General information
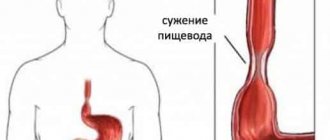
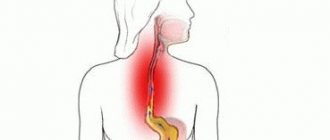
Gastroptosis is a prolapse of the pyloric part of the stomach or its lesser curvature.
Less common is prolapse of the entire organ. The pathology can be congenital or acquired. The disease mainly affects young women. Most often, gastroptosis occurs in patients aged 15 to 45 years, however, the pathology can also be diagnosed in older age groups. The predisposition to the disease in the fairer sex is associated with excessive thinness, frequent diets, childbirth with subsequent sprain of the ligaments and muscles of the abdominal wall. In males, gastroptosis develops when lifting heavy objects with improper load distribution and poor physical activity. Prolapse of the stomach can be easily corrected with massage sessions, therapeutic exercises and other conservative methods.
Symptoms
The initial stage of gastroptosis may not be manifested by a deterioration in well-being - the disease occurs in a latent form. The following symptoms should alert you:
- frequent heartburn;
- problems with bowel movements;
- loss of appetite and sudden change in taste;
- constant flatulence - rumbling in the stomach and bloating;
- frequent nausea and vomiting.
In some patients, food preferences and eating habits also change. Suddenly a person feels a craving for spicy and salty foods. In this case, they visit a doctor for diagnostics - the condition cannot be ignored.
With the development of the disease and the transition of gastroptosis to stage 3, the following occur:
- symptoms of vitamin deficiency: pale and dry skin, cracks in the corners of the mouth, frequent colds, constant fatigue and apathy, bleeding from the gums while brushing teeth, exacerbation of chronic ailments (fungal infections, psoriasis, herpes);
- belching with a rotten smell;
- painful sensations in the abdominal area and intensification of the symptom during sudden movements;
- increased diarrhea and constipation, which replace each other.
It is noteworthy that even at the last stage of the disease, the pain goes away as soon as the patient assumes a lying position. As a result, he loses the ability to carry out normal work activities, and sometimes just move around.
This condition affects the mental health of the patient, so signs of neurosis appear:
- dizziness;
- irritability;
- increased heart rate;
- attacks of fear or apathy.
During the development of gastroptosis, signs characteristic of one sex or another appear. The stomach puts pressure on neighboring organs: in women - on the uterus, and in men - on the bladder and prostate gland (on the anus). As a result, the following manifestations arise:
- increased frequency of urination in men;
- increased pain during menstruation in women.
Causes
Congenital gastroptosis is formed as a result of the specific structure of the body:
- high growth;
- asthenic body type;
- hereditary weakness of the ligamentous apparatus.
Most often, prolapse of the distal stomach is associated with elongation of the mesentery of the large intestine, which is connected to the gastric ligament apparatus. The intestine sinks down due to the mesentery being too long and pulls the stomach with it. Hereditary gastroptosis is characterized by some features:
- long fingers and limbs;
- high growth;
- lack of weight;
- narrow chest.
Reasons provoking the development of acquired gastroptosis:
- sudden weight loss;
- sudden loss of fluid after ascites ;
- removal of large tumors from the abdominal cavity.
Gastroptosis is often diagnosed in women in the postpartum period, which is explained by overstretching and weakening of the ligamentous apparatus and muscle corset during pregnancy. Prolapse of internal organs, including the stomach, is observed in many diseases that are accompanied by cachexia .
The condition of the diaphragm, which sinks down during massive pleurisy, neoplasms of the respiratory system and other lung diseases caused by increased pressure in the abdominal cavity, is important.
Causes of illness in men and women
Gastroptosis, depending on its origin, is classified into:
- congenital;
- acquired.
The congenital disease is observed in the patient from birth. This pathology is dictated by the anatomical characteristics of a person.
The main causes of this form of gastroptosis may be:
- pathological ligament laxity;
- natural thinness and insignificant volume of muscle tissue;
- excessively tall;
- abnormally elongated intestinal mesentery, which pulls down the stomach.
Acquired pathology is formed in a person under the influence of certain factors.
Heavy, unhealthy foods and overeating can lead to the development of gastroptosis.
