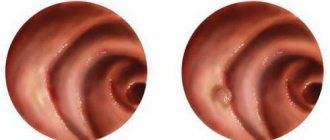
What is an esophageal ulcer
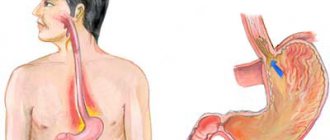
To digest food, the stomach produces hydrochloric acid, which creates an environment that is aggressive to the esophagus. It destroys the walls of the esophagus and leads to the formation of a hiatal hernia. Under the influence of gastric juice entering the lower section of the hollow tube, irritation of the mucous structures occurs. An esophageal ulcer is a disease that is characterized by an open wound on the surface of the organ. The disease causes pain and discomfort to the patient.
Damage to the organ develops in the lower and upper parts of the hollow tube. It can be single or multiple. Wounds appear on the walls of the esophagus under the aggressive influence of gastric juice, which enters the esophagus in small quantities. The lesion is chronic, recurrent and periodically worsens.
The disease can occur due to alcohol abuse, smoking and other negative factors. Bad habits have a direct impact on the development of the lesion. A hiatal hernia develops and the disease becomes chronic.
Description and types
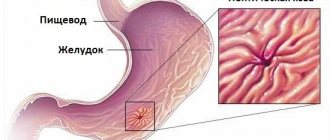
An esophageal ulcer is a defect that forms when the mucous layer of the organ is corroded by acidic gastric juice. In this case, mucous, submucosal and muscle tissues are affected. Patients complain of pain and difficulty swallowing, and feel a lump in the throat. If left untreated, narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus or stenosis may occur (when swallowing food becomes difficult or completely impossible). In addition, tumors may occur due to congestion or compression of the walls of the esophagus.
An esophageal ulcer can be:
- acute form, which forms in the postoperative period or in diseases with frequent vomiting;
- a chronic form that occurs against the background of other organic and systemic pathologies.
There are single and multiple mucosal defects. There are two main types of this pathology:
- Peptic ulcer of the esophagus . It is formed against the background of the reflux of active aggressive enzymes (pepsin, hydrochloric acid) into the esophagus. Usually observed in men over 45 years of age and adolescents 13–15 years of age. Smoking, drinking alcohol, diaphragmatic hernia, and gastroesophageal reflux can provoke or accelerate the development of an ulcerative process. The disease manifests itself in periodic attacks.
- Symptomatic esophageal ulcer . It is formed when the mucous membrane is injured, for example, by surgical instruments during surgery, by long-term use of certain medications, or by the development of a tumor that compresses the walls of the organ.
Types of ulcers
The disease associated with displacement of the esophageal ring can be acute or chronic and localized in any part of the esophagus. As a rule, the appearance of a wound is accompanied by a peptic ulcer of the stomach and intestines. To develop an esophageal ulcer, it is enough to eat poorly or suffer from chronic stomach diseases.
There are two types of organ ulcers:
- peptic;
- symptomatic.
Defects in the mucous membrane can be quite deep. The formation of a hole in the wall of the esophagus is associated with the irritating effect of gastric juice. The wound is accompanied by various unpleasant symptoms and requires treatment.
Peptic
The etiology of peptic ulcers is associated with the expansion of the esophageal ring and the appearance of a hiatal hernia. Under the influence of intra-abdominal pressure, some part of the esophagus moves into the chest cavity, resulting in the formation of a hernia.
The disease can also cause a small amount of gastric juice to reflux into the esophagus. If the walls of the esophagus are normal, then there is nothing dangerous in reflux esophagitis. However, if the protection of the walls is impaired, the mucous membrane of the esophagus suffers. Low tone of the organ develops, blood supply to cells is disrupted, and the condition of the inner surface of the esophagus worsens. Sometimes a peptic ulcer develops due to increased acidity of gastric juice.
