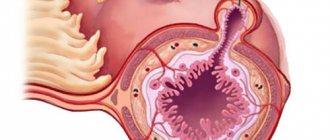
A hiatal hernia occurs as a result of the displacement of a certain organ into the chest cavity through the opening of the diaphragm. More often, a similar phenomenon occurs in the stomach. As a person ages, the muscle and connective tissues of the diaphragm weaken, which leads to the expansion of the opening and the displacement of organs into the abdominal cavity.
There are also numerous provoking factors (constipation, overeating, coughing). Modern treatment methods make it possible to eliminate a hiatal hernia without surgery. It is important to go to the hospital in a timely manner and undergo examination.
Types of disease
In medicine, there are 3 main types of hiatal hernia:
| Name | Description |
| Sliding (axial) hernia | In most cases it is accompanied by reflux esophagitis. The esophageal sphincter is located above the diaphragm. Pathological processes disrupt the functioning of the cardia, namely closing activity. |
| Paraesophageal | There is no change in the position of the cardia. Against the background of reflux esophagitis, there is a greater curvature of the stomach and an exit of the bottom of the esophagus. Pathology is diagnosed in 5% of cases. |
| Short esophagus | The phenomenon often accompanies a sliding (axial) hiatal hernia. Occurs due to spasm and inflammation on the walls of the trachea. A rare form of the disease characterized by abnormal development of the esophagus. |
There is also a mixed type of hernia. A combination of sliding and paraesophageal forms of the disease.
Depending on the degree of displacement of certain areas (volume, level), the following types of hiatal hernia are distinguished:
| Name | Description |
| Cardiac | The cardiac sphincter passes through the opening of the esophagus of the diaphragm, which separates the esophagus and stomach. In 95% of cases, it is a cardiac hernia of the esophagus that doctors diagnose. |
| Cardiofundal | A disease in which the upper part of the stomach moves freely. |
| Subtotal | The stomach appears partially or completely above the diaphragm. |
Esophageal hernia (treatment without surgery is carried out under the strict supervision of a gastroenterologist) requires careful medical diagnosis to determine the type of disease and select effective therapy.
Treatment of sliding hiatal hernia
Treatment of a sliding hiatal hernia involves symptomatic drug therapy and a radical solution to the problem with surgery.
Therapeutic treatment
Treatment without surgery consists of following a strict diet and lifelong use of medications that reduce stomach acidity, improve motility, relieve spasms, and sedatives. Dietary restrictions apply to chocolate, citrus fruits, tomatoes, onions, garlic, mint. It is necessary to exclude sweet carbonated drinks, kvass, beer, champagne, strong coffee and tea. Prescribed drugs of the omeprazole group, antacids containing aluminum and magnesium, and digestive enzymes.
Therapeutic conservative tactics have significant disadvantages. Long-term use of PPIs (Omez, Losek, Pariet, Nexium) increases the risk of complications in the form of intestinal and gastric polyps, gastropathy, and malignant lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Surgery
A sliding hiatal hernia can only be cured surgically. Approaches to surgical elimination of the problem are determined individually. The choice of treatment method depends on the size of the hernial sac and hernial orifice, the presence of strangulation, bleeding, and erosions.
In the arsenal of surgeons, the classic Nissen fundoplication, modified by Toupet, and crurorrhaphy - reduction of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm to natural parameters.
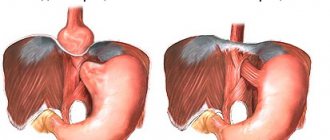
Nissen fundoplication
The canonical operation is performed by open access or laparoscopy, depending on the size of the hernia and the gate. The stomach is adjusted to its normal position. The fundus of the stomach is wrapped around the lower part of the esophagus a full turn and secured with a suture. After the operation, a tight sleeve at the site of the cardiac sphincter prevents natural manifestations of the body - belching, vomiting. This prevents a person from living fully.