The development of the disease can lead to:
- surgical interventions in the peritoneum;
- sudden weight loss (for example, due to excessive dieting);
- addiction to soda;
- constant overeating, abuse of heavy food;
- elimination of ascites (fluid accumulated in the peritoneum);
- pregnancy, frequent childbirth (especially those accompanied by various difficulties);
- disease of neighboring organs (pleurisy, emphysema);
- severe physical exertion and injuries to the ligamentous apparatus or muscle tissue.
Symptoms of gastroptosis
Clinical manifestations depend on the degree of gastric prolapse.
At the initial stage, patients do not show any complaints. Vivid clinical symptoms appear with pronounced prolapse of the organ. The main symptoms of prolapsed stomach:
- pain in the epigastric region that appears immediately after eating;
- discomfort in the stomach after physical activity, jumping, running.
The pain syndrome is associated with overstretching of the stomach and a change in the process of movement of the food bolus through the digestive tract. The pain is aching, dull in nature and can radiate behind the sternum, simulating pain in the heart. When the abdomen is pulled up and the body is in a horizontal position, the pain syndrome is relieved.
Clinical symptoms can be caused not only by the manifestation of gastroptosis , but also by concomitant damage to internal organs. With severe gastroptosis, an inflection of the duodenum is formed, which significantly complicates the passage of a bolus of food through the intestine. Patients complain of belching, constipation, and nausea. Prolapse of the stomach may be accompanied by hepatoptosis and enteroptosis .
Gastroptosis prognosis
With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable. If therapy for gastroptosis is not carried out, the disease continues to progress, the stomach begins to put pressure on the intestines, which also shifts and begins to put pressure on the prostate in men, the uterus in women, which leads to the appearance of new unpleasant symptoms and a further deterioration in the patient’s quality of life.
In addition, the consequences of gastroptosis can be:
- weakening of the motor and secretory functions of the stomach;
- slowing down the movement of the food coma through the gastrointestinal tract;
- development of stomach and intestinal cancer.
Tests and diagnostics
Gastroptosis can be suspected already upon examination based on a number of external signs. Patients experience sagging abdomen, laxity of the anterior abdominal wall, and lack of weight. Patients complain of fatigue, fatigue, and have an asthenic body type . Palpation determines the downward displacement of the borders of the stomach; in more advanced cases, the fundus of the stomach may descend into the small pelvis.
- FGDS . The study allows you to evaluate the peristalsis of the stomach and diagnose the expansion of its cavity. Normally, the stomach has the shape of a fishhook, but with gastroptosis it lengthens and takes a vertical position.
- R-graphy of the abdominal wall organs . Gastroptosis may not be detected by plain X-ray of the stomach. Only an X-ray with contrast can reveal prolapse, expansion and elongation of the stomach, diagnose a decrease in its motility and a change in its normal position. The injected contrast agent cannot be retained by the walls of the stomach, falls into its lower part and accumulates there. Gastric motility is significantly reduced, evacuation of contents is slowed down.
- Electrogastrography . The study allows you to confirm gastric hypotension.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs . The ultrasound research method is considered informative only for the pathology of other organs located in the abdominal cavity.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you suspect a pathology, you should contact a gastroenterologist.
- when interviewing and examining the patient, the doctor will reveal weight loss, flabbiness of the abdomen, and sagging; displacement of the stomach can be determined even by palpation;
- EGD will help to see a change in the shape of the stomach, its lengthening, decreased motility, and establish increased acidity of the environment;
- X-rays with a contrast solution will clarify the diagnosis: the contrast agent accumulates at the bottom of the stomach and lingers there for a long time, without moving towards the intestines;
- Ultrasound is prescribed if an abnormal condition is suspected in other abdominal organs at the same time.
Diet for gastroptosis
Diet for indigestion
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 20 days
- Terms: from 2 months or more
- Cost of products: 1400-1500 rubles. in Week
Meals during gastroptosis should be frequent and in small portions, which avoids overstretching the walls of the stomach. It is recommended to maintain a horizontal position for 1.5-2 hours after eating. Nutritionists help patients select the optimal therapeutic diet in each specific case. The main goal of diet therapy is to provide the body with all the necessary microelements and vitamins , as well as restore normal body weight. Correct eating habits formed during a relapse of the disease allow you to avoid exacerbations throughout your life.
Treatment of gastroptosis
Stages 1, 2 and 3 gastric prolapse cannot be corrected surgically. It is impossible to surgically influence the cause of the disease - weakening of the muscle corset. The effectiveness of therapeutic procedures depends on the behavior and lifestyle of the person himself.