Symptomatic
Pathology of this type is accompanied by various stagnation phenomena. The lesion compresses the walls of the esophagus, resulting in painful sensations. A symptomatic ulcer can be caused by taking medicinal herbs - this pathology is regarded by doctors as a side effect of taking herbal decoctions.
Often, a symptomatic ulcer is caused by stress, acute stomach irritation, or chronic disease of the digestive organs.
Important! Often, with a peptic ulcer, a protrusion of part of the esophagus develops, in which food stagnates. The pathology requires urgent medical intervention.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of esophageal ulcers is carried out both inpatient and outpatient. It includes:
- diet therapy;
- drug therapy;
- If conservative treatment is ineffective or in case of complications, surgical treatment is performed.
Drug therapy
When treating esophageal ulcers, clinical guidelines include:
- work and rest schedule, with a full night's sleep; you need to sleep with the head of the bed raised and avoid stressful situations in every possible way;
- give up cigarettes and alcohol;
- You should not wear tight clothes with tight belts;
- avoid physical and mental fatigue;
- avoid stress on the abdominals.
Drug therapy for ulcers of the esophagus and stomach is very similar, it includes:
- Antacid drugs (tablets, gels, suspensions) that reduce the destructive effect of H+ ions on the organ mucosa (Maalox, Gastal, Phosphalugel, Vikair).
- Antisecretory drugs that increase the pH of gastric juice PPI (Omez, Razo, Controloc) and IGR (Kvamatel, Zantac).
- Prokinetics are medications that accelerate the release of food from the stomach, eliminate congestion, and increase the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter (Ganaton, Motilium).
- If H. Pylori, the causative agent of gastric ulcer, is detected, treatment is carried out with antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Metronidaeol, Amoxiclav, Clarithromycin).
- Sedatives (Valerian, Motherwort, antipsychotics)
- Vitamin complexes (Triovit).
Diet therapy
You need to eat regularly, in small portions. Avoid hyperphagia. Diets No. 1 a and No. 1 b according to Pevzner are prescribed. Individual adjustments to these diets for a given patient are prescribed by the attending physician. Foods that reduce sphincter tone and irritate the mucous membrane should be excluded from the menu.
Food for peptic ulcers of the esophagus should be steamed or boiled.
How to treat peptic ulcer of the esophagus with folk remedies
All traditional medicine can be taken only after consulting a doctor. Only known herbs can be used at home.
| Main Ingredient | Action | Cooking method | Taking the drug |
| Plantain leaves | Anti-inflammatory, healing. It is used only in the remission stage, as it lowers the pH of gastric juice. | Pour boiling water over it, dry it, grind it in a blender and squeeze out the juice, add honey to the juice and boil for 15 minutes. | Drink syrup 30 minutes before meals |
| Potato | Increases the pH of gastric juice, relieves inflammation, stimulates gastrointestinal motility | Squeeze the juice | Take 1 glass of freshly squeezed juice in the morning 30 minutes before meals. |
| Aloe | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, aseptic, regenerating effect | Mix aloe juice, honey, chopped walnuts in equal proportions | Take one teaspoon in the morning before meals |
| Althea | Enveloping, anti-inflammatory, healing effect | Marshmallow root + licorice + comfrey: take the raw material in equal parts, pour 1 spoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water and cook for 5 minutes | Take before bed |
| Propolis | Reduces stomach acidity, relieves spasms, heals ulcers, reduces inflammation | Add 30 drops of propolis to a quarter glass of water | Drink a freshly prepared solution an hour before meals |
Symptoms
Manifestations of the symptomatic form of the disease are accompanied by chest pain and difficulty swallowing. When diagnosing an esophageal ulcer, symptoms and treatment are of particular importance.
As the disease develops, complications and consequences are possible; prevention of symptoms of the disease should be aimed at preventing dangerous processes. Heartburn and vomiting with blood may indicate a serious condition of the patient.
