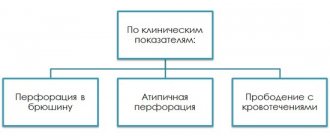
There are no clinical recommendations in oncology for duodenal cancer, but they have been awarded to its anatomically tiny structural part - the duodenal major or papilla of Vater, into which the duct common to bile and pancreatic enzymes opens.
Traditionally, all serious duodenal diseases are automatically considered together with pathologies of the stomach, although the duodenum is the initial part of the intestine, and the duodenum is united with the stomach only by anatomical proximity.
- Anatomy of the duodenum
- Causes of duodenal cancer
- Diagnosis of duodenal cancer
- Stages of duodenal cancer
- Prognosis for duodenal adenocarcinoma
- How does duodenal cancer manifest?
- Treatment of duodenal cancer
Anatomy of the duodenum
The duodenum has one task - to receive the food mass treated with the acid of gastric juice, mix it with bile and pancreatic enzymes to prepare it for entry into the alkaline environment of the intestine.
A horseshoe-like section of the digestive tube is only 12 fingers or fingers long (in diameter), connected to the stomach by a bulb, and the pancreas is tightly adjacent to the duodenum.
The duodenal bulb is so named for its great similarity, and the folds of the mucous membrane are also like those of an onion - from top to bottom, whereas in other parts of the intestine they are predominantly transverse. In the bulb, the acidic gastric secretion mixes with the alkaline intestinal secretion and it is here that ulcers most often arise, and malignant tumors, on the contrary, rarely develop - in every seventh of all those suffering from duodenal carcinomas.
Next is the descending part with the pancreatic papilla and common bile ducts opening into it; bile produced by the liver and aggressive pancreatic enzymes enter this section. In two out of three cases, it is in this part of the duodenum that a malignant process develops.
Next come the horizontal and ascending parts, the frequency of malignant tumors also goes downwards - neoplasms in these sections are quite rare.
Diagnostics
An ulcer of the duodenal bulb is diagnosed quite easily, given that patients seek help from a doctor already at the height of the disease, when discomfort prevents them from living normally.
First, the doctor collects anamnesis and conducts an examination. Of course, palpating the abdomen does not provide much information, but it is possible to suspect, with a high degree of probability, an ulcerative process. Then the patient is sent for a blood test, biochemical markers, a stool test for occult blood, and gastrin levels and Helicobacter pylori activity are determined.
The most common diagnostic procedure remains esophagogastroduodenoscopy, or, more simply, endoscopy. It allows you to examine the mucous membrane of the digestive tube, cauterize all identified ulcers, and take tissue and fluids for examination. Radiography is also informative. Images with contrast will clearly show the location of the ulcers and the condition of the gastric and duodenal mucosa.
Causes of duodenal cancer
It is believed that the causes of the development of a malignant tumor of the duodenum are almost the same as those of stomach cancer; little is known about them either.
- A connection with Helicobacter pylori infection is suspected. Ulcers associated with bacteria in the duodenum are more common - in eight out of ten cases, while in the stomach only in six patients. Peptic ulcer disease affects the duodenal mucosa four times more often than the gastric mucosa. Mostly women suffer from duodenal ulcers, and men suffer from gastric ulcers.
- There has been a connection between duodenal cancer and obesity.
- There is an assumption about the influence of national nutritional characteristics, which has not been proven by statistics.
By and large, there is no clarity about the causes of gastric cancer, much less the root cause of duodenal carcinomas.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Causes
An ulcer of the duodenal bulb occurs due to the corrosive effect of hydrochloric acid (which is part of the digestive juice) on the mucous membrane of the small intestine. There are several reasons that cause an increase in acidity:
- excessive release of gastrin (a hormone that regulates digestion);
- passion for spicy, bitter, salty, sour, fried and fatty foods;
- insufficient food intake during the day and overeating in the evenings;
- long-term use of hormonal or anti-inflammatory drugs;
- regular exposure to stress;
- smoking and drinking alcohol, especially on an empty stomach.
In rare cases, the appearance of erosions and ulcers in the duodenum may be associated with an increase in calcium levels in the body, decreased liver and kidney function, and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases.
Diagnosis of duodenal cancer
Malignant neoplasms are rightly classified as diseases of aging; the vast majority of patients have already celebrated their 65th birthday; in women, the process occurs 5–10 years later.
Russian oncology statistics about duodenal carcinoma are silent; no one knows the number of cases and does not analyze the characteristics of patients by stage at the time of detection. Things are no better abroad.
How to check the duodenum for cancer? The same as for the stomach - do an FGDS or fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy. During gastroscopy for any gastric problem, the duodenum must be examined, and a biopsy is taken from suspicious areas. In case of pathology of the biliary tract and pancreas, the duodenum is also examined first.
Comprehensive diagnostics are very effective - a combination of endoscopy with ultrasound or endosonography, which allows you to see the entire thickness of the intestinal wall.
X-ray examination is also available in different projections - polypositional with contrast. CT scan perfectly reveals pathology, but laparoscopy, unlike gastric carcinoma, is not always used, but only in advanced stages.
