The pancreas is an important organ of the body. It has an endocrine and exocrine part that produces insulin and digestive enzymes. Diseases of the pancreas cause malfunctions that lead to serious problems. Bend of the pancreas may be a normal variant or a manifestation of the disease. Having detected a change in the shape of the pancreas, a detailed examination is necessary. If a disease is detected, the necessary treatment will be required.
The pancreas is involved in metabolism and digestion
Form
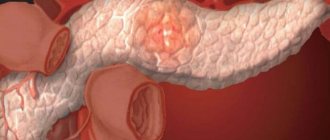
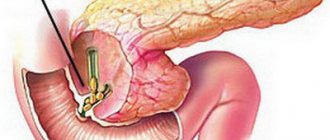
The pancreas consists of 3 main parts: head, body and tail. It has an elongated, curved shape. It is located on the posterior wall of the peritoneum, partially located in the left hypochondrium. Most of the gland is exocrine. The smaller part is represented by pancreatic islets - endocrine glands.
The shape of the pancreas can change throughout a person's life. The child is characterized by a natural curve and even has a wedge-shaped appearance. In an adult, it takes on a more elongated shape, maintaining a slight natural curvature. Pathological is the enlargement of the organ and the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms. In this case, a diagnosis is carried out and the cause of the manifestation is determined.
It is important to know! When the pancreas is damaged, pain and poor digestion often occur. Having noticed such symptoms, a person should consult a doctor for a full examination.
Diet for pancreatic disease
When it comes to pancreatic dysfunction in a child, the first thing parents should do is normalize the diet. Here are some basic principles of diet during illness:
- You should eat food in small portions. The interval between doses is at least four hours;
- It is necessary to exclude from the diet any foods that “irritate” the pancreas: fatty, spicy foods, concentrated juices, chocolate, fast food. It is recommended to boil or steam the products and serve them in crushed form;
- you need to avoid extremes and not oversaturate the menu exclusively with protein dishes. It is important to maintain balance by making your diet varied and including carbohydrate foods.
Before starting self-medication, it is strongly recommended to consult your doctor! This way you can more accurately determine the diagnosis and only then take appropriate measures.
Deformation
A bend is not a pathology if there are no symptoms. If only a bend was detected through hardware examination, the doctor will advise you to adhere to preventive standards and undergo the examination again after a certain period of time.
The most accessible and informative research method is ultrasound.
It will be necessary to treat the pathology if a hidden disease is detected. Based on the research carried out, a diagnosis is made, then a scheme for influencing the disease is drawn up.
Why is the pancreas deformed in adults and children?
Among the reasons for deformation are:
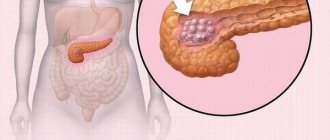
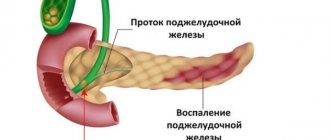
- inflammatory process (pancreatitis);
- cystic formation;
- tumor formation.
If, along with the deformation, there are characteristic changes and symptoms of the disease, an in-depth study is required. Pancreatitis can lead to severe modification of the pancreas due to inflammation and insufficient outflow of enzymes. The formation of a cancerous tumor leads to tissue degeneration. The cyst leads to uncharacteristic deformation.
Note! Sometimes the doctor prescribes several additional examinations.
The appearance of pancreatic deformation in adults and children may be normal. In some cases, the curvature appears and later disappears on its own. This often happens in childhood, so don’t start panicking right away.
Bend or bend of an organ - what's the difference?
In medicine, the term bending of the pancreas is practically not used, because it can change its shape while remaining fully functional. In most cases, symptoms of bending in a child are completely absent. If the doctor speaks of a bend, this may mean that the organ has taken an unnatural position. If the deformed pancreas affects neighboring organs, preventing it from working, it is necessary to prevent the development of complications.
Causes of the disease
Bend of the gallbladder: clearly
The reasons that can cause organ deformation are varied. Depending on the cause of the disease, symptoms of a bent gallbladder appear, and appropriate therapy is prescribed. Deformation of the bladder can be caused by various diseases of the organ, in particular, cholecystitis in acute or chronic form, cholelithiasis, etc. The inflammation accompanying the disease covers the outer wall of the organ and leads to the appearance of adhesions, which deform the organ.