Damage to the walls of the organ is often accompanied by vomiting of acidic stomach contents. It is impossible not to pay attention to such a symptom.
Signs of peptic ulcers
Symptoms of the lesion usually occur immediately after eating. The mucous membrane is irritated by an ulcer of the esophagus; therefore, symptoms are expressed after food and gastric juice enter the mucous membrane of the organ.
The main signs of pathology are:
- frequent belching;
- painful sensations;
- heartburn;
- regurgitation of stomach contents.
The disease is also characterized by a burning sensation in the chest and discomfort in the upper chest. Signs of a hernia include a night cough, tightness in the center of the chest, and a feeling of a lump in the throat. The patient does not tolerate ulcerative lesions well; the symptoms of an esophageal ulcer and signs of the disease cause general weakness and loss of appetite.
Manifestation of the symptomatic form of the disease
The most commonly diagnosed symptoms of esophageal ulcers include nausea and heartburn. Severe discomfort develops in the epigastric zone. In some clinical cases, eating is so difficult that the sick person often chokes and coughs. Often, sour belching turns into vomiting.
Important! Chest pain is a common symptom of esophageal ulcers. It can radiate to the left area of the scapula and provoke a heart attack.
The symptoms of reflux, hiatal hernia and ulcers are very similar. Only a thorough diagnosis will allow you to recognize an accurate diagnosis, so do not delay your visit to the doctor.
Causes
The following situations can be considered as the main factors influencing the formation of esophageal ulcers:
- The formation of a hernia in the diaphragmatic opening, in which, thanks to the opening at the bottom of the esophagus and cardia, which is a muscular ring, stomach tissue penetrates into the chest.
- Reflux with repeated reflux of hydrochloric acid into the esophagus, which causes irritation.
- Insufficient functioning of the cardium with disturbances during the closure of the ring separating the esophagus and stomach.
- Weak gastric motility with a simultaneous increase in the tone of the pylorus, formed from circular muscle tissue in the section of the intestine at the junction with the stomach. This condition causes a lump of undigested food, but with acid, to be thrown back into the food tube.
- Lesions that form in the stomach or intestines.
- The probable cause of the development of ulcers in the esophagus are bad habits, such as smoking, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, and in doses exceeding the norm.
- The factor that contributes to the development of pathology in the esophagus is often a systemic type of scleroderma, expressed in thickening and decreased elasticity of connective tissues.
Not least important in the causes of the formation of ulcerative lesions in the esophagus are causes of a neurotic nature caused by brain injuries or diseases developing in it.
The following conditions can be considered the causes of various forms of esophageal ulcers:
- Stagnant ulcers occur with the development of various types of neoplasms, which can be benign or malignant in nature and, by their appearance, put pressure on the walls of the esophagus.
- Drug-induced ulcers are formed as a result of long-term use of certain medications.
- Neurotrophic or stress ulcers begin to appear under the influence of terminal conditions as a result of severe injuries, with extensive and deeply penetrating burns, serious pathological conditions in various organs, and be the result of fungal infections. In comparison with other species, they are capable of exhibiting particularly pronounced symptoms and are distinguished by the severe nature of the disease, as well as more frequent complications in the form of bleeding or perforation.
- A hypoxic ulcer occurs against the background of diseases and is often hidden behind their symptoms.
- Decubital types of ulcers form in older people at the time of bacterial infection, in the postoperative period, as well as in the event of injury to the mucous membrane with a probe during this type of feeding.
In addition, it has been noted that medicinal types of ulcers at a younger age occur without prior damage to the esophagus. Their appearance is associated with the direct irritating effect of the drug itself on the mucous membrane or the effect of an intermediate substance released during the breakdown of this drug.
Stages of disease development
There are several stages in the development of the disease:
- At the initial stage, a small wound is formed on the mucous membrane of the organ, and erosive changes in the surface of the walls occur. The lesion at the initial stage of the disease is superficial.
