Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract reduce the quality of life, forcing the patient to constantly follow a diet, look for analogues of some medications (many tablets irritate the stomach and intestines, increasing unpleasant symptoms) and choose a field of professional activity that allows small, frequent snacks.
Similar restrictions apply to people suffering from:
- stomach and intestinal ulcers;
- gastritis;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- biliary dyskinesia.
This group of diseases includes Barrett's syndrome. The diet menu for Barrett's esophagus excludes dishes that negatively affect the esophagus, cause irritation, and therefore increase the risk of inflammation and adverse changes.
What is Barrett's esophagus
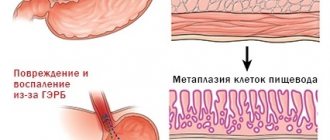
This term is used by doctors to describe a condition in which, instead of normal cells for the esophagus - squamous multilayer epithelium - its walls are lined with columnar epithelium. Examination (biopsy performed during gastroendoscopy) reveals goblet cells. This is intestinal metaplasia. Normally, a healthy person should not have such cells in the esophagus.
You can suspect the presence of the disease based on the following symptoms:
- heartburn;
- periodic nausea, vomiting;
- coughing;
- the appearance of a sour taste in the mouth;
- belching.
The disease is precancerous, and therefore requires special attention and constant monitoring on the part of the patient and the doctor.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
Barrett's esophagus is a disease that occurs throughout life, often due to the following factors:
- insufficiency of the lower esophageal sphincter, due to which the contents of the stomach (acidic environment) enter the esophagus;
- double reflux - when gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and duodenogastric reflux disease (DGR) develop simultaneously;
- weakened contractile function of the esophagus;
- increased secretion of hydrochloric acid;
- exogenous factors - smoking, dietary errors, excess weight, alcohol abuse, combination chemotherapy.
The most common forms of pathological changes in the mucous membrane of the esophagus, which can lead to BE:
- Dysplasia is a disorder of the normal structure of the mucous membrane, in which cell aging occurs and the tendency to their uncontrolled division increases. This condition is called precancer, since there is a risk of degeneration into oncology, although small. Moderate and severe degrees of dysplasia are distinguished; in severe cases, the risk of developing BE is higher. If provoking factors are excluded, the disease does not progress.
- Metaplasia - in this condition, the normal mucous membrane of the esophagus is replaced by cells unusual for this zone, most often gastric or intestinal. The condition is persistent, it does not disappear even if risk factors are excluded. There is evidence that with a metaplasia length of 3 cm or more, the likelihood of developing a malignant tumor - adenocarcinoma of the esophagus - is higher.
- Erosive form - the presence of erosions and erosive-ulcerative defects (both acute and epithelial) on the mucous membrane of the esophagus in the lower third (usually in the projection of the transition of the esophagus to the stomach).
Main patient complaints and signs of Barrett's esophagus
- pain during swallowing food throughout the esophagus, behind the sternum or in the epigastrium;
- belching with sour contents, especially after eating, heartburn;
- sore throat that occurs after eating, worsens when bending over, hoarseness of voice;
- dysphagia, when the patient complains that it is difficult or painful for him to swallow food, especially solid food;
- nausea and regurgitation after eating, especially when straining or belching;
- thinning of tooth enamel.
You should not ignore the listed symptoms and put off going to the doctor; it is better to prevent the disease and start treatment in the early stages, because the processes occurring at the cellular level are not reversible.
About the importance of therapeutic nutrition
Compliance with the principles of proper nutrition is of great importance for patients. Despite the fact that a diet for Barrett's esophagus is not able to get rid of the pathology, it helps to curb its progression and prevent complications.
Nutrition for Barrett's esophagus is gentle; the diet does not contain spicy or salty foods, which cause increased production of gastric juice.
One of the main principles is that food should be taken 5-6 times a day, in small portions. Fractional meals do not overload the stomach and esophagus, the process of digesting food is easier.
Disability
The disease does not yet serve as an indication for the appointment of a group. Disability can result from the development of complications of pathology, for example, ulcers, stenosis, malignancy.
Barrett's esophagus is a precancerous condition and can lead to the death of the patient if treated incorrectly or untimely. In the initial stages, only drug therapy is permissible.
If the pathology progresses, then only surgical intervention can stop it . To prevent serious health problems, you need to monitor your diet: do not eat before bed, avoid overeating, give up bad habits, promptly treat gastrointestinal diseases and be examined by a gastroenterologist.
