When the surface epithelial layer is damaged, duodenal erosion is formed - one of the common diseases of the digestive system. With appropriate treatment it goes away without leaving any traces.
Stress, disturbances in diet and lifestyle cause one of the most common diseases of the digestive system - the appearance of wounds on the duodenal mucosa or erosion. Despite the superficial damage to the mucous membranes, the disease can significantly reduce the patient’s standard of living.
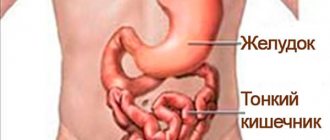
The structure of the duodenum and erosion
The initial section of the small intestine, 12 fingers long (about 300 centimeters), starts from the stomach and flows into the jejunum. Diameter – 45-47 mm. Its upper part is thickened like an onion (ampule). Depending on the bends of the organ, the upper part, descending and horizontal, ascending, are distinguished.
The walls of the duodenum consist of several layers:
- the outer shell is a continuation of the outer shell of the stomach;
- a muscular middle layer, consisting of two types of bundles - longitudinal and circular, which allows the intestine to contract and reduce its diameter;
- the internal mucous layer that forms folds - longitudinal in the upper part, circular - in the remaining parts of the organ.
The lining of the intestine has formations called intestinal villi, at the base of which there are glands that produce intestinal juice and a number of digestive hormones. In the central part of the villi there are blood and lymphatic vessels that are involved in the process of transporting nutrients to the body.
In the downward part of the organ there is a formation in the form of a tubercle - the nipple of Vater. Bile and pancreatic juice, necessary for digestive processes, flow through it; the flow is regulated by the sphincter of Oddi.
The main role of the duodenum:
- transport - the contents of the stomach after additional processing move further into the intestine;
- motor - contractions of muscle fibers allow the contents of the intestines and digestive juices to mix;
- enzymatic - glands at the base of the villi produce food enzymes and hormones (enterokinase, gastrin, cholecystokinin).
Erosion of the duodenum - damage to the superficial internal mucous layer, which looks like wounds of various shapes and sizes, ranks second in the world among diseases of the digestive organs in terms of frequency of detection.
The lesions do not penetrate into the muscle layer, as with an ulcer, the healing process has a specific course and does not leave traces, which allows us to consider erosion of the duodenum 12 as an independent disease, and not the initial stage of a peptic ulcer.
Symptoms of pathology
Manifestations of the disease in the early stages go unnoticed; patients attribute it to ordinary eating disorders. Subsequently, complaints arise about:
- nausea and vomiting;
- decreased appetite;
- weight loss;
- abdominal pain after eating.
During the examination, the doctor determines pain in the upper abdomen. The appearance of discomfort after eating depends on the location in the intestines where the symptoms of erosion are located.
Most often, mucosal destruction occurs in the upper parts of the duodenal bulb. In such cases, pain will appear an hour after eating. Such a lesion is considered the most dangerous - the upper part of this organ is located near the nerve plexuses (vagus nerve) and causes a large number of neurological pathologies.
Erosion of the bulb over a long period of time develops into a peptic ulcer, the treatment of which is always long and difficult. The main symptoms that indicate this type of pathology are the following:
- loss of appetite;
- poor digestion;
- heartburn;
- belching;
- flatulence.
The order of these symptoms manifests itself individually and depends on the characteristics of the body. At certain stages, pain of a different nature may occur:
- dull;
- aching;
- spasmodic;
- burning;
- radiating into the chest.
The pain is most often felt at night and on an empty stomach, although it is never permanent. Discomfort after eating resembles bloating - even a small amount of food causes a feeling of fullness.
Additional symptoms of acute duodenal erosion include:
- intestinal and gastric bleeding, which is indicated by the dark color of the stool, caused by the effect of specific intestinal contents on fresh blood;
- nausea and vomiting of clotted blood;
- weakness and anemia;
- manifestations of general intoxication;
- intermittent stools;
- stool disorders.
With erosion of the stomach and duodenum, symptoms may occur that indicate the occurrence of neurological symptoms:
- discomfort and heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- heaviness and pain in the upper abdomen;
- pain in the heart area;
- pressure behind the sternum.
When diagnosing, the doctor is faced with the task of separating duodenal erosion and symptoms of possible heart or liver diseases.
Classification of erosions
Duodenal erosions can be benign or malignant.
Benign varieties of the disease include:
- acute erosion;
- chronic lesions of the mucous membrane (they can be single or multiple);
- gastritis with the development of erosive lesions;
- erosive-hemorrhagic inflammation of the mucous membranes of the stomach and duodenum.
Erosion is defined as acute if it epithelializes within 2 days to a week. If the area of pathology does not undergo regression within a month, then the disease is chronic.
