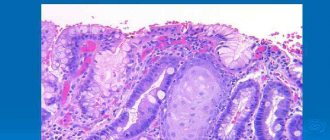
Diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon is a disorder when seals, called hernias, appear on the walls of the intestinal tract. These growths are called diverticula. They can remain in the intestines for many years, but do not show symptoms at all.
If an infection enters the intestinal tract, the diverticula become inflamed—diverticulitis. Formations come in different sizes. It all depends on the stages of formation of the disease. The pathological process is localized in the sigmoid colon - a section of the large intestine. The disease shakes sigma itself. During an exacerbation, the quality of life worsens. Let's analyze the issue of diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon, information about symptoms, treatment of the disease.
Expert opinion
Sevastyanov Roman
General practitioner, hepatologist, gastroenterologist, highest qualification category. Site Expert
Previously, we talked about 5 symptoms of polyps in the intestines, we recommend that you read this information at this link.
Causes of pathology
There are several circumstances under which people develop sigmoid diverticulosis. Let's look at the reasons in more detail:
- Age. When the muscles of the intestinal walls become weak, the process of destruction of the digestive organs begins.
- Weak connective tissues. This phenomenon can be observed at birth or after a failure in the formation of collagen fibers.
- Intestinal motility problems. With high pressure in the cavity of the intestinal tract, the fibers of the walls are weakened, and characteristic compactions appear.
- Muscle spasm. This activates contraction of intestinal vessels and disruption of blood circulation. As a result, the area near the vessels atrophies, and stretch marks appear. As a result, diverticula grow inside the intestinal tract.
- Hereditary character. The threat of getting sick increases a couple of times when elderly family members have difficulties with diverticula.
- Nutrition. Many studies have proven that in African countries, where people have been eating plant foods for a long time, they suffer from diverticulosis much less often than in the West, where meat foods predominate in the diet.
Treatment methods
It is recommended to treat the disease in its early stages. Treatment tactics depend on the course of the disease and its clinical signs.
Treatment of asymptomatic diverticulosis
The asymptomatic course of the disease does not require medical attention. The patient is recommended to follow preventive measures to prevent complications: maintain proper nutrition, include dietary foods rich in fiber, vitamins and minerals in the diet. Gas-forming and fixing products, on the contrary, are excluded.
Drug treatment of uncomplicated forms of the disease
During the period of uncomplicated diverticulosis, accompanied by such manifestations as constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, pain, in addition to diet, the doctor prescribes the use of medications:
| Drug group | Drugs |
| Laxatives | Duphalac Goodluck Romphalac |
| Anti-diarrhea medications | Lopedium Loperamide Silix |
| Painkillers | No-shpa Spazmalgon Drotaverine |
| Drugs to stimulate gastrointestinal motility | Domperidone Motilium |
| Enzyme preparations | Mezim Creon Pancreatin |
| Broad-spectrum antibiotics | Ceftriaxone Ampicillin Amoxicillin |
Drug therapy is prescribed by the attending physician; independent treatment with the use of drugs is strictly prohibited.
Indications for surgery
Treatment with surgery is performed if the following indications exist:
- heavy bleeding in the intestines;
- perforation of the intestinal walls;
- diffuse peritonitis;
- acute intestinal obstruction;
- fistulas, abscesses;
- constant progression of the disease.
In uncomplicated forms of pathology, surgical treatment is performed in the event of a severe decrease in the patient’s quality of life due to existing symptoms of diverticulosis.
The surgical technique depends on the diagnosis of the individual patient. The operation is carried out using a closed or open method and involves removing the affected part of the intestine.
Stages, signs and possible complications
Table of stages of the disease.
| Stages | Description |
| Disease without symptoms | Often the patient does not know about the presence of the disease and only after a random examination for another reason does the doctor discover the pathology. |
| Acute diverticulosis | Distinctive symptoms are spasms of the walls of the sigmoid colon. |
| Complicated disease | The last stage of the disease, which is characterized by a dangerous health condition. Requires immediate medical attention. |
| Diverticulitis | It is formed as diverticula are filled with feces, which creates a suitable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. |
| Peri-intestinal infiltrate | In this case we are talking about inflammation of the peritoneum. |
| Intestinal fistula | Spontaneous detection of an abscess is typical, which leads to the formation of fistulas. With this form, surgery is necessary. Intraintestinal hemorrhage. It occurs due to damage to the intestinal mucosa due to the influence of hardened feces. |
| Diverticulum perforation | When perforation affects the peritoneal area, there is a high probability of peritonitis. |
To notice the disease in its premature stages and begin treatment, you should know the symptoms in full. Let's analyze the signs of the disease:
- Abdominal pain is the main and first criterion for the formation of the disease. It is often missed by doctors, because in the initial stages the pain is not severe and disappears after defecation. Such unhealthy feelings are considered as poor nutrition, short-term disorders.