- The second stage of the pathology is characterized by scattered wounds and swelling of the walls of the organ. The pathology continues to develop in the thickness of the mucous membrane.
- At the third stage, swelling and inflammation become larger. The mucous membrane is destroyed and turns red.
- The mucous membrane is covered with numerous ulcers. They are observed to bleed.
The most dangerous are stages 1 and 2 of the disease. The situation requires urgent medical intervention. Risks of bleeding develop. In the last stages of the disease, the organ narrows and shrinks in size. Deformation of the esophagus occurs.
Stages of the disease
According to the classification of the disease, the patient has 4 stages of the disease.
| Stage | Signs |
| 1st | Characterized by superficial damage to the mucous membrane. However, there is already swelling and redness. The surface begins to ulcerate. |
| 2nd | Ulceration progresses. The number of ulcers increases. The bottom of the esophageal tube and the upper edematous folds in the ulcers. |
| 3rd | Ulcers are found in large numbers. It is possible for them to merge with each other. The surface of the mucosa has a pronounced red color, there is obvious swelling. |
| 4th | There is not only ulceration of the affected areas of the mucous membrane of the esophageal tube, but also ulcerative bleeding. |
Diagnostics
Esophagoscopy and radiography are the main diagnostic methods used in pathology. Modern gastroenterology provides many opportunities for identifying a diagnosis; diagnostics in gastroenterology and endoscopy make it possible to clarify the location of the lesion and its features.
A common diagnostic method is endoscopy. A special diagnostic device is inserted into the esophagus and the condition of the organ’s mucosa is examined. To perform a biopsy, a piece of biomaterial is taken and sent to the laboratory. The purpose of the study is to identify the nature of tumors and cancer.
To determine the functioning of the digestive system, stool analysis is performed. The nature of feces confirms or excludes dehydration and indicates the digestibility of food. With different infections, stool will vary significantly.
Prevention
In order to prevent the formation of ulcers in the esophagus, you should follow the usual recommendations for such conditions:
- see a gastroenterologist and be examined by him at least once a year;
- do not ignore the slightest signals of trouble in the gastrointestinal tract;
- adhere to a proper diet;
- do not have late dinners;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- avoid stressful conditions;
- promptly eliminate diseases that may result in damage to the esophagus.
It is unacceptable to delay a visit to a gastroenterologist and ignore any, even minor, symptoms of the disease. The prognosis for esophageal ulcers is considered favorable provided that you seek medical help in a timely manner.
Treatment
Treatment of ulcers of the esophagus is long and difficult - it is necessary to strengthen the healing process, correct digestion, and restore the functions of the organ. An integrated approach to the treatment of the disease is highly effective.
Competent drug regimens help:
- eliminate nausea;
- improve the production of juice in the stomach;
- prevent the development of complications;
- stabilize stomach acidity.
The fight against the disease includes various techniques and methods. In particularly dangerous situations, surgery is prescribed.
Drug therapy
A qualified doctor will tell you how to treat ulcers of the esophagus. You should consult a specialist if you feel constant burning, pain and discomfort in your chest. The doctor will select the optimal drug regimen depending on the specifics of the diagnosis.
The following are prescribed in therapy:
- proton pump inhibitors;
- antacid drugs;
- prokinetics.
Among the medications, the most commonly prescribed are Almagel, Omeprazole or Omez, Noflux. The action of the drugs is aimed at improving the functions of the organ and neutralizing the aggressive environment in the stomach. Also, with the help of medications, the functions of the cardiac sphincter are stabilized. To normalize digestion, Bismofalk, Ventrisol and their analogues are prescribed.
Important! If the disease progresses, do not postpone your visit to the doctor. Wall perforation and bleeding may occur.
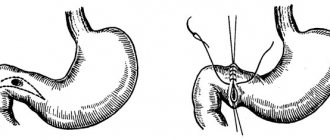
Surgical methods
The operation is indicated for deep damage to the mucous membrane. It is carried out if previous treatment with medications did not give the desired positive result. The ulcer and lesion are removed by a surgeon under general anesthesia. The essence of the operation is to completely eliminate the pathological focus.