Causes
The main factors for the occurrence of duodenal erosion are the same as for gastric erosion and peptic ulcer. This:
- infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- constant stressful environmental pressure;
- low level of immune defense;
- recent viral diseases, surgical interventions;
- violation of the eating regime, consumption of too spicy, hot and rough foods;
- smoking and alcohol;
- use of certain medications - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, aspirin, some hormonal drugs;
- cirrhosis of the liver (it is believed that acute erosion most often accompanies cirrhosis caused by viral hepatitis, chronic erosion - with alcoholic liver damage);
- neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the digestive system (disturbances in the functioning of the gallbladder, which reduces the disinfection function of bile).
The exact mechanism of the occurrence of erosions is unknown; an approximate diagram of the formation of pathology looks like this:
- the level of protection of the mucous membrane of the duodenum and stomach decreases due to a decrease in the production of protective mucus;
- the rate of regeneration of the mucosal epithelium decreases;
- blood circulation in the walls of the stomach and intestines is disrupted;
- under the influence of the two previous factors, the intestinal mucosa cannot quickly restore the areas on the mucous membranes affected by aggressive digestive enzymes.
Erosion can be acute and last no more than a week, then drag on without a trace, and chronic, which is open for a month or more.
What is a disease
Erosion of the duodenal bulb is a relatively little-studied dysfunction of the digestive tract. Accurate diagnosis has become possible due to the widespread introduction of endoscopes into clinical practice.
Erosion is the second most common pathology of the gastrointestinal tract after ulcers. The disease is often detected in patients with severe peptic ulcers, hepatitis, cirrhosis, tumors of the digestive tract, pathologies of the heart, blood vessels and respiratory organs.
Erosion differs from other diseases in etiological factors, severity of the pathological process and healing rate, and general symptoms.
Diagnostics
When a patient complains of abdominal pain and indigestion, nausea, the doctor determines the disease by:
- taking anamnesis;
- external examination of the patient, palpation of the abdominal wall;
- prescribing a general and biochemical blood test;
- laboratory testing of urine and feces (for occult blood);
- blood tests for HIV and viral hepatitis;
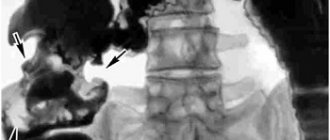
- prescribing an X-ray examination with a contrast agent;
- carrying out endoscopic examination.
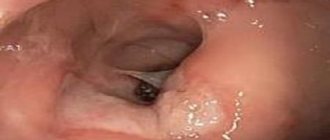
The most accurate diagnosis can be established by performing a diagnostic endoscopic examination (fibrogastroduodenoscopy). Visual examination of the mucosal surface under magnification allows you to see and carefully examine all affected areas. If necessary, during such an examination, you can take particles of mucous membranes to determine:
- acidity;
- epithelial conditions;
- presence of Helicobacter pylori and other infectious agents.
The doctor needs to exclude the presence of intestinal bleeding from the erosion zone - this greatly weakens the patient and should be stopped first.
Based on the results of the examination, the type of erosion is determined:
- hemorrhagic acute;
- chronic;
- single or multiple;
- erosive-hemorrhagic duodenitis.
With erosion of the bulbs there are:
- focal erosion;
- drain (when several local foci are connected);
- hemorrhagic.
Areas affected by erosion on the surface of the duodenum can be combined with ulcerative lesions of the mucous membranes, which affects the muscular layer of the organ.
Erosion in the stomach: types
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor always determines whether it belongs to one species or another. They differ according to multiple classifications.
Based on the form of the disease, there are 2 types of erosion:
- Spicy. A sudden change in well-being, which is the main “call” of the body. For treatment, complex treatment is used, which well combines traditional and official medicine. Usually the course of treatment does not last more than 14 days.
- Chronic. Characterized by periodic bursts. There are moments of calm, and then the symptoms return with renewed vigor. This form of the disease has a high risk of ulcers.
The location is the lower part of the antrum of the stomach. At the bottom of the inflamed area there are dilated capillaries.
Treatment periods vary, but generally therapy ranges from 2 to 6 months.
According to the type of damage to the gastric mucosa, erosions are distinguished:
- Hemorrhagic. Red dots form at the affected areas, and bleeding occurs at the edges.
- Superficial. They are distinguished by a smooth, erosive surface, without convex formations. They have different sizes. Sometimes there is a whitish coating.
- Full. A distinctive feature is growths similar to polyps or warts. Localized in the antrum. In this case, the mucous membrane may have swelling and redness, or may not change at all.
The distinctive features of erosion can be seen in the photo.
By type of progression they mean:
- Independent.
- Obtained as a result of the appearance of malignant tumors.
- Arising due to various disorders in the body.