What can you eat if you are sick?
If the disease is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe treatment and will definitely indicate to the patient the need to follow a dietary diet. What can you eat? The list of permitted products includes:
- porridge (but not all cereals are equally healthy);
- heat-treated fruits and vegetables;
- low-fat soups;
- kefir, cottage cheese, yoghurts.
You are allowed to eat almost everything that is included in the list of recommended foods for those with a history of gastritis or stomach ulcers. The principles of food selection in this case are the same.
What not to include in your diet
When asked what you shouldn’t eat, the gastroenterologist will answer as follows: “Dishes that increase irritation of the walls of the stomach and esophagus should be excluded from your diet. For symptoms of Barrett's esophagus, treatment and diet are equally important, because failure to comply with the latter will lead to the neutralization of the results of the former.”
The menu for Barrett's esophagus is designed in such a way that the recipes are quite varied, since it is necessary to ensure that the body receives the entire range of vitamins and nutrients.
But do not forget about the restrictions that apply to:
- salty;
- spicy;
- smoked;
- sour;
- roast.
Marinades are undesirable due to the presence of vinegar in them. Dishes with a high percentage of fat content (kebabs, pork soups, salads with mayonnaise) should not be consumed. Such food is heavy on the stomach, digestion is difficult, and with Barrett's esophagus it is necessary to ensure the supply of easily digestible foods.
Reduce your consumption of dishes containing pearl barley, legumes, and cabbage, as they cause increased gas formation.
The diet for esophageal disease prohibits:
- sweet soda;
- strong tea;
- alcohol.
These drinks irritate the gastrointestinal tract. Try to limit your consumption of coffee, chocolate, and baked goods.
Avoid alcohol. You can afford a glass of wine occasionally, after having a snack.
Basic principles for creating your own menu for the week
The menu for patients suffering from gastritis and (or) diagnosed with Barrett's esophagus contains approximately the same dishes - the diet is the same.
When creating a menu for the week, take as a basis the dietary dishes recommended by gastroenterologists from table No. 1.
You can cook for yourself separately from the rest of the family, this will avoid the temptation to eat something forbidden.
Take the following dishes as a basis:
- rice and semolina porridges;
- jelly and weakly brewed tea;
- boiled fish and meat;
- vegetable stew;
- from sweets - honey, marshmallows.
Snacks between meals are a must. For these snacks, take:
- dried bread (white);
- cracker;
- dried fruits in small quantities.
Detailed menu for the week
Let's see what you can cook for yourself during the week.
Table 1. Diet for Barrett's esophagus: menu and recipes
| Day of the week | Breakfast | Dinner | Dinner |
| Monday | Boiled egg, buckwheat porridge | Light fish soup, mashed potatoes | Stewed zucchini with a piece of boiled chicken |
| Tuesday | Semolina | Vegetable stew with chicken | Boiled rice and a piece of stewed meat (preferably veal) |
| Wednesday | Rice porridge with milk | Cream soup, pasta with steamed cutlet, without ketchup | Vegetable stew |
| Thursday | Tea with toast, boiled egg | Chicken soup, stewed potatoes with fish | Stew |
| Friday | Milk noodle soup | Cream soup, fish fillet | Buckwheat |
| Saturday | Dried bread, mild cheese, cocoa | Vegetable soup, optional without meat (as a relief), rice and steamed cutlet | Salad, but without fatty mayonnaise. It is better to choose olive or sunflower oil for dressing. |
| Sunday | Oatmeal porridge with dried fruits | Borscht, boiled or stewed potatoes with hedgehogs | Cottage cheese |
Drink weakly brewed tea, cocoa with milk, jelly, compotes. Snack on dry cookies, kefir, dried fruits, marmalade, marshmallows, and stewed fruits. The last meal is no later than 2 hours before bedtime.
What menu is recommended for Barrett's esophagus disease – Gastrology
Barrett's esophagus is a phenomenon in which the lining of the lower esophagus changes - normal squamous epithelial cells are replaced by atypical columnar cells.
Like other cases of pathological tissue degeneration, this syndrome is characterized as a precancerous condition, so it is very important to prescribe the correct treatment for the disease.
Following a certain diet will help alleviate the patient's condition.
The importance of diet in Barrett's esophagus
Due to changes in the morphology of the epithelium in the esophagus, Barrett's syndrome is most often accompanied by reflux disease - the reflux of stomach contents into the lower esophagus.