The recovery period after surgery can take 6-8 months. At this time, it is necessary to strictly adhere to medical recommendations.
Diet and lifestyle normalization
In the treatment of stomach ulcers, diet therapy cannot be avoided. The diet should be gentle on the esophageal mucosa and exclude foods that irritate its surface. Various sodas, herbs and spices, fried foods and smoked foods must be excluded.
Meals for ulcers should be fractional - that is, the daily amount of food should be taken in small portions throughout the day. Drinks such as coffee and lemonade are excluded. Solid foods in the form of crackers, biscuits, and cookies are prohibited. You should also not eat citrus fruits, which irritate the organ mucosa.
Nutrition for illness resembles the diet for gastritis, when nothing spicy, salty, sweet, or smoked is allowed. The use of well-cooked porridges is recommended - oatmeal, buckwheat, semolina.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine recipes will become a reliable assistant in the fight against the disease. The following recipes will help eliminate pathology:
- Aloe leaves need to be pre-cooled in the refrigerator, then grind them in a meat grinder. The mixture is poured with honey and after 3 days a glass of red wine. Take the product for 2 months, 1-2 tablespoons on an empty stomach.
- Take 2 tablespoons of chopped cherry twigs and brew them with boiling water. The product is infused, after which 60 ml of the product are taken.
- A mixture of propolis and vegetable oil heals the affected mucous membrane well. The ingredients should be mixed and kept in a water bath for 15 minutes. Then the product is cooled and taken 1 tbsp. spoon on an empty stomach.
It is better to coordinate the choice of folk remedies in advance with your doctor. Consulting a specialist in the traditional treatment of the disease will help you avoid mistakes.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of esophageal ulcers involves not only taking medications, but also strictly following a diet. In most cases, the diet will need to be followed for life. This is especially true for older people.
Initially, the intestines are cleansed of toxins and other harmful substances. The procedure must be carried out if the patient has the following symptoms:
- unstable stool;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- bloating;
- unhealthy skin color.
This clinical picture indicates that the process of intoxication of the body has begun. This is dangerous because the poisons produced can spread throughout the body. This can lead to other diseases.
The procedure for cleansing the intestines is carried out using colon hydrotherapy. In some cases, the patient may be prescribed therapeutic fasting so that the body is completely cleansed.
Drug therapy involves taking drugs with the following spectrum of action:
- antacids;
- alginides;
- bismuth preparations;
- prokinetics.
If the patient experiences severe pain, a painkiller is prescribed.
Treatment of esophageal ulcers should be carried out comprehensively. In the event that general therapy does not bring the desired result, the disease is treated surgically.
Possible complications
In particularly difficult situations of the development of the disease, the question often concerns life and death. In severe situations, holes may appear in the walls of the esophagus. This condition requires their immediate removal by surgery. After surgery, if the recovery period is unfavorable, bleeding may occur.
Under the influence of hydrochloric acid, the disease can worsen. In the chronic form, pathological changes in organic structures spread to neighboring internal organs. It is necessary to monitor the ulcer constantly and strictly follow all doctor’s recommendations and take the necessary medications.
Surgery
The main indications for surgical intervention are the presence of the following conditions:
- ineffectiveness of the therapy;
- presence of complications;
- threat of malignancy of the ulcer with transition to a malignant state;
- formation of a stricture with severely narrowed areas of the esophagus;
- formation of an esophageal type of ulcer, accompanied by persistent reflux.
Before surgery, patients with uncomplicated esophageal ulcers are usually treated with an intensive course of therapy to reduce the size of the affected area and eliminate swelling of the surrounding tissues. The most favorable period for surgery is the moment of scarring of the ulcer, as this avoids the possibility of developing postoperative complications.
