Why does deformation occur?
If the patient has only the superficial layers of the intestine damaged, that is, erosions form on them, then the healing process occurs without the formation of scars. In patients suffering from ulcers, the wounds are deeper, reaching into the muscle tissue. But if the patient followed all the doctor’s recommendations, the peptic ulcer was well treated, then where the ulcer was, a small linear defect forms, which does not affect the functioning of the intestine.
When the disease was not treated, the patient did not want to follow a diet, and there were many ulcers on the surface, the upper intestine will be covered with connective tissue that appears at the site of the defect, and such tissue is different from what was there before the scar appeared.
The intestines of such a patient change greatly and will never recover. Scars deform the duodenal bulb. The resulting connective tissue begins to tighten this section of the intestine, and it becomes deformed.
Diagnostics
An ulcer of the duodenal bulb is diagnosed quite easily, given that patients seek help from a doctor already at the height of the disease, when discomfort prevents them from living normally.
First, the doctor collects anamnesis and conducts an examination. Of course, palpating the abdomen does not provide much information, but it is possible to suspect, with a high degree of probability, an ulcerative process. Then the patient is sent for a blood test, biochemical markers, a stool test for occult blood, and gastrin levels and Helicobacter pylori activity are determined.
The most common diagnostic procedure remains esophagogastroduodenoscopy, or, more simply, endoscopy. It allows you to examine the mucous membrane of the digestive tube, cauterize all identified ulcers, and take tissue and fluids for examination. Radiography is also informative. Images with contrast will clearly show the location of the ulcers and the condition of the gastric and duodenal mucosa.
Why is the duodenal bulb deformed?
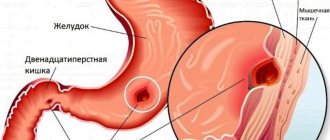
The duodenum consists of 4 sections. If you look at the upper intestine on x-rays, you can see that part of it resembles a ball or onion in shape. Therefore, this part was called the “duodenal bulb.”
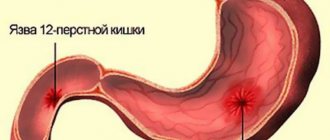
Most often, the ulcer affects the bulb, since it is the boundary that separates the acidic environment characteristic of the stomach and the alkaline environment in the intestines. Other parts may also be affected, but this is quite rare. If a malfunction occurs in the patient’s body, and a lot of acid gets into the duodenum, then it is the bulb that suffers. Acid destroys the intestinal mucosa, first leading to the formation of erosions, then ulcers.
Symptoms of duodenal bulb erosion
Symptoms of the disease resemble ulcerative lesions, but in 20% of cases chronic hemorrhagic lesions are observed, which is indicated by the general condition of the patient - lethargy, anemia.
- Melena (black stool) appears in only 2% of patients; in the rest, occult blood is detected in stool analysis.
- Depending on the severity of bleeding, patients may detect occult blood during stool analysis and vomit “coffee grounds” or viscous mucus. Anemia develops against the background of blood loss.
- The accompanying symptoms of the disease clinically resemble the signs of ulcerative lesions, but the pain is not constant.
- They can occur in the form of cramping pain or have a pulling nature. In most cases, they appear 2 hours after eating. In addition to the painful effect, sour-tasting belching and heartburn occur. Symptoms largely depend on the nature and size of the lesion.
- During inflammatory processes, the branches of the vagus nerve are affected, which leads to neurological changes. The heart rate decreases, chronic fatigue and drowsiness appear, and sweating increases.
Why is deformation dangerous?
Cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb is not normal; digestive function is impaired.
As a result, the patient will have a feeling of discomfort and pain, will suffer from diarrhea or constipation, and belching. But the worst complication is a decrease in the intestinal lumen. Due to scar deformation, the intestinal passage narrows significantly, and the food bolus gets stuck in the stomach.
There are compensated and decompensated intestinal obstruction. In the first case, that is, if the obstruction is compensated, the intestinal passage narrows significantly, but is not completely blocked, so it can partially cope with its work.
If this is decompensated patency, the diameter of the lumen is less than 0.5 cm or it is absent. Such a patient urgently needs surgery.
Epidemiology
An ulcer of the duodenal bulb is usually secondary to damage to the gastric mucosa. Therefore, the diagnosis usually writes “stomach and duodenal ulcer”, without specifying the location.
About 5% of all people on Earth have this pathology. In men it occurs 4 times more often than in the fair sex. And the ratio of city dwellers to rural residents is approximately 2 to 1. Most likely, this is due to the quality of products, eating habits and work activities of residents of urbanized areas.
Symptoms of the disease
Cicatricial ulcerative deformation of the duodenal bulb can be dangerous, especially if the patient does not care about his health and neglects the advice of a doctor. But if the patient completes the course of treatment on time and does not give up the diet and other doctor’s recommendations, the deformed tissue of the duodenal bulb will soon straighten out and the intestines will be able to function normally. Then the patient will not experience unpleasant symptoms. They only bother you when the connective tissue tightens the gap between two organs.
