What kind of pain could it be?
Pain in the abdominal area can be chronic or acute, and manifest itself in attacks. They may intensify gradually, or they may appear suddenly. As a rule, chronic pain is not pronounced, passes over time, but tends to return.
In some cases, the pain has a specific localization and the patient can show exactly where it hurts. But it also happens that it covers the entire abdomen, and only a specialist can determine the source.
Localization of pain syndrome and causes of its occurrence
Discomfortable sensations can be concentrated in different parts of the abdomen. Depending on this sign, doctors suspect the development of certain pathologies.
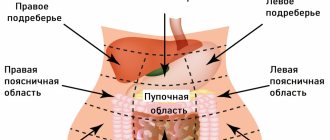
Epigastric region
Placed centrally below the sternum between the ribs. When pain syndrome appears in the epigastrium, doctors suspect the presence of gastric pathologies - gastritis, peptic ulcer. The discomfort usually worsens after eating spicy or sour foods. If an ulcer is present, all symptoms intensify after a long food break. In the epigastrium, the pain is usually dull, aching, very rarely sharp.
Discomfort in this area also occurs with indigestion or after overeating. Sometimes epigastric pain is explained by cardiac pathologies.
Right hypochondrium
Pain in the area of the right hypochondrium can occur due to problems with the functioning of the liver and gallbladder. Common pathologies are cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, cirrhosis, hepatitis.
Left hypochondrium
The stomach is not exactly in the center of the abdomen. It is slightly shifted to the left. Therefore, when pain appears in the hypochondrium, gastric pathologies are suspected - gastritis, ulcers.
Diseases of the pancreas (pancreatitis) provoke discomfort on the left side. The pain is also explained by problems with the spleen and heart.
Periumbilical region
Unpleasant sensations in the central part of the abdomen are caused by diseases of the small intestine. Infections, enzyme deficiency, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis lead to pain near the navel. Pancreatitis can also lead to pain in the area.
Left and right side
Pain in the center of the abdomen, displaced to any side, is most often caused by problems with the urinary system. Pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, and inflammation of the urinary tract lead to discomfort. If these pathologies are present, the pain also radiates to the lumbar region and perineum.
Pain in the side of the abdomen can be caused by the accumulation of gases in the colon. Flatulence is caused by gastrointestinal diseases, consumption of certain foods, and overeating. Pain is also explained by colitis and diverticulosis.
Right iliac region
If an adult or child has pain in the lower abdomen on the right, you should immediately consult a doctor. This indicates acute appendicitis - inflammation of the appendix of the cecum. This disease is characterized by sudden sharp pain. There are cases when the discomfort is mild at first, but then increases in intensity.
Suprapubic region
If the lower abdomen hurts, a person is suspected of having a disease of the urinary system. Pyelonephritis, prolapse of the ureter, and the presence of kidney stones lead to similar symptoms.
With the development of lower abdominal pain in women, there is a high risk of gynecological diseases:
- acute or chronic inflammation of the appendages;
- adhesive disease;
- tumors or cysts;
- endometriosis;
- ectopic pregnancy.
A characteristic disease in women that provokes pain is called varicose veins in the pelvis (it also occurs in men). In this case, discomfort increases during physical activity, after sexual intercourse, and during menstruation. Pain in the suprapubic region also appears with colitis, dysbacteriosis, helminthic infestations, and sigmoiditis.
Possible reasons
- Cramping type pain (colic) can be caused by irritated nerve receptors that are located inside the hollow organs. As a result, spasms of the smooth muscles of the corresponding organs occur. Gastralgia can be strong and painful, but it does not last long. After a few minutes it goes away. There may be several attacks in a row, with increasing and decreasing unpleasant sensations.
- A very common cause of colic is errors in diet (overeating, fatty foods, spicy or highly salty foods).
- Painful attacks can occur with fever, severe chills, and changes in the color of urine and feces.
- If there was an injury to the abdominal area, colic may subsequently occur due to stretching of the ligamentous apparatus of the organs or their prolapse.
- Poor circulation can also provoke gastralgia. With stagnation in the vessels of the peritoneum, pain occurs when the digestive organs are most active, for example, after eating.