Preventive measures
- Much attention should be paid to a healthy lifestyle and your diet. Eating healthy foods and avoiding fast foods and spices will reduce the load on the esophagus. Following the rules of a healthy diet will help eliminate the occurrence of an aggressive environment for the organ and normalize gastric secretion. It is recommended to have dinner a couple of hours before going to bed. This measure will allow you not to overload the stomach and intestines during the night's rest.
- It is important to completely eliminate bad habits. Smoking and alcohol include harmful compounds that constantly irritate the mucous membranes of internal organs. Alcohol and cigarette abuse contributes to the development of many gastrointestinal diseases. As a result, the secretion of the stomach is disrupted, its environment becomes more aggressive for the esophageal tube.
- It is important to avoid psycho-emotional tension and stress. The release of hormones into the blood contributes to the creation of unfavorable factors for the development of various diseases. You need to bring yourself into inner balance.
- At the same time, it is important to get rid of chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines. Stabilizing health and improving the functionality of the body contributes to longevity and the elimination of pathologies with the stomach and esophageal tube.
- It is important to undergo regular preventive examinations with a gastroenterologist and follow his instructions. The doctor assesses the condition of the mucous membrane of the organ and will be the first to notice destructive changes in the organic walls.
Treatment of the disease must be entrusted to a specialist. An esophageal tube ulcer is a disease that requires close medical attention and some effort on the part of the patient.
Diet
The diet for esophageal ulcers is intended to eliminate the symptoms of the disease, heal damage to the mucosa and prevent relapses. Such results prevent the development of other complications and improve the quality of life of patients. The basic principle of the diet is to eat small meals frequently. Depending on the condition of the esophagus, various types of diets are prescribed in the form of a standard diet, a diet for exacerbations and a diet that must be followed during periods of remission. When choosing dishes for such patients, it is necessary to take into account their maximum gentle effect, both chemical, with weak stimulation of secretion, and mechanical - with the exception of products that have an irritating effect. The method of preparing the finished dish also matters.
The most gentle effect is achieved by consuming only slimy soups, boiled porridges, jellies and jelly with the addition of honey, milk, pureed cottage cheese, eggs in the form of an omelet or soft-boiled. Meat and poultry are used only in the form of cutlets or as minced meat. As your condition improves, more complex dishes from the main menu may be added.
Symptoms of the disease
As the disease progresses, the following signs may be observed:
- General weakness;
- Belching, heartburn, nausea (may even be vomiting);
- Abdominal pain, bloating, irregular bowel movements;
- Chest pain;
- Difficulty passing food through the esophagus;
- Unhealthy skin color;
- Increased temperature (usually at night).
In addition to the above signs, an asymptomatic course of the disease may well occur. With this development of the disease, there may be no signs. Here diagnosis is difficult.
Symptoms of esophageal ulceration
The reasons for the formation of the disease determine all manifestations of peptic ulcer disease. So, if the basis of the disease lies in the reflux process, then before the main disorder is identified, the patient develops heartburn, which intensifies after meals and in case of violations of the dietary regime.
This is how the esophagus gives a signal about the presence of a destructive factor, as a result of which the function of the organ is distorted. In a normal state, an alkaline environment is established in the esophageal tube, and gastric juice entering it disrupts the alkalinity, which negatively affects the natural protective barriers of the organ. Thus, with long-term and systematic exposure, the organ becomes ulcerated.
The presence of the following symptoms makes it possible to doubt the normal state of the esophagus:
- Pain in the chest area, often of a burning nature. Usually begins to bother after eating. There are frequent cases of pain attacks at night, as well as pain that appears as a result of little activity immediately after eating;
- Dyspepsia;
- Belching with a sour taste;
- Regurgitation;
- Heartburn that occurs spontaneously or during physical activity;
- Vomiting or direct vomiting, sometimes with bloody impurities;
- Possibility of regurgitation in case of stenosis.