Compensation phase
The patient already has problems with the movement of the food bolus due to the fact that the duodenal bulb is deformed. However, these changes are insignificant; food is delayed for only 6-8 hours. But patients experience a number of unpleasant symptoms:
- there is a feeling of heaviness that bothers you after eating;
- patients complain of nausea and occasional vomiting;
- sour belching bothers you;
- if the patient has inflammation, pain may appear.
Subcompensation phase
If parts of the duodenum are significantly deformed, then the food bolus remains in the stomach much longer, up to 24 hours. This cannot but affect the well-being of patients:
- they are bothered by a constant feeling of heaviness, which appears not only after eating, but lasts all day;
- belching occurs, but with a rotten smell;
- patients have bad breath;
- they are bothered by frequent vomiting, sometimes it happens in the morning, even before the patients have eaten. All eaten food comes out with vomiting, but with signs of fermentation; low-grade fever may appear;
- patients have intoxication and dehydration of the 2nd degree.
Decompensation phase
What is the decompensation phase? In the area of cicatricial deformation, the lumen is completely blocked, and the patient is diagnosed with intestinal obstruction. He also has vomiting, which very early becomes fecal in nature. Patients may experience slight bloating and cramping pain. Intoxication and dehydration of the 3rd degree, dehydration increases rapidly.
Dehydration is the partial dehydration of a patient; his water-electrolyte balance is disturbed. If a patient has a mild degree of dehydration, then he loses only 5-6% of water, with a moderate degree - 5-10%, and with severe - more than 10%. If fluid loss exceeds 20%, the person dies. Therefore, a patient with intestinal obstruction must be urgently taken to a doctor.
Signs and symptoms
As such, there are no clear symptoms that would make it clear whether there is a scar or not. After a few years, the intestinal walls smooth out on their own and everything returns to normal. But if the peptic ulcer is repeated every time, then the scars, accordingly, become more numerous. This leads to a gradual narrowing of the intestinal walls and ultimately to complete intestinal obstruction. The signs of duodenal ulcer are the following:
- Pain that is localized in the upper abdomen. Such pain can be influenced by various factors. Their cause may be food intake, but then the pain appears after a couple of hours, or as a result of acidic contents entering the walls of the duodenum.
- Disorders due to disturbances in the normal functioning of the stomach. It is caused by increased acidity and is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, constipation or bloating. Due to these disorders, a person loses his appetite and, as a result, loses weight.
Diagnosis and treatment
To prescribe treatment, the doctor must conduct a series of examinations, including an X-ray examination of the duodenum. A laboratory test is also needed to see what the dehydration has caused.
If a person has a moderate deformation of the bulb, treatment of this pathology is not necessary. It develops against the background of an ulcer, so it is important to treat the underlying disease, and this is not only taking medications, but also strictly adhering to a diet. And after some time, the bulb itself will be able to recover.
But if the patient has forgotten about treating the ulcer, new wounds regularly appear and heal in the area of the duodenum, leaving behind strong scars that can tighten the lumen. Food will not be able to enter the duodenum, and the person’s well-being will deteriorate significantly. In this case, drug treatment will not help; the patient will have to undergo surgery. If the lumen is narrow, but the food bolus passes through it, the doctor may prescribe medications that will relieve the symptoms of the pathology. Then you can do without surgical intervention.
The patient must be properly prepared for the operation. He can undergo gastric lavage, and also be given intravenous medications that will help normalize the water-electrolyte composition, protein balance, restore carbohydrate metabolism, and so on.
Causes and treatment of scar-ulcerative deformation of the duodenal bulb – Gastrology
Cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb is formed in the initial section of the intestine. The disease develops after an ulcer in the place where the wounds were. The disease is characterized by the formation of scars, which can change shape and disrupt the functioning of the bulb.
Most often, an ulcer forms on the bulb, which is located on the border of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract. Scars form during the healing process of wounds. The principle is very similar to the healing of a wound on the human body when a scar is formed.
If duodenal ulcers are poorly treated, the patient may develop scars. Soon, deformation of the duodenal bulb can lead to the formation of a lumen, and food can leave the stomach.
In this case, surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
Scar-ulcerative deformation of the duodenal bulb directly depends on the etiology of the ulcer. There can be many reasons for the development of peptic ulcers:
- poor nutrition;
- stress;
- frequent use of medications;
- bacteria.
A healed duodenal ulcer can form from the same factors. Failure to comply with the course of treatment can also provoke the development of such a disease.
The fact that scarring of the ulcer has begun is indicated by a small number of symptoms. The disease is an asymptomatic illness. It can develop over many years and not show any significant signs.