This leads to various unpleasant symptoms - primarily heartburn - which diet helps to alleviate.
However, a certain set of products cannot affect the structure of the mucous membrane, and the changed epithelium will not return to its normal state without drug or surgical treatment of the cause of the pathology.
The diet recommended by a gastroenterologist also performs a number of important functions:
- reduces the aggressive effect on the mucous membrane and prevents the disease from progressing quickly;
- reduces the likelihood of complications;
- relieves the load on the digestive tract, improving the body's absorption of the active ingredients of medications.
Thus, correctly selected products give the patient the opportunity to live a normal life, despite the pathological processes occurring in his body.
Basic principles of dietary nutrition
The main requirement for a diet is to provide the body with a full range of necessary substances. The diet must be balanced and, despite restrictions, provide the patient with the optimal amount of energy and building material for cells.
The diet should be compiled in accordance with the following principles:
- products that have an aggressive effect on the mucous membrane, increase the acidity of gastric juice, increase the frequency of reflux and provoke the progression of pathology are excluded;
- the consumption of foods that envelop the wall of the esophagus, do not create a load on the gastrointestinal tract and quickly pass through the digestive system increases.
In addition to the actual set of products, you should improve your nutritional culture - accustom yourself to observing a number of food intake rules.
To keep the load on the body minimal, meals should be fractional - in small portions 5 times a day, the last meal should be 2-4 hours before bedtime.
Dishes should be as simple and familiar as possible, without unfamiliar or exotic options. It is better to cook by steaming; you can also boil or stew food, but do not fry.
To relieve heartburn, you should not lie down after eating, but you need to rest - spend 1-1.5 hours, avoiding bending over and physical activity. It is advisable to give up bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol and large amounts of coffee.
It is not necessary to follow the recommendations exactly - it is important to listen to your feelings. If after eating you feel heaviness in the stomach or heartburn, the dish should be excluded from the diet, even if its consumption is acceptable.
How to make a diet correctly
When preparing a diet, you need to follow several rules:
- Methods of preparing permitted foods are important - boiled, stewed and steamed dishes are acceptable;
- You cannot add seasonings, sugar, or fatty sauces to food, even if without them the food seems tasteless;
- You can wash down your food only with milk, weak tea, non-acidic compote or plain water;
- You can combine products in any way, the main thing is to keep the portions small to avoid filling your stomach.
Prohibited foods can be gradually reintroduced into the diet as the condition develops lastingly as a result of drug therapy.
What can you eat
For Barrett's esophagus, the following foods are allowed for consumption:
- Fruits and vegetables, herbs, nuts contain a large number of compounds that help fight histological pathologies of a cancerous nature. It is not recommended to consume fresh plant products, as they increase the acidity of gastric juice and worsen heartburn - it is better to eat them steamed or stewed. The broth from cooked vegetables can be used to prepare soups with finely ground ingredients and pureed soups.
- Slightly stale wheat bread, dry biscuits, marmalade.
- High fiber foods speed up the exit of food from the stomach and quickly pass through the intestines. These include cereals in the form of porridges, bran, plant seeds, herbs, vegetables, and berries.
- Red meat - poultry, veal, rabbit, beef in small quantities.
- Vegetable oils (except sunflower), fish oil.
- Foods rich in complex carbohydrates.
- Dairy products, if there is no heartburn, are lactic acid.
- Boiled eggs.
Dishes made from these products do not irritate the mucous membrane of the esophagus and reduce the risk of developing cancer.
Products prohibited for consumption
It is recommended to exclude spices, hot spices, alcohol, and sour foods from the diet - they most actively contribute to inflammation of the wall of the esophagus. In addition, the use of:
- fried, fatty foods - pork, high-fat dairy products, sauces, animal oils;
- canned vegetables, fresh sour fruits and herbs (cabbage, sorrel);
- pasta, millet and pearl barley;
- bread, except wheat (it can only be dried), butter and puff pastries, confectionery, chocolate;
- strong tea, coffee, carbonated drinks, juices;
- Sahara;
- legumes
Basically, the ban is imposed on foods that cause heartburn. This effect is individual - if a particular dish does not lead to the manifestation of reflux symptoms, it can be carefully returned to your diet. This is explained simply - since there is no heartburn, it means that the contents of the stomach are not thrown into the esophagus, there is no aggressive effect on the mucous membrane, and Barrett's syndrome does not develop.