Nutrition
- When diagnosing this pathology, it is necessary to often eat in small portions so as not to further stretch the stomach;
- A large amount of fiber is introduced into the diet: whole grain products, vegetable dishes;
- After eating, rest is recommended: lie down for one and a half to two hours;
- Food should be satisfying and easily digestible; A nutritionist will tell you how to restore normal body weight and restore the balance of vitamins and microelements in the body.
Physical training
- In order to train the diaphragm and adjacent muscles, breathing exercises are shown: before going to bed, while lying in bed, breathe deeply - inhale as deeply as possible and exhale the same.
- Therapeutic gymnastics is first performed under the guidance of a specialist, then you can move on to independent training. To help your stomach move into the correct position, do the exercises while lying on your back with your legs elevated. Gymnastics aims to strengthen the abdominal and core muscles. They keep the internal organs at the required level, so physical therapy should be done daily in sufficient quantities to eliminate the possibility of the disease returning.
- Please note: heavy physical activity and carrying bags are strictly contraindicated!
Medicines
To restore the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, drugs that increase appetite, herbal laxatives, gastric juice substitutes, and anabolic hormones are prescribed.
Physiotherapy
- Professional massage plays a significant role in recovery: light circular massage movements lasting a few minutes, which a specialist performs after physical exercise. In the future, you can switch to self-massage.
- Treatment of third-degree gastroptosis is also facilitated by wearing a special bandage, which is worn while lying on your back.
- An excellent way is sanatorium-resort treatment: therapeutic showers, various water procedures, mineral baths.
Prognosis and prevention
With gastroptosis, the prognosis is considered favorable. Early training of children in gymnastics, swimming and other moderate exercises is considered the best prevention of pathology. Before planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to strengthen the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. During pregnancy you need to wear a special bandage. It is recommended to completely avoid vigorous physical activity. If the patient’s work involves heavy physical labor, then it is necessary to switch to easier work.
Prevention of displacement of internal organs
The pathology in question can be corrected if all recommendations are followed, bed rest is avoided, and an active lifestyle is not associated with excessive stress.
The main preventive measures are:
- moderate sports training already in childhood - morning exercises, swimming, outdoor games;
- expectant mothers should consider including abdominal exercises in their daily schedule, and during pregnancy do not refuse to wear a bandage;
- Hiking is good in the fresh air for any age;
- adherence to diet; it is necessary to exclude overeating - eat 5-6 times a day, but little by little;
- visiting a massage therapist;
- try to lead a measured lifestyle: eat on time, go to bed on time, do not overwork.
Remember the dangers of increased loads - consider your capabilities!
List of sources
- Stepanov N.P., Ivanov A.I., Tobokhov A.V., Nikolaev V.N., Sleptsov V.D. “Diagnostics and surgical correction of gastroptosis”, article in the journal “Clinical Medicine”
- Shulgai A.M., Kabakova A.B., Klim L.A., Glushko K.T. “The problem of gastroptosis as a manifestation of undifferentiated connective tissue dysplasia in the practice of a pediatric gastroenterologist,” article in the journal “Clinical Medicine”
- Plechev V.V., Latypov R.Z. “Pancreatobiliary complications in gastroptosis”, article in the journal “Clinical Medicine”
Treatment methods for gostroptosis
Doctors prefer to treat the first and second degree of the disease with conservative methods. In this case, medications play a secondary role. Their task is to relieve symptoms. Such drugs as Mezim, Maalox, Motilium cope well with this.
In case of the third degree of the disease, more serious drugs are prescribed:
- Bixadol to combat diarrhea.
- Drotaverine and No-shpu to eliminate intestinal spasms.
- Papaverine to stimulate gastric secretion.
Since patients often have a disturbance in their psycho-emotional state, they are prescribed sedatives.
Folk remedies can be used as maintenance therapy, but they must be pre-approved by the attending physician.
Herbs such as St. John's wort infusion, tea collection from centaury and dandelion root give a good effect.
For the first and second degrees of gastroptosis, the main emphasis is on physiotherapy, diet and special physical exercises. It is impossible to cure the disease with exercise alone, but it can stop its progression.
Physiotherapy
At first, all exercises for gastroptosis are performed in a lying position. This avoids unnecessary stress on the digestive organs.