Often, a kinked bladder is a congenital disease. In this case, they are not talking about pathology, but about the unusual shape of the organ. As a rule, congenital inflection of the bladder does not lead to disruption of its functions and digestion in general and is diagnosed accidentally during an ultrasound or x-ray examination of the abdominal organs for some other reason.
Often sudden movements or heavy lifting lead to a short twisting or bending of the bubble along its axis. In the vast majority of cases, such painful conditions are asymptomatic. Most often, they are diagnosed in older people who have severe prolapse of internal organs, an enlarged gallbladder, and the presence of stones in it. It is extremely rare that, as a result of strong physical exertion or heavy lifting, the bladder twists around its axis several times. This leads to impaired blood circulation in the organ, the appearance of cracks in its walls and the outpouring of bile into the abdominal cavity. This condition, accompanied by acute pain and a sharp deterioration in health, requires emergency medical attention.
In children, as well as elderly people, the bending of the gallbladder is caused by poor nutrition and excess body weight. Excess fat is deposited on the walls of internal organs, including the walls of the gallbladder, which can lead to deformation of the organ.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
You can understand the state of the pancreas using hardware methods. The most common:
- ultrasonography;
- radiography;
- computed tomography.
The doctor selects specific diagnostic methods.
To obtain a complete picture, you will need to take a number of laboratory tests: blood, feces, urine. A general biochemical blood test will reveal the inflammatory process and estimate the amount of enzymes in the blood. Using a coprogram, the state of digestion is assessed. The presence of fats and fatty acids in the stool indicates that a small amount of pancreatic enzymes enter the intestines.
Helpful information! Using ultrasound and CT, you can understand whether there are deviations in the size and shape of the gland, and identify diffuse tissue changes.
Why is the pancreas deformed in children?
In children, the pancreas is at risk of developing all kinds of serious diseases that can appear due to genetic predisposition, poor or irregular nutrition, as well as many other reasons.
The pancreas can often become deformed when a disease occurs, such as chronic pancreatitis or acute pancreatitis in children.
If a violation is detected in the location of an internal organ, this does not at all indicate the presence of a disease. Meanwhile, the child requires a full examination to prevent the possible development of a particular disease.
In any case, changes in the pancreas in children should be a cause for concern. After the doctor examines the patient and identifies the true cause of the deformation of the internal organ, the child is prescribed the necessary treatment.
The pancreas in children can become deformed either with a displacement to the side or without a change in location. Most often, modification of the internal organ occurs in conjunction with an enlargement of the pancreas.
The effectiveness and speed of treatment of the disease in a child depends on how early the abnormal shape of the organ was detected.
If a child has a bend in the pancreas, there is no need to worry, since this is a temporary phenomenon that is age-related. It is necessary to carefully monitor the child’s nutrition in order to protect him from the development of any diseases, and carefully monitor the functioning of the digestive system. In case of any deviations, you should consult a doctor.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=vRu40lzXJYc
Forms of chronic pancreatitis are classified according to etiological factors, morphological characteristics, clinical manifestations, functional characteristics and condition, as well as phases.
There is no single generally accepted classification of chronic pathology. Some doctors make a diagnosis in accordance with the forms of A. S. Loginov, other medical specialists use the international Marseille-Roman classification.
In accordance with the ICD (International Classification of Diseases), chronic pancreatitis exists under code K86.0, which implies an alcoholic origin of the pathological process.
Code K86.1 includes other types of sluggish disease - infectious origin, recurrent form, etc.
Treatment of the disease
Symptoms and treatment are closely related to each other. Therapy begins after a person consults a doctor with complaints or a pathology is accidentally discovered during a routine examination. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of the disease. After normalization of the condition, the pancreas will take its usual shape. For treatment, medications, proper diet, and food enzymes are used.
Medicines
Drug treatment is used for acute and chronic lesions. If a doctor has diagnosed a person with pancreatitis, the following classes of medications may be needed:
- painkillers;
- enzyme agents;
- inhibitors of proteolytic enzymes.