- As the painful course develops, the pain intensifies, becomes dull or pulling, and is expressed in the form of attacks. The main thing is to focus on the fact that unhealthy feelings are localized closer to the navel on its lower side. After eating, the pain worsens, which should alert you.
- In some cases, unhealthy feelings radiate to the right side of the abdominal cavity. Therefore, pain is often confused with exacerbation of appendicitis.
- The pain disappears after the gas subsides.
- There is also heaviness in the abdomen and bloating.
- Frequent constipation with pain. After constipation, diarrhea begins (lots of mucus).
If you experience regular constipation and pain, even minor ones, you need to visit a doctor.
Clinical picture of the disease
Diverticulosis of the colon occurs in three forms:
- asymptomatic;
- uncomplicated;
- complicated.
The asymptomatic course does not cause discomfort; the person is often unaware of the presence of the disease. Sometimes there are minor stool disorders and mild discomfort during bowel movements. Diverticulosis is discovered accidentally during an examination of the intestines.
With uncomplicated diverticulosis, the symptoms of the disease become more pronounced, spasms, painful sensations in the lower abdomen, periodic stool disorders, and nausea appear. After defecation, there is a feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
The complicated form of diverticulosis is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- Frequent pain in the lower abdomen.
- Alternating diarrhea with constipation.
- Flatulence, rumbling stomach.
- Heat.
- Nausea.
- Internal bleeding.
- Blood in the stool.
The above symptoms serve as a reason for urgent hospitalization and complex treatment of the disease.
Diagnostics
Since the disease does not initially show symptoms, doctors use certain examination methods. Diagnosis of diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon is as follows:
- X-ray examination of the intestinal tract with a barium mixture. As a result, the diverticula become filled and visible;
- Irigoscopy - study to examine the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon;
- Colonoscopy is a process similar to the previous examination, only the mucous membrane of the large intestinal tract is examined.
Complications and consequences
Complications that arise when the diverticulum sac is perforated through the peritoneal wall, peritonitis develops. When a breakthrough occurs in the retroperitoneal region, phlegmon occurs. When it enters the fiber located between the layers of the mesentery of the colon, a paracolic abscess is formed. The breakthrough of purulent abscesses into the abdominal cavity is especially dangerous.
Preventing complications is easier than correcting them. An abscess rupture is fatal. In this situation, urgent hospitalization followed by surgery is indicated.
Stagnation of feces leads to the development of ulcers, erosions, and inflammatory processes. As a result of constipation, rectal cracks may occur. Trying to treat the disease yourself is a direct path to worsening the condition and developing complications. Without a diagnostic examination, it is impossible to detect a damaged part of the colon. Folk remedies for illness can be used only after consultation with a doctor.
We recommend: How to recognize bowel cancer by symptoms
Drugs
Treatment with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory substances is justified for diverticulitis. Conservative therapy, in addition to antibacterial agents, for inflammation, looks like this:
- substances to improve intestinal motility;
- antispasmodics;
- laxatives;
- vitamin complexes;
- medications for hemoglobin growth.
In case of complications in the hospital, medications are administered intravenously, which increases the effectiveness of treatment. Nutrition is administered parenterally, which makes it possible to “rest” the gastrointestinal tract.