In addition to the products listed, you should avoid medications that relax the esophageal sphincter - these include antidepressants, nitrates, hormonal medications, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Weekly menu option
The easiest way to create a menu is to consult a specialist - a gastroenterologist or nutritionist. However, taking into account the recommendations described above, you can create a list of dishes yourself. The diet for Barrett's esophagus is similar to that for other diseases of the esophagus.
Daily nutrition is divided into five meals:
- Breakfast. Cutlets made from steamed lean meat with a side dish of buckwheat or rice. Steamed omelette or boiled eggs. Weak tea without sugar with milk.
- Lunch. Kissel or fruit compote, milk. Wheat bread crackers. Cracker.
- Dinner. Puree vegetable soup with rice or barley, steamed chicken, meatballs. Fruit jelly, non-acidic compote.
- Afternoon snack. Boiled egg with tea without sugar. Dried wheat bread, biscuits. Steamed casserole.
- Dinner. Boiled lean river fish, buckwheat porridge, chopped red meat with mashed potatoes. This meal should be light in order to be completely digested before nightfall.
You should have dinner at least an hour and a half before bedtime. To avoid reflux at night, you should sleep on a bed with the head of the bed raised 15°.
Thus, there are many dietary restrictions for patients with Barrett's esophagus.
The basic principles are not advisory, but prescriptive in nature - all patients should follow them, since following the rules will help alleviate the condition and make treatment of the pathology more effective and faster, as well as avoid complications. The positive side of the diet is that it is not lifelong - after completing a course of therapy, you can return to your usual diet.
Source:
Barrett's esophagus - diet (food, what not to eat), menu for the week
Barrett's esophagus is a disease in which atypical columnar cells are formed in place of normal squamous epithelial cells of the esophagus. This happens due to the prolonged influence of aggressive stomach contents on the mucous membrane of the esophagus with existing gastroesophageal reflux disease.
How does the pathology manifest itself and what is the danger of it?
The syndrome can be identified by the following symptoms:
- sour belching;
- persistent feeling of sourness in the mouth;
- heartburn;
- such unpleasant sensations behind the sternum as burning and pain;
- difficulty swallowing liquids and solid foods.
If the disease is not cured in time, then there is a high probability that the patient will develop oncology and a hiatal hernia. For this reason, if the above symptoms appear, the patient should consult a specialist as soon as possible.
Do I need to change my diet somehow?
Diet for Barrett's esophagus is necessary. Yes, it does not help get rid of the disease. If the patient eats some foods and refuses others, the atypical cells will not change to normal. However, there are still benefits from following the doctor’s recommendations in terms of nutrition. Which one?
Firstly , following a diet reduces the manifestation of pathological symptoms, for example, esophagitis.
Secondly , the risk of complications is reduced.
Thirdly , the disease itself develops more slowly, as the aggressive effect on the epithelial cells of the esophagus is reduced.
Fourthly , medications are better absorbed in the body due to the reduced load on the digestive tract.
It is for these reasons that patients should listen to the doctor’s advice and, if possible, try to comply with all his dietary instructions. Thus, the patient will be able to live normally even with this disease and not be afraid that his health will soon deteriorate significantly.
What you should know about the diet
Refusing one food and forcing yourself to eat another is only a small part of what you need to know about the diet proposed by doctors for Barrett's esophagus. It also includes a number of rules, if not followed, all attempts to improve well-being will be useless. They are as follows:
- You need to eat often, but in small portions. There should be at least 5 meals per day;
- You can't eat at night. You can eat your last meal no later than 2 hours before going to sleep;
- smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited;
- It is recommended to eat boiled, stewed or steamed dishes;
- until the treatment of the disease has ended, introducing new and even more exotic products is prohibited;
- smoked, fried, spicy foods should be excluded from the diet;
- adding seasonings and spices to soups, sauces and other dishes is prohibited;
- fruits and vegetables must also be subjected to heat treatment;
- There is no need to rush to eat the product quickly. You need to eat slowly, chewing everything thoroughly;
- meals should occur at the same time. You should wash down your food with either water, or weak tea, or milk, or non-acidic compote;
- It is not recommended to perform any exercise after eating;
- It is undesirable to wear things that tighten the stomach.
Three main principles when creating a menu
- You need to eat foods that envelop the wall of the esophagus, quickly pass through the stomach, and also do not create a load on the digestive organs.