Your doctor will be able to draw up a specific treatment regimen. The specific medicine, dosage, and duration of use are selected individually. If pancreatitis is not treated in time, it can seriously deform the pancreas.
Phytotherapy
The use of herbal medicine is advisable if the pathology is not serious. It can improve digestion and relieve inflammation of the gland. This way you can treat the identified bend. The following herbal remedies are used:
- Rosehip infusion. Pour 20 g of rose hips into 150 ml of boiling water. Drink the resulting infusion throughout the day, dividing it into 3-4 doses. Rose hips reduce the severity of inflammation, strengthen the immune system, and supply the body with vitamins.
- St. John's wort decoction. Pour a tablespoon of dry St. John's wort into 300 ml of boiling water. Then continue boiling for 5 minutes. St. John's wort is taken 1-2 times a day before meals in small quantities. Helps relieve inflammation and pain.
The ingredients are purchased at the pharmacy.
Before using herbal medicine, consult with the treating gastroenterologist.
Symptoms of the disease
In most cases, a bend in the pancreas does not cause any unpleasant symptoms. It is worth emphasizing that people often confuse the bend of the pancreas and the gall bladder. The bend of the second may be a congenital feature that is not a disease and does not cause much discomfort.
However, if the bubble is twisted several times along its axis, the child, like an adult, may experience the following symptoms:
- cutting pain in the abdomen;
- rapid breathing;
- increased salivation;
- vomiting and nausea;
- gastric reflux, which can cause erosion and duodenal ulcers.
Diet during illness
To achieve a pronounced result, you need to adhere to a special diet, which includes:
- exclusion of alcohol, fatty, fried, salted, smoked foods;
- fractional meals 5-6 times a day;
- eating steamed food.
The diet should be as light as possible.
To quickly normalize digestion, you need to start using specialized enzymes.
Forms of indolent pancreatitis
The disease can be primary or secondary. In the first case, the abnormal process begins directly in the pancreas. In the second option, the pathology is diagnosed due to diseases of nearby internal organs - the gallbladder, stomach, etc.
The causes of the primary disease include alcohol dependence, genetic predisposition, drug intoxication, long-term smoking, constant stress and neuroses.
The etiology of the secondary disease is caused by pathologies of the gallbladder (cholecystitis with the formation of stones), cirrhosis of the liver, chronic forms of hepatitis, parasitic diseases, cystic fibrosis (a congenital disease accompanied by damage to the exocrine glands).
According to Loginov, depending on the clinic, chronic pancreatitis can be:
- Recurrent form. This disease is characterized by periods of relapse of the disease, which are followed by periods of remission.
- The painful form is accompanied by constant painful sensations.
- Pseudotumor form. The main clinical sign is obstructive jaundice.
- Painless or latent form. Exocrine insufficiency is most often diagnosed, and intrasecretory insufficiency is somewhat less common.
- Sclerosing pancreatitis. This disease is accompanied by severe failure of the internal organ and develops along with other pathologies.
In accordance with the Marseille-Roman classification, the disease is of the following types:
- Calcifying form. The disease occurs with the development of protein plugs or stones in the gland ducts. It is observed in approximately 50-85% of all clinical pictures. In turn, it is divided into subgroups. In the first case, regular solid crystals are formed, the etiology is due to bad eating habits and alcohol intoxication. In the second option, soft stones, formation is based on heredity.
- Obstructive pancreatitis is accompanied by obstruction of the pancreatic ducts or a tumor.
- Inflammatory form. There is fibrosis of the gland.
- Pseudocysts or true cysts (cystic form).
In accordance with Loginov’s classification, sluggish pancreatitis has several degrees of severity - mild, moderate and severe.
Treatment methods
Therapy for DP includes medications, conservative methods and surgery. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the child should be treated in a hospital under the supervision of doctors. The duration of hospitalization depends on the degree of damage to the digestive system. After discharge, parents are given recommendations, compliance with which will help prevent repeated attacks of the inflammatory process. Some alternative medicines are allowed to be used as an addition to primary therapy.