A small area of the digestive tract is not easy to examine even with a very good endoscope, since opaque bile is constantly injected and the intestine is in constant motion, but this is done perfectly by specialists from the European Clinic, who have accumulated experience in examining patients for years.
Stages of duodenal cancer
In the overwhelming majority, mucous adenocarcinoma develops in the duodenal wall; anatomical features make it possible to diagnose it in the early stages.
Staging is based on the degree of involvement of the intestinal wall in the malignant process and the presence of metastases in the lymphatic collector:
- Tumor within the mucous membrane - stage 1;
- Neoplasm within the wall with metastasis to the lymph nodes near the organ - stage 2;
- Cancer of the intestinal wall grows into the abdominal cavity and involves nearby anatomical structures - stage 3;
- With any size of tumor lesion of the duodenal wall, the appearance of metastases in other organs - stage 4 is unconditionally established.
How does duodenal cancer manifest?
Signs of early cancer are subtle and do not differ from the symptoms of any other gastric disease:
- strange discomfort
- vague pain in the epigastric region unrelated to meals,
- occasional nausea
- periodic flatulence.
Usually, those who have been suffering from various “indigestion” of the gastrointestinal tract for a long time mistake these symptoms for an exacerbation of chronic gastritis, colitis or peptic ulcer - anything but a malignant tumor.
Clinical manifestations of a neoplasm in the duodenum in most cases are caused by a narrowing or complete closure of the lumen of the digestive tube:
- When the tumor is localized in the initial section, the symptoms of stenosis of the gastric outlet come to the fore: constant overfilling and overdistension of it with stagnant food, vomiting of recently eaten food.
- When carcinoma is located in the descending part, the first symptom may be obstructive jaundice due to blocking the outflow of bile through the common duct, as well as clinical signs of acute pancreatitis.
- If the lower part of the duodenum is affected or there is complete obstruction of the intestinal lumen at any level, a clinic of intestinal obstruction can develop: a progressively worsening condition with foul-smelling vomiting and absence of stool for more than 3 days, increasing intoxication.
- Invasion of the entire thickness of the intestinal wall can manifest itself as bleeding with black diarrhea and brown vomiting against a background of progressive weakness.
- Involvement of the pancreas in the tumor conglomerate will be complicated by severe pain, similar to the symptoms of acute pancreatitis.
- In the metastatic stage, symptoms reflect the localization of lesions in organs and tissues, with parallel progressive weight loss and increasing weakness.
Symptoms
How does a duodenal bulb ulcer manifest itself? Its symptoms and treatment are closely related, so it is important to understand which syndrome is prevalent. The clinical phenomena are very intense and cause a lot of inconvenience to the patient.
The very first and main symptom is pain in the umbilical area. It can be either acute or aching, it all depends on the quantity and quality of meals. In addition, at first it is easy to get rid of it by drinking antacids. Sometimes the pain may return at night and radiate to the lower back.
Every ulcer sufferer knows: to get rid of nausea, belching or pain, you just need to have a snack. Preferably something like jelly. But this remedy is not universal, because vomiting can return after eating, “bringing” with it heartburn and a feeling of heaviness as a “bonus”. From time to time, these people suffer from bowel problems in the form of constipation and flatulence.
Treatment of duodenal cancer
Radical treatment includes surgery to remove the affected duodenal segment with adjacent tissues - gastropancreatoduodenectomy or complete removal of the entire organ - pancreatoduodenectomy.
In all situations, together with the duodenum, the outlet of the stomach, the head of the pancreas with the tissue where the lymph nodes are located, are removed as a single block.
In case of initial jaundice, at the first stage, with the help of palliative surgery, the outflow of bile is restored and active “washing” is carried out with droppers, and only when the condition and biochemical parameters of the blood are normalized, special treatment is started - surgery or chemotherapy for technically impossible surgical intervention.
The standard treatment for duodenal adenocarcinoma has not been developed, so they focus on the therapeutic approach for stomach cancer, so in case of questionable operability, several courses of chemotherapy are carried out with the inclusion of fluorouracil and a platinum derivative.
There is no evidence of the absolute effectiveness of preventive chemotherapy after surgery for stages 2–3; however, for poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma or a large lesion, such treatment is possible, but not earlier than 6–8 weeks after surgery when the wound has completely healed.
Duodenal cancer is not a rare cancer with an incidence of one to two in a million, but researchers have not paid enough attention to it and have not developed a standard approach that gives the best outcome for the vast majority of patients.
For each patient with duodenal carcinoma, a personal treatment program is developed taking into account everything known about the morphology of cancer, therefore attention to detail and excellent knowledge of scientific material is required, which is the absolute norm of clinical practice for our clinic.
| More information about treatment at the European Clinic: | |
| Oncologist-gastroenterologist | 5100 rub. |
| Chemotherapy appointment | 6900 rub. |
| Emergency oncology care | from 11000 rub. |
| Palliative care in Moscow | from 40200 per day |
| Radiologist consultation | 10500 rub. |
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78