General rules
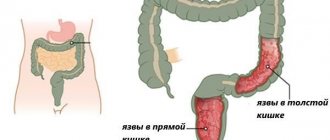
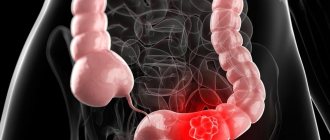
Cancer of the intestinal mucosa is a widespread type of cancer, especially in the age group after 55 years. The main morphological variant of oncological tumors are adenocarcinomas . Most often, malignant neoplasms are formed in the tissues of the rectum/colon ( colorectal cancer ), which is characterized by early metastasis through lymphogenous/hematogenous routes to the lymph nodes, liver, peritoneum, bones, as well as germination into the pelvic organs.
The high incidence of this type of cancer is due to the specific function of this part of the intestine, in which there is prolonged contact of feces ( toxins , products of metabolic reactions) with the intestinal mucosa, diseases ( sigmoiditis , ulcerative colitis , polyps, Crohn's disease ) and the nature of the diet, which is dominated by animal fats, proteins and refined foods with insufficient intake of plant fiber into the body. With this type of nutrition, putrefactive processes predominate in the intestines, and the products of protein putrefaction and bile acids produced by the intestinal microflora have a carcinogenic effect.
The main clinical symptoms of colorectal cancer are:
- weight loss, lack of appetite;
- aversion to meat products;
- long-term bowel disorders (constipation/diarrhea);
- the presence of blood in the stool (even black);
- feeling of heaviness, abdominal pain;
- and also, in later stages, weakness, increased fatigue, anemia.
Treatment of colorectal cancer is surgical followed by (preliminary) radiation / chemotherapy . Diet for bowel cancer is an integral method of maintenance therapy, allowing to improve treatment results, reduce the side effects of radiation/chemotherapy and improve the quality of life of patients. Nutrition for intestinal cancer is based on a number of factors, namely the presence/severity of nutritional deficiency, especially during radiation/chemotherapy, the presence and type of metabolic disorders, the period of the disease (pre/postoperative), the physical and psychological state of the patient .
Nutrition in the preoperative period in the absence of tumor-induced weight loss is based on the principles of rational nutrition with an energy balance at the level of 2400-2600 kcal/day. The diet provides for a reduction in fat consumption by 20-25% of the total daily calorie content due to refractory animal fats, limiting the content of refined (easily digestible) carbohydrates, foods containing food additives, fast food, sausages, semi-finished products, carbonated drinks, chips, confectionery products, salt/salty foods and food, fatty red meat, especially fried and smoked, increasing the proportion of fruits, vegetables and grains in the diet.
The diet for intestinal oncology should be balanced in terms of basic food nutrients, include all food groups with a predominance of dairy and plant products (at least 600 g of vegetables/fruits, whole grains and fermented milk products).
In cases of anorexia-cachexia and even with normal body weight, patients with a high risk of its development need to receive enhanced nutrition 10-14 days before surgery, since surgery for intestinal cancer causes nitrogen losses and increases the need for energy even in the absence of correction nutrition can lead to the development of a negative nitrogen balance and various water and electrolyte disorders. Therefore, timely transition of the patient to enhanced nutrition helps protect against weight loss in the postoperative period and during radiation/chemotherapy.
The energy component of the diet during this period should be 3500-4000 kcal/female. According to the recommendations, the daily protein requirement should be 1.2-1.5 g/kg, and the energy requirement should be 25-35 kcal/kg, which is achieved by including high-calorie foods in the diet: sprats, red caviar, creams, chocolate, pates, eggs, honey, cream, nuts, cream, cheeses, which are recommended to be consumed both as main products on the menu and used for snacks.
In the postoperative period, dietary nutrition should be as gentle as possible. After resection of an intestinal tumor, a surgical Diet 0A - fasting for 1-2 days, then the diet is gradually expanded, starting with rice water, weak broth, and berry jelly. In the following days, slimy soups, well-mashed porridge cooked in water (oatmeal, buckwheat), a protein omelet/soft-boiled egg, and later a steamed soufflé/puree of fish and meat are added.
From the second week, the diet includes rice soup with pureed vegetables, milk/semolina and pureed buckwheat porridge, mashed potatoes, cottage cheese diluted with cream, steamed meat cutlets, sour cream, baked apple puree, yogurt, jelly. This diet provides maximum rest for the intestines, forms little feces, and does not cause flatulence . If constipation occurs, from the 7th day onwards, the diet includes boiled beets, dried apricot/prune puree, and kefir.
After removal of an intestinal tumor in the first 4-6 months, Table No. 4B :
- Food should be well pureed, fresh and easily digestible.
- You need to eat food in small portions 5-6 times a day, chewing thoroughly.
- Soups (cereals/vegetables) are prepared in a weak broth with the addition of meatballs and minced meat.
- Cereals are pureed, vegetables (zucchini, carrots, potatoes) are finely chopped.
- It is important to drink enough fluids to prevent constipation.