Conservative treatment
The goal of conservative treatment of DP is to provide the affected organ with functional rest, relieve symptoms of inflammation and eliminate the causes of its occurrence. During the therapy period, measures are taken to prevent chemical or mechanical effects on the digestive tract. On the first day, the child is recommended to take a “food break” (fasting for two to three days). It is allowed to drink alkaline mineral waters without gas. Nutrition begins on the third day with gentle foods and small portions.
Other conservative treatment measures:
- intravenous administration of glucose solutions and proteolytic enzyme blockers (Contrical);
- bed rest and complete rest of the body;
- fasting for 48 hours after hospitalization.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy for DP is carried out not only to relieve the symptoms of the disease, but also to improve the functional state of the digestive system. Drugs are selected individually. If there are complications, the treatment regimen is supplemented with antibiotics. In hospital settings, most medications are prescribed to children by injection.
You can take tablet medications only after restoring your diet.
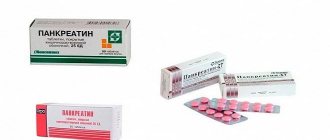
Examples of drugs for the treatment of DP:
- antisecretory agents (Famotidine, Pirenzepine);
- antispasmodics and analgesics (Papaverine, No-shpa, Analgin, Baralgin);
- antihistamines;
- means for improving microcirculation (Pentoxifylline);
- pancreatic enzyme preparations (Pancreatin);
- antibiotics;
- protease inhibitors (Pentoxyl).
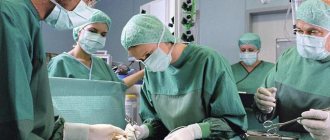
Surgery
Surgical intervention is used in the presence of serious complications of DP and the failure of other treatment methods. Surgeries may involve resection of part of the affected organ, drainage of an abscess in tissue, or removal of a necrotic area. Surgical procedures are radical measures and in the treatment of children they are used only if there is a threat to the life of the small patient.
Disease severity
The chronic form can constantly recur, which leads to an exacerbation of the pathological process. Inflammation can lead to severe organ failure in a short period of time.
With a long-term disease, irreversible changes are observed in the organ, leading to complete dysfunction of it. In medical practice, the disease is divided depending on the severity.
The initial (first stage) lasts no more than ten years. It is characterized by long periods of remission, however, no less long periods of exacerbation. The pain at this stage is wandering, most often the pain syndrome is localized on the left hypochondrium. Dyspeptic syndrome after treatment is completely leveled.
Subsequently, the disease progresses. Signs of exocrine insufficiency are observed; they are intense. The pain syndrome decreases slightly, but doctors note that this is bad, since new foci of inflammatory processes form in the pancreas.
In severe forms of the pathological process, various complications develop. There is severe pain; usually painkillers do not help relieve them. The stability of the dyspeptic syndrome is noted.
Complications arise (according to Ivashkin’s classification):
- The flow of bile is disrupted.
- Portal form of hypertension.
- Infectious abscesses.
- Inflammatory transformations - cysts, cholecystitis, acute form of renal failure, bleeding in the stomach, etc.
- Endocrine disorders: pancreatic diabetes mellitus, hypoglycemia.
The likelihood of developing pancreatic cancer in patients diagnosed with chronic pancreatitis increases significantly.
Methods for treating deformity
Treatment for bending of the pancreas depends on the presence of the diseases that provoked it. These pathologies are treated first. The inflammatory process is stopped by therapeutic agents, oncologists are involved in the presence of tumors, and in case of injuries, compression and the development of intestinal obstruction, they turn to surgeons.
Timely treatment of the most common cause of bending - pancreatitis - can quickly restore the normal position of the organ. For this purpose, the following medications are prescribed:
- antispasmodics;
- antibacterial agents;
- painkillers;
- antienzyme drugs.
Physiotherapeutic measures are used in the treatment of pancreatitis. During the acute stage, children and adults are prescribed to drink warm mineral still water. The amount of fluid taken is controlled by the doctor. After a few weeks, physical therapy is prescribed for:
- eliminating spasms;
- normalization of pancreatic juice secretion;
- relieving inflammation;
- normalization of blood circulation in affected areas of the organ;
- establishing gastrointestinal motility.
