should be crushed as much as possible. In this case, it will be much easier for both the stomach and duodenum to digest it. Under no circumstances should you starve or overeat. This will all lead to the formation of new ulcers.
If a person experiences everyday stress, it is advisable to take a course of sedatives. A common cause of ulcer formation is the Helicobacter bacterium. Antibiotics are prescribed to destroy foreign infection. The treatment is long-term. Under no circumstances should you stop taking antibacterial drugs halfway through the course of treatment. The bacterium is insidious in that it can appear again in the future and have a destructive effect on the mucous membrane.
To prevent the development of deformation of the duodenal bulb, people diagnosed with gastritis or peptic ulcer disease need to undergo a diagnostic examination during periods of possible exacerbation (autumn, spring).
Scar-ulcerative deformity is a pathology that can lead to quite serious consequences. We must not forget that an ulcer is the first step in the development of stomach and duodenal cancer.
Treatment of scars in the duodenum
Any damage to the mucous membranes and skin after healing is reminiscent of scars. The same thing is observed with peptic ulcer disease: if ulcers constantly appear in one section, they lead to the formation of scars in the duodenum.
Our readers successfully use Monastic Tea to treat gastritis and ulcers. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Scarring in the duodenum is a complication of a peptic ulcer or a negative manifestation after surgery.
- 1 Education mechanism
- 2 Signs and symptoms
- 3 Diagnosis of scars in the duodenum
- 4 What are the dangers of scars?
- 5 Treatment and prevention
Education mechanism
More often, scars appear at the junction of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract. This part is called the bulb. Like any other scar, the scar tightens the area around it. Deformation occurs when many such scars are concentrated in one place. The development of peptic ulcers can be caused by many factors. This includes constant nervous tension, smoking, alcohol abuse, non-compliance with diet, and refusal to take special medications.
There are two main mechanisms due to which duodenal ulcer develops:
- increased acidity and its negative effect on the mucous membrane;
- Helicobacter, which release harmful substances that destroy the intestinal walls.
Return to contents
Signs and symptoms
As such, there are no clear symptoms that would make it clear whether there is a scar or not. After a few years, the intestinal walls smooth out on their own and everything returns to normal. But if the peptic ulcer is repeated every time, then the scars, accordingly, become more numerous. This leads to a gradual narrowing of the intestinal walls and ultimately to complete intestinal obstruction. The signs of duodenal ulcer are the following:
- Pain that is localized in the upper abdomen. Such pain can be influenced by various factors. Their cause may be food intake, but then the pain appears after a couple of hours, or as a result of acidic contents entering the walls of the duodenum.
- Disorders due to disturbances in the normal functioning of the stomach. It is caused by increased acidity and is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, constipation or bloating. Due to these disorders, a person loses his appetite and, as a result, loses weight.
Return to contents
Diagnosis of scars in the duodenum
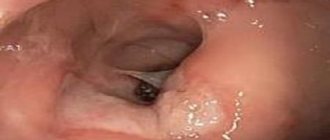
Scarring of the walls of the duodenum is detected during gastroscopy.
The regular appearance of ulcers in one place leads to the appearance of a large number of scars in this place. Due to the large number of scars, the duodenum is at risk of cicatricial deformation. The intestinal walls are constantly narrowing, which can lead to complete obstruction of the bulbous part of the duodenum. If you experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, drowsiness or weakness, you should consult a physician.
This is followed by a visit to a gastroenterologist, who will prescribe the necessary examination. The most effective method for diagnosing cicatricial deformity is gastroscopy. This method will help to examine the deformed part of the intestine and determine its current condition.
Return to contents
What are the dangers of scars?
By following a special diet and taking the necessary medications, a person does not need to worry about anything. However, if these requirements are ignored, a number of complications will follow. First of all, these are disturbances and malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract. All this is accompanied by abdominal pain, diarrhea and constipation.
The most unpleasant consequence is intestinal obstruction. There are two types of obstruction. In the first case, a small space remains through which the digested food passes, in the second case there is no such space, only surgical intervention is necessary.
Return to contents
Treatment and prevention
Severe scar damage in the intestine can be eliminated surgically, and relapse can only be prevented with supportive care and regular examinations.
One of the most common types of treatment is to take a drug that neutralizes the acidic environment, thereby preventing it from irritating the intestinal walls. They take medications that stop the production of gastric juice.
Severe deformation of the duodenum can only be treated with surgery. In milder cases, this disease is treated with proper and balanced nutrition, taking the necessary medications, and do not forget about a healthy lifestyle. The main requirement for a therapeutic diet is a temporary refusal of salty, fried, smoked, and too sweet foods. It is recommended to exclude carbonated and alcoholic drinks and quit smoking during treatment. All these foods and bad habits increase gastric secretion, which irritates damaged intestinal walls.
To avoid cicatricial deformation of the duodenum, it is necessary to prevent the development of peptic ulcers. If gastritis or an ulcer is detected, you must immediately consult a doctor and follow his instructions. But the best way out is careful health care, proper nutrition and as little alcohol consumption as possible. After all, the earlier a disease is detected, the easier it is to cure it.