Toupet operation
The modified Toupet operation involves turning the stomach around the esophagus only 180-270°. The anterior right surface of the esophagus remains free. The duration of the operation is 2-3 hours, access is open or through five punctures of the abdominal wall. A cuff about 4 cm long is formed. The normal connection between the esophagus and stomach is restored. An anti-reflux barrier is created that prevents acidic gastric contents from irritating the esophagus.
Crurorrhaphy
This is the name of the operation for suturing the esophageal opening of the diaphragm. Crurorrhaphy complements fundoplication and prevents the development of recurrent prolapse. The most popular method of operation is Allison. Access is on the left, between 7-8 ribs. The legs of the diaphragm are sewn together with 3-5 interrupted sutures. At the end of the operation, a drainage tube is installed to remove wound exudate.
A sliding hiatal hernia can be congenital or acquired with age. The main symptoms are constant heartburn, sour belching, chest pain. Diagnosed by X-ray with contrast agent. Treatment consists of taking acid neutralizers or performing surgery to restore normal topography, physiology and anatomy of the organs.
We recommend: How to identify and treat candidal esophagitis?
Stages and degrees
Considering the extent of the spread of pathological changes, doctors distinguish the following stages of development of a hiatal hernia:
| Name | Description |
| Stage I | Only the abdominal part of the esophagus exits through the esophageal hiatus into the area above the diaphragm. The cardiac section is at the same level with it. The stomach is adjacent to the diaphragm, but located slightly higher. |
| Stage II | Above the diaphragm is the abdominal segment and the esophageal sphincter. The stomach is located as close as possible to the opening. |
| Stage III | Part of the stomach passes through the hole along with the abdominal area and sphincter. |
Based on the duration of the course, temporary, transient and permanent esophageal hernia are distinguished. At each stage of the development of the disease, characteristic symptoms arise that require careful diagnosis and accurate diagnosis.
Symptoms
A small esophageal hernia occurs without clinical signs.
Its increase leads to the appearance of characteristic symptoms:
| Name | Description |
| Pain syndrome | In most cases, non-coronary cardialgia (retrosternal pain) resembles the clinical picture, as with myocardial infarction or angina. Unpleasant sensations occur more often after eating or physical activity, with severe bloating, in a lying position, or during coughing. The pain syndrome disappears or decreases after belching, vomiting, or taking a deep breath. The same thing happens if you change your body position or drink water. The pain intensifies when the person leans forward. |
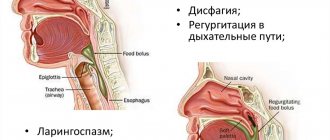
| Dysphagia | A pathognomonic symptom of the disease, which is characterized by impaired passage of the food bolus. Occurs when taking liquid food, cold or hot water. Dysphagia also develops when a person eats quickly or against the background of traumatic factors. |
| Belching air | In some situations, this single sign indicates a hiatal hernia. Appears 15-20 minutes after eating any food. The severity of air belching can be so strong that it causes discomfort to a person. After it, a sore throat appears and the voice disappears. |
| Acid reflux | The acidic contents of the stomach enter the esophagus. Causes an inflammatory process that provokes bleeding and rupture of blood vessels. The level of red blood cells decreases and the likelihood of developing anemia increases. |
| Heartburn | Occurs after eating or changing body position. Against the background of increased tone of the vagus nerve, heartburn worries a person more often at night. |
Concomitant symptoms of a hiatal hernia also include discomfort after eating, a sour taste in the mouth, and heavy breathing. In some situations, hiccups, vomiting, shortness of breath and severe nausea occur.
Seven more signs of a hiatal hernia
Heartburn
Normally, the lower esophageal sphincter tightly closes the opening between the esophagus and the stomach, preventing aggressive gastric contents from flowing back into the esophagus.
