In the treatment of intestinal diseases, proper nutrition plays a major role. A diet for enterocolitis helps avoid complications, promotes disrupted processes and restores intestinal microflora. It is quite easily tolerated, but requires significant restrictions not only in the products consumed, but also in the volume of portions.
Depending on the nature of the inflammatory reaction, various dietary options are used. During the acute phase of enteritis and colitis, it is recommended to adhere to dietary diet No. 4. If the inflammatory process occurs in a chronic form, then patients are recommended to adhere to dietary diet No. 3 according to Pevzner.
What could cause
Often, such a disease develops along with acute gastritis and develops due to the fact that a person eats low-quality foods, which, most likely, were contaminated with substances from natural bacteria, also if you eat a lot of fatty foods, spicy or rough (constant dryness) .
Fruits or vegetables that are not yet ripe can also become one of the causes of the disease. In addition, enterocolitis accompanies a number of other diseases that are associated with the intestines.
Symptoms
It is difficult to identify signs that would accurately indicate that the patient has enterocolitis. All symptoms are not specific and reflect only the severity of this pathology.
Main symptoms
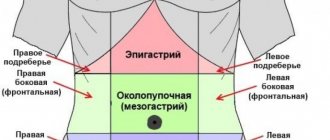
- Abdominal pain is a key symptom of gastrointestinal pathology. The pain intensifies upon palpation, is paroxysmal in nature and is localized in the navel area and along the flanks.
- Diarrhea or constipation. In the chronic form, these conditions can replace each other.
- General manifestations. We are talking about fever, weakness, muscle pain.
- Flatulence. Patients complain of bloating and gases. This is due to disruption of digestive processes.
- Scatological changes. Feces may change in color and consistency, and fatty patches, streaks of blood, and mucus may appear. All this may confuse the patient, and he will consult a doctor.
What to do and in what cases
It is in this case that diets for enterocolitis play an important role in order to stabilize your body and remove all harmful foods from your diet, replacing them with better ones. The diet for acute enterocolitis begins with the fact that you cleanse your stomach by doing a fasting day. If this is a child, then during the day you need to give a little weak tea, Borjomi.
The diet for exacerbation of enterocolitis consists of the fact that you must relieve inflammation with medication and also take a fasting day, drinking only tea or water, preferably natural water (Borjomi), during the day. What kind of diet is there for this disease? The main principle is that on the first day of the enterocolitis diet, you spend an “easy” day on your stomach. But diet 4 for enterocolitis is the diet you should be on constantly.
Features of therapeutic nutrition
In the treatment of pathology, treatment table No. 4 is used, as well as its varieties for the treatment of various forms of enterocolitis. During exacerbation, strict restrictions are prescribed, and during recovery, they switch to subtypes 4B and 4B. There is also a separate type of diet designed for people with constant constipation.
The “Healing Table No. 4” diet was compiled many years ago by Professor Pevzner. Its goal is to satisfy the nutritional needs of the body, eliminate the processes of decay and fermentation in the intestines, and reduce inflammatory reactions.
Therapeutic nutrition helps patients recover quickly and prevents the development of complications.
The purpose of a diet for enterocolitis is determined by a number of factors:
- site of gastrointestinal tract lesion;
- type of processes occurring;
- nature of the disorders.
If the small intestine is affected, the diet includes proteins, B vitamins, and minerals. During putrefactive transformation processes, the amount of protein is reduced, the consumption of coarse fiber and fermented milk products is reduced.
There are 3 types of diet for enterocolitis:
No. 4 - used for exacerbation;
No. 3 - prescribed during the chronic period;
No. 2 - when remission occurs, that is, a decrease in the manifestations of the disease or complete disappearance of symptoms.
Treatment of the disease with proper nutrition increases the chances of a quick recovery several times.
Forecast
Enterocolitis is a condition that requires medical attention. Inflammation in the body poses a danger to the digestive tract. A person must promptly detect the ailment and visit a specialist. Enterocolitis should be treated at the acute stage of development, since the chronic form is difficult to get rid of. The sick person will have to restrict himself in nutrition, take medications, and suffer from abdominal pain. The pathology also disrupts the function of other internal organs. The man is lethargic and drooping.