The following exercises are considered the most effective:
- The patient should lie on his back and place a small object, such as a book, on his stomach slightly above the navel. It is needed to control breathing. Next, the patient must breathe using the diaphragm. If the book on your stomach lowers and rises in time with your breathing, then the exercise is performed correctly.
- The man lies on his back. Legs extended, arms at your sides. You need to lift your limbs one by one.
- Raise your legs to a height of 15 cm while inhaling. Lowering while exhaling.
- Bend your legs at the knee as you inhale and press them to your stomach with your hands as you exhale. After a 5 second delay, return to the starting position. The exercise should be repeated at least 5 times alternately with each leg.
- The patient pedals an imaginary bicycle while lying on his back.
After completing the first course of therapeutic exercises, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition. If positive dynamics are observed, the patient is allowed to move on to exercises in a standing position:
- Step in place with high knees for 1 minute.
- Raising your arms while simultaneously moving one leg to the side.
- Turn the body left and right while fixing the position for 10 seconds.
All exercises should be performed at least 5-7 times in one approach. After training, you need to lie down for at least 30 minutes to give your body a rest.
Diet food
Eating with a prolapsed stomach should not be plentiful. Food should be taken in small portions and often. This avoids the feeling of hunger and at the same time does not burden the digestive system. After each meal you should lie down for at least 30 minutes.
The diet for gastroptosis should include the following products:
- Boiled meat.
- Fresh and stewed vegetables.
- Fruit purees and fresh fruits.
- Dairy products.
The patient will have to give up seasonings, spices, white bread, semolina and rice. You will also need to exclude fatty and spicy foods.
Surgical intervention in the treatment of gastroptosis is considered undesirable. However, when other treatments fail to stabilize the patient's condition, doctors are forced to return the stomach to its anatomically correct position using a scalpel.
After surgical treatment, the patient must strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending physician, otherwise he will face a relapse of the disease.
Tibetan medicine distinguishes three constitutions: “Bile”, “Wind” and “Mucus”.
Gastroptosis occurs differently in each constitution. In people with the “Wind” constitution, it is often congenital due to an asthenic physique, nervous system, and the stomach takes on an elongated shape. Bile may develop complications such as ulcers, hot-type diabetes, the stomach can be more regular in shape, horizontally located. In mucus, it can stretch to the shape of a bag.
At Naran, gastroptosis is treated comprehensively, i.e. We use massage, acupuncture, moxotherapy, Tibetan cupping and herbal remedies.
Treatment with herbal remedies is completely harmless and safe, since they consist only of natural ingredients, do not cause any allergies and are very effective. The preparations “Shiser” and “Sembru” improve digestion, intestinal motility, not only the stomach, but also the intestines rise, and their functioning improves.
“Pills-Qi” are also suitable for improving the functioning of the digestive system; they work to improve the tone of the stomach, its ligaments, and work energetically, i.e. raise Qi energy (life energy). We recommend combining them with herbal preparations, for example, a decoction that eliminates indigestion “Baikal Collection No. 7” improves digestion, stomach function, it eliminates indigestion, especially in those with the Mucus constitution, since their stomach sinks, turns into a shapeless bag and does not work well. It is useful to combine this collection with Tibetan collection No. 46 “Mucus” (morning collection), Tibetan Collection No. 47 “Bile” (day collection) and Tibetan collection No. 48 “Wind” (evening collection), regardless of the bodily constitution, to maintain health and improving the condition in general.
You can purchase the fees at any Naran clinic located in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Kazan and Yekaterinburg, or in the online store naranfito.ru.
Clinical picture
In most cases, G. of the first and second degrees is asymptomatic. Some patients complain of a feeling of heaviness, bloating, and fullness in the epigastric region, especially after a heavy meal; dull aching pain in the epigastrium, less often in the lower back, which decreases with the patient lying down. Sometimes short-term transient abdominal pain occurs while running or jumping. Frequent complaints are nausea, loss of appetite, and constipation.
Patients with constitutional G. often present complaints of a neurotic nature.
When examining persons with acquired G., a saggy abdomen is noted; when pulled up, the pain often decreases or disappears, and sometimes the outline of the stomach is visible. G. can be determined by palpation of the pylorus and the greater curvature of the stomach according to the method of V.P. Obraztsov; with a large prolapse, the lesser curvature is also palpated in the form of a fold lying deep on the spine or to the left of it at the level or below the navel.