It is almost impossible to find out that the duodenal bulb has begun to deform. During research and identification of repeated attacks of peptic ulcer, in which new scars are formed, a narrowing of the lumen between the intestines and the stomach becomes noticeable.
However, the disease has some significant symptoms that are a bit similar to those of an ulcer:
- nausea before meals, in the morning and on an empty stomach;
- colic;
- flatulence;
- heartburn;
- constant feeling of hunger;
- there may be bleeding.
Protrusion and deformation of the duodenal bulb
To identify the disease, the doctor prescribes the same examination methods to the patient as for a stomach ulcer. Instrumental methods can help identify affected areas:
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- X-ray of the stomach and duodenum;
- Ultrasound of the stomach.
Additionally, ultrasound of the digestive organs and gallbladder, endoscopic and X-ray examination of the intestines can be performed.
The doctor also resorts to laboratory diagnostic methods. To do this, the patient needs to undergo the following tests:
- blood;
- feces;
- study of hydrochloric acid levels.
A peptic ulcer must be treated, especially if it has begun to heal. The disease can affect all organs, the symptoms will become stronger and malignant tumors may form. Doctors prohibit treating duodenal ulcers with any folk remedies. Therapy can only be prescribed by a doctor, which should consist of medications and diet.
Drug therapy is aimed at protecting the duodenal bulb from hydrochloric acid.
During treatment, the patient needs to adhere to the correct diet. The diet excludes the consumption of spicy, fried and fatty foods, ham, smoked meats, yeast products, and canned food. Doctors advise patients to eat:
- White bread;
- vegetables;
- soups without cabbage;
- cooked meat and fish;
- slimy porridge.
Nutrition for duodenal ulcer
In order for the duodenal ulcer to heal, it is also recommended to consume dairy products - natural cream, cottage cheese, cheese. You can cook an omelet. In case of pathology, you can eat sweet fruits without rough peels.
Duodenal ulcer scars can take a long time to heal, but it is important for the patient to follow all the doctor’s instructions. Otherwise, you may encounter serious complications:
- violation of the digestive system - acid in large doses will enter the intestines, and pancreatic juice and bile from the intestine into the stomach;
- narrowing of the lumen with the formation of obstruction.
If the treatment of a peptic ulcer is successful and correct, then the bulb will not be deformed, and a small scar may form on the organ. Large ulcers can cause tightening of the intestinal walls, which leads to obstruction.
With proper therapy, the healed section of the intestine can return to its original position for several months or a year. If the patient is faced with a severe form of duodenal ulcer, then quick and complete restoration of the organ is impossible.
In order not to encounter cicatricial deformation of the intestinal bulb, a person needs to follow preventive measures that are associated with ulcers and peptic ulcers. If it was not possible to avoid these diseases, then the patient needs:
- listen to the doctor's recommendations;
- undergo timely and correct treatment;
- do not break your diet;
- take medication.
In this case, all ulcers will be able to heal safely, and the peptic ulcer will not progress.
Source:
Why does cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb occur?
Cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb is a condition of the first section of the gastrointestinal tract, which develops as a result of an ulcer located in the above section of the intestine. This condition is characterized by the formation of scars, characterized by the ability to change shape and contribute to a malfunction of the bulb.
1Etiology of the disease
Most often, duodenal ulcers form in the bulb (the border region located between the upper and lower parts of the gastrointestinal tract). The retrobulbar (bulb) areas are affected by ulcers less often.
The reason is that it is in this area that the border between the acidic environment of the stomach and the alkaline environment of the intestine is located.
In case of minor failures, by the beginning of the inflammatory process, a significant part of the acid ends up in the bulb, provoking destructive processes in the mucous membrane, the appearance of erosions and ulcers. In this case, the onion is the very first one to be hit.
What are the causes of scar-ulcerative deformation of the duodenal bulb? During the healing of the ulcer, these parts of the organ recreate a scar, just as scars form on damaged skin as it heals. Similar to this process, after an ulcer, normal healthy tissue cannot be restored and is replaced by a dense “tie” of connective tissue - a scar.
If the wound is poorly healed, festers and the person does not see a doctor, a scar will appear instead, disfiguring the skin. The larger the surface of the affected area, the more serious the consequences of its healing.
This also applies to the retrobulbar formation of the duodenum.
If the patient did not heal the ulcer in a timely manner, allowed relapses to form, did not follow the rules of dietary nutrition, and did not take medications, the worse his duodenum will work, which, in turn, will affect the functional entire gastrointestinal tract.
In complicated forms of development, the pathology of the duodenum over time closes the deformed lumen of this section of the gastrointestinal tract, which prevents the possibility of food leaving the stomach. In such a situation, a crippling surgical intervention to dispose of the site and recreate an artificial intestinal connection cannot be avoided.