If you seek help in time, you can eliminate enterocolitis and prevent the development of complications. The gastrointestinal tract is very important for a person’s successful life. Healthy food will improve your mood, relieve inflammation and overcome stress. There is no need to injure the digestive system, then chronic enterocolitis will be avoided. Since this form limits the intake of many foods.
We recommend: The best recipes for folk remedies for the treatment of intestinal adhesions
General principles of dietary nutrition
The basis of the diet for intestinal enterocolitis consists of foods that are safe for the mucous membrane and do not injure internal organs with hard particles. These can be boiled porridges, jelly and well-ground soups at the acute stage. Other foods are introduced gradually and only after the patient feels better. Basic nutrition rules:
- small portions – up to 250 g at a time;
- frequent meals – up to 6 times a day;
- refusal of fried, salty, sour and spicy foods;
- refusal of store-bought sauces and seasonings;
- reducing salt to 10 g;
- on the first day - therapeutic fasting and drinking plenty of fluids;
- warm food - up to 60 degrees, too cold and hot dishes injure the intestines;
- calorie content up to 2000 kcal per day, minimum fat;
- during the recovery period, food should contain the necessary vitamins B and C;
- in acute enterocolitis, food is crushed and ground;
- You can only eat thermally processed food, prepared by boiling or stewing;
- every day after eliminating acute symptoms, no more than 3 new dishes are added to the food;
- To improve digestion, it is important to chew food thoroughly;
- It is advisable to eat at the same time to help the stomach better process foods with juice;
- per day the patient requires up to 60 g of unrefined vegetable and animal fats, 80 g of carbohydrates and up to 200 g of protein.
Similar rules apply for children, only the amount of protein, fats and carbohydrates is reduced by 20-30%.
After following a strict diet for enterocolitis, adults and children are transferred to a balanced, gentle diet - treatment table No. 4B. You can stick to it for 2 months. The list of products is quite extensive, so you can create a varied menu. Its main goal is to eliminate pathological processes in the body and normalize stool.
After restoration of the intestines, diet No. 4B for enterocolitis is recommended for adults and children. It allows you to eat more vegetable fats and vegetables. You can avoid completely pureed foods and add whole foods to your diet. You can also include savory baked goods.
Food for children
With a diagnosis of enterocolitis, a child is prescribed the same diet as an adult. Having determined the disease, the specialist prescribes a complex of vitamins, medications, and a diet menu for the baby, depending on the symptoms.
For intestinal infections, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, and painkillers are used. The regimen and diet are established by the attending nutritionist; after the prescription is written, you must strictly adhere to it.
At first, difficulties may arise with treatment; it is difficult for the baby to understand why he is not given sweets or other foods that the child likes. Young patients need to be fed at least 5-6 times a day.
A child's diet may consist of:
- crushed soups, porridges;
- low-fat light broths;
- Cabbage juice will help relieve pain;
- steamed fish, meat;
- a little later - savory pies and buns.
It is advisable not to consume prohibited foods in front of the child, so as not to tempt the child, otherwise the psyche may be damaged.
Treatment of enterocolitis with diet
Doctors purely conventionally distinguish between the acute and chronic phases of this disease, but the treatment protocol in both cases is not very different from each other. One of the ways to resolve the problem is to treat enterocolitis with diet. At the same time, medical nutritionists developed a special diet - table No. 4 - which took into account all the requirements of the restrictions.
At the time of exacerbation, the patient must be switched to a lighter diet. The main postulates of this nutritional adjustment can be summarized in several rules:
- In case of a certain clinical picture (acute phase of the disease), the doctor prescribes the patient a day or two of complete fasting. During this period, the patient needs to drink only water often, but in small sips.
- Dishes should be easy for the stomach to digest.
- Eliminate heavy, fatty foods.
- It is advisable to cook dishes by steaming, or, in extreme cases, by scalding.
- Any porridge is allowed, especially those with water, mucous ones.
- Cereal decoctions. For example, rice is useful.
Enterocolitis is rarely diagnosed independently. In most cases, it is still accompanied by another pathology, that is, the inflammation spreads to other organs. Therefore, the diet, like all treatment, is prescribed based on this fact.
