The first thing you should do when you learn that your child is complaining of abdominal pain is to calm down and not panic. Next you need to identify the symptoms. Depending on the causes, abdominal pain can be varied: dull and aching, sharp and cramping, stabbing and cutting. It can be constant or occur periodically, be localized in the upper or lower part of the abdomen, extend to one of the hypochondriums or, alternatively, to one of the sides. Determining the causes of pain is the first step in dealing with it.
The child's stomach hurts. What can be given if pain occurs as a result of poor nutrition?
In a situation where a child complains of pain in the abdomen, the first thing parents think about is how to save him from suffering. If the problem is the baby’s malnutrition, you need to carefully review his diet. It is necessary to exclude from it milk, mushrooms, kvass, any carbonated drinks, salty and smoked foods, as they cause active gas evolution. Vegetables and fruits, on the contrary, need to be added to the diet, because they help improve the digestion process.
So, if a child has a stomach ache, what to give at home should be decided based on the causes of the illness. If there are complaints of bloating and flatulence, you should immediately give the tablet “Disflatil” or the well-known “Espumizan”.
If a child has a stomach ache, what can be given to cure it is easy to decide. When unpleasant sensations appear after eating, Mezim, Enterosgel or Festal will help.
You observe that your child goes to the toilet frequently. Perhaps he has diarrhea, then Laktovit or Linex will help.
Preventive actions
Preventing indigestion:
- proper nutrition - the absence of so-called unhealthy foods, sweet carbonated drinks from the menu and the inclusion of fresh seasonal vegetables, berries, fruits, and dairy products in the diet;
- proper nutrition for a nursing mother - avoidance of foods that cause increased gas formation and colic;
- physical activity;
- strengthening the immune system;
- eating vegetables, berries and fruits only after thorough washing;
- comfortable psychological atmosphere in the house;
- regular visits to the doctor.
Prolonged pain is a signal to call an ambulance
If a child has a stomach ache, what can be given must be decided only after finding out the origin and causes of the pain. Pain that lasts more than half an hour in a row, especially if it is accompanied by symptoms such as nausea and/or fever, is a clear signal to call an ambulance.
The causes of pain are extremely varied. Usually they are not serious and harmless, but there are also those that require immediate intervention, and it is impossible to eliminate them without the help of a specialist. The true cause of abdominal pain cannot be found out simply by interviewing the child; it will become obvious only after consultation with a certified specialist: after examination, examination and carrying out the necessary tests.
Drugs most often found in prescriptions for pediatric gastroenterologists
To relieve painful spasms, you can turn to analgesics. Also, if a child has a stomach ache, you can give Noshpa. If there is no increase in temperature, nausea and/or vomiting, treatment can be temporarily stopped, taking a wait-and-see approach. Provided that after the end of the medication the pain does not recur, nothing more should be done. But if the pain returns, moreover, intensifies, and new symptoms appear, you should definitely seek advice from a gastroenterologist.
Any further treatment should be carried out exclusively in accordance with his recommendations. If a child has a stomach ache, what can be given should be decided by the doctor. The most common drugs found in prescriptions are:
- For complaints of diarrhea and diarrhea - “Gastrolit” and “Regidron”.
- If a child has a stomach ache and vomiting, what can you give? 6 years is the age at which indigestion is quite common. In this case, give activated carbon, Polyphepan, Enterodes and Smecta.
- For bloating and heartburn - Almagel, Rennie, Maalox and Phosphalugel.
- For heaviness in the stomach area, a feeling of overeating - “Festal”, “Creon” and “Mezim”.
- For diseases of the genitourinary system, kidneys, and stomach, “No-spa” will help perfectly.
Preventive measures
To prevent the appearance of painful sensations in the abdominal area, it is recommended to adhere to the following tips:
- follow the established meal plan, and if you have chronic diseases, stick to a diet;
- reduce the consumption of fried, spicy and fatty foods to a minimum;
- if possible, eliminate or minimize the consumption of confectionery, pizza, soda;
- consume fermented milk products, fruits and vegetables, lean meat and fish more often;
- move more often, which will help strengthen the immune system;
- dress warmly in winter to avoid hypothermia;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene before and after meals;
- maintain a calm atmosphere in the family without stressful situations.