- Acute arthralgia can occur during an attack of appendicitis, with an ulcer or its perforation, with a developing tumor and other reasons.
- The appearance of astralgia can be caused by pathologies of other organs not located in the abdominal cavity. For example, with a heart attack, pleurisy or diseases of the esophagus, often unpleasant sensations radiate to the abdominal area.
- Stress or fear can also trigger the appearance of gastralgia, in some cases even acute.
Which doctor should I consult if my stomach hurts?
There are two scenarios for the development of events: the patient goes to a budget clinic (where you do not have to pay money for services provided) or to a private diagnostic center (where services are provided at the price indicated in the price list).
A gastroenterologist is a doctor who treats diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. He is the one you should turn to if you have a stomach ache.
When contacting a budget clinic, the algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Contact the reception with the question: “I have a stomach ache, which doctor should I go to?” Some government agencies may issue a voucher directly to a gastroenterologist, but more often they will first refer you to a local physician.
- The therapist conducts an objective examination. The patient talks in detail about his problems. You definitely need to clarify the purpose of your visit (stomach pain - what kind of doctor you need). Don't be shy to ask questions.
- After the examination, the therapist will write out a referral for mandatory tests (blood biochemistry, general analysis of urine and feces).
- Based on the test results and patient complaints, he will issue vouchers for visits to specialists. This is a gastroenterologist, hepatologist, endocrinologist, immunologist.
- The patient is sent to see a specialist, where he expresses his complaints about pain in the stomach. A gastroenterologist (or hepatologist) conducts an examination and, if necessary, gives a referral for additional studies. Prescribes treatment.
- If necessary, you should come for additional examinations every few months to monitor the progression of the disease.
In private diagnostic centers, everything is simpler: there you can immediately get to a gastroenterologist, bypassing the stage of examination by a therapist. If the patient is unsure which specialist he needs, he can ask at the reception: “Which doctor should I make an appointment with if my stomach hurts?” The patient will be given a ticket to either a hepatologist or a gastroenterologist. Then you need to appear for examination on the appointed day and time.
Epigastric region
The epigastrium is located in the center, in the upper abdomen, just below the ribs. As a rule, pain in this area appears with stomach diseases. This may simply be inflammation of the mucous membrane (gastritis) or a developed ulcer of this organ. The same sensations can cause inflammation in the duodenum (dowdenitis). As a rule, symptoms occur after eating salty, spicy or fried foods.
The sensations are dull, aching in nature and can very rarely be acute. An exception is perforation (perforation) of an ulcer, when an attack of very severe pain occurs, from which the abdominal muscles “turn to stone.” With such symptoms, immediate surgical attention is required.
General signs indicating gastric pathology
Three groups of characteristic signs indicate dysfunction of this organ.
- Pain in the epigastric region, most often associated with meals.
- Gastric discomfort - a feeling of heaviness even after small portions of food.
- Dyspeptic disorders - belching (food or sour), heartburn, nausea, and sometimes vomiting.
Unlike other diseases of the digestive system, the symptoms of gastric pathologies are somehow related to food intake.
to contents ^
Right iliac zone
The appendix, a branch of the cecum, is located in this area. When it becomes inflamed, severe cutting pain occurs that occurs suddenly. In rare cases, the pain may increase gradually. At first it can be localized near the navel, after which it moves to the right. There have been cases where irradiation was in the lower back, or in the kidney area. This is a dangerous disease that requires emergency surgery.
In women, pain may radiate to this area due to polycystic disease of the right ovary. It is important not to confuse the symptoms and make a correct diagnosis. Because delay is fraught with serious, life-threatening consequences.
The most common causes of abdominal pain
Most often, pain in the stomach is caused by the following problems:
- gastritis of various etiologies;
- peptic ulcer;
- release of bile into the stomach (accompanied by bitterness in the mouth);
- parasitic infestations;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- chronic cholecystitis;
- some chronic liver diseases;
- neoplasms;
- polyps and erosions;
- poor nutrition – strict diets and hunger strikes.
Whatever the cause of the pain, treatment should be prescribed by a gastroenterologist. If the examination reveals that the cause of the discomfort is chronic liver disease, then an additional consultation with a hepatologist will be required.