The following procedures will be effective:
- electrophoresis using novocaine and antispasmodics, therapeutic mud;
- Ultrasound therapy pulses: restore gastric secretion and have a good analgesic effect.
Find out how to plan a diet for intestinal pain.
What is childhood pancreatitis?
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory-dystrophic lesion of the pancreas. A distinctive feature of the disease in childhood is its mild symptoms, which resemble other diseases of the digestive tract. Pathology develops against the background of the active influence of pancreatic enzymes (a kind of self-destruction of the organ occurs).
Provoking factors include dietary errors, some chronic diseases of the digestive tract and the consequences of infectious processes.
At what age can the disease appear?
Symptoms of pancreatitis can appear in children from a very early age, but preschoolers and schoolchildren are at particular risk. This factor is associated with the diversity of diet and errors in it.
Symptomatic picture
Symptoms of bending of the pancreas are absent or mild. Often this pathological process is confused with a bend in the gallbladder. But this is not true, because deformation of the pancreas can be congenital.
If the bend of the pancreas in a child is accompanied by severe curvature or compression of the duodenum, then the first signs will begin to appear in the form of:
- strong painful feeling in the abdominal area. The pain can be sharp, sharp, aching or dull;
- rapid breathing;
- gastric reflux. This process can lead to the formation of ulcers on the stomach and intestinal walls;
- nausea and vomiting;
- strong secretion of saliva.
Some patients report pain and cramping after eating. Others complain of heartburn and belching of sour matter or air. In most cases, constipation is observed, since when the pancreas bends, the function of the pancreas is partially limited.
Clinical picture
Symptoms during bending appear only in the case of organic tissue damage with the development of permanent deformation. With a bend of the pancreas that is functional (non-pathological) in nature, no signs of disease are observed.
Type of organ with pancreatitis
The main reason for the development of deformity is chronic pancreatitis, which is the outcome of an acute process of inflammation in the tissues of the gland. Therefore, parents should be alert to the appearance of symptoms such as:
- sharp pain in the left hypochondrium, side or around the navel (in small children), sometimes of a girdling nature;
- irradiation (spread) of pain to the lumbar region, under the shoulder blade;
- nausea;
- uncontrollable repeated vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
- flatulence;
- bowel dysfunction (diarrhea, constipation or their alternation);
- local tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
With congenital pathology of the organ, symptoms appear from birth and are manifested by the following conditions:
- poor weight gain;
- frequent, profuse regurgitation, unrelated to neurological diseases;
- admixture of bile in vomit;
- baby's anxiety;
- sluggish breast or pacifier sucking, refusal to feed;
- bloating;
- meconium ileus in the neonatal period;
- large stools with a lot of fat;
- prolonged jaundice;
- respiratory pathology.
With a ring-shaped head of the pancreas, signs of high intestinal obstruction may occur. In this case, on the first day there appears abundant regurgitation with an admixture of bile (green), bloating of the upper abdomen, and absence of peristaltic sounds in the intestines.
Prevention methods
It is almost impossible to prevent the development of congenital deformation of the pancreas, since it occurs at the stage of embryonic development in the first months of pregnancy.
The expectant mother should eat right, lead an active lifestyle and forget about smoking, drinking alcohol, and medications that affect the fetus. Chronic infections should be identified and treated before conception.
Considering the fact that pancreatitis is the main cause of structural changes in the gland, it is necessary to prevent this disease in a child. To do this, parents can carry out the following activities:
- Timely identify and treat diseases of the digestive tract, liver and biliary tract.
- Exclude fatty, spicy and fried foods, “stall” food from your diet, and limit your consumption of fast food.
- Organize diet and complementary feeding in accordance with age.
- Vaccinate the child according to the vaccination schedule and according to epidemic indications.
- Prevent infection by viruses, bacteria, parasites.
Functional curves arise due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the child’s body; they cannot be prevented and, apart from dynamic observation, no action is required.
You can find out about drugs for the treatment of pancreatitis in children here...
Source of the article: https://lechigastrit.ru/podzheludochnaya-zheleza/patologii/zagib-u-rebyonka.html