- It is necessary to add dishes to the diet that contain a significant amount of vitamins and minerals.
- You should avoid foods that increase the production of gastric acidity, have an aggressive effect on the epithelial cells of the esophagus, and also increase the frequency of reflux.
Source: https://gastrologpro.ru/diagnostika/kakoe-menyu-rekomendovano-pri-zabolevanii-pishhevod-barretta.html
Cooking recipes for people with Barrett's disease
Let's give an example of a couple of recipes for dishes that can be prepared while following a diet for Barrett's disease.
Vegetable stew with chicken
Wash a small piece of chicken fillet, cut it into pieces, place it in a pan with water (at the bottom) with a minimum amount of oil. While the chicken is stewing, cut the vegetables available in the house:
- carrot;
- bell pepper;
- potato;
- onion.
If you have beets, you can use them too, but it is better to grate them, otherwise they will take a long time to cook. In summer you can add young zucchini, zucchini, squash, and Jerusalem artichoke.
Add vegetables to chicken and simmer until done. Salt (minimal quantity). Ready.
Stewed fish
Place a piece of fish (pollock, hake, and if funds allow, a piece of pink salmon or salmon) into a pan with hot water.
You can omit the oil at all or pour a little oil over the fish when it is ready.
Simmer for 15-20 minutes, making sure there is water in the pan all the time. At the end of the process, add salt, remove the fish, and let the water drain. For spices, you can add a little dill and parsley. It is better not to use pepper and other irritating seasonings.
Menu for Barrett's esophagus: recipes for the week
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract reduce the quality of life, forcing the patient to constantly follow a diet, look for analogues of some medications (many tablets irritate the stomach and intestines, increasing unpleasant symptoms) and choose a field of professional activity that allows small, frequent snacks.
Similar restrictions apply to people suffering from:
- stomach and intestinal ulcers;
- gastritis;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- biliary dyskinesia.
This group of diseases includes Barrett's syndrome. The diet menu for Barrett's esophagus excludes dishes that negatively affect the esophagus, cause irritation, and therefore increase the risk of inflammation and adverse changes.
- Barrett's disease
- Medical nutrition
- What can you eat
- Prohibited foods
- Principles of diet for illness
- Detailed menu for the week
- Recipes Vegetable stew with chicken
- Stewed fish
What is Barrett's esophagus
This term is used by doctors to describe a condition in which, instead of normal cells for the esophagus - squamous multilayer epithelium - its walls are lined with columnar epithelium. Examination (biopsy performed during gastroendoscopy) reveals goblet cells. This is intestinal metaplasia. Normally, a healthy person should not have such cells in the esophagus.
You can suspect the presence of the disease based on the following symptoms:
- heartburn;
- periodic nausea, vomiting;
- coughing;
- the appearance of a sour taste in the mouth;
- belching.
The disease is precancerous, and therefore requires special attention and constant monitoring on the part of the patient and the doctor.
About the importance of therapeutic nutrition
Compliance with the principles of proper nutrition is of great importance for patients. Despite the fact that a diet for Barrett's esophagus is not able to get rid of the pathology, it helps to curb its progression and prevent complications.
Nutrition for Barrett's esophagus is gentle; the diet does not contain spicy or salty foods, which cause increased production of gastric juice.
One of the main principles is that food should be taken 5-6 times a day, in small portions. Fractional meals do not overload the stomach and esophagus, the process of digesting food is easier.
What can you eat if you are sick?
If the disease is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe treatment and will definitely indicate to the patient the need to follow a dietary diet. What can you eat? The list of permitted products includes:
- porridge (but not all cereals are equally healthy);
- heat-treated fruits and vegetables;
- low-fat soups;
- kefir, cottage cheese, yoghurts.
You are allowed to eat almost everything that is included in the list of recommended foods for those with a history of gastritis or stomach ulcers. The principles of food selection in this case are the same.
What not to include in your diet
When asked what you shouldn’t eat, the gastroenterologist will answer as follows: “Dishes that increase irritation of the walls of the stomach and esophagus should be excluded from your diet. For symptoms of Barrett's esophagus, treatment and diet are equally important, because failure to comply with the latter will lead to the neutralization of the results of the former.”
The menu for Barrett's esophagus is designed in such a way that the recipes are quite varied, since it is necessary to ensure that the body receives the entire range of vitamins and nutrients.