The cause of painful sensations in the abdomen is colic and increased gas formation resulting from the consumption of certain types of foods. Then diet can help. However, these symptoms may also indicate more serious problems - gastritis or stomach ulcers. Acute pain can be a harbinger of appendicitis or cystitis and requires calling an ambulance. For any type of stomach pain that occurs in a child, you should consult a doctor for advice.
Source
Dyspeptic disorders
Such disorders tend to develop in the absence of a sufficient amount of enzymes necessary for digesting food in the intestines. In such cases, children experience a feeling of fullness in the stomach; belching, heaviness in the stomach, nausea and even vomiting are often observed. Often, disturbances in the functioning of the stomach are accompanied by abdominal pain and abnormal bowel movements. In such cases, the child can be cured by radically changing his diet. First of all, you need to immediately eliminate solid foods, soda, caffeine, sweets, fruit juices and milk. Give a few tablets of activated carbon or Mezim.
Possible reasons
Most often, when young parents experience nausea and abdominal pain in their child, they suspect overeating or food poisoning. But we must not forget that these symptoms are also characteristic of other pathological conditions.
For example, nausea and pain in the epigastric region immediately or some time after eating may indicate the presence of gastritis or a stomach ulcer. These conditions are quite common, especially among adolescents due to irregular and low-quality nutrition.
Also, unpleasant symptoms are characteristic of the following diseases:
- gastroenteritis . This gastrointestinal pathology is manifested by nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and increased body temperature. It has infectious (viruses, bacteria, protists) and non-infectious genesis (individual intolerance). Gastroenteritis usually begins acutely;
- ARVI . The condition is characterized by body aches, fever, nausea, cough and runny nose. Sometimes there may also be abdominal pain;
- appendicitis . Pathology occurs due to inflammation in the appendage of the cecum. In this condition, the child experiences severe pain in the abdomen and lower back when moving, hyperthermia, nausea, and impaired bowel movements;
- intestinal obstruction . It can be acquired as a result of intussusception or congenital if caused by a developmental defect. This disease is characterized by the absence of bowel movements, severe bloating, nausea, pain, and vomiting. If feces come out in small quantities, then blood inclusions are observed in them;
- cholecystitis . It is an inflammation of the gallbladder. Manifested by abdominal pain and nausea. In acute cases, vomiting, hyperthermia, and weakness are possible. Symptoms intensify after the child eats fatty foods, overeats, or goes hungry;
- duodenal ulcer . The disease is chronic. It develops quite quickly. May adversely affect the functioning of internal organs;
- constipation _ Accompanied by mild abdominal pain, nausea, and lack of appetite. Constipation often occurs due to insufficient fluid intake, against the background of cholecystitis, addiction to sweets and flour products;
- acetonemic syndrome . It occurs occasionally, accompanied by vomiting and abdominal pain. Caused mainly by dietary errors, which leads to an increase in the plasma concentration of ketone bodies. In most cases, it goes away on its own after 5 years;
- hepatitis, liver cirrhosis . In addition to abdominal pain and nausea in the child, parents will notice yellowing of the skin, hyperthermia, and weakness;
- helminthic infestation . Accompanied by signs of intoxication. The baby may experience sudden weight loss, changes in taste preferences, and itching in the anus.
Nausea and abdominal pain often occur in children who do not eat enough
Also, abdominal pain and nausea appear during hunger. In this case, they disappear after eating. Determining the exact cause of the pathological condition can be difficult. To understand why a child feels unwell, you need to analyze his lifestyle, nutrition, and undergo a series of diagnostic procedures.
Abdominal pain and nausea may be psychological in nature. This applies to overly emotional guys. There are often cases when, against the background of worries and stress, the baby experiences unpleasant sensations in the abdomen. Diarrhea and vomiting are sometimes observed.
If a child has a stomach ache, what to give? 7 years - school and first lunches in the cafeteria
Food poisoning is common among children of primary school age. The cause of the disease is the consumption of food that is unusual for the child or spoiled. Most often, cases of poisoning of children are observed during their first visits to the school canteen. In addition to abdominal pain, malaise can cause a pre-vomiting state and directly vomiting and diarrhea. Quite often, the result of indigestion in children is general intoxication of the body and fever. The first thing to do is to do a gastric lavage and an enema. If a child has a stomach ache, what to give? 7 years is the age at which a child’s body is already able to cope with such an illness as mild food poisoning. In this case, he should be given to drink as much pure, non-carbonated, unsweetened water as possible. And if the abdominal pain is accompanied by diarrhea, you should give him activated charcoal and Furazolidone.