Early stage sigmoid diverticulosis can be treated with medication. The main medications on the list are:
| Alpha Normix | An antibiotic belonging to the broad-range group. Presented in the treatment of infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon. Recommendations for use prescribe a dosage of 200 mg for adults and children over the age of twelve years. Reception is carried out every 8 hours. The duration of therapy does not exceed 7 days. The medicine can be taken in a repeated course, but only after a break of a month. Price from 650 rubles. |
| Amoxiclav | Belongs to the group of penicillins. Prescribed for inflammation of the urinary tract, problems with the gastrointestinal mucosa. The dosage is 1 pill. The break between doses is also 8 hours. The dosage is prescribed for adults and children over twelve years of age. Cost from 200 rubles. |
| No-Shpa | Shows a calming effect on spasms of the smooth muscles of the digestive organs. The dosage for an adult is from 120 to 240 mg throughout the day. The drug can be divided into 3 doses. Cost from 50 rubles. |
| Buscopan | Prescribed to relieve spasm of the muscles of internal organs, reduces the secretion of the digestive glands. The instructions for use indicate a dosage of 1-2 pills after meals. Take up to 5 times within 24 hours. Cost from 330 rubles. |
| Duphalac | The drug belongs to the laxative group and is sold in syrup form. Helps with long-term constipation. According to the instructions, you can take from 15 to 45 ml. The medicine does not need to be diluted. Cost from 290 rubles. |
| Domperidone | An antiemetic drug that eliminates the feeling of nausea. The drug alleviates dyspeptic symptoms associated with decreased gastric emptying. Adults and children over five years of age are prescribed 10 mg three times within 24 hours, thirty minutes before meals. |
| Linex | A complex remedy that belongs to the group of drugs that normalize intestinal microflora. Prescribed when the composition of the normal intestinal flora changes. A child over twelve years old and an adult are prescribed two capsules per day. Cost from 250 rubles. |
Intestinal diverticula
Treatment of patients with an uncomplicated form of diverticulosis is carried out in the gastroenterology department, and in case of severe complications - in a surgical hospital. Patients with acute or exacerbation of chronic diverticulitis, intoxication, high fever, severe concomitant pathology, impossibility of enteral nutrition, as well as those over 85 years of age are hospitalized. If there is a clinic with an acute abdomen, an urgent operation is performed.
Conservative treatment
If a patient is accidentally diagnosed with an asymptomatic intestinal diverticulum, no special treatment is required. In the presence of uncomplicated diverticula, a diet rich in fiber, antispasmodics, and prokinetics are prescribed. If all recommendations for treatment of the disease are followed, a lasting clinical effect is usually achieved. If the patient has developed diverticulitis, the use of intestinal antiseptics, antibiotics, and osmotic laxatives is recommended.
To normalize intestinal function, cleansing enemas and uncontrolled use of laxatives should be abandoned. A positive effect is also achieved when moderate physical activity is introduced into the daily routine - they help strengthen the muscular corset of the torso and normalize intestinal motility. To reduce pressure in the intestinal lumen, a diet rich in fiber is prescribed (except for very coarse fibers - pineapples, persimmons, turnips, radishes). The amount of fiber in the diet is increased to 32 g/l. It is necessary to exclude gas-forming foods, legumes, and carbonated drinks. To achieve the desired effect, you should drink at least two liters of water daily.
The use of stimulant laxatives and morphine-based painkillers for diverticula is contraindicated, as they provoke further impairment of intestinal motility and aggravate the course of the disease. To improve the passage of food masses through the intestines, osmotic laxatives are prescribed - they increase the volume of feces and accelerate their movement through the digestive tract. For diarrhea, sorbents and astringents are prescribed, and simethicone preparations are prescribed to relieve flatulence.
Acute diverticulitis requires hospitalization of the patient in a surgical hospital, the appointment of detoxification and plasma replacement agents, and antibacterial drugs. Treatment lasts at least two to three weeks; after discharge from the hospital, maintenance therapy is similar to that carried out for uncomplicated diverticula.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is indicated for the development of life-threatening complications: perforation, abscess formation, intestinal obstruction, profuse bleeding, fistula formation. Also, planned surgery is prescribed for recurrent bleeding and diverticulitis. Usually, a part of the intestine affected by diverticulosis is resected and an anastomosis is performed. In difficult situations, a colostomy is performed to facilitate the outflow of feces, and after stabilization of the condition, reconstructive surgery is performed.
Example of a diet for 7 days
Many gastroenterologists believe that patients with diverticulosis need to follow a separate nutrition method - consume proteins separately from carbohydrates. The body acquires a maximum of nutrients, and the process of digesting food is facilitated. Taking into account the advice of nutritionists and doctors, below is a 7-day diet for patients with diverticulosis of the large intestinal tract. The menu for each day is presented below:
- Monday and Tuesday. It is preferable to eat liquid food (soups with vegetables), fruits, herbal tea.
- Wednesday. During the day - unload the body. You can drink kefir or eat only apples.
- Thursday. Fish day. You can use the broth with not very fatty river or sea fish.
- Friday. You can eat oatmeal or buckwheat porridge. For lunch you can eat boiled meat and pureed vegetables. It is preferable to eat an orange or banana for an afternoon snack. In the evening you can eat a few spoons of lean cottage cheese.
- Saturday. The day starts with a white omelet. A steamer is useful for cooking. It is preferable to season vegetable salad or porridge with vegetable oil. You can have yogurt for dinner.