But do not forget about the restrictions that apply to:
- salty;
- spicy;
- smoked;
- sour;
- roast.
Marinades are undesirable due to the presence of vinegar in them. Dishes with a high percentage of fat content (kebabs, pork soups, salads with mayonnaise) should not be consumed. Such food is heavy on the stomach, digestion is difficult, and with Barrett's esophagus it is necessary to ensure the supply of easily digestible foods.
Reduce your consumption of dishes containing pearl barley, legumes, and cabbage, as they cause increased gas formation.
The diet for esophageal disease prohibits:
- sweet soda;
- strong tea;
- alcohol.
These drinks irritate the gastrointestinal tract. Try to limit your consumption of coffee, chocolate, and baked goods.
Avoid alcohol. You can afford a glass of wine occasionally, after having a snack.
Basic principles for creating your own menu for the week
The menu for patients suffering from gastritis and (or) diagnosed with Barrett's esophagus contains approximately the same dishes - the diet is the same.
When creating a menu for the week, take as a basis the dietary dishes recommended by gastroenterologists from table No. 1.
You can cook for yourself separately from the rest of the family, this will avoid the temptation to eat something forbidden.
Take the following dishes as a basis:
- rice and semolina porridges;
- jelly and weakly brewed tea;
- boiled fish and meat;
- vegetable stew;
- from sweets - honey, marshmallows.
Snacks between meals are a must. For these snacks, take:
- dried bread (white);
- cracker;
- dried fruits in small quantities.
Detailed menu for the week
Let's see what you can cook for yourself during the week.
Table 1. Diet for Barrett's esophagus: menu and recipes
| Day of the week | Breakfast | Dinner | Dinner |
| Monday | Boiled egg, buckwheat porridge | Light fish soup, mashed potatoes | Stewed zucchini with a piece of boiled chicken |
| Tuesday | Semolina | Vegetable stew with chicken | Boiled rice and a piece of stewed meat (preferably veal) |
| Wednesday | Rice porridge with milk | Cream soup, pasta with steamed cutlet, without ketchup | Vegetable stew |
| Thursday | Tea with toast, boiled egg | Chicken soup, stewed potatoes with fish | Stew |
| Friday | Milk noodle soup | Cream soup, fish fillet | Buckwheat |
| Saturday | Dried bread, mild cheese, cocoa | Vegetable soup, optional without meat (as a relief), rice and steamed cutlet | Salad, but without fatty mayonnaise. It is better to choose olive or sunflower oil for dressing. |
| Sunday | Oatmeal porridge with dried fruits | Borscht, boiled or stewed potatoes with hedgehogs | Cottage cheese |
Drink weakly brewed tea, cocoa with milk, jelly, compotes. Snack on dry cookies, kefir, dried fruits, marmalade, marshmallows, and stewed fruits. The last meal is no later than 2 hours before bedtime.
Cooking recipes for people with Barrett's disease
Let's give an example of a couple of recipes for dishes that can be prepared while following a diet for Barrett's disease.
Vegetable stew with chicken
Wash a small piece of chicken fillet, cut it into pieces, place it in a pan with water (at the bottom) with a minimum amount of oil. While the chicken is stewing, cut the vegetables available in the house:
- carrot;
- bell pepper;
- potato;
- onion.
If you have beets, you can use them too, but it is better to grate them, otherwise they will take a long time to cook. In summer you can add young zucchini, zucchini, squash, and Jerusalem artichoke.
Add vegetables to chicken and simmer until done. Salt (minimal quantity). Ready.
Stewed fish
Place a piece of fish (pollock, hake, and if funds allow, a piece of pink salmon or salmon) into a pan with hot water.
You can omit the oil at all or pour a little oil over the fish when it is ready.
Simmer for 15-20 minutes, making sure there is water in the pan all the time. At the end of the process, add salt, remove the fish, and let the water drain. For spices, you can add a little dill and parsley. It is better not to use pepper and other irritating seasonings.
Conclusion
Barrett's disease is an unpleasant diagnosis, but if you follow all the doctor's instructions and regularly check the condition of the esophagus and stomach, you can avoid the development of complications. Be sure to stick to a diet - this is one of the conditions that allows you to stabilize the condition and curb the progression of the pathology.
Recommended materials:
Diseases of the salivary glands: symptoms and treatment
Can Barrett's esophagus be cured?
Source: https://stomach-diet.ru/pischevod-barretta-dieta/