Symptoms of diseases
In order to understand what is causing the discomfort, it is necessary to localize the pain. Each disease is characterized by pain in a certain place:
- If the baby has a dull pain on the right side in the upper abdomen, which may also be accompanied by nausea, a rise in temperature to 39-40°C, as well as diarrhea with mucous discharge, painful urination, then in this case we may be talking about appendicitis.
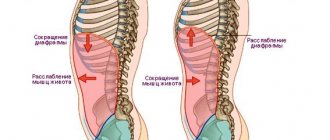
- Painful sensations on the left under the ribs. This may indicate a pancreatic disease. If after the activity of the baby, as well as during intense physical activity, pain occurs, then we are talking about improper functioning of the diaphragm, which can be caused by a severe bruise.
- Pain in the stomach extends to the navel area. This may indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract. This may be a consequence of improper and irregular nutrition. If painful sensations are also accompanied by elevated temperature, then we are most likely talking about poisoning through heavy metals.
- Acute pain in the abdomen. With these painful sensations, the child has difficulty moving, severe tension in the abdominal wall appears, and all this is accompanied by a high temperature. Here we can talk about chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract or the appearance of an intestinal infection.
- Pain occurs on the side. This may indicate inflammatory processes in the kidneys (nephritis). Sharp pain combined with elevated temperature is a reason to urgently call a doctor.
- If there is severe pain in the abdomen, and at the same time the child has an elevated temperature, then it is quite possible that we are talking about peritonitis. Difficulties arise when the child moves. This condition may be caused by complications of gastritis, intestinal obstruction, or exacerbation of appendicitis.
Systematic constipation
If a child complains that he wants and cannot go to the toilet “for the most part,” and at the same time he is tormented by abdominal pain and nausea, the first first aid that parents can provide in this case is laxatives for children or an enema. Next, in order to avoid recurrence of such situations, you should change the child’s diet. More unsweetened non-carbonated liquid, vegetables and fruits, more movement. Less spicy, fatty and heavy foods.
If you approach the problem of constipation from the point of view of traditional medicine, then it is solved this way: for two weeks you should drink flax seed brewed according to a special recipe. The recipe is as follows: pour 1 tablespoon of seeds into 150 ml of boiling water, leave for half an hour, stirring every 10 minutes. Another good way to get rid of constipation is to drink tea made from dried apples, fresh cherries, decoctions of mint, plantain, cumin, and fennel. You can drink yogurt. It is also an excellent laxative.
Flatulence and colic
One of the common causes of abdominal pain in a child is the accumulation of gases. If such symptoms appear in infants under six months of age, it means that the nursing mother is not eating properly or the formula that the baby is fed is not selected correctly. If a child has a stomach ache, traditional medicine can advise what you can give him. In this case, the first aid will be a tummy massage, and if it does not help, then most likely you need to change the mother’s diet or start feeding the baby with a properly selected formula. It is often recommended to give your baby dill water - a decoction of fennel seeds.
There is also a more dangerous cause of flatulence and colic in a baby - a congenital pathology in the intestinal area.
This disease is a problem not only for infants, but also for adolescents. If a child in adolescence complains of symptoms of flatulence, you can try to help him with folk remedies. For example, dull pain and heaviness in the stomach can be relieved by taking dandelion decoction half an hour after eating.
Diagnostic measures and therapy
Before treating colic and spasms, it is important to determine the cause of their occurrence. This requires a medical examination. Using a general blood test, anemia and inflammation are detected. Biochemical analysis helps determine disturbances in the activity of the liver, kidneys and pancreas, as well as find out the proportion of electrolytes. Thanks to the corpogram, the composition of the child’s stool is examined. You can’t do without a general urine test. Colonoscopy, CT, radiography and ultrasound will help you obtain accurate information about disorders in the body. FEGDS is also mandatory.
In case of intense pain and its intensification, emergency medical care is required. Before doctors arrive, you should not use medications, enemas or heating pads. Otherwise, you can aggravate the situation or blur the clinical picture. The treatment method directly depends on what cause caused the colic and spasms. In some cases, surgery may be required.
The following pharmacological drugs are used in the treatment of spasms and colic:
- sorbents – Sorbex, Activated carbon, Enterosgel, Atoxil;
- antidiarrheal drugs containing simethicone - Espumisan, Smecta;
- sedatives - Valerian;
- antispasmodics - Buscopan, Drotaverine and Duspatalin.