- Sunday. You can make vegetable soup, bake fish, eat fruits, drink compote.
general description
Diverticular disease of the colon is a chronic disease in which pouch-like protrusions through the muscle layer form in the wall of the large intestine.
The protrusions themselves form in weak spots of the intestinal wall, where blood vessels pass through it. Typically, the size of diverticula varies from 5 to 10 mm. Diverticular disease includes:
- Diverticulosis - the presence of several diverticula in the intestine
- Diverticulitis - inflammation of the diverticulum
The prevalence of the disease among young people is very low - about 2-5%, with obese men most affected. With age, the risk of developing the disease increases and by the age of 70-80 reaches 65%. Up to 70 years of age, the incidence among men prevails over women.
Diagnostic methods
Preliminary diagnosis of diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon is possible only in the presence of characteristic complaints and clinical manifestations. The following studies will help you make an accurate diagnosis:
- Colonoscopy is a visual examination of all parts of the colon through the anus using special optical equipment (fobrocolonoscope or videocolonoscope). Allows you to directly identify diverticula, determine their prevalence and complications. The method is the most reliable of the existing ones.
- Irrigoscopy is the filling of the intestines with a barium suspension (X-ray contrast agent) through the anus in the form of an enema. After this, the person is placed under an X-ray machine and examined. An image of the barium-filled sigmoid colon is displayed on the monitor, which makes it possible to study its structure in detail and detect diverticulosis.
- Laparoscopy is a gentle surgical operation performed through abdominal punctures under anesthesia. It consists of a visual examination of the intestines from the abdominal cavity. It is used in rare cases when other methods are either contraindicated, or there are serious suspicions of inflammatory and suppurative complications requiring surgical treatment.
- Computed tomography is a special study showing the layer-by-layer structure of organs. The method is informative, but is more often used for differential diagnosis of complicated diverticulosis with other clinically similar diseases.
- Laboratory tests - general and biochemical analysis of blood and urine. They are of no value in the diagnosis of uncomplicated diverticula. Informative for determining the activity of inflammatory and suppurative processes as a result of diverticulitis (high leukocytes - more than 12 g/l), as well as diverticular bleeding (decrease in hemoglobin less than 120 g/l and red blood cells).
Ultrasound of the abdomen is a method that cannot diagnose uncomplicated sigmoid diverticulosis. It can be used to determine signs of certain complications and to rule out other diseases.
Diagnosis of diverticulosis - photo gallery
This is how colonoscopy is done - the main method for diagnosing diverticulosis. Laparoscopic surgery This is what the intestine looks like filled with barium during irrigoscopy
Differential diagnosis
Diseases similar in clinical picture to sigma diverticulosis:
- Irritable bowel syndrome;
- colitis;
- gastric bleeding and small intestinal obstruction;
- tumors of the colon and rectum;
- inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs;
- pathology of the pelvic organs in women;
- kidney and bladder diseases.
Therefore, the patient’s symptoms require careful comparison with the potential pathology and targeted implementation of the most informative research methods.
Symptoms of diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon
ICD-10 code: K57
In most patients, diverticulosis occurs without significant symptoms and is detected incidentally during diagnostic tests for other diseases.
Some patients occasionally experience slight discomfort in the left iliac region after eating. Sometimes bloating is accompanied by pain; when the gases are released, the pain and flatulence are relieved.
If inflammation of the intestinal walls occurs, the following symptoms appear:
• increased tempera reaction; • intoxication: nausea and vomiting; • dizziness; • increased abdominal pain.
Going to the toilet does not bring relief.
When a diverticulum ruptures, signs consistent with peritonitis are present. The appearance of blood after defecation indicates damage to the vessels of the sigmoid colon. The more blood is lost, the more severe the anemia, and the less strength remains to fight the disease.
Causes
The main causes of diverticular disease are:
- Dystrophic changes in the muscle wall of the large intestine
- Changes in her motor skills, weakness of the muscle component
- Impaired blood supply to the intestinal wall and the development of atherosclerosis with ischemic changes
Increased intraintestinal pressure due to prolonged spasm, leading to divergence of muscle fibers.
Diverticula are the final manifestation of intestinal wall disease, atrophy and expansion in sloping areas.
There are some prerequisites for the development of diverticula in the colon:
- the presence of an outer muscle layer in the form of three stripes, helping to weaken the intestine before external and internal influences
- the presence of haustra, in which increased intraintestinal pressure is generated