- Meat consumption is limited; it is preferable to eat lean fish. It is important to have yogurt and “live” kefir in the diet, which help normalize the intestinal microflora.
- Bread - only dried wheat bread in small quantities.
- Vegetables are boiled and well pureed.
- Porridges are prepared in water, excluding corn, barley, millet, and pearl barley.
- Whole milk, cream/sour cream are added to dishes, fermented milk products are allowed to be consumed without restrictions.
- Recommended drinks include juices diluted with water, rosehip infusion, weak tea, and still mineral water.
Excluded from the diet are fatty broths, fatty varieties of red meat, wholemeal bread, coarse and irritating vegetables (radish, garlic, radishes, spinach, onions, celery), canned meat/fish, any fresh bread, legumes, hot sauces, margarine, natural milk, smoked meats, cooking fat, butter dough, coarse cereals, pepper, pork and beef fat, mustard, cakes, ice cream, chocolate, carbonated drinks.
In the later stages, the diet should contain an increased amount of dietary fiber and vitamins (in the absence of diarrhea) due to the inclusion of cereals, whole grain bread, vegetables and fruits. Meat should be consumed with caution, giving preference to sea/river fish and seafood.
Animal fats and products containing trans fats should be completely excluded from the diet, giving preference to vegetable oils containing large quantities of antioxidants. It is still prohibited to consume foods that promote rotting/fermentation and stimulate the secretion of digestive juices (celery, sorrel, mushrooms, horseradish, radish, mustard, radishes, turnips). Gradually, pureed foods are reduced in the diet and well-cooked, not pureed food is introduced. Good tolerability indicates normalization of intestinal secretory/motor function.
Food option
What should be the diet for colorectal cancer? Oncology is often provoked by unhealthy diet. A special diet for rectal cancer is mandatory. Carcinogens can lead to the appearance of cancer cells. Therefore, it is important to completely exclude products that contain them from the daily menu. These include:
- hydrogenated oil (which is colored and has a high amount of fatty acids);
- fish grown in artificial reservoirs (using antibiotics for nutrition);
- sweeteners (refined sugar, soda);
- white flour (when it is produced, chlorine-containing substances are used, it contains practically no useful elements);
- meat products (bacon, sausages, frankfurters);
- alcoholic products;
- fast food.
Authorized Products
Dietary nutrition for intestinal cancer includes the following products in the diet:
- Dried wheat bread.
- Soups cooked in weak meat broth/vegetable broth with well-cooked vegetables and cereals. You can add meatballs to the soup.
- Dietary varieties of poultry (chicken and turkey), steamed, boiled or cooked in the form of cutlets.
- Low-fat fish in the form of cutlets/quenelles or in pieces.
- Crumbly porridges (except pearl barley, wheat), chopped pasta, vermicelli, noodles, cooked in water or with the addition of milk (cream), you can make casseroles, make pancakes, puddings.
- One or two steamed/soft-boiled eggs per day.
- Low-fat fermented milk products/freshly prepared cottage cheese are allowed to be consumed daily; sour cream, cream and milk can only be added to ready-made dishes. Butter up to 10 g per serving per dish.
- Vegetables (carrots, potatoes, zucchini, cauliflower - finely chopped, boiled). If tolerated well, you can add green peas, beets and green beans to soup.
- Garden greens are allowed.
- Homemade sauces with meat/fish broth and milk.
- Sweet and ripe fruits without peel, at least 200 g per day.
- Desserts - marshmallows, marmalade, caramel, marshmallows, jam.
- Drinks include coffee/tea with milk, cocoa with water/milk, juices diluted with water (except grape and cabbage), still mineral water, compotes, jelly, rosehip decoction.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| boiled cauliflower | 1,8 | 0,3 | 4,0 | 29 |
| boiled potatoes | 2,0 | 0,4 | 16,7 | 82 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| boiled beets | 1,8 | 0,0 | 10,8 | 49 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
Fruits | ||||
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried pears | 2,3 | 0,6 | 62,6 | 249 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| Wheat groats | 11,5 | 1,3 | 62,0 | 316 |
| white boiled rice | 2,2 | 0,5 | 24,9 | 116 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| milk pasta | 11,5 | 2,9 | 67,1 | 345 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| meringues | 2,6 | 20,8 | 60,5 | 440 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| condensed milk | 7,2 | 8,5 | 56,0 | 320 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| boiled chicken drumstick | 27,0 | 5,6 | 0,0 | 158 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| soft-boiled chicken eggs | 12,8 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 159 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| pink salmon | 20,5 | 6,5 | 0,0 | 142 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| cod roe | 24,0 | 0,2 | 0,0 | 115 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| vegetable oil | 0,0 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 899 |
| peasant unsalted butter | 1,0 | 72,5 | 1,4 | 662 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| Orange juice | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| Cherry juice | 0,7 | 0,0 | 10,2 | 47 |
| jelly | 0,2 | 0,0 | 16,7 | 68 |
| Strawberry juice | 0,6 | 0,4 | 7,0 | 31 |
| tangerine juice | 0,8 | 0,3 | 8,1 | 36 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| Apple juice | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 42 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Diet during surgery and treatment: chemotherapy and radiation
What can you eat for bowel cancer during chemotherapy and radiation if patients suffer from side effects:
- fatigue;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- taste changes;
- food aversions;
- nausea and vomiting.