With a hiatal hernia, the locking function of the sphincter is very often disrupted, and the contents of the stomach enter the esophagus. In this case, inflammation of the walls of the esophagus and their chemical burn inevitably occur. This is manifested by heartburn, which occurs especially often in a lying position or when lying in a forward position for a long time.
Belching and bitterness in the mouth
Patients with hiatal hernia are often bothered by belching: sour, air, food. It usually appears after eating and, depending on the type of hiatal hernia, can be moderate or very pronounced.
Also, most people with a diaphragmatic hernia complain of a bitter taste in the mouth.
Sudden regurgitation
In a healthy person, regurgitation is preceded by nausea. In a patient with hiatal hernia, regurgitation occurs unexpectedly, without nausea. Most often this happens when lying down, for example at night.
Swallowing disorders
Very typical of hiatal hernias are problems swallowing food. An alarming sensation of “lump in the throat” appears. Most often it occurs after eating liquid or semi-liquid food, especially if it was cold or very hot.
Unlike esophageal cancer, which is also characterized by difficulty swallowing, with a diaphragmatic hernia such difficulties are intermittent, and difficulties with the passage of solid food rarely occur.
Anemia
Dizziness, pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, “unmotivated weakness” and darkening of the eyes can be signs of anemia.
If, when examining blood parameters, it turns out that the level of hemoglobin and/or red blood cells is reduced, it is possible that damage to the walls of the esophagus by gastric juice has led to the development of internal bleeding. In such situations, the doctor should check with the patient whether he has noticed the appearance of black, liquefied stools.
Tongue pain and hoarseness
With a hiatal hernia, hoarseness may appear due to a burn of the larynx by gastric juice.
A rare but typical symptom is pain in the tongue caused by a burn of the oral cavity by the contents of the stomach.
Cough and lung diseases
Patients with a hiatal hernia often wake up in the middle of the night coughing, which is accompanied by severe chest pain. Most often this occurs if the day before a person had a heavy dinner shortly before bed.
The cause of cough lies in the flow of gastric contents into the esophagus, and from the esophagus into the larynx, trachea and even bronchi. For the same reason, patients with hiatal hernia often develop aspiration pneumonia, bronchitis or attacks of bronchial asthma.
Reasons for appearance
A hiatal hernia (non-surgical treatment is carried out after a full medical diagnosis under the supervision of a doctor) is a consequence of high pressure in the abdominal cavity. This happens with severe bloating, constipation, vomiting, sudden bending, or due to severe obesity.
The same goes for ascites, blunt trauma to the abdomen.
Negative factors that contribute to the development of the disease also include the following reasons:
- underdeveloped diaphragm (the first symptoms in a person appear in infancy);
- penetrating injuries to the chest or stomach;
- frequent births, multiple pregnancies;
- dry cough.
Chronic diseases of the digestive system (stomach ulcer, esophagitis, pancreatitis) also increase the risk of a hiatal hernia. Pathological processes develop against the background of impaired innervation of the diaphragm. In older people (over 60 years old), changes appear due to weakened tone of the diaphragm.
Physiology of the issue
A sliding hernia is a pathology when the abdominal part of the esophagus through the enlarged opening of the diaphragm can enter both the chest and back into the abdominal cavity. Because of this, it is called a sliding hernia. In addition, one wall of the formation sac is an internal organ in the retroperitoneal space.
More often, this pathology is identified in women, and with age, the risks of such a hernia increase. It often develops without any symptoms. The patient’s complaints will directly depend on the degree of the hernia, as well as existing concomitant gastrointestinal pathologies.
There are a number of physiological openings in the diaphragm between the thoracic and abdominal zones. Vessels, nerves and the esophagus pass through here. Normally, all holes are sealed due to connective tissue. It is worth understanding that the pressure in the abdominal cavity is stronger than in the sternum, which means that under a number of provoking factors, the thin barrier can stretch, as a result of which movement from the bottom up begins. This is how a hiatus hernia is formed.
Question answer
Why do esophageal spasms occur?