2Why is this condition dangerous?
If the ulcer is cured well, then at the site of localization there is a linear defect, insignificant in parameters, which does not affect the functions performed by the organ. With large, poorly treated, numerous ulcers and their recurrences, deformation can develop from a slight tightening of the walls to a state of obstruction.
After several months, in most cases, the duodenal bulb returns to its original state, but in the presence of a complicated form of the disease and the patient refuses to follow a diet or take medications, this does not happen.
This condition is dangerous due to a malfunction of the digestive system. Along with the bulb, the functionality of the pylorus of the stomach deteriorates.
As a result, a significant amount of acid from the organ enters the intestines, and bile and pancreatic juice, on the contrary, in a different direction - into the stomach. Neither one nor the other process should occur in the body.
The result is a malfunction of digestion, the presence of diarrhea, constipation, pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen, and bitter belching.
Source: https://gastrologpro.ru/lechenie/prichiny-i-lechenie-rubtsovo-yazvennoj-deformatsii-lukovitsy-dpk.html
Prevention
Not everyone is ready to undergo surgery, but other treatment for narrowing the lumen will not help. Those who want to avoid surgery should treat the ulcer, since bulb deformation is always a complication of this disease. What exactly should be done?
- Take all medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Avoid heavy physical labor and active sports.
- Walk outdoors more often.
- It is better to avoid stress and take calming pills.
- It is necessary to give up bad habits, that is, do not abuse alcohol, do not smoke.
- Diet is very important. The patient should eat frequently, every 3 hours, eating only warm cooked or steamed foods.
- In autumn and spring, when a recurrence of the disease is possible, be examined by a doctor.
Proper treatment of a duodenal ulcer will help avoid such a serious complication as deformation of the duodenal bulb. It sometimes leads to intestinal obstruction, which the doctor can only cure with surgery. It is worth taking care of yourself even before complications arise, since later it will be difficult to establish normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Even the best doctors cannot yet perform miracles, and no expensive drugs can restore your lost health.
Treatment and prevention
Severe scar damage in the intestine can be eliminated surgically, and relapse can only be prevented with supportive care and regular examinations.
One of the most common types of treatment is to take a drug that neutralizes the acidic environment, thereby preventing it from irritating the intestinal walls. They take medications that stop the production of gastric juice.
Severe deformation of the duodenum can only be treated with surgery. In milder cases, this disease is treated with proper and balanced nutrition, taking the necessary medications, and do not forget about a healthy lifestyle. The main requirement for a therapeutic diet is a temporary refusal of salty, fried, smoked, and too sweet foods. It is recommended to exclude carbonated and alcoholic drinks and quit smoking during treatment. All these foods and bad habits increase gastric secretion, which irritates damaged intestinal walls.
To avoid cicatricial deformation of the duodenum, it is necessary to prevent the development of peptic ulcers. If gastritis or an ulcer is detected, you must immediately consult a doctor and follow his instructions. But the best way out is careful health care, proper nutrition and as little alcohol consumption as possible. After all, the earlier a disease is detected, the easier it is to cure it.
What else to read:
- Symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the duodenum Contents of the article:1 Classification of duodenitis2 Chronic duodenitis2.1 Symptoms2.2 How to treat3 Acute duodenitis4 Consequences5 Prevention Duodenitis - inflammation of the duodenum - occurs quite often, especially in pediatric patients. This……
- Symptoms and treatment of chronic gastroduodenitis in the acute stage Contents of the article:1 About the disease2 Causes of appearance3 Symptoms4 Pain5 Indigestion6 General deterioration of health7 Diagnosis8 Treatment Chronic gastroduodenitis is a disease in which both the mucous membrane of the stomach and...
- Symptoms and treatment of catarrhal duodenitis Contents of the article:1 Causes of the disease2 Symptoms of the disease3 Diagnosis4 Treatment4.1 Drug treatment4.2 Diet4.3 Traditional methods of treatment Catarrhal duodenitis is an acute inflammatory process that affects the mucous membrane of the duodenum…….
Symptoms
How does a duodenal bulb ulcer manifest itself? Its symptoms and treatment are closely related, so it is important to understand which syndrome is prevalent. The clinical phenomena are very intense and cause a lot of inconvenience to the patient.
The very first and main symptom is pain in the umbilical area. It can be either acute or aching, it all depends on the quantity and quality of meals. In addition, at first it is easy to get rid of it by drinking antacids. Sometimes the pain may return at night and radiate to the lower back.
Every ulcer sufferer knows: to get rid of nausea, belching or pain, you just need to have a snack. Preferably something like jelly. But this remedy is not universal, because vomiting can return after eating, “bringing” with it heartburn and a feeling of heaviness as a “bonus”. From time to time, these people suffer from bowel problems in the form of constipation and flatulence.