Treatment
After determining the diagnosis, treatment for duodenal erosion is prescribed. The treatment strategy is determined by the attending physician depending on:
- presence of bleeding;
- Helicobacter pylori infection.
Main goal of treatment:
- restoration of the integrity and functionality of mucous membranes;
- raising the immune status of the body.
There are no differences in the treatment regimen for erosions in any area - lesions on the bulb are treated in the same way as on any part of the duodenum. All prescriptions and adjustments of therapy are carried out exclusively by a doctor.
Main directions in treatment:
- decreased acidity of gastric juice;
- stopping bleeding;
- destruction of Helicobacter pylori;
- symptomatic treatment;
- sedatives;
- restorative therapy;
- treatment with folk remedies;
- diet and lifestyle changes.
Regulating the acidity of gastric juice is carried out using:
- drugs with acidity-regulating action (ranitidine, cimetidine, Relzer);
- proton pump inhibitors (Omez, Omeprazole, Nolpaza).
To relieve pain use:
- antispasmodics Drotaverine and Spasmol;
- products with an enveloping effect Maalox, Almagel.
To eliminate infectious agents, use:
- Clarithromycin and Amoxicillin;
- Ampiox;
- Metronidazole.
When treating hemorrhagic forms of erosion, treatment is prescribed to replenish blood loss: blood transfusions or plasma administration. Preliminary medications are administered to stop blood loss. As a general strengthening therapy, immunostimulating therapy and vitamin preparations (groups B, C, E, PP) are prescribed.
Inpatient treatment can be replaced with outpatient treatment if the lesions are minor and do not cause bleeding. Alternative treatment is used only in the absence of bleeding and after consultation with the doctor.
Prevention
Preventive measures consist of strict adherence to the principles of a healthy lifestyle, doctor’s recommendations regarding treatment and proper nutrition. It is necessary to correctly use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which can provoke inflammation.
Patients with a history of inflammatory pathologies of the gastrointestinal mucosa should stop smoking and drinking alcohol. It is recommended to maintain physical activity and avoid physical inactivity.
Erosion of the duodenum can sometimes be cured by correcting the diet and using antacids. Early consultation with a doctor helps to improve the condition and stable remission . In the absence of medical assistance, complications develop, the most dangerous of which is cancer.
Traditional medicine recipes
Folk remedies are used in consultation with a doctor.
Recommended:
- sea buckthorn oil in capsules three times a day before meals (not recommended for diseases of the liver or biliary tract);
- herbal mixture of yarrow, chamomile, mint, St. John's wort flowers and sage leaves in equal parts. Brew a teaspoon per glass of hot water and drink 150 grams before meals;
- a mixture of carrot juice and raw chicken yolks, half a glass 2 times a day before meals;
- chamomile infusion at the rate of 1 teaspoon (or sachet) of the product per cup of very hot water.
For treatment, a decoction of nettles (a tablespoon per glass of water) and a decoction of oat grains (in the same ratio) are also used. The decoctions are filtered, mixed and drunk ½ cup 30 minutes before each meal.
Healthy eating rules
A special diet is an integral part of the treatment of any diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The basic rules of nutrition for erosion are to avoid eating food that irritates the mucous membranes and avoid overeating. You need to eat small portions 5-6 times a day. The diet is aimed at reducing the acidity of gastric juice, restoring and protecting the intestinal mucous membranes. It is recommended to consume no more than 12 g of table salt per day. During an exacerbation, a salt-free diet is recommended.
Dishes should be steamed, boiled or stewed. Fried, fatty, smoked and salty foods should be avoided. Avoid eating foods that are too cold or too hot. A special diet must be followed for at least 60 days. After signs of the disease disappear, changes can be gradually made to the diet. The introduction of any new product must be agreed with the attending physician. Products allowed for consumption are: lean meat, cereals, pasta, yoghurts, low-fat cheeses, eggs, vegetable oils. It is necessary to limit the consumption of confectionery products, yeast bread, and sugar. It is recommended to dilute juices with boiled water. It is better to remove fruits and dried fruits from compote.
Products that should not be included in the diet: mushrooms, canned food, fatty meat and fish broths, hard-boiled eggs, margarine, pickled vegetables. It is necessary to completely avoid drinking alcoholic beverages and fast food. Coffee, black tea and sour fruits irritate the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines, so they are removed from the diet. Propolis and honey can be used as a food additive. These products have a beneficial effect on the inflamed mucous membranes of the digestive system. Honey should be eaten on an empty stomach in small quantities. It is diluted with boiled water and taken 1 hour before meals. Erosion in the duodenum is easy to treat, but folk methods alone cannot get rid of them. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, it is necessary to undergo examination and begin drug treatment.