Diagnostics
It is impossible to determine pathological processes on your own, since the disease is accompanied by numerous symptoms similar to other disorders of the digestive system. Diagnostics will allow you to establish an accurate diagnosis.
The following studies are used:
| Name | Description |
| X-ray with barium sulfate contrast | The results will show a high location of the esophageal sphincter, the presence of a cardia above the diaphragm. The subdiaphragmatic section of the esophagus is absent, the diameter of its opening is widened. A diagnostic method that allows you to determine the size of the hernia, its mobility, and the presence of a short esophagus. |
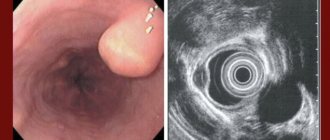
| Esophagoscopy | Endoscopic examination of the esophagus. Allows you to determine the condition of the mucous membrane. |
| Computed tomography (CT) | The most informative examination method, which is used in difficult situations. Helps confirm or refute volvulus of paraesophageal hernia. The method is also used to diagnose repeated relapses of the disease. |
| Biopsy | Histological studies of a small area of the esophageal mucosa. The material is taken during esophagoscopy. |
| Endoscopy | The study will show a displacement of the esophagogastric line above the diaphragm, erosion, and ulcers. |
| Esophagomanometry | A diagnostic method that allows you to determine the state of motility of the esophagus, the location of the legs of the diaphragm and the lower sphincter. |
Esophageal hernia (treatment without surgery is carried out if the disease is detected at an early stage) in some situations is diagnosed accidentally, during an X-ray examination of the chest organs.
Additionally, daily pH measurements are also performed (acidity in the lumen of the esophagus and stomach is measured). It is important to differentiate the disease in order to select the most effective treatment and prevent serious complications.
When to see a doctor
You should visit a gastroenterologist as soon as the first symptoms of a hiatal hernia appear. Without timely assistance, the risk of an emergency condition increases. A blockage or strangulation of a hiatal hernia leads to disruption of blood flow in the stomach area.
The patient experiences severe nausea, vomiting, and the process of gas separation and emptying is disrupted. Pain in the chest area may indicate more than just a hiatal hernia. Similar symptoms are accompanied by numerous diseases (heart, peptic ulcer), which are important to identify in a timely manner.
Prevention
It is difficult to prevent the development of a hiatal hernia, but there are useful recommendations and advice from a gastroenterologist that will help reduce the risk of developing pathological changes:
- Control your weight, get rid of extra pounds.
- Do not lift too heavy loads yourself.
- Engage in moderate exercise that works your abdominal muscles.
- Do not strain during bowel movements.
- Do not tighten the straps too tightly.
It is necessary to strengthen the abdominal muscles, treat constipation in a timely manner, eat properly and rationally, and get rid of bad habits. If a patient has been diagnosed with a disease, clinical observation is recommended.
How to treat
Hernia treatment is carried out both conservatively and surgically. It is necessary to seek advice from both a gastroenterologist and a surgeon. Therapy is often complex. Here it is worth understanding that after detecting a formation, it is necessary to begin therapy as quickly as possible in order to reduce the risk of complications. If we are talking about non-surgical treatment, then the following measures are used. Firstly, it's diet. It is recommended to eat split meals, every 3 hours, but the portions should be small - about 200-300 g. Naturally, it is necessary to exclude potentially dangerous and always classified as dangerous foods - fried, fatty, pickled, smoked and other foods. After all, they irritate the mucous membranes and further increase the production of gastric juice. The optimal solution would be to shift the diet towards the consumption of boiled and steamed dishes, fresh fruits, lean meat, etc. Depending on the severity of the situation, they may be advised to eat pureed food or dishes with a liquid consistency.
In this situation, the normalization of the regime and lifestyle is also of no small importance. Naturally, and this is not even subject to discussion, you need to give up bad habits, get proper rest and engage in physical activity in moderation. Abdominal exercises - various loads and bending - are contraindicated in this situation.