To prevent these disorders from leading to weight loss, you need to restore your appetite with high-calorie foods: nuts and dried apricots, raisins and prunes, with a pleasant smell: strawberries and other “fragrant” berries and fruits, vegetables, mushrooms and meat: liver and poultry, lamb, rabbit with fragrant herbs and seasonings. You need to eat food at room temperature, it smells better.
Vegetable and animal oils should not have an old and rancid odor that discourages appetite. Oil bottles should not be stored in metal containers or exposed to light. Dishes should be prepared only from fresh products, there should be no “dry food” - any sandwiches, large quantities of biscuits and crackers. Dishes should not burden the liver and kidneys, so as not to aggravate nausea and vomiting, and also to quickly remove harmful carcinogens and chemical drugs.
After the operation, food should be reasonably fractional and ground, as indicated above. Vegetables grown in a greenhouse are not suitable after chemical and irradiation because they contain pesticides. To restore your appetite, you can eat a salad with a sour or pickled (fermented) apple and cabbage in small quantities or drink a glass of tomato juice.
After surgery and therapy, the menu should contain 4 main product groups:
- protein;
- fermented milk;
- bread and cereals;
- fruit, berry and vegetable.
Conclusions! Healthy and fresh foods and a proper diet will help defeat such a terrible disease as intestinal cancer. After surgery and therapy, intestinal flora can be restored by home-prepared yoghurts, kefir, whey, and appetite by foods with a pleasant smell: young vegetables, mushrooms and herbs, citrus berries and fruits.
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for intestinal cancer includes the exclusion of the following foods:
- Any fresh bread, pastries, muffins, products made from refined flour.
- Animal/cooking fats, smoked meats, fatty meat/fish, poultry meat, any canned food, mayonnaise, margarine, sausages, marinades, pickles.
- Concentrated broths.
- Fried food.
- Products containing stabilizers, dyes, emulsifiers, preservatives, sweeteners, which are highly oncogenic substances.
- Legumes and foods that irritate the intestinal mucosa (onions, garlic, radishes, radishes).
- Strong coffee, chocolate drinks with carbonation.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| parsnip | 1,4 | 0,5 | 9,2 | 47 |
| parsley (root) | 1,5 | 0,6 | 10,1 | 49 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| celery (root) | 1,3 | 0,3 | 6,5 | 32 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried fruits | 2,3 | 0,6 | 68,2 | 286 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Bakery products | ||||
| Old Russian grain bread | 9,6 | 2,7 | 47,1 | 252 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
| butter cookies | 10,4 | 5,2 | 76,8 | 458 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| seasonings | 7,0 | 1,9 | 26,0 | 149 |
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Eggs | ||||
| hard-boiled chicken eggs | 12,9 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 160 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| vegetable oil | 0,0 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 899 |
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| rendered pork fat | 0,0 | 99,6 | 0,0 | 896 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
| black coffee | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 2 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| grape juice | 0,3 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 54 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Reviews and results
According to patients, therapeutic nutrition for intestinal cancer does not cause much psychological discomfort and promotes the rapid restoration of intestinal function.
- “... She underwent surgery for sigmoid colon cancer, and then radiation therapy. At first I felt terrible - constant nausea and vomiting, I had to force myself to eat. Then, after 2 weeks, my appetite began to recover. I'm on a diet. Everything is stewed, finely ground, no spices. I practically don’t eat fresh vegetables, as I get bloating and flatulence. The doctor says that over time, intestinal function will be restored, but you will have to follow a more or less strict diet for the rest of your life.”
- “... They removed the intestinal tumor along with part of the intestine. I walked with a colostomy for 2 months, and then everything was “returned” to its place. I adhere to a strict diet and cook everything in a double boiler, which makes the process of preparing dietary dishes much easier. For the first six months, the diet included only steamed dishes. Now I’m introducing baked and little by little raw vegetables and fruits into my diet. I introduce new foods little by little and look at the intestinal reaction, trying to create the right diet.”
Principles of proper nutrition
Compliance with certain rules helps to minimize the consequences of disruption of digestive processes in case of rectal cancer:
- the menu must include fresh dishes (long-term storage of food in the refrigerator is unacceptable);
- Only steaming or boiling is suitable;
- food is crushed to the maximum extent (pureed), served at room temperature;
- During the eating process, it is important to thoroughly chew with abundant wetting of the food with saliva;
- Foods that provoke constipation, gas formation, and the transition of healthy cells to malignant ones should be removed from the diet;
- Monotony is prohibited, as it can cause a weakening of the patient’s mental and physical condition.