For your information! There are so-called “silent” signs of esophageal ulceration. In these cases there are no symptoms. Only sometimes does the patient feel symptoms of heartburn when bending over the upper body or while lying down (during the reflux of hydrochloric acid into the esophageal cavity). An illness may be hidden behind the manifestations of another disease process, and in such cases, the symptoms of other diseases come first.
If the patient suffers from the disease for a long period of time, the ulcers may heal, forming scars. Scarring narrows the diameter of the esophagus (stenosis) and deforms the organ. In these cases, patients often experience the phenomenon of regurgitation of undigested foods. In certain cases, the following symptoms are added to the listed symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- the occurrence of weakness;
- feeling of constant nausea.
For your information! So how can you determine that the cause of pain is the esophagus? Pain that signals the presence of pathology in this hollow organ almost always occurs in response to eating or fasting, when gastric juice is already secreted and hydrochloric acid begins to affect the walls of the esophageal tube.
ethnoscience
Treatment of esophageal ulcers with folk remedies also demonstrates a pronounced effect. However, the traditional method of therapy and folk recipes must be used in combination.
In search of a solution to how to treat such an ailment, people tried various methods, and here are some of them that have gained the most popularity:
- Potato juice. It should be drunk raw and on an empty stomach. It has alkaline properties and thereby promotes tissue regeneration. The course of treatment should be at least one and a half months.
- Flax seeds. This recipe is actively used in the treatment of esophagitis and its complications. Just pour a teaspoon of seeds into a glass of hot water and then strain. The resulting mucous decoction gently envelops the affected areas and quickly relieves inflammation.
- Propolis. This beekeeping product has pronounced healing properties. It is recommended to mix the thoroughly crushed substance with olive oil in a ratio of 40g/500 ml and heat it in a water bath. Take a tablespoon before meals.
Note: Vinilin, or Polivinox balm, which was previously actively used to treat esophageal ulcers and other erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, turned out to be undeservedly forgotten. It creates a protective film on the damaged surface and has a powerful bactericidal, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect.
In conclusion, it should be noted that the prognosis of this disease is considered favorable. If you follow the prescribed recommendations, visible improvement will occur within 2-4 weeks. To avoid relapses of the disease, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right and support your immune system by taking vitamins.
Treatment of stomach ulcers
Diet
Treatment of this problem takes place in several steps. And all these steps are very significant. If you miss even one, it is unlikely that a person will be able to recover. You must not interrupt treatment, because there is not much time, the disease is progressing every day.
The main step towards a healthy esophagus is diet. The diet is compiled by gastroenterologists, but basically it is almost the same.
You need to stop eating fatty, fried and too much food. Drinking coffee and any carbonated water is also prohibited. Under no circumstances should you eat dry food in the form of crackers. There is also a categorical ban on all citrus fruits.
Diet also determines the nature of nutrition. Food should be taken about five times a day in small portions. You can't eat before bed. It is forbidden to eat in a lying position, and you should not lie down immediately after eating.
The diet for esophageal ulcers is almost the same as the diet for involuntary regurgitation disease. Both diseases are global problems for the human gastrointestinal tract, so it is necessary to be treated. There is no time to break down and eat everything. A long time without treatment will gradually kill a person, the disease will begin to progress and give the person a reason to die.
Doctors do not advise resorting to folk remedies for this problem. This treatment involves taking any natural components internally. Doing this is strictly prohibited, because one or another “natural drug” will irritate the esophagus and deepen the ulcerative scar.
Only a doctor can cure such a problem and nothing more, so you need to contact him immediately and not waste time on dubious traditional medicine.
Alcohol occupies a special place in the diet. It is strictly forbidden to consume ethyl drinks. In this case, it is better not to drink even in small quantities, there will be fewer problems. Alcohol with its ethyl alcohol will irritate the gastrointestinal tract, which will lead to exacerbation of ulcers. And in the future, ulcerative scars will form much more actively.