Herbal medicine deserves special attention; before using it, you should consult a doctor. If colic occurs against the background of constipation, then decoctions prepared from licorice, buckthorn, elderberry and anise will help eliminate the problem and improve bowel movements; such herbs are also used when a child has bloating. A complex of alder cones, oak bark and bird cherry will help eliminate putrefactive and fermentation processes. They should be steamed in a steam bath. The daily dose is 250 milliliters.
If your baby has a stomach ache, contact a gastroenterologist or pediatrician. Do not ignore symptoms, as they may be a signal from the body about the progression of a dangerous disease. Feeding a child must be based on dietary principles prescribed by the attending doctor.
helminthic infestations
If a child (3 years old) has a stomach ache, what can be given must be decided based on the causes of the pain. If symptoms such as accumulation of gases, flatulence and pain in the stomach are observed simultaneously, they signal the occurrence of helminthic infestations in the child’s body, that is, that worms have appeared. This disease is accompanied by poor appetite, allergies, and anemic (pallor) skin. To cure a child of worms, you need to give him grated carrots, onions, garlic and walnuts and, of course, pay close attention to hygiene. Traditional medicine also recommends the following recipe for treatment of helminthic infestations: 1 tsp. Stir the flower buds of tsitvarny wormwood with the same amount of honey. The resulting product should be given to the baby on an empty stomach. After that, do not give the child anything to eat for two hours and repeat the medication. The final stage of treatment will be a laxative. Glauber's salt can be used as a laxative. It should be given to a child at the rate of 1 gram per 1 year of life. The child should remain calm throughout the treatment, and a warm heating pad placed in the stomach area will help reduce pain and speed up recovery.
GERD in children: what you need to pay attention to
If your baby constantly regurgitates food after feeding, it may be due to GERD.
GERD - what is it?
GERD is a disease in which reflux of stomach contents causes pain and/or complications. Therefore, GERD is different from simple belching, which we talked about before.
GERD can have different symptoms. For some people, reflux is accompanied by heartburn or an acidic sensation at the back of the mouth. In other cases, it can lead to inflammation of the esophagus (esophagitis).
Why does GERD occur?
As a rule, the cause of this is the weakening of the muscle ring, which we mentioned above. Because of this, the baby's stomach acid can often rise up the esophagus. Unlike the gastric mucosa, the esophageal mucosa in children and adults is not able to withstand the irritating effects of stomach acid. Therefore, if the mixture that the baby spits up contains a lot of it, the child may experience pain. Sometimes they are similar to heartburn symptoms.
GERD is most common in babies with low birth weight and in babies who were born prematurely. The disease also occurs in infants who are allergic to cow's milk or suffer from nerve or muscle disorders, such as cerebral palsy.
Detecting GERD in a child
Here are some typical signs of GERD.
If your child:
- often regurgitates food immediately after eating or within two hours (most likely, if this happens later, then the child does not have reflux, but vomiting);
- arches the back during feeding or immediately after it;
- refuses food, even if he calmly sucks a pacifier or pacifier;
- has difficulty falling asleep;
- irritated and often cries;
- has bad breath;
- coughs and/or has trouble breathing.
When should you see a doctor?
You should visit your doctor if your child develops any of the signs described above. If you notice any of the following symptoms in addition to the previous signs, you should immediately take your child to the doctor:
- if regurgitation turns into “fountain” vomiting;
- if the vomit contains bile (green or yellow-green) or traces of blood;
- if there are new signs of malnutrition, feeding difficulties or growth retardation;
- if regurgitation continues after the first year of the child’s life.
If you think your child may be allergic to baby food or cow's milk, you should tell your doctor. A skin rash, vomiting, or diarrhea may be signs of an allergy.
Another cause of reflux (quite rare) may be the presence of a blockage in the child's gastrointestinal tract. Doctors usually consider this possibility when all others have already been ruled out.
Tests needed to detect GERD
If your child has symptoms that concern your doctor, he or she will refer you to your pediatrician for evaluation. There are different types of examinations that will help establish a diagnosis.
Endoscopy
A long, thin, flexible tube is inserted into the baby's esophagus like a telescope to try to find any problems. An endoscope can also be used to take a small sample of tissue from the esophagus. This procedure is known as a biopsy. The laboratory analyzes tissue samples. If your child's doctor prescribes this procedure, your child may also be given sedatives and oxygen therapy before the procedure.