If we talk about drug therapy, antacids may be offered to reduce acidity, drugs that suppress the production of hydrochloric acid, drugs for belching and heartburn, drugs to relieve pain, drugs to restore the protective properties of the mucous membrane of the digestive system.
If there are serious complications, such as bleeding, doctors prescribe additional therapy. These may be means to restore iron balance, etc. The issue of surgical intervention may also be considered.
Therapy must be carried out in consultation with a doctor and exclusively according to his recommendations - this is the only way to guarantee a high-quality result.
Treatment methods
Esophageal hernia (treatment without surgery is carried out comprehensively) requires the help of a gastroenterologist. Properly selected therapy helps restore gastric motility, reduce the negative manifestations of a hernia and alleviate the patient’s condition. Conservative therapy involves following a strict diet, using medications, physiotherapeutic procedures and folk remedies.
Medications
Medicines are selected by a gastroenterologist after a complete medical diagnosis, taking into account the results and individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Antacids | "Phosphalugel", "Maalox" | Medicines reduce acidity, prevent the development of hyperacid gastritis and eliminate the inflammatory process. Patients are prescribed 16-40 g 2-3 times. per day, taking into account the degree and severity of the disease. |
| Histamine receptor blockers | Ranitidine, Famotidine | The drugs reduce the secretion of stomach acid. The daily dosage is 0.3 g. The dose can be divided into 2 times. The course of therapy lasts from 4 to 8 weeks. |
| Prokinetics | "Domrid", "Motilium" | Medicines restore motor function of the stomach. The drug is taken 15-20 minutes before meals. The recommended dosage is 10-20 mg 3 times a day. per day. |
| Bile acids | "Urohol", "Ursofalk" | Reduce the negative impact of acid that enters the esophagus from the stomach. The medicine is taken 10-20 drops. 3 r. per day before meals 20 minutes. Therapy lasts from 5 days to 1 month, taking into account the degree of development of the pathology. |
| Proton pump inhibitors | "Omeprazole", "Controloc" | Reduce acid production. Medicines cause fewer side effects than blockers. It is recommended to take 20 mg 1 time in the morning. per day for 4-8 weeks. |
The medicine should be taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor, since many drugs cause side effects. Self-treatment is not recommended to avoid the development of serious complications.
Traditional methods
Complex therapy for hiatal hernia involves the use of recipes from healers and healers, unless there are serious contraindications. It is recommended to discuss treatment with your doctor, since many components of traditional medicine can cause complications.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Herbal collection | Mix flax seeds, coltsfoot leaves, yarrow and mint. Pour hot water over the ingredients and place on low heat. Boil for 5 minutes. Cool and strain. | The medicine is taken 3 times. per day 0.5 tbsp. The product reduces pain and discomfort. |
| Shoe decoction | Pour 1 tsp. herbs with boiling water, leave for 2-3 hours. Strain the resulting mixture and take for medicinal purposes. You can add a small amount of honey for taste. | For a hiatal hernia, it is recommended to drink ¼ tbsp. 2-3 r. per day. |
| Gooseberry infusion | The leaves of the plant are first dried and crushed. Pour 1 tbsp. hot water (500 ml) and leave for 2 hours. | The finished medicine is taken in 120 ml 4 times. per day. |
| Phytocollection | Mix chamomile flowers (150 g), gooseberry leaves (50 g), cumin seeds (50 g), peppermint (100 g). Pour 1 tsp. herbal mixture with boiling water (180 ml). Infuse the medicine for 5 minutes, strain and drink in small sips. | The medicine can be taken at any time up to 5 p.m. per day. |
Potato, pumpkin and carrot juice, as well as orange peels, help eliminate severe heartburn. Honey and aloe can help you cope with belching. Abdominal bloating is reduced by a decoction with the addition of yarrow, fennel fruit and St. John's wort.