Consequences of not following the diet
The dietary program recommended for colitis is a mandatory part of therapy. Thanks to menu adjustments, the recovery trend can be significantly accelerated. Violation of the diet can provoke an exacerbation of the inflammatory process in the shortest possible time. Products with irritating effects neutralize the pharmacological properties of some medications. For example, if you take painkillers, but abuse fatty or fried foods, then there will be no effect from the therapy.
Consequences of poor diet:
- frequent attacks of exacerbation of pathology;
- risk of ulcerative colitis;
- development of peritonitis;
- intestinal obstruction;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- lack of tendency to recovery.
Video - Therapeutic diet (TABLE) No. 4 (Acute and chronic intestinal diseases with diarrhea.
The essence of the diet for enterocolitis
Restriction in nutrition and a number of foods is one of the key points in the treatment of many diseases, especially in the pathology of organs directly related to the digestive process. Since the small and large intestines are precisely such organs, the result of their treatment is directly related to the diet that a person should adhere to while undergoing treatment for the disease in question.
The essence of the diet for enterocolitis:
- Complete exclusion of hard to digest and fatty foods.
- Peppered and spicy dishes are also prohibited.
- Spices, baked goods, and smoked foods should be removed from the diet.
- Raw vegetables and fruits are prohibited, especially those that cause increased gas formation or may contribute to the fermentation process in the stomach.
A number of other products are subject to exclusion, which will be discussed in more detail below.
Supermarket products that contain stabilizers, dyes, flavor enhancers, and preservatives should disappear from the table of such a patient.
Categorical refusal of fast food products.
Avoid overeating. Meals should be frequent and in small portions.
At the same time, nutrition must be complete and provide a person with a full volume and set of nutrients and a vitamin and mineral complex.
The basis of the diet is pureed soups, jelly, porridge - a mess. Only after the patient’s well-being improves, other products are gradually added to the patient’s diet: lean meat products in the form, for example, of meatballs or steamed cutlets, boiled fish or fish meat cutlets.
The period of adherence to dietary nutrition is mainly based on the stage of the disease (acute or chronic) and its severity. With properly selected therapy and compliance with the necessary diet, on average, dietary restrictions affect one and a half months.
If the disease was recognized at an early stage of development, complete recovery is possible. The prolonged course of the disease and its transition to the chronic stage can cause irreversible pathological changes in tissues, which adversely affects the human body as a whole. In this case, the patient will have to limit himself in nutrition for the rest of his life.
Chemical composition of diet No. 4:
- proteins up to 100 g (60-70% animal origin, 30-40% plant origin);
- fats 70 g (50-60% vegetable, 40-50% animal origin);
- carbohydrates 250 g (no more than 45 g sugar);
- salt 10 g;
- liquid 1.5-2 l.
Weight of daily ration: 2.5-3 kg.
Daily intake of diet No. 4: 2000-2050 kcal.
Diet: 5-6 times a day.
Indications for use of diet No. 4:
- chronic colitis;
- acute gastroenterocolitis (at the beginning of the disease, after days of fasting);
- enterocolitis in the acute phase;
- dysentery;
- typhoid fever;
- intestinal tuberculosis (first 5-7 days).
General dietary recommendations
After the cause of enterocolitis has been determined, a diet is prescribed. During an exacerbation - diet 4 or 3, without an exacerbation - table No. 2.
Meals should be fractional, 5-6 times a day, in small portions.
You need to give up sour, spicy, fried and salty foods. Use seasonings and sauces within reasonable limits.
The first 2 days after an exacerbation should be hungry, the patient receives only plenty of fluids and broths. On the third day, the diet for enterocolitis is enriched with slimy porridges, soups, compotes and fruit drinks.
Monitor the temperature of the food served (50-55 degrees). Very cold or hot food has a negative effect on the mucous membrane.
The calorie content of the diet should be no more than 2000 kcal; do not overuse fats - they overload the diseased intestines.
Be sure to enrich your diet with vitamins B, C, and PP.
All food is prepared in pureed or crushed form. It is best to boil or steam food.
The menu needs to be expanded gradually, adding 2-3 new items per week, monitoring the body’s reaction.
Stick to your diet, avoid dry food and eating on the run.
Chew your food thoroughly: you will make it easier to digest and relieve yourself of pain.