Monitoring acidity (pH-metry) of the esophagus
This test allows you to determine the amount of fluid and acid in your child's esophagus. To carry out the procedure, a small tube is inserted through the mouth or nose into the baby's tummy and left there for about a day. All this time, the device is connected to a monitor, which measures and records the amount of fluid that can pass through the child’s esophagus.
X-ray examination of the esophagus with barium
First, the child will need to drink a barium suspension that will coat the gastrointestinal tract. After this, the child will be sent for an X-ray examination to obtain an image of the gastrointestinal tract. Barium will show the shape of the gastrointestinal tract on the image and help determine the presence of the disease.
The results of one or all studies together are necessary for specialists to make a diagnosis.
Stress and anxiety as a cause of abdominal pain in children
Most often, abdominal pain due to increased anxiety and stress is observed in children under 10 years of age. In this case, parents ask themselves the following questions: what to do if a child’s stomach hurts, what to give? 10 years is the age when children are already able to thoroughly and consistently explain the causes of anxiety and stress and successfully deal with them.
Children under 10 years old can tell what exactly is bothering them only with the help of parents asking leading questions. Abdominal pain that occurs under the influence of stress disappears after eliminating the causes that caused the child to feel restless and anxious. Under no circumstances should he be allowed to withdraw into himself. In such a situation, parents should establish maximum contact with the child and help him deal with his fears. The previously mentioned analgesics and No-shpa will help you from painful spasms.
What types of abdominal pain are there?
Pain in a child's abdomen can be caused by irritation of the sensory nerves of internal organs (visceral pain), irritation of the peritoneum, or referred pain from other organs. The nature of the pain can tell parents and, especially, the doctor what is happening to the child.
Visceral pain occurs when irritants impact an internal organ such as the stomach or intestines. Tension, stretching and poor circulation stimulate sensitive nerve endings and are transmitted in the form of pain along nerve fibers to the spinal cord. Since the irritated nerves enter the spinal cord at several levels and lack the “insulating” myelin sheath, the pain is usually dull, vague in location, and most often manifests itself as pain in the middle of the abdomen.
- The pain is felt as “in the upper abdomen” if the pathological process is located in the lower esophagus or in the stomach.
- Pain “around the navel” is felt if the small intestine is irritated
- Pain in the “lower abdomen” is felt if there are problems in the colon.
Pain due to irritation of the peritoneum occurs when it is exposed to various factors, such as stretching, inflammation or impaired local circulation. Pain resulting from ischemia (compression), inflammation or stretching of the peritoneum is transmitted through myelinated (sheathed) nerve fibers, which very accurately convey the location of pain. Therefore, pain from irritation of the peritoneum is usually acute, severe and limited in location, and coughing and movement can intensify it. Such pain occurs in cases where inflammation has spread beyond the organ and began to affect the abdominal cavity and peritoneum, as, for example, with appendicitis, peritonitis, perforation (breakthrough) of a stomach or intestinal ulcer.
Referred pain , although it has many of the characteristics of pain from peritoneal irritation, is caused by damage to an organ outside the abdominal cavity. This is due to the fact that several organs may share some of the same nerve fibers, and when the pain impulse reaches the brain, its perception is disrupted. A classic example is the pain experienced by a child with pneumonia localized in the lower lobes of the lungs. At the same time, this pain is felt as if “the stomach hurts.”
Still have questions?
Get an online consultation from leading pediatricians in St. Petersburg!
A professional and experienced pediatrician will answer your questions.
Medical care for a child without leaving home at a convenient time.
sign up for a consultation
A Skype consultation lasts 45 minutes.
How to prevent pain from occurring?
There are a number of rules to help prevent abdominal pain in children. If they are followed, the chance of such illnesses occurring is reduced to a minimum.
- It is imperative to ensure that the child drinks plenty of fluids (anything except carbonated drinks). It is desirable that it be clean water.
- You will have to exclude from your diet everything salty, fatty, fried, smoked, spicy and very sweet.
- Ensure that the child’s diet consists exclusively of fresh, high-quality products.
- Make sure that the child washes his hands after returning from the street and before each meal. Require him to wash all fruits, vegetables and berries that he intends to eat. It is prohibited to pick up anything edible from the ground on the street.
- Prevent your child from feeling hungry.
- Feed the child at least three to four times a day in small portions, excluding cases of overeating.