Suprapubic region
Most often, pain in the lower abdomen is caused by pathology in the bladder and urinary tract. Acute attacks can cause bladder stones.
For women, localization of pain in the suprapubic part is typical for various gynecological diseases: inflammation of the appendages (acute and chronic), the presence of adhesions in the fallopian tubes, ovarian cysts and tumors, ectopic pregnancy. Also, the cause may be prolapse of the ureter or varicose veins of the pelvic vessels (occurs only in women). In such cases, pain may intensify after intercourse or after physical work.
For men, the presence of pain in the suprapubic area, in addition to problems with the bladder, can signal problems with the prostate. When inflammation of the gland occurs chronically, aching, nagging pain in the lower abdomen is observed. With acute prostatitis, sharp and acute pain appears, radiating to the perineum. Pain syndrome can also be observed with inflammation and cysts of the seminal vesicles.
Constipation, colitis and flatulence are another cause of gastralgia, common to both sexes.
List of doctors
If discomfort occurs in the abdominal cavity, an adult needs to go to an appointment with a local therapist at the clinic. If necessary, he refers to a specialist:
- in the presence of pathologies from the digestive system - see a gastroenterologist;
- if you suspect problems with the urinary organs, see a urologist;
- if there are symptoms of gynecological diseases, see a gynecologist;
- if acute pain is detected, see a surgeon.
Children who develop discomfort in the abdominal cavity are treated by a pediatrician.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
If you suspect that the cause of the pain lies in overeating or other confectionary excesses, then give the body time to cleanse itself so that it can recover naturally. It is useful to drink decoctions of medicinal herbs: chamomile, calendula and others.
A mandatory visit to a doctor is necessary when:
- pain appeared for the first time;
- you feel discomfort (not pain) in your stomach for several days. If pain occurs, do not wait more than 1 day, but go to the hospital;
- suffers from flatulence for more than 2 days;
- when urinating, you feel a burning or stinging sensation, and it has become frequent;
- upset stool for more than 1 day;
- you feel pain, and at the same time there is a rise in temperature;
- irradiation of pain to the neck, shoulders in the chest area;
- During pregnancy, any abdominal pain requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
Diagnostic measures for abdominal pain
After visiting a doctor, the patient must describe in detail his complaints, lifestyle, and answer all questions. In turn, the specialist carries out a general assessment of the patient’s condition – his movements and activity, the color of the skin and mucous membranes, and the nature of his breathing.
The doctor asks the person to expose the abdomen and chest for palpation and percussion. He probes and taps certain parts of the body to check for the presence of pain, the extent of its spread, and the presence of muscle tension. The specialist must listen to the patient’s lungs and heart and measure blood pressure and heart rate.
In some cases, the doctor performs a visual examination of the rectum to identify hemorrhoids and fissures. For men, an examination of the genitals by a urologist is indicated, for women - by a gynecologist.
Laboratory research
If there is abdominal pain, a person needs to undergo a blood test to determine morphology, creatine levels, and glucose. Quite often, doctors prescribe biochemistry, with the help of which it is possible to identify many gastrointestinal diseases. A high level of white blood cells indicates the presence of infection in the body, a low concentration of hemoglobin indicates internal bleeding.
A urine test is required. With its help, it is possible to identify most pathologies of the urinary system. If an infection is suspected, bacteriological urine culture is prescribed.
Stool analysis is necessary to identify disorders in the digestive system. Using this study, it is possible to establish the presence of intestinal infections and parasites.
Instrumental methods
To clarify the diagnosis, doctors often refer the patient to the following procedures:
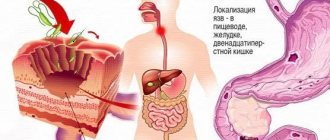
- Gastroscopy: reveals pathologies of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. To perform the procedure, a person must swallow a long tube with a small chamber at the end.
- Colonoscopy. The study is carried out to determine the condition of the mucous membrane of the large intestine and rectum.
- Biopsy. The procedure is performed in the presence of formations of unknown origin.