Train yourself to eat at the same time: the stomach will secrete hydrochloric acid and juice, and will cope with digestion faster. If food does not arrive at the prescribed hour, the acid further irritates the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines.
The diet should be complete: 200g of proteins, 60g of fats, 80g of carbohydrates, as well as vitamins, micro- and macroelements necessary for the body.
Permitted and prohibited products
If the pain is severe, the patient is advised to fast for the first two days. Mineral water, herbal tea, and saline solution are given in small doses throughout the day. Gradually you can move on to diet No. 2:
- Gradually include lean beef and chicken in the menu. The meat must be cleaned of skin, tendons and cartilage.
- Boiled fish (hake, pike, carp, tuna).
- Semolina, oatmeal, rice porridge on water.
- Mashed cottage cheese.
- Slimy cereal soups and low-fat broths.
- Stale white bread (up to 150g per day).
- Berry jelly, jellies, juices diluted with water.
- After the acute manifestations of the disease disappear, you can expand the menu:
- You can eat boiled vegetables (pumpkin, carrots, potatoes, zucchini, cucumber).
- Low-fat kefir, mild cheese, yogurt and sour cream.
- Turkey, rabbit.
- Buckwheat and wheat porridge, boiled pasta.
- Eggs (no more than 2 pieces per day).
- Fruit mousses and compotes, baked fruits.
- Butter (up to 20g per day), vegetable oils (olive, sunflower).
- Sour cream sauces, herbs.
- Rose hip decoction, weak coffee and tea.
- Biscuits, white crackers.
- A strict diet should be followed for up to 2 months until the structure of the mucous membrane and intestinal function are restored.
If you have enterocolitis, you should avoid:
- Fatty meats and fish.
- Legumes, cabbage, turnips, spinach, onions, mushrooms, radishes - they cause fermentation in the intestines and aggravate discomfort.
- Black and fresh white bread.
- Sweets, baked goods.
- Unripe fruits and berries with thick skin.
- Fatty, spicy, smoked and salty foods.
- Canned food and marinades.
- Carbonated drinks and alcohol.
- Spices, seasonings.
- Milk.
- Barley, pearl barley and millet cereals.
Diet number 4 for colitis: what is possible, what is not?
Products recommended for diet table number 4:
- Stale white bread.
- Lean varieties of poultry, veal, beef in the form of stewed meatballs, meatballs or steam cutlets. Boiled meat soufflé.
- Boiled or baked lean fish.
- From dairy products - pureed unleavened cottage cheese or calcined freshly prepared cottage cheese.
- You can add fresh butter to your dishes.
- A couple of eggs a day in the form of a steam omelet or soft-boiled.
- Puree porridges cooked in water (buckwheat, oatmeal, rice).
- Vegetables in the form of decoctions added to soups.
- Cocoa and black coffee with water, tea (preferably green), diluted fruit juices from fruits and berries (except for grapes, apricots, plums), rosehip decoction.
- Raw mashed apples.
During the diet the following are excluded:
- Various savory snacks.
- Fatty and strong broths, soups with vegetables and cereals.
- Fatty fish, meat and poultry, canned fish and meat, smoked meats.
- Barley and pearl barley, millet.
- Berries, vegetables and fruits in their natural form, legumes.
- Cold and carbonated drinks, cocoa and coffee with milk, all sweets.
Diet No. 4 (table No. 4): menu for the week
Diet No. 4 is varied and healthy. Below is a sample menu for the week. Dishes must be consumed in liquid or semi-liquid form, as well as pureed. Cooking method: steam or boil in water. Eat only warm.
| Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner | |
| Monday | pureed rice, steam omelette, tea | rosehip decoction | meatball soup, steam soufflé | pear jelly | buckwheat porridge, steamed fish cutlets |
| Tuesday | oatmeal, cottage cheese, cocoa on water | applesauce | cream soup with rice and egg flakes, steamed quenelles | quince jelly | semolina porridge with meat broth, soft-boiled egg |
| Wednesday | buckwheat porridge, 2 soft-boiled eggs | rosehip decoction | fish soup with oatmeal, steamed fish | apple mousse | rice porridge, steamed quenelles |
| Thursday | cottage cheese, cocoa | blueberry decoction | broth with egg flakes, steamed chicken cutlets | semolina pudding | rice porridge with minced chicken |
| Friday | oatmeal, steamed omelette | baked apple | soup with meatballs and croutons | rosehip decoction | mashed potatoes, fish soufflé |
| Saturday | buckwheat porridge, jelly | jelly | rice porridge, buckwheat-beef meatballs | bird cherry decoction | fish balls, omelette |
| Sunday | cottage cheese with applesauce, coffee | fruit jelly | meat broth with egg flakes, croutons | rosehip decoction | liquid semolina, chicken soufflé |
Features of the diet for children
If an infant is sick, you must adhere to the following rules:
- reduce the volume of food, but increase the frequency of feedings - the reduction should be 20% of the total volume;
- it is necessary to exclude any complementary foods for a while, adding them gradually after the acute symptoms have resolved;
- if possible, you should feed only breast milk or fermented milk formulas based on beneficial bacteria;
- When artificial feeding, I make sure to compensate for the entire volume with liquid.
You should not feed your child formulas that are not suitable for the treatment of enterocolitis and other intestinal disorders. Children over 6 months old can be given fermented milk mixtures diluted with buckwheat or rice porridge or puree soup.
Additionally, prebiotics are used to restore the intestines. All actions must be discussed with the doctor. It is best to choose from these medications: Linex, Bifiform, Colibacterin.
How to switch to a regular diet correctly
To prevent the acute process from becoming chronic, it is recommended to follow the sequence of diet expansion. After diet 4, the following foods and dishes are added to the diet:
- soup in a weak broth of meat, fish, vegetables. Small noodles or vermicelli, pureed cereals and vegetables, and meatballs are poured into it;
- dried white bread (yesterday's), biscuits, dryers;
- milk and cream are used for sauces, soups, porridge (half diluted with water);
- low-fat homemade cottage cheese, kefir and yogurt are recommended to be made independently from milk and pharmacy starter cultures;
- mild cheese is added to dishes;
- only minced meat or beef stroganoff. First, the skin is removed from the bird, all films and tendons are removed;
- lean fish is steamed, boiled in water or used for steamed cutlets, meatballs, soufflés;
- From vegetables, the most digestible ones are first selected - seedless zucchini, cauliflower, pumpkin, potatoes and carrots;
- All previously permitted porridges remain; boiled vermicelli is also prepared as a side dish;
- You can add a little fresh herbs to dishes for taste;
- baked apples, boiled pears. gradually try fresh sweet fruits without skin;
- compotes, jelly, berry and fruit mousse;
- diluted juice of apples, tangerines, oranges, cherries.
Only after adaptation to such a diet can you gradually reduce mechanical grinding, and then gradually introduce new dishes; it is important to monitor your reaction to them.
Prevention
Expert advice:
- Follow a proper diet and drink enough water.
- Take medications as prescribed by your doctor and according to the instructions, do not abuse medications, and do not purchase them at your own discretion.
- Do not violate basic hygiene rules, be vigilant and careful in preventive measures.
- Avoid low-quality foods such as fast foods and irritants.
- Avoid carbonated drinks and alcohol.
- When the first symptoms of the disease appear, contact the clinic in a timely manner.
- Treat gastrointestinal disorders promptly.
- Visit your gastroenterologist several times a year.
Sources: https://hudey.net/dieta-pri-enterokolite-rekomendacii-po-pitaniyu-razreshennye-i-zapreshhennye-produkty-i-menyu-na-nedelyu.html diarey.net/pitanie/kak-pitatsya-pri -enterokolite.html https://dietabez.ru/pri-kolite/dieta-pri-ostrom-enterokolite-u-vzroslyh-i-detey-pri-ponose.html medicina.dobro-est.com/dieta-4-stol -4-pitanie-pri-kolite-enterokolite-dizenerii-bryushnom-tife-i-tuberkuleze.html https://ilive.com.ua/food/dieta-pri-enterokolite_111941i15882.html https://polzaili.ru/dieta -pri-enterite-i-kolite-v-ostroj-i-xronicheskoj-formax/ gastritam.net/dieta/lechebnye/dieta-pri-enterokolite.html https://proktolog-info.ru/kolit/enterokolit-dieta/ dietamigom.ru/diety/lechebnye/pri-enterokolite.html This material is exclusively subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/19/2020