Other methods
It is recommended to treat a hiatal hernia using complex methods. You can get rid of disorders without surgery at an early stage if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. The gastroenterologist recommends giving up bad habits. Cigarettes relax the gasoestrophageal sphincter and surrounding muscles, which leads to organ displacement. The same goes for alcoholic drinks and coffee.
Physical work is also contraindicated for patients. You should not wear tight belts or bandages, as they increase intra-abdominal pressure. It is recommended that a person sleep with his head elevated. Proper nutrition (5-6 times a day) will reduce the unpleasant symptoms of a hiatal hernia and prevent its exacerbation.
There are foods that increase the secretion of gastric juice and increase the risk of developing the disease.
| Prohibited Products | Recommended Products |
|
|
Before cooking meat, it is recommended to completely remove fat. During meals, food is consumed slowly, chewing thoroughly. Do not forget about the drinking regime; every day you need to drink 1.5-2 liters of clean still water.
The article discusses effective methods of treating hiatal hernia without surgery.
Physiotherapeutic procedures contribute to the overall recovery of the entire body. Treatment is recommended for concomitant pathologies together with a hiatal hernia.
Patients are prescribed the following procedures:
| Name | Application |
| Drug electrophoresis | Antispasmodic medications are used. |
| Paraffin therapy | Eliminates spasms and improves metabolic processes. |
| Therapeutic baths | Calms and removes toxins from the body. |
| Ultrasound therapy | Increases the body's resistance to negative environmental factors. Accelerates the process of regeneration of damaged tissue in the stomach and esophagus. |
Physiotherapy improves health, eliminates inflammation and pain, and relaxes muscle tissue.
Possible complications
In the absence of timely and correct treatment, a hiatal hernia entails serious consequences:
| Name | Description |
| Cardiovascular diseases | Coronary pain during hiatal hernia occurs due to irritation of the vagus nerve. Subsequently, spasm of the coronary vessels of the heart occurs. Pathological changes lead to the development of cardiovascular diseases, including myocardial infarction. |
| Aspiration pneumonia | One of the symptoms of a hernia is belching stomach contents or air. A large amount of regurgitated contents, especially at night, leads to the development of aspiration pneumonia. The pathological process occurs due to contraction of the esophagus. |
| Esophageal strangulation | A dangerous complication of a hernia, which is accompanied by severe pain in the chest area. The swallowing process is also impaired. |
| Gastric perforation | Through holes appear in the walls of the stomach or duodenum. Its contents flow into the abdominal cavity. |
| Peptic stricture | A type of cicatricial narrowing in which the esophageal mucosa is damaged from the negative effects of hydrochloric acid and bile. |
| Reflux esophagitis | A chronic pathology that occurs against the background of an unexpected and periodically occurring reflux of stomach contents into the lower esophagus. An inflammatory process develops on the mucous membrane. |
The most serious complication of a hiatal hernia is an ulcer or scar narrowing (stricture). Long-term pathological processes provoke malignant degeneration of cells and the development of cancer. There is also a high probability of internal bleeding, which threatens a person’s life.
A hiatal hernia at an early stage of development does not require serious medical procedures. Treatment is carried out without surgery; medications and doctors’ recommendations make it easy to restore the mobility of the diaphragm. The advanced form of the disease requires complete diagnosis and therapy selected by a gastroenterologist.
Why is this hernia difficult to recognize?
It is often really very difficult to suspect a hiatal hernia.
- In half of the cases, the pathology does not manifest itself at all.
- In 35% of cases, the main complaint of patients is interruptions in the functioning of the heart and chest pain, which are often very similar to those that occur with coronary heart disease.
- The majority of patients are elderly people, who usually already have a whole “bouquet” of health problems.
- The presence of a hiatal hernia does not at all exclude the presence of cardiovascular pathology.
All this creates serious diagnostic problems. Many patients continue to undergo treatment with a cardiologist for years, all to no avail, while the actual disease continues to progress.