Medicines
The next step on the road to recovery is to take the right pills.
- H2-antihistamines. They minimize the negative effect of stomach acid on the esophagus.
- Products containing magnesium carbonate.
- Tablets that slow down certain reactions in the body.
- Vitamin tablets that help food release nutrients.
- Antispasmodic tablets that relieve spasms from the human gastrointestinal tract.
- Medicines that coat the stomach. As a rule, they are drunk for meals. The medicine protects the stomach and esophagus from acid.
- Medicines to stimulate the gastrointestinal tract.
- Medicines for the restoration of ulcerative scars. Such medications promote the formation of new mucosal cells at the site of the ulcerative cut.
All enveloping medications must be taken slowly, in small sips and spread out over 15 minutes.
Most often, medications are prescribed in groups, that is, you need to take several at once. And they should only be consumed while lying on your back.
This stage of treatment lasts up to three months.
But what is the purpose of these drugs anyway? The first goal is primarily to restore ulcerative scars. That is, the active substances of the tablets help cells in their restoration. The scar will heal only when the cells begin to regenerate.
Medicines also aim to reduce pain and spasms in the gastrointestinal tract. They have a gentle effect on the system, relaxing it. For such problems, a regular painkiller will not work because it will be harsh on the stomach. Doctors prescribe special mild and effective remedies.
The third goal is to lower the level of hydrochloric acid in the stomach and prevent its active production. The acid-base balance must be normal, otherwise new scars will form and old scars will progress. The acid seems to wash away the cells of the diseased area, and their chances of normal recovery are reduced.
With the disease in question, a symptom occurs that consists of uncontrolled regurgitation. That is, the esophagus pushes the food product back into the pharynx. The fourth goal is to prevent this problem. To exclude it, the gastrointestinal tract must work more actively, but this is not possible due to diseased areas.
The final purpose of medications is to tighten scars. Medications are prescribed to help the scars heal.
Endoscopy treatment
This procedure is simply necessary in the treatment of esophageal ulcers.
A plastic endoscope is carefully inserted into the human esophagus to cauterize the ulcerative scar.
But there are times when this method will not help. Then they resort to a proven method - surgery.
Surgical assistance
For doctors to perform surgery on the gastrointestinal tract, medical conditions are necessary for which there is no other treatment option. These include:
- Treatment with all kinds of drugs did not help and did not improve the person’s condition in any way.
- Severe complications of the disease. These may include the opening of an ulcer and excessive bleeding.
- An ulcerative scar gave rise to oncological formation in the esophagus.
- Severe deformations of the gastrointestinal tract. These include its narrowing in different areas.
- The disease began to progress and another one appeared - the disease of uncontrolled reflux of food back into the throat.
For a certain period of time before the procedure, gastroenterologists prescribe a special course of therapy for the person, which is aimed at relieving swelling, smoothing out the folds of the organ and reducing the ulcerative scar.
Surgery is usually performed only during the period of time when the ulcerative area begins to heal. This time will give a chance for the absence of complex symptoms after surgery and for the successful healing of the affected area.
Also, during the procedure, the human organ will be covered with biological tissue, which will contribute to a speedy recovery of the person.
Gastroenterologists perform these procedures as painlessly as possible.
This stage is the last step in the treatment path. After it, you need to return to the first stage and stay there. You need to follow a strict diet all the time. Sometimes you can indulge in prohibited foods, but in moderate prohibited quality.
Rehabilitation
Treatment of esophageal ulcers requires a serious approach and timely treatment. A patient after surgery needs careful care, a strict diet and a long period of rehabilitation. A specially selected diet and medications that reduce stomach acidity will promote organ regeneration. The patient is required to be registered at the dispensary and is under observation for a long time.
For your information! The possibility of consuming the desired food or certain medications is discussed only with the attending physician.
With adequate and timely treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. That is why it is important to undergo examinations on time and, at the slightest suspicion of the presence of a disease, to visit a doctor.