To identify many pathological conditions, x-rays and ultrasound examination of internal organs are prescribed. In severe cases, MRI, CT, irrigoscopy, and angiography are used.
Many people have stomach pain these days. Many people experience similar symptoms, but not everyone goes to the doctor to solve this problem. If it hurts in the area of the anterior part of the sternum, then treatment ends with visiting pharmacies and taking your own medications. With ordinary gastritis, improvements may occur, but with an ulcer, such a treatment method can become fatal. In order to avoid complications, you need to consult a doctor who will conduct the necessary diagnostic tests and prescribe effective and safest therapy. Which specialist should you go to if you experience epigastric pain?
If your stomach hurts and you don’t know which specialist to go to for a consultation, then you can contact a therapist who will compare the symptoms of the disease and recommend a consultation with another doctor. Most often, with an ulcer or if this disease is suspected, the patient is referred to an appointment with a gastroenterologist. Pain can appear not only with an ulcer, but also with exacerbation of gastritis. In this case, it is also necessary to take special measures to eliminate the cause of the development of unpleasant symptoms that cause discomfort.
Note! Symptoms of pathologies of the digestive organs may not be clearly expressed, so it is quite difficult to make a correct diagnosis on your own. If your stomach hurts, you should immediately consult a specialist.
When is emergency medical attention required?
There are conditions when you cannot do without urgent medical help:
- sudden acute pain;
- the person’s behavior has changed (he suddenly became lethargic, apathy appeared);
- sudden vomiting with pain;
- lack of stool for several days;
- a person refuses to eat;
- weakness, accompanied by cold sweat, pale skin, rapid pulse;
- fever (high temperature);
- the wall of the abdomen is very tense, as if stiff.
If any of these symptoms appear, you must immediately call an ambulance.
Which doctor should I contact if I have a high fever and stomach pain?
An increase in temperature to 38.5 degrees indicates an infectious process. Most likely, the cause is rotavirus infection or another inflammatory process of the gastrointestinal tract.
If you have stomach pain accompanied by fever and heat, you should call an ambulance. They are obliged to deliver the patient to a hospital setting, where highly specialized doctors (gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, hepatologist) will prescribe the necessary tests and studies and find out the exact cause of the pathological condition.
You should not suppress your fever by taking antipyretic drugs on your own if you have an infectious process, as this can lead to complications and the development of chronic diseases.
What characteristics of pain matter?
The pain can be very intense, “dagger-like”, unexpected. Then you should not hesitate to call an ambulance and do not try to rinse the stomach yourself or apply a heating pad. In such cases, time decides the issue of the patient’s life. Even pain relief may be associated with necrosis or purulent melting of nerve endings, and not with recovery.
Therefore, in case of acute, sudden pain, examination and assistance from a doctor are necessary immediately. When recommended to go to a hospital, you cannot refuse. Simple observation of the patient and control tests are easier to carry out in a specialized department.
You can’t “wait until the morning, until Monday,” and hope for a doctor to call you at home
Acute pain is caused by an attack of appendicitis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, renal colic, a stomach ulcer when the wall is perforated, a violation of the integrity of the intestine due to Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis. In women, they occur with apoplexy (hemorrhage) of the ovary, torsion of the epididymal cyst, or ectopic pregnancy.
Very intense increasing pain occurs with strangulated abdominal hernias, exacerbation of stomach and duodenal ulcers, pancreatitis, intestinal obstruction, inflammation of the ovaries in women, prostate inflammation in men, stagnation of bile in the bladder, and cancerous tumors. Repeated attacks indicate the presence of a chronic pathology.
According to the mechanism of formation, pain sensations are distinguished:
Why does my stomach and abdomen hurt?
- cramping type - characteristic of spasms of hollow organs under the influence of strong nerve impulses (intestines, uterus, ureter, gall bladder, stomach);
- dull aching - caused by stagnation in hollow formations;
- bursting, gradually increasing - occur in parenchymal (dense) organs, such as the liver, pancreas, they are caused by an increase due to edema, tumor growth, and stretching of the capsule;
- pulling - characteristic of chronic inflammatory processes accompanied by the formation of adhesions; during pregnancy they are formed due to